บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติคือแอปที่ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้กรอกแบบฟอร์มได้ง่ายขึ้น โดยการแทรกข้อมูลลงในมุมมองของแอปอื่นๆ บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติยังสามารถ ดึงข้อมูลผู้ใช้จากมุมมองในแอปและจัดเก็บไว้เพื่อใช้ในภายหลังได้ด้วย โดยปกติแล้ว บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติจะให้บริการโดยแอปที่จัดการข้อมูลผู้ใช้ เช่น เครื่องมือจัดการรหัสผ่าน
Android ช่วยให้การกรอกแบบฟอร์มง่ายขึ้นด้วยเฟรมเวิร์กการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติที่มีใน Android 8.0 (API ระดับ 26) ขึ้นไป ผู้ใช้จะใช้ประโยชน์จากฟีเจอร์ป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติได้ก็ต่อเมื่อมีแอปที่ให้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติในอุปกรณ์
หน้านี้แสดงวิธีติดตั้งใช้งานบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติในแอป หากคุณกำลังมองหาตัวอย่างโค้ดที่แสดงวิธีติดตั้งใช้งานบริการ โปรดดูตัวอย่าง AutofillFramework ใน Java หรือ Kotlin ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีการทำงานของบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติได้ที่
หน้าอ้างอิงสำหรับคลาส AutofillService และ
AutofillManager
การประกาศและสิทธิ์ในไฟล์ Manifest
แอปที่ให้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติต้องมีการประกาศที่อธิบาย
การใช้งานบริการ หากต้องการระบุการประกาศ ให้ใส่องค์ประกอบ
<service> ในไฟล์ Manifest ของแอป องค์ประกอบ <service> ต้องมีแอตทริบิวต์และองค์ประกอบต่อไปนี้
- แอตทริบิวต์
android:nameที่ชี้ไปยังคลาสย่อยของAutofillServiceในแอปที่ใช้บริการ - แอตทริบิวต์
android:permissionที่ประกาศสิทธิ์BIND_AUTOFILL_SERVICE - องค์ประกอบ
<intent-filter>ซึ่งมีองค์ประกอบย่อย<action>ที่ต้องระบุ การดำเนินการandroid.service.autofill.AutofillService - องค์ประกอบ
<meta-data>ที่ไม่บังคับซึ่งคุณใช้เพื่อระบุพารามิเตอร์การกำหนดค่าเพิ่มเติมสำหรับบริการได้
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงการประกาศบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ
<service
android:name=".MyAutofillService"
android:label="My Autofill Service"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_AUTOFILL_SERVICE">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.service.autofill.AutofillService" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.autofill"
android:resource="@xml/service_configuration" />
</service>
องค์ประกอบ <meta-data> มีแอตทริบิวต์ android:resource ที่
ชี้ไปยังทรัพยากร XML ที่มีรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับบริการ service_configuration ในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ระบุการทำงาน
ที่อนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้กำหนดค่าบริการ ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงทรัพยากร XML ของ service_configuration
<autofill-service
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:settingsActivity="com.example.android.SettingsActivity" />
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับทรัพยากร XML ได้ที่ภาพรวมของทรัพยากรแอป
แจ้งให้เปิดใช้บริการ
แอปจะใช้เป็นบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติได้หลังจากที่ประกาศ
BIND_AUTOFILL_SERVICEสิทธิ์และผู้ใช้เปิดใช้ใน
การตั้งค่าอุปกรณ์ แอปสามารถยืนยันได้ว่าแอปเป็นบริการที่เปิดใช้หรือไม่โดยการเรียกใช้เมธอด
hasEnabledAutofillServices() ของคลาส AutofillManager
หากแอปไม่ใช่บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติปัจจุบัน แอปจะขอให้ผู้ใช้เปลี่ยนการตั้งค่าการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติได้โดยใช้ Intent ACTION_REQUEST_SET_AUTOFILL_SERVICE Intent จะแสดงค่า
เป็น RESULT_OK หากผู้ใช้เลือกบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติที่ตรงกับ
แพ็กเกจของผู้โทร
กรอกข้อมูลมุมมองของลูกค้า
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติจะได้รับคำขอให้กรอกข้อมูลในมุมมองไคลเอ็นต์เมื่อผู้ใช้ โต้ตอบกับแอปอื่นๆ หากบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติมีข้อมูลผู้ใช้ที่ตรงกับคำขอ ระบบจะส่งข้อมูลดังกล่าวในการตอบกลับ ระบบ Android จะแสดง UI การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติพร้อมข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ ดังที่แสดงในรูปที่ 1
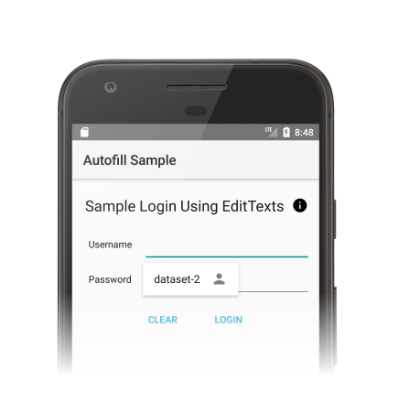
เฟรมเวิร์กการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติจะกำหนดเวิร์กโฟลว์เพื่อกรอกข้อมูลในมุมมองที่ออกแบบมาเพื่อ
ลดเวลาที่ระบบ Android เชื่อมโยงกับบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ใน
แต่ละคำขอ ระบบ Android จะส่งออบเจ็กต์ AssistStructure ไปยัง
บริการโดยการเรียกใช้เมธอด onFillRequest()
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติจะตรวจสอบว่าสามารถตอบสนองคำขอด้วยข้อมูลผู้ใช้
ที่จัดเก็บไว้ก่อนหน้านี้ได้หรือไม่ หากทำตามคำขอได้ บริการจะจัดแพ็กเกจข้อมูลในออบเจ็กต์ Dataset บริการจะเรียกใช้เมธอด
onSuccess() โดยส่งผ่านออบเจ็กต์ FillResponse ที่มีออบเจ็กต์ Dataset หากบริการไม่มีข้อมูลที่จะตอบสนองคำขอ
ก็จะส่ง null ไปยังเมธอด onSuccess() บริการจะเรียกใช้เมธอด
onFailure() แทนหากเกิดข้อผิดพลาดในการประมวลผลคำขอ
ดูคำอธิบายโดยละเอียดเกี่ยวกับเวิร์กโฟลว์ได้ที่คำอธิบายใน
AutofillServiceหน้าอ้างอิง
โค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างของเมธอด onFillRequest()
Kotlin
override fun onFillRequest(
request: FillRequest,
cancellationSignal: CancellationSignal,
callback: FillCallback
) {
// Get the structure from the request
val context: List<FillContext> = request.fillContexts
val structure: AssistStructure = context[context.size - 1].structure
// Traverse the structure looking for nodes to fill out
val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure)
// Fetch user data that matches the fields
val (username: String, password: String) = fetchUserData(parsedStructure)
// Build the presentation of the datasets
val usernamePresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1)
usernamePresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username")
val passwordPresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1)
passwordPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username")
// Add a dataset to the response
val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(
parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(username),
usernamePresentation
)
.setValue(
parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(password),
passwordPresentation
)
.build())
.build()
// If there are no errors, call onSuccess() and pass the response
callback.onSuccess(fillResponse)
}
data class ParsedStructure(var usernameId: AutofillId, var passwordId: AutofillId)
data class UserData(var username: String, var password: String)
Java
@Override
public void onFillRequest(FillRequest request, CancellationSignal cancellationSignal, FillCallback callback) {
// Get the structure from the request
List<FillContext> context = request.getFillContexts();
AssistStructure structure = context.get(context.size() - 1).getStructure();
// Traverse the structure looking for nodes to fill out
ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure);
// Fetch user data that matches the fields
UserData userData = fetchUserData(parsedStructure);
// Build the presentation of the datasets
RemoteViews usernamePresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
usernamePresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username");
RemoteViews passwordPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
passwordPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username");
// Add a dataset to the response
FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(new Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(userData.username), usernamePresentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(userData.password), passwordPresentation)
.build())
.build();
// If there are no errors, call onSuccess() and pass the response
callback.onSuccess(fillResponse);
}
class ParsedStructure {
AutofillId usernameId;
AutofillId passwordId;
}
class UserData {
String username;
String password;
}
บริการหนึ่งๆ อาจมีชุดข้อมูลมากกว่า 1 ชุดที่ตรงตามคำขอ ในกรณีนี้ ระบบ Android จะแสดงตัวเลือกหลายรายการ ซึ่งมีตัวเลือกหนึ่งสำหรับชุดข้อมูลแต่ละชุดใน UI การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธี ระบุชุดข้อมูลหลายชุดในการตอบกลับ
Kotlin
// Add multiple datasets to the response
val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.username), username1Presentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.password), password1Presentation)
.build())
.addDataset(Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.username), username2Presentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.password), password2Presentation)
.build())
.build()
Java
// Add multiple datasets to the response
FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(new Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.username), username1Presentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.password), password1Presentation)
.build())
.addDataset(new Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.username), username2Presentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.password), password2Presentation)
.build())
.build();
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติจะไปยังออบเจ็กต์ ViewNode ใน AssistStructure เพื่อดึงข้อมูลการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติที่จำเป็นต่อการดำเนินการตามคำขอ
บริการสามารถดึงข้อมูลการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติได้โดยใช้วิธีการของคลาส ViewNode เช่น getAutofillId()
บริการต้องอธิบายเนื้อหาของมุมมองเพื่อตรวจสอบว่าสามารถตอบสนองคำขอได้หรือไม่
การใช้แอตทริบิวต์ autofillHints เป็นแนวทางแรก
ที่บริการต้องใช้เพื่ออธิบายเนื้อหาของมุมมอง อย่างไรก็ตาม
แอปไคลเอ็นต์ต้องระบุแอตทริบิวต์อย่างชัดเจนในมุมมองของตนก่อนที่แอตทริบิวต์นั้นจะ
พร้อมใช้งานในบริการ
หากแอปไคลเอ็นต์ไม่ได้ระบุแอตทริบิวต์ autofillHints บริการจะต้อง
ใช้ฮิวริสติกของตัวเองเพื่ออธิบายเนื้อหา บริการสามารถใช้วิธีการ
จากคลาสอื่นๆ เช่น getText() หรือ getHint() เพื่อรับ
ข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับเนื้อหาของมุมมอง ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่ระบุ
คำแนะนำสำหรับการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีไปยัง AssistStructure และดึงข้อมูลการเติมข้อความอัตโนมัติจากออบเจ็กต์ ViewNode
Kotlin
fun traverseStructure(structure: AssistStructure) {
val windowNodes: List<AssistStructure.WindowNode> =
structure.run {
(0 until windowNodeCount).map { getWindowNodeAt(it) }
}
windowNodes.forEach { windowNode: AssistStructure.WindowNode ->
val viewNode: ViewNode? = windowNode.rootViewNode
traverseNode(viewNode)
}
}
fun traverseNode(viewNode: ViewNode?) {
if (viewNode?.autofillHints?.isNotEmpty() == true) {
// If the client app provides autofill hints, you can obtain them using
// viewNode.getAutofillHints();
} else {
// Or use your own heuristics to describe the contents of a view
// using methods such as getText() or getHint()
}
val children: List<ViewNode>? =
viewNode?.run {
(0 until childCount).map { getChildAt(it) }
}
children?.forEach { childNode: ViewNode ->
traverseNode(childNode)
}
}
Java
public void traverseStructure(AssistStructure structure) {
int nodes = structure.getWindowNodeCount();
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++) {
WindowNode windowNode = structure.getWindowNodeAt(i);
ViewNode viewNode = windowNode.getRootViewNode();
traverseNode(viewNode);
}
}
public void traverseNode(ViewNode viewNode) {
if(viewNode.getAutofillHints() != null && viewNode.getAutofillHints().length > 0) {
// If the client app provides autofill hints, you can obtain them using
// viewNode.getAutofillHints();
} else {
// Or use your own heuristics to describe the contents of a view
// using methods such as getText() or getHint()
}
for(int i = 0; i < viewNode.getChildCount(); i++) {
ViewNode childNode = viewNode.getChildAt(i);
traverseNode(childNode);
}
}
บันทึกข้อมูลผู้ใช้
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติต้องใช้ข้อมูลผู้ใช้เพื่อกรอกข้อมูลในมุมมองในแอป เมื่อผู้ใช้ กรอกข้อมูลในมุมมองด้วยตนเอง ระบบจะแจ้งให้บันทึกข้อมูลลงในบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ปัจจุบัน ดังที่แสดงในรูปที่ 2
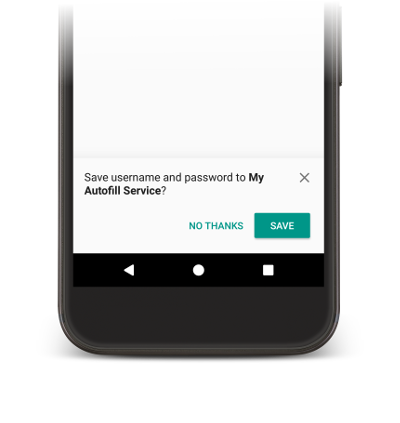
หากต้องการบันทึกข้อมูล บริการต้องระบุว่าต้องการจัดเก็บข้อมูล
เพื่อใช้ในอนาคต ก่อนที่ระบบ Android จะส่งคำขอให้บันทึกข้อมูล
จะมีคำขอเติมที่บริการมีโอกาสกรอกข้อมูลใน
มุมมอง หากต้องการระบุว่าสนใจบันทึกข้อมูล บริการ
จะรวมออบเจ็กต์ SaveInfo ไว้ในการตอบกลับคำขอเติม ออบเจ็กต์
SaveInfo มีข้อมูลต่อไปนี้อย่างน้อย
- ประเภทข้อมูลผู้ใช้ที่บันทึกไว้ ดูรายการค่า
SAVE_DATAที่ใช้ได้ที่SaveInfo - ชุดมุมมองขั้นต่ำที่ต้องเปลี่ยนแปลงเพื่อทริกเกอร์คำขอให้บันทึก
เช่น โดยปกติแล้วแบบฟอร์มเข้าสู่ระบบจะกำหนดให้ผู้ใช้อัปเดตมุมมอง
usernameและpasswordเพื่อทริกเกอร์คำขอให้บันทึก
ออบเจ็กต์ SaveInfo เชื่อมโยงกับออบเจ็กต์ FillResponse ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
override fun onFillRequest(
request: FillRequest,
cancellationSignal: CancellationSignal,
callback: FillCallback
) {
// ...
// Builder object requires a non-null presentation
val notUsed = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1)
val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(
Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, null, notUsed)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, null, notUsed)
.build()
)
.setSaveInfo(
SaveInfo.Builder(
SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_USERNAME or SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_PASSWORD,
arrayOf(parsedStructure.usernameId, parsedStructure.passwordId)
).build()
)
.build()
// ...
}
Java
@Override
public void onFillRequest(FillRequest request, CancellationSignal cancellationSignal, FillCallback callback) {
// ...
// Builder object requires a non-null presentation
RemoteViews notUsed = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(new Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, null, notUsed)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, null, notUsed)
.build())
.setSaveInfo(new SaveInfo.Builder(
SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_USERNAME | SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_PASSWORD,
new AutofillId[] {parsedStructure.usernameId, parsedStructure.passwordId})
.build())
.build();
// ...
}
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติสามารถใช้ตรรกะเพื่อคงข้อมูลผู้ใช้ไว้ในเมธอด onSaveRequest() ซึ่งมักจะเรียกใช้หลังจากกิจกรรมไคลเอ็นต์เสร็จสิ้น หรือเมื่อแอปไคลเอ็นต์เรียกใช้ commit() โค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดง
ตัวอย่างของเมธอด onSaveRequest()
Kotlin
override fun onSaveRequest(request: SaveRequest, callback: SaveCallback) {
// Get the structure from the request
val context: List<FillContext> = request.fillContexts
val structure: AssistStructure = context[context.size - 1].structure
// Traverse the structure looking for data to save
traverseStructure(structure)
// Persist the data - if there are no errors, call onSuccess()
callback.onSuccess()
}
Java
@Override
public void onSaveRequest(SaveRequest request, SaveCallback callback) {
// Get the structure from the request
List<FillContext> context = request.getFillContexts();
AssistStructure structure = context.get(context.size() - 1).getStructure();
// Traverse the structure looking for data to save
traverseStructure(structure);
// Persist the data - if there are no errors, call onSuccess()
callback.onSuccess();
}
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติต้องเข้ารหัสข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อนก่อนที่จะบันทึกข้อมูล อย่างไรก็ตาม ข้อมูลผู้ใช้อาจมีป้ายกำกับหรือข้อมูลที่ไม่ใช่ข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อน ตัวอย่างเช่น บัญชีผู้ใช้ อาจมีป้ายกำกับที่ระบุว่าข้อมูลเป็นของบัญชีงานหรือส่วนตัว บริการต้องไม่เข้ารหัสป้ายกำกับ การไม่เข้ารหัสป้ายกำกับจะช่วยให้บริการ ใช้ป้ายกำกับในมุมมองการนำเสนอได้หากผู้ใช้ยังไม่ได้ตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ จากนั้น บริการจะแทนที่ป้ายกำกับด้วยข้อมูลจริงหลังจากที่ผู้ใช้ ตรวจสอบสิทธิ์แล้ว
เลื่อน UI การบันทึกการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ
ตั้งแต่ Android 10 เป็นต้นไป หากคุณใช้หลายหน้าจอเพื่อใช้เวิร์กโฟลว์การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ
เช่น หน้าจอหนึ่งสำหรับช่องชื่อผู้ใช้และอีกหน้าจอหนึ่งสำหรับ
รหัสผ่าน คุณสามารถเลื่อน UI การบันทึกการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติได้โดยใช้
ค่าสถานะ SaveInfo.FLAG_DELAY_SAVE
หากตั้งค่าสถานะนี้ ระบบจะไม่ทริกเกอร์ UI การบันทึกการป้อนอัตโนมัติเมื่อมีการคอมมิตบริบทการป้อนอัตโนมัติ
ที่เชื่อมโยงกับSaveInfoการตอบกลับ แต่คุณสามารถ
ใช้กิจกรรมแยกต่างหากภายในงานเดียวกันเพื่อส่งคำขอโฆษณาที่เหลือในอนาคต
แล้วแสดง UI โดยใช้คำขอบันทึกแทน ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่
SaveInfo.FLAG_DELAY_SAVE
ต้องมีการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ของผู้ใช้
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติสามารถเพิ่มระดับความปลอดภัยได้โดยกำหนดให้ ผู้ใช้ต้องตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ก่อนจึงจะป้อนข้อมูลในมุมมองได้ สถานการณ์ต่อไปนี้เป็น ตัวอย่างที่ดีในการใช้การตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ผู้ใช้
- ต้องปลดล็อกข้อมูลผู้ใช้ในแอปโดยใช้รหัสผ่านหลักหรือ การสแกนลายนิ้วมือ
- ต้องปลดล็อกชุดข้อมูลที่เฉพาะเจาะจง เช่น รายละเอียดบัตรเครดิต โดย ใช้รหัสยืนยันบัตร (CVC)
ในกรณีที่บริการกำหนดให้มีการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ผู้ใช้ก่อนปลดล็อกข้อมูล
บริการจะแสดงข้อมูลมาตรฐานหรือป้ายกำกับและระบุ Intent ที่จัดการการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ได้ หากต้องการข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเพื่อ
ประมวลผลคำขอหลังจากขั้นตอนการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์เสร็จสมบูรณ์ คุณสามารถเพิ่มข้อมูลดังกล่าว
ลงใน Intent ได้ จากนั้นกิจกรรมการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์จะส่งคืนข้อมูลไปยังคลาส
AutofillService ในแอป
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีระบุว่าคำขอต้องมีการ ตรวจสอบสิทธิ์
Kotlin
val authPresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply {
setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "requires authentication")
}
val authIntent = Intent(this, AuthActivity::class.java).apply {
// Send any additional data required to complete the request
putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, "my_dataset")
}
val intentSender: IntentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity(
this,
1001,
authIntent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT
).intentSender
// Build a FillResponse object that requires authentication
val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder()
.setAuthentication(autofillIds, intentSender, authPresentation)
.build()
Java
RemoteViews authPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
authPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "requires authentication");
Intent authIntent = new Intent(this, AuthActivity.class);
// Send any additional data required to complete the request
authIntent.putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, "my_dataset");
IntentSender intentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity(
this,
1001,
authIntent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT
).getIntentSender();
// Build a FillResponse object that requires authentication
FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder()
.setAuthentication(autofillIds, intentSender, authPresentation)
.build();
เมื่อกิจกรรมทําตามขั้นตอนการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์เสร็จแล้ว กิจกรรมจะต้องเรียกใช้เมธอด
setResult() โดยส่งค่า RESULT_OK และตั้งค่า
EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT เพิ่มเติมไปยังออบเจ็กต์ FillResponse ที่
มีชุดข้อมูลที่สร้างขึ้น โค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างวิธี
แสดงผลลัพธ์เมื่อขั้นตอนการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์เสร็จสมบูรณ์
Kotlin
// The data sent by the service and the structure are included in the intent
val datasetName: String? = intent.getStringExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME)
val structure: AssistStructure = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_ASSIST_STRUCTURE)
val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure)
val (username, password) = fetchUserData(parsedStructure)
// Build the presentation of the datasets
val usernamePresentation =
RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply {
setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username")
}
val passwordPresentation =
RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply {
setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username")
}
// Add the dataset to the response
val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(
parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(username),
usernamePresentation
)
.setValue(
parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(password),
passwordPresentation
)
.build()
).build()
val replyIntent = Intent().apply {
// Send the data back to the service
putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, datasetName)
putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, fillResponse)
}
setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, replyIntent)
Java
Intent intent = getIntent();
// The data sent by the service and the structure are included in the intent
String datasetName = intent.getStringExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME);
AssistStructure structure = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_ASSIST_STRUCTURE);
ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure);
UserData userData = fetchUserData(parsedStructure);
// Build the presentation of the datasets
RemoteViews usernamePresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
usernamePresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username");
RemoteViews passwordPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
passwordPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username");
// Add the dataset to the response
FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(new Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId,
AutofillValue.forText(userData.username), usernamePresentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId,
AutofillValue.forText(userData.password), passwordPresentation)
.build())
.build();
Intent replyIntent = new Intent();
// Send the data back to the service
replyIntent.putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, datasetName);
replyIntent.putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, fillResponse);
setResult(RESULT_OK, replyIntent);
ในกรณีที่ต้องปลดล็อกชุดข้อมูลบัตรเครดิต บริการ สามารถแสดง UI ที่ขอ CVC ได้ คุณซ่อนข้อมูลได้จนกว่าจะปลดล็อกชุดข้อมูลโดยการแสดงข้อมูลมาตรฐาน เช่น ชื่อธนาคารและตัวเลข 4 หลักสุดท้ายของหมายเลขบัตรเครดิต ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธี กำหนดให้มีการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์สำหรับชุดข้อมูลและซ่อนข้อมูลจนกว่าผู้ใช้จะระบุ CVC
Kotlin
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data
val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure)
val paymentData: Payment = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure)
// Build the presentation that shows the bank and the last four digits of the
// credit card number, such as 'Bank-1234'
val maskedPresentation: String = "${paymentData.bank}-" +
paymentData.creditCardNumber.substring(paymentData.creditCardNumber.length - 4)
val authPresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply {
setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, maskedPresentation)
}
// Prepare an intent that displays the UI that asks for the CVC
val cvcIntent = Intent(this, CvcActivity::class.java)
val cvcIntentSender: IntentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity(
this,
1001,
cvcIntent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT
).intentSender
// Build a FillResponse object that includes a Dataset that requires authentication
val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(
Dataset.Builder()
// The values in the dataset are replaced by the actual
// data once the user provides the CVC
.setValue(parsedStructure.creditCardId, null, authPresentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.expDateId, null, authPresentation)
.setAuthentication(cvcIntentSender)
.build()
).build()
Java
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data
ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure);
Payment paymentData = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure);
// Build the presentation that shows the bank and the last four digits of the
// credit card number, such as 'Bank-1234'
String maskedPresentation = paymentData.bank + "-" +
paymentData.creditCardNumber.subString(paymentData.creditCardNumber.length - 4);
RemoteViews authPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
authPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, maskedPresentation);
// Prepare an intent that displays the UI that asks for the CVC
Intent cvcIntent = new Intent(this, CvcActivity.class);
IntentSender cvcIntentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity(
this,
1001,
cvcIntent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT
).getIntentSender();
// Build a FillResponse object that includes a Dataset that requires authentication
FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder()
.addDataset(new Dataset.Builder()
// The values in the dataset are replaced by the actual
// data once the user provides the CVC
.setValue(parsedStructure.creditCardId, null, authPresentation)
.setValue(parsedStructure.expDateId, null, authPresentation)
.setAuthentication(cvcIntentSender)
.build())
.build();
เมื่อกิจกรรมตรวจสอบ CVC แล้ว กิจกรรมควรเรียกใช้เมธอด setResult()
โดยส่งค่า RESULT_OK และตั้งค่า EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT เพิ่มเติมเป็นออบเจ็กต์ Dataset ที่มีหมายเลขบัตรเครดิตและวันที่หมดอายุ
ชุดข้อมูลใหม่จะแทนที่ชุดข้อมูลที่ต้องมีการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ และระบบจะ
กรอกข้อมูลมุมมองทันที โค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างวิธีแสดงชุดข้อมูล
เมื่อผู้ใช้ระบุ CVC
Kotlin
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data.
val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure)
val paymentData: Payment = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure)
// Build a non-null RemoteViews object to use as the presentation when
// creating the Dataset object. This presentation isn't actually used, but the
// Builder object requires a non-null presentation.
val notUsed = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1)
// Create a dataset with the credit card number and expiration date.
val responseDataset: Dataset = Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(
parsedStructure.creditCardId,
AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.creditCardNumber),
notUsed
)
.setValue(
parsedStructure.expDateId,
AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.expirationDate),
notUsed
)
.build()
val replyIntent = Intent().apply {
putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, responseDataset)
}
Java
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data.
ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure);
Payment paymentData = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure);
// Build a non-null RemoteViews object to use as the presentation when
// creating the Dataset object. This presentation isn't actually used, but the
// Builder object requires a non-null presentation.
RemoteViews notUsed = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1);
// Create a dataset with the credit card number and expiration date.
Dataset responseDataset = new Dataset.Builder()
.setValue(parsedStructure.creditCardId,
AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.creditCardNumber), notUsed)
.setValue(parsedStructure.expDateId,
AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.expirationDate), notUsed)
.build();
Intent replyIntent = new Intent();
replyIntent.putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, responseDataset);
จัดระเบียบข้อมูลเป็นกลุ่มตรรกะ
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติต้องจัดระเบียบข้อมูลในกลุ่มตรรกะที่แยกแนวคิด จากโดเมนต่างๆ ในหน้านี้ กลุ่มเชิงตรรกะเหล่านี้เรียกว่าพาร์ติชัน รายการต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างทั่วไปของพาร์ติชันและฟิลด์
- ข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบ ซึ่งรวมถึงช่องชื่อผู้ใช้และรหัสผ่าน
- ที่อยู่ ซึ่งรวมถึงช่องถนน เมือง รัฐ และรหัสไปรษณีย์
- ข้อมูลการชำระเงิน ซึ่งรวมถึงหมายเลขบัตรเครดิต วันที่หมดอายุ และ ช่องรหัสยืนยัน
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติที่แบ่งพาร์ติชันข้อมูลอย่างถูกต้องจะปกป้องข้อมูลของผู้ใช้ได้ดียิ่งขึ้นโดยไม่เปิดเผยข้อมูลจากพาร์ติชันมากกว่า 1 รายการในชุดข้อมูล เช่น ชุดข้อมูลที่มีข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบไม่จำเป็นต้องมี ข้อมูลการชำระเงิน การจัดระเบียบข้อมูลในพาร์ติชันช่วยให้บริการของคุณ แสดงข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวข้องขั้นต่ำที่จำเป็นต่อการตอบสนองคำขอได้
การจัดระเบียบข้อมูลในพาร์ติชันช่วยให้บริการต่างๆ สามารถป้อนกิจกรรมที่มี มุมมองจากหลายพาร์ติชันได้ในขณะที่ส่งข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวข้องในปริมาณขั้นต่ำ ไปยังแอปไคลเอ็นต์ ตัวอย่างเช่น ลองพิจารณากิจกรรมที่มีมุมมองสำหรับ ชื่อผู้ใช้ รหัสผ่าน ถนน และเมือง รวมถึงบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติที่มี ข้อมูลต่อไปนี้
| พาร์ติชัน | ฟิลด์ 1 | ฟิลด์ 2 |
|---|---|---|
| ข้อมูลรับรอง | work_username | work_password |
| personal_username | personal_password | |
| ที่อยู่ | work_street | work_city |
| personal_street | personal_city |
บริการนี้สามารถเตรียมชุดข้อมูลที่มีการแบ่งพาร์ติชันข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบสำหรับ ทั้งบัญชีงานและบัญชีส่วนตัว เมื่อผู้ใช้เลือกชุดข้อมูลแล้ว การตอบกลับการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติในภายหลังจะระบุที่อยู่สำหรับที่ทำงานหรือที่อยู่ส่วนตัวได้ ขึ้นอยู่กับการเลือกครั้งแรกของผู้ใช้
บริการสามารถระบุฟิลด์ที่ทำให้เกิดคำขอได้โดยการเรียกใช้เมธอด isFocused() ขณะที่ข้ามผ่านออบเจ็กต์ AssistStructure
ซึ่งช่วยให้บริการเตรียม FillResponse ด้วย
ข้อมูลพาร์ติชันที่เหมาะสมได้
ป้อนรหัสแบบใช้ครั้งเดียวทาง SMS โดยอัตโนมัติ
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติจะช่วยผู้ใช้กรอกรหัสแบบใช้ครั้งเดียวที่ส่งโดยใช้ SMS Retriever API ได้
หากต้องการใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ คุณต้องมีคุณสมบัติตรงตามข้อกำหนดต่อไปนี้
- บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติทำงานใน Android 9 (API ระดับ 28) ขึ้นไป
- ผู้ใช้ให้ความยินยอมให้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติอ่านรหัสแบบครั้งเดียว จาก SMS
- แอปพลิเคชันที่คุณให้การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติยังไม่ได้ใช้ SMS Retriever API เพื่ออ่านรหัสแบบใช้ครั้งเดียว
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติใช้ SmsCodeAutofillClient ได้โดยการเรียก SmsCodeRetriever.getAutofillClient() จากบริการ Google Play 19.0.56 ขึ้นไป
ขั้นตอนหลักในการใช้ API นี้ในบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติมีดังนี้
- ในบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ให้ใช้
hasOngoingSmsRequestจากSmsCodeAutofillClientเพื่อพิจารณาว่ามีคำขอที่ใช้งานอยู่สำหรับชื่อแพ็กเกจของแอปพลิเคชันที่คุณกำลังป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติหรือไม่ บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ต้องแสดงข้อความแจ้งคำแนะนำก็ต่อเมื่อฟังก์ชันนี้แสดงผลเป็นfalseเท่านั้น - ในบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ให้ใช้
checkPermissionStateจากSmsCodeAutofillClientเพื่อตรวจสอบว่าบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติมีสิทธิ์ ป้อนรหัสแบบครั้งเดียวโดยอัตโนมัติหรือไม่ สถานะสิทธิ์นี้อาจเป็นNONE,GRANTEDหรือDENIEDบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติต้องแสดงข้อความแจ้งคำแนะนำสำหรับสถานะNONEและGRANTED - ในกิจกรรมการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ให้ใช้สิทธิ์
SmsRetriever.SEND_PERMISSIONเพื่อลงทะเบียนBroadcastReceiverที่รอรับSmsCodeRetriever.SMS_CODE_RETRIEVED_ACTIONเพื่อรับผลลัพธ์รหัส SMS เมื่อพร้อมใช้งาน เรียกใช้
startSmsCodeRetrieverในSmsCodeAutofillClientเพื่อเริ่ม ฟังรหัสแบบใช้ครั้งเดียวที่ส่งผ่าน SMS หากผู้ใช้ให้สิทธิ์ แก่บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติเพื่อดึงรหัสแบบครั้งเดียวจาก SMS บริการจะค้นหา ข้อความ SMS ที่ได้รับในช่วง 1-5 นาทีที่ผ่านมาหากบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติต้องขอสิทธิ์จากผู้ใช้เพื่ออ่านรหัสแบบใช้ครั้งเดียว
Taskที่startSmsCodeRetrieverแสดงผลอาจล้มเหลวโดยมีResolvableApiExceptionแสดงผล หากเกิดกรณีนี้ คุณต้องเรียกใช้เมธอดResolvableApiException.startResolutionForResult()เพื่อแสดงกล่องโต้ตอบความยินยอมสำหรับคำขอสิทธิ์รับผลลัพธ์รหัส SMS จาก Intent แล้วส่งคืนรหัส SMS เป็น การตอบกลับการป้อนอัตโนมัติ
เปิดใช้การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติใน Chrome
Chrome อนุญาตให้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของบุคคลที่สามป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติในแบบฟอร์มโดยกำเนิด ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ได้รับประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ราบรื่นและง่ายดายยิ่งขึ้น หากต้องการใช้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของบุคคลที่สามเพื่อป้อนรหัสผ่าน พาสคีย์ และข้อมูลอื่นๆ เช่น ที่อยู่และข้อมูลการชำระเงินโดยอัตโนมัติ ผู้ใช้ต้องเลือกป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติโดยใช้บริการอื่นในการตั้งค่า Chrome
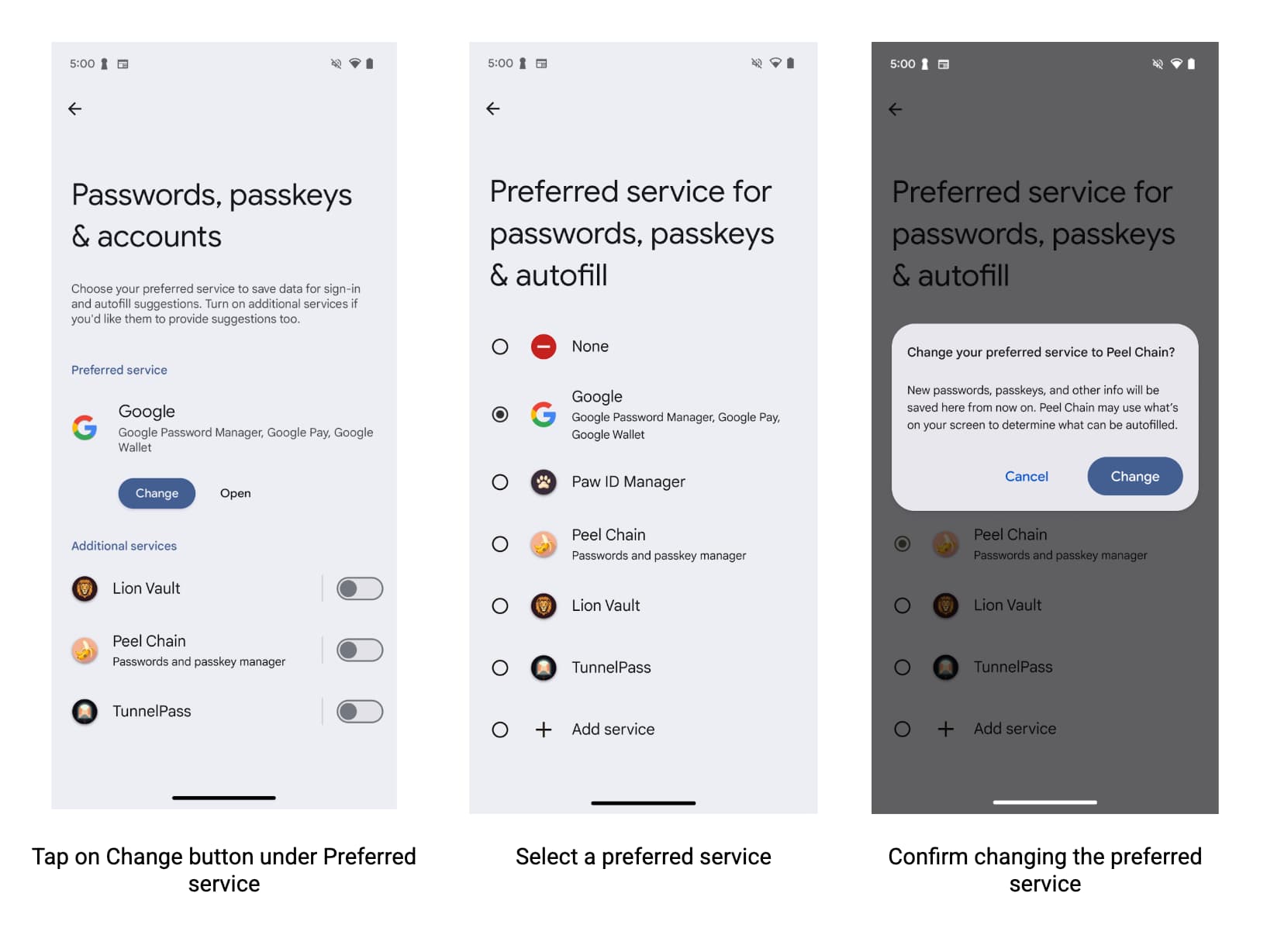
เพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ได้รับประสบการณ์การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติที่ดีที่สุดเท่าที่จะเป็นไปได้ด้วยบริการของคุณและ Chrome ใน Android ผู้ให้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติควรสนับสนุนให้ผู้ใช้ระบุผู้ให้บริการที่ต้องการในการตั้งค่า Chrome
นักพัฒนาแอปสามารถทำสิ่งต่อไปนี้เพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้เปิดปุ่มสลับได้
- ค้นหาการตั้งค่า Chrome และดูว่าผู้ใช้ต้องการใช้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของบุคคลที่สามหรือไม่
- Deep Link ไปยังหน้าการตั้งค่า Chrome ที่ผู้ใช้สามารถเปิดใช้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของบุคคลที่สามได้
ระบุเวอร์ชัน Chrome สูงสุดสำหรับโหมดความเข้ากันได้
Chrome หยุดรองรับโหมดความเข้ากันได้ตั้งแต่เวอร์ชัน 137 เพื่อรองรับ การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของ Android การใช้โหมดความเข้ากันได้อาจทำให้เกิดปัญหาด้านความเสถียร ระบุเวอร์ชันสูงสุดของแพ็กเกจ Chrome ที่รองรับโหมดความเข้ากันได้เพื่อความเสถียรดังนี้
<autofill-service>
...
<compatibility-package android:name="com.android.chrome" android:maxLongVersionCode="711900039" />
<compatibility-package android:name="com.chrome.beta" android:maxLongVersionCode="711900039" />
<compatibility-package android:name="com.chrome.dev" android:maxLongVersionCode="711900039" />
<compatibility-package android:name="com.chrome.canary" android:maxLongVersionCode="711900039" />
...
</autofill-service>
อ่านการตั้งค่า Chrome
แอปใดก็ได้อ่านได้ว่า Chrome ใช้โหมดป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของบุคคลที่สามที่อนุญาตให้ใช้
การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของ Android หรือไม่ Chrome ใช้ ContentProvider ของ Android เพื่อสื่อสาร
ข้อมูลดังกล่าว ประกาศในไฟล์ Manifest ของ Android ว่าคุณต้องการอ่านการตั้งค่าจากช่องใด
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_USER_DICTIONARY"/>
<queries>
<!-- To Query Chrome Beta: -->
<package android:name="com.chrome.beta" />
<!-- To Query Chrome Stable: -->
<package android:name="com.android.chrome" />
</queries>
จากนั้นใช้ ContentResolver ของ Android เพื่อขอข้อมูลดังกล่าวโดย
สร้าง URI ของเนื้อหา ดังนี้
Kotlin
val CHROME_CHANNEL_PACKAGE = "com.android.chrome" // Chrome Stable.
val CONTENT_PROVIDER_NAME = ".AutofillThirdPartyModeContentProvider"
val THIRD_PARTY_MODE_COLUMN = "autofill_third_party_state"
val THIRD_PARTY_MODE_ACTIONS_URI_PATH = "autofill_third_party_mode"
val uri = Uri.Builder()
.scheme(ContentResolver.SCHEME_CONTENT)
.authority(CHROME_CHANNEL_PACKAGE + CONTENT_PROVIDER_NAME)
.path(THIRD_PARTY_MODE_ACTIONS_URI_PATH)
.build()
val cursor = contentResolver.query(
uri,
arrayOf(THIRD_PARTY_MODE_COLUMN), // projection
null, // selection
null, // selectionArgs
null // sortOrder
)
if (cursor == null) {
// Terminate now! Chromium versions older than this don't provide this information.
}
cursor?.use { // Use the safe call operator and the use function for auto-closing
if (it.moveToFirst()) { // Check if the cursor has any rows
val index = it.getColumnIndex(THIRD_PARTY_MODE_COLUMN)
if (index != -1) { // Check if the column exists
val value = it.getInt(index)
if (0 == value) {
// 0 means that the third party mode is turned off. Chrome uses its built-in
// password manager. This is the default for new users.
} else {
// 1 means that the third party mode is turned on. Chrome forwards all
// autofill requests to Android Autofill. Users have to opt-in for this.
}
} else {
// Handle the case where the column doesn't exist. Log a warning, perhaps.
Log.w("Autofill", "Column $THIRD_PARTY_MODE_COLUMN not found in cursor")
}
}
} // The cursor is automatically closed here
Java
final String CHROME_CHANNEL_PACKAGE = "com.android.chrome"; // Chrome Stable.
final String CONTENT_PROVIDER_NAME = ".AutofillThirdPartyModeContentProvider";
final String THIRD_PARTY_MODE_COLUMN = "autofill_third_party_state";
final String THIRD_PARTY_MODE_ACTIONS_URI_PATH = "autofill_third_party_mode";
final Uri uri = new Uri.Builder()
.scheme(ContentResolver.SCHEME_CONTENT)
.authority(CHROME_CHANNEL_PACKAGE + CONTENT_PROVIDER_NAME)
.path(THIRD_PARTY_MODE_ACTIONS_URI_PATH)
.build();
final Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(
uri,
/*projection=*/new String[] {THIRD_PARTY_MODE_COLUMN},
/*selection=*/ null,
/*selectionArgs=*/ null,
/*sortOrder=*/ null);
if (cursor == null) {
// Terminate now! Chromium versions older than this don't provide this information.
}
cursor.moveToFirst(); // Retrieve the result;
int index = cursor.getColumnIndex(THIRD_PARTY_MODE_COLUMN);
if (0 == cursor.getInt(index)) {
// 0 means that the third party mode is turned off. Chrome uses its built-in
// password manager. This is the default for new users.
} else {
// 1 means that the third party mode is turned on. Chrome forwards all
// autofill requests to Android Autofill. Users have to opt-in for this.
}
Deep Link ไปยังการตั้งค่า Chrome
หากต้องการ Deep Link ไปยังหน้าการตั้งค่า Chrome ที่ผู้ใช้สามารถเปิดใช้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของบุคคลที่สามได้ ให้ใช้ Intent ของ Android อย่าลืมกำหนดค่า
การกระทำและหมวดหมู่ตามที่แสดงในตัวอย่างนี้
Kotlin
val autofillSettingsIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_APPLICATION_PREFERENCES)
autofillSettingsIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_DEFAULT)
autofillSettingsIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_APP_BROWSER)
autofillSettingsIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_PREFERENCE)
// Invoking the intent with a chooser allows users to select the channel they
// want to configure. If only one browser reacts to the intent, the chooser is
// skipped.
val chooser = Intent.createChooser(autofillSettingsIntent, "Pick Chrome Channel")
startActivity(chooser)
// If the caller knows which Chrome channel they want to configure,
// they can instead add a package hint to the intent, e.g.
val specificChromeIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_APPLICATION_PREFERENCES) // Create a *new* intent
specificChromeIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_DEFAULT)
specificChromeIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_APP_BROWSER)
specificChromeIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_PREFERENCE)
specificChromeIntent.setPackage("com.android.chrome") // Set the package on the *new* intent
startActivity(specificChromeIntent) // Start the *new* intent
Java
Intent autofillSettingsIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_APPLICATION_PREFERENCES);
autofillSettingsIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_DEFAULT);
autofillSettingsIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_APP_BROWSER);
autofillSettingsIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_PREFERENCE);
// Invoking the intent with a chooser allows users to select the channel they
// want to configure. If only one browser reacts to the intent, the chooser is
// skipped.
Intent chooser = Intent.createChooser(autofillSettingsIntent, "Pick Chrome Channel");
startActivity(chooser);
// If the caller knows which Chrome channel they want to configure,
// they can instead add a package hint to the intent, e.g.
autofillSettingsIntent.setPackage("com.android.chrome");
startActivity(autofillSettingsIntent);
สถานการณ์การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติขั้นสูง
ใช้การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติในสถานการณ์ต่อไปนี้
ผสานรวมกับแป้นพิมพ์
ตั้งแต่ Android 11 เป็นต้นไป แพลตฟอร์มจะอนุญาตให้คีย์บอร์ดและ โปรแกรมแก้ไขวิธีการป้อนข้อมูล (IME) อื่นๆ แสดงคำแนะนำการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติในบรรทัดแทน การใช้เมนูแบบเลื่อนลง ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีที่บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติรองรับฟังก์ชันนี้ได้ที่หัวข้อผสานรวมการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติกับคีย์บอร์ด
แบ่งหน้าชุดข้อมูล
การตอบกลับการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติขนาดใหญ่อาจเกินขนาดธุรกรรมที่อนุญาตของออบเจ็กต์
Binder ซึ่งแสดงถึงออบเจ็กต์ที่สามารถเข้าถึงจากระยะไกลที่จำเป็นต่อการประมวลผลคำขอ
หากต้องการป้องกันไม่ให้ระบบ Android ยกเว้นในสถานการณ์เหล่านี้
คุณสามารถทำให้ FillResponse มีขนาดเล็กได้โดยการเพิ่มออบเจ็กต์ Dataset ไม่เกิน 20 รายการในแต่ละครั้ง หากคำตอบของคุณต้องการชุดข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม คุณสามารถเพิ่ม
ชุดข้อมูลที่แจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบว่ามีข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและดึง
ชุดข้อมูลกลุ่มถัดไปเมื่อเลือก ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่
addDataset(Dataset)
บันทึกข้อมูลที่แยกเป็นหลายหน้าจอ
แอปมักจะแบ่งข้อมูลผู้ใช้ในหลายหน้าจอภายในกิจกรรมเดียวกัน เช่น การสร้างบัญชีผู้ใช้ใหม่ เช่น หน้าจอแรกอาจขอชื่อผู้ใช้ และหน้าจอที่ 2 ขอรหัสผ่าน ในกรณีเหล่านี้ บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของคุณต้องรอจนกว่าผู้ใช้จะป้อนข้อมูลในช่องที่เกี่ยวข้องทั้งหมดก่อนจึงจะแสดง UI การบันทึกการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ โปรดทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้เพื่อจัดการสถานการณ์ดังกล่าว
- ในคำขอการแสดงโฆษณาแรก ให้เพิ่มชุดสถานะไคลเอ็นต์ใน การตอบกลับที่มีรหัสการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติของฟิลด์บางส่วนที่อยู่ใน หน้าจอ
- ในคำขอการแสดงโฆษณาที่ 2 ให้เรียกข้อมูลชุดสถานะไคลเอ็นต์ รับ
รหัสการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติที่ตั้งค่าไว้ในคำขอก่อนหน้าจากสถานะไคลเอ็นต์ แล้วเพิ่ม
รหัสเหล่านี้และค่าสถานะ
FLAG_SAVE_ON_ALL_VIEWS_INVISIBLEลงใน ออบเจ็กต์SaveInfoที่ใช้ในการตอบกลับที่ 2 ในคำขอการบันทึก ให้ใช้ออบเจ็กต์
FillContextที่เหมาะสมเพื่อรับค่าของแต่ละฟิลด์ มีบริบทการแสดงโฆษณา 1 รายการต่อคำขอแสดงโฆษณาดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่บันทึกเมื่อข้อมูลแยกเป็นหลายหน้าจอ
ระบุตรรกะการเริ่มต้นและการสิ้นสุดสำหรับคำขอแต่ละรายการ
ทุกครั้งที่มีคำขอป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ ระบบ Android จะเชื่อมโยงกับบริการ
และเรียกใช้เมธอด onConnected() เมื่อบริการประมวลผลคำขอแล้ว ระบบ Android จะเรียกใช้เมธอด onDisconnected() และ
ยกเลิกการเชื่อมโยงกับบริการ คุณสามารถใช้ onConnected() เพื่อระบุโค้ด
ที่ทำงานก่อนประมวลผลคำขอ และ onDisconnected() เพื่อระบุโค้ด
ที่ทำงานหลังประมวลผลคำขอ
ปรับแต่ง UI การบันทึกการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ
บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติสามารถปรับแต่ง UI การบันทึกการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติเพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจได้
ว่าจะอนุญาตให้บริการบันทึกข้อมูลหรือไม่ บริการสามารถให้
ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสิ่งที่บันทึกไว้ได้ทั้งผ่านข้อความหรือผ่านมุมมองที่
ปรับแต่งแล้ว นอกจากนี้ บริการยังเปลี่ยนลักษณะที่ปรากฏของปุ่มที่
ยกเลิกคำขอให้บันทึกและรับการแจ้งเตือนเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะปุ่มนั้นได้ด้วย
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่หน้าอ้างอิงของ SaveInfo
โหมดความเข้ากันได้
โหมดความเข้ากันได้ช่วยให้บริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติใช้โครงสร้างเสมือนของการช่วยเหลือพิเศษเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ในการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติได้ ซึ่งมีประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งสำหรับ การให้บริการฟังก์ชันการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติในเบราว์เซอร์ที่ไม่ได้ใช้ API การป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติอย่างชัดเจน
หากต้องการทดสอบบริการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติโดยใช้โหมดความเข้ากันได้ ให้เพิ่ม เบราว์เซอร์หรือแอปไปยังรายการที่อนุญาตที่ต้องใช้โหมดความเข้ากันได้อย่างชัดเจน คุณตรวจสอบได้ว่าแพ็กเกจใดอยู่ในรายการที่อนุญาตแล้วโดยเรียกใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้
$ adb shell settings get global autofill_compat_mode_allowed_packages
หากแพ็กเกจที่คุณทดสอบไม่อยู่ในรายการ ให้เพิ่มโดยเรียกใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้
โดยที่ pkgX คือแพ็กเกจของแอป
$ adb shell settings put global autofill_compat_mode_allowed_packages pkg1[resId1]:pkg2[resId1,resId2]
หากแอปเป็นเบราว์เซอร์ ให้ใช้ resIdx เพื่อระบุรหัสทรัพยากรของ
ช่องป้อนข้อมูลที่มี URL ของหน้าที่แสดง
โหมดความเข้ากันได้มีข้อจำกัดต่อไปนี้
- ระบบจะทริกเกอร์คำขอให้บันทึกเมื่อบริการใช้แฟล็ก
FLAG_SAVE_ON_ALL_VIEWS_INVISIBLEหรือมีการเรียกใช้เมธอดsetTrigger()FLAG_SAVE_ON_ALL_VIEWS_INVISIBLEจะตั้งค่าโดยค่าเริ่มต้นเมื่อใช้ โหมดความเข้ากันได้ - ค่าข้อความของโหนดอาจไม่พร้อมใช้งานในเมธอด
onSaveRequest(SaveRequest, SaveCallback)
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโหมดความเข้ากันได้ รวมถึงข้อจำกัด
ที่เกี่ยวข้องได้ที่ข้อมูลอ้างอิงคลาส AutofillService
