콘텐츠 제공자는 애플리케이션이 단독으로 저장되었거나 다른 앱에 의해 저장된 데이터에 대한 액세스를 관리하도록 돕고 다른 앱과 데이터를 공유하는 방법을 제공할 수 있습니다. 데이터를 캡슐화하고 데이터 보안을 정의하는 메커니즘을 제공합니다. 콘텐츠 제공자는 한 프로세스의 데이터를 다른 프로세스에서 실행 중인 코드와 연결하는 표준 인터페이스입니다.
콘텐츠 제공자를 구현하면 많은 장점을 누릴 수 있습니다. 가장 중요한 점은 그림 1과 같이 다른 애플리케이션에서 앱 데이터에 안전하게 액세스하고 수정할 수 있도록 콘텐츠 제공자를 구성할 수 있다는 것입니다.
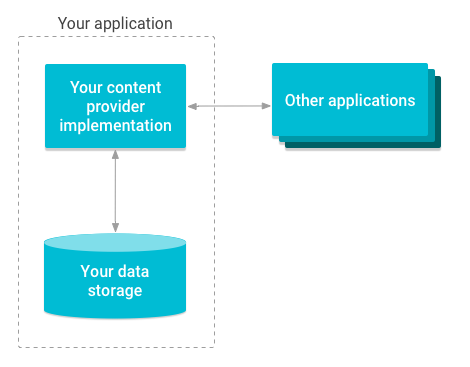
그림 1. 콘텐츠 제공자가 저장소에 대한 액세스를 관리하는 방법의 개요 다이어그램
데이터를 공유할 계획이라면 콘텐츠 제공자를 사용하세요. 데이터를 공유할 계획이 없다면 사용하지 않아도 되지만 데이터 액세스에 의존하는 다른 애플리케이션에 영향을 주지 않고 애플리케이션 데이터 스토리지 구현을 수정할 수 있는 추상화를 제공하기 때문에 데이터를 공유할 수 있습니다.
이 시나리오에서는 콘텐츠 제공자만 영향을 받고 여기에 액세스하는 애플리케이션은 영향을 받지 않습니다. 예를 들어, SQLite 데이터베이스를 대체 저장소로 교체할 수 있습니다(그림 2 참고).
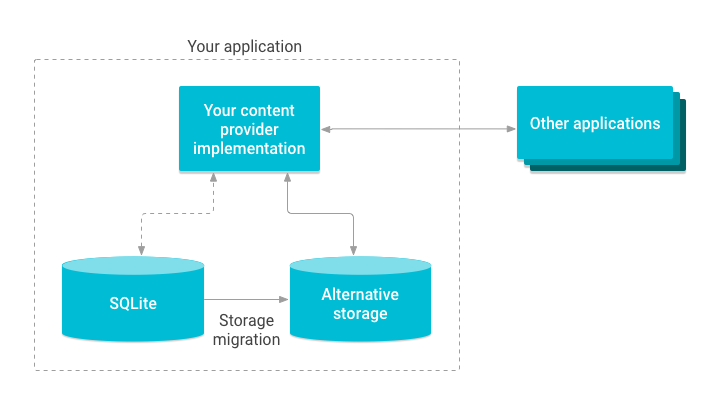
그림 2. 콘텐츠 제공자 저장소를 마이그레이션하는 모습.
다음과 같이 ContentProvider 클래스를 사용하는 다른 클래스도 많이 있습니다.
이러한 클래스를 사용하는 경우 애플리케이션에 콘텐츠 제공자를 구현해야 합니다. 동기화 어댑터 프레임워크를 사용할 때 대안으로 스텁 콘텐츠 제공업체를 만들 수도 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 스터브 콘텐츠 제공업체 만들기를 참고하세요. 또한 다음과 같은 경우에는 자체적인 콘텐츠 제공자가 필요합니다.
- 애플리케이션에 맞춤 추천 검색어를 구현하기 위해
- 위젯에 애플리케이션 데이터를 노출하기 위해
- 복잡한 데이터나 파일을 애플리케이션에서 다른 애플리케이션으로 복사하여 붙여넣기
Android 프레임워크에는 오디오, 동영상, 이미지, 개인 연락처 정보 등의 데이터를 관리하는 콘텐츠 제공자가 포함되어 있습니다. 그중 일부는 android.provider
패키지의 참조 문서에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 일부 제한사항이 있지만 이러한 제공자는 모든 Android 애플리케이션에서 액세스할 수 있습니다.
콘텐츠 제공자를 사용하면 구조화된 데이터(예: SQLite 관계형 데이터베이스) 또는 구조화되지 않은 데이터(예: 이미지 파일)를 포함한 다양한 데이터 저장소 소스의 액세스를 관리할 수 있습니다. Android에서 사용 가능한 저장소 유형에 관한 자세한 내용은 데이터 및 파일 저장소 개요 및 데이터 저장소 설계를 참고하세요.
콘텐츠 제공자의 장점
콘텐츠 제공자는 데이터 액세스 권한에 대한 세분화된 제어 기능을 제공합니다. 애플리케이션 내에 있는 콘텐츠 제공자로만 액세스를 제한하거나, 다른 애플리케이션의 데이터에 액세스할 수 있는 포괄적인 권한을 부여하거나, 데이터 읽기 및 쓰기와 관련된 다른 권한을 구성할 수 있습니다. 콘텐츠 제공자를 안전하게 사용하는 방법에 관한 자세한 내용은 데이터 저장을 위한 보안 팁 및 콘텐츠 제공자 권한을 참조하세요.
콘텐츠 제공자를 사용하여 애플리케이션의 여러 데이터 소스에 액세스하기 위한 세부정보를 추상화할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 애플리케이션은 동영상 및 오디오 파일과 함께 구조화된 레코드를 SQLite 데이터베이스에 저장할 수 있습니다. 콘텐츠 제공업체를 사용하여 이 모든 데이터에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
또한 CursorLoader 객체는 콘텐츠 제공자를 사용하여 비동기 쿼리를 실행한 다음 애플리케이션의 UI 레이어로 결과를 반환합니다. CursorLoader를 사용하여 백그라운드에서 데이터를 로드하는 방법에 관한 자세한 내용은
로더를 참고하세요.
다음 주제에서는 콘텐츠 제공자에 대해 좀 더 자세히 설명합니다.
- 콘텐츠 제공자 기본사항
- 기존 콘텐츠 제공자를 사용하여 데이터에 액세스하고 데이터를 업데이트하는 방법
- 콘텐츠 제공자 만들기
- 자체 콘텐츠 제공자를 설계하고 구현하는 방법
- 캘린더 제공자 개요
- Android 플랫폼의 일부인 캘린더 제공자에 액세스하는 방법입니다.
- 연락처 제공자
- Android 플랫폼의 일부인 연락처 제공자에 액세스하는 방법
