على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 8.0 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 26 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث، يتم إقران الأجهزة المصاحبة من خلال إجراء عملية بحث عن أجهزة قريبة باستخدام البلوتوث أو Wi-Fi نيابةً عن تطبيقك بدون الحاجة إلى إذن ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. ويساعد ذلك في زيادة إجراءات حماية خصوصية المستخدمين. استخدِم هذه الطريقة لإجراء عملية الإعداد الأوّلية للجهاز المصاحب، مثل ساعة ذكية متوافقة مع تقنية البلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة (BLE). بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يتطلّب إقران الجهاز المرافق تفعيل "خدمات الموقع الجغرافي".
لا يؤدي إقران الجهاز المصاحب إلى إنشاء اتصالات تلقائيًا أو تفعيل البحث المستمر. يمكن للتطبيقات استخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات الاتصال عبر البلوتوث أو Wi-Fi لإنشاء اتصالات.
بعد إقران الجهاز، يمكنه استخدام الإذنَين
REQUEST_COMPANION_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND
و
REQUEST_COMPANION_USE_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND
لبدء التطبيق من الخلفية. يمكن للتطبيقات أيضًا استخدام إذن
REQUEST_COMPANION_START_FOREGROUND_SERVICES_FROM_BACKGROUND
لبدء خدمة تعمل في المقدّمة من الخلفية.
يمكن للمستخدم اختيار جهاز من القائمة ومنح التطبيق أذونات للوصول إلى الجهاز. يتم إلغاء هذه الأذونات إذا ألغيت تثبيت التطبيق أو اتّصلت
بـ disassociate().
ويتحمّل التطبيق المصاحب مسؤولية محو عمليات الربط الخاصة به إذا لم يعُد المستخدم بحاجة إليها، مثلاً عند تسجيل الخروج أو إزالة الأجهزة المرتبطة.
تنفيذ عملية إقران الجهاز المصاحب
يوضّح هذا القسم كيفية استخدام CompanionDeviceManager لإقران تطبيقك بالأجهزة المصاحبة عبر البلوتوث والبلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة وشبكة Wi-Fi.
تحديد الأجهزة المصاحبة
يوضّح نموذج الرمز التالي كيفية إضافة العلامة <uses-feature> إلى ملف بيان. يُعلم ذلك النظام بأنّ تطبيقك يهدف إلى إعداد أجهزة مصاحبة.
<uses-feature android:name="android.software.companion_device_setup"/>
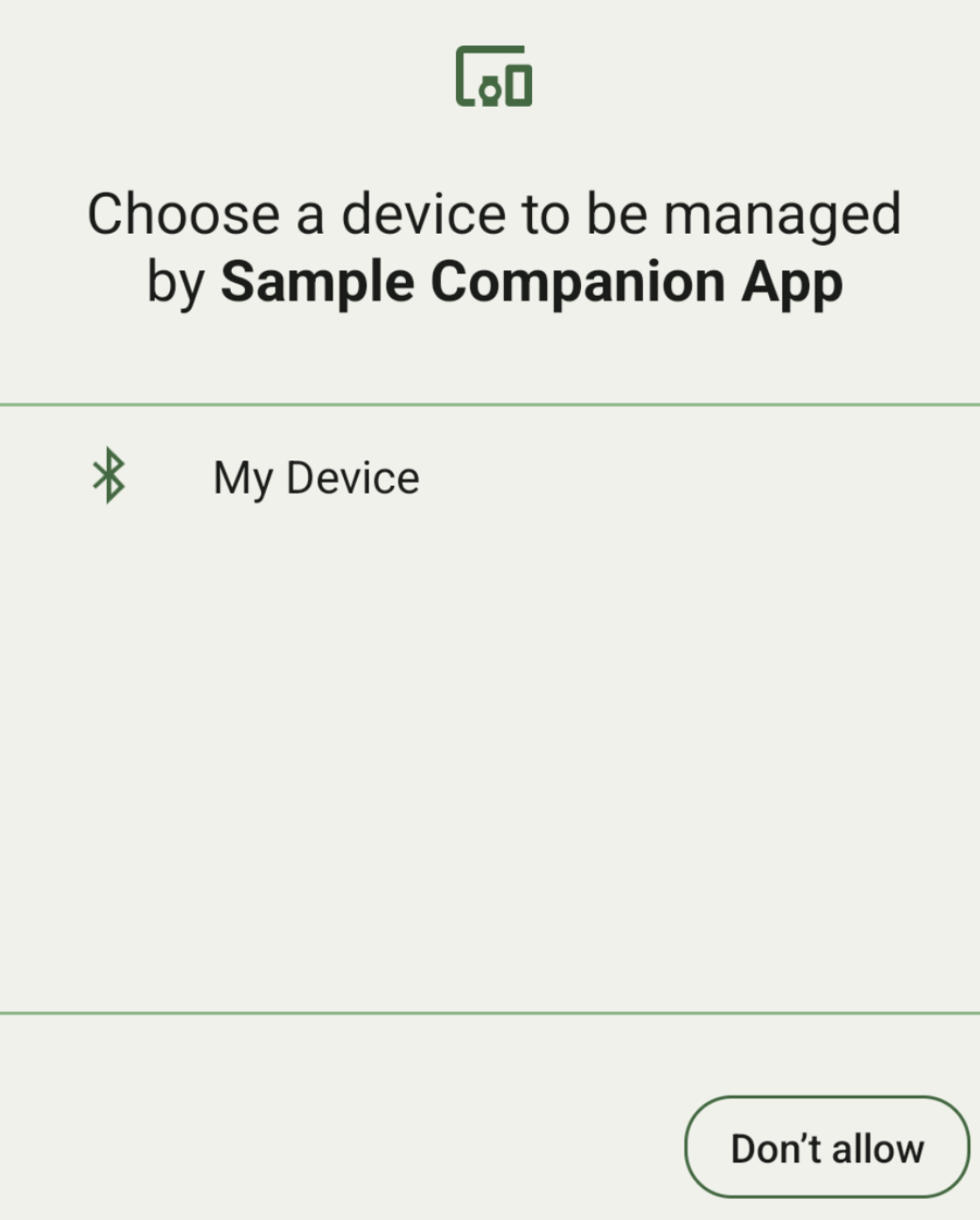
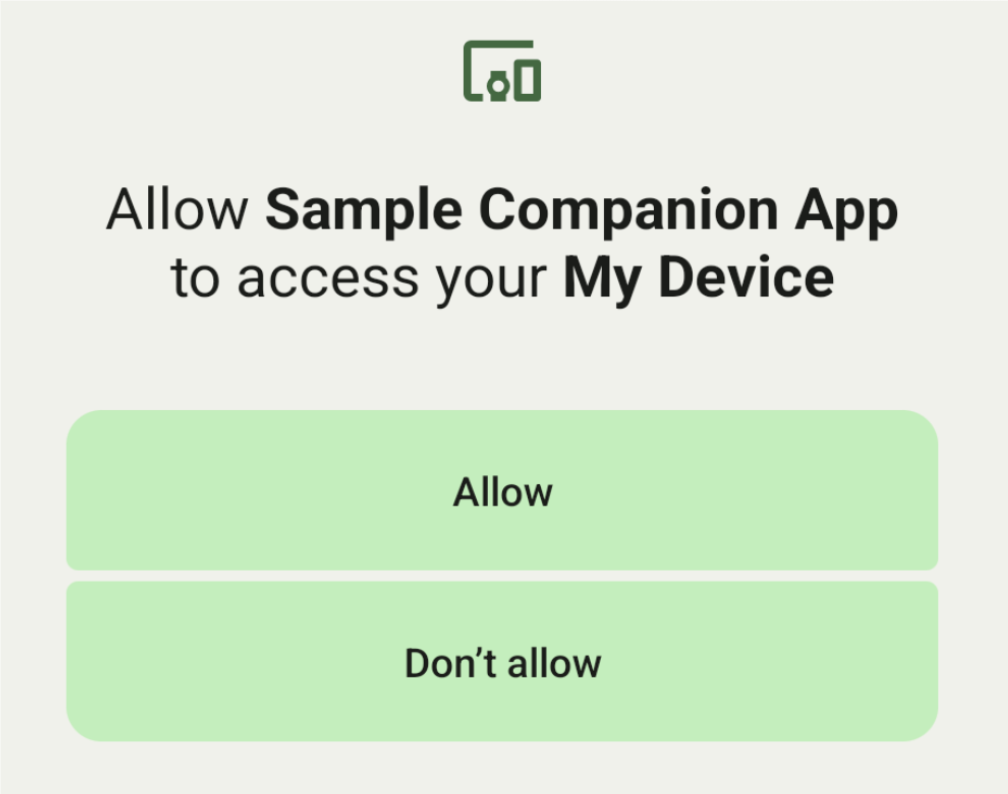
عرض قائمة الأجهزة حسب DeviceFilter
يمكنك عرض جميع الأجهزة المساعدة المتوافقة مع النطاق والتي تتطابق مع
DeviceFilter
الذي تقدّمه (كما هو موضّح في الشكل 1). إذا أردت حصر عملية الفحص على جهاز واحد فقط، يمكنك النقر على setSingleDevice()
لضبطه على true (كما هو موضّح في الشكل 2).
في ما يلي الفئات الفرعية من DeviceFilter التي
يمكن تحديدها في AssociationRequest:
تحتوي جميع الفئات الفرعية الثلاث على أدوات إنشاء تعمل على تبسيط عملية إعداد الفلاتر.
في المثال التالي، يبحث جهاز عن جهاز بلوتوث يحمل BluetoothDeviceFilter.
Kotlin
val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build()
Java
BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build();
اضبط DeviceFilter على AssociationRequest كي تتمكّن CompanionDeviceManager من تحديد نوع الأجهزة التي يجب البحث عنها.
Kotlin
val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build()
Java
AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build();
بعد أن يُعدِّل تطبيقك AssociationRequest، شغِّل الدالة associate() على CompanionDeviceManager. تتلقّى الدالة associate()
AssociationRequest وCallback.
تعرض الدالة Callback
IntentSender في
onAssociationPending عندما يعثر CompanionDeviceManager على جهاز
ويكون جاهزًا لعرض مربّع حوار موافقة المستخدم.
بعد أن يؤكّد المستخدم الجهاز، يتم عرض AssociationInfo
للجهاز في onAssociationCreated.
إذا لم يعثر تطبيقك على أي أجهزة، سيعرض الرمز onFailure
مع رسالة خطأ.
على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 13 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 33 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث:
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // An association is created. } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } })
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // An association is created. } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // To handle the failure. });
على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار Android 12L (المستوى 32 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأقدم (تم إيقافها نهائيًا):
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } }, null)
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // To handle the failure. } }, null);
يتم إرسال نتيجة اختيار المستخدم إلى الجزء في
onActivityResult()
من نشاطك. يمكنك بعد ذلك الوصول إلى الجهاز المحدّد.
عندما يختار المستخدم جهاز بلوتوث، توقَّع ظهور
BluetoothDevice.
عندما يختار المستخدم جهاز Bluetooth LE، من المتوقّع أن تظهر له قيمة
android.bluetooth.le.ScanResult.
عندما يختار المستخدم جهاز Wi-Fi، توقَّع ظهور
android.net.wifi.ScanResult.
Kotlin
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } }
Java
@Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } }
اطّلِع على المثال الكامل:
على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 13 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 33 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث:
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } val mBluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter by lazy { val java = BluetoothManager::class.java getSystemService(java)!!.adapter } val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. var associationId: int = associationInfo.id var macAddress: MacAddress = associationInfo.deviceMacAddress } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } ) override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // do not include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. int associationId = associationInfo.getId(); MacAddress macAddress = associationInfo.getDeviceMacAddress(); } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // Handle the failure. }); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار Android 12L (المستوى 32 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأقدم (تم إيقافها نهائيًا):
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } }, null) } override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // don't include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { // failed to send the intent } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // handle failure to find the companion device } }, null); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
الملفات الشخصية للأجهزة المصاحبة
في نظام التشغيل Android 12 (المستوى 31 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث، يمكن للتطبيقات المصاحبة التي تدير أجهزة مثل الساعات استخدام ملفات تعريف الأجهزة المصاحبة لتسهيل عملية الإعداد من خلال منح الأذونات اللازمة عند الاقتران. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على ملفات تعريف الأجهزة المرافقة.
إبقاء التطبيقات المصاحبة نشطة
بدءًا من Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)،
تم إيقاف CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence(String) وCompanionDeviceService.onDeviceAppeared() نهائيًا.
عليك استخدام
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence (ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)لإدارة ربطCompanionDeviceServiceالذي نفّذته تلقائيًا.- تتم إدارة حالة ربط
CompanionDeviceServiceتلقائيًا استنادًا إلى حالة توفّر الجهاز المصاحب المرتبط به:- يتم ربط الخدمة عندما يكون الجهاز المصاحب ضمن نطاق البلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة أو عند الاتصال باستخدام البلوتوث.
- تتم إزالة ربط الخدمة عندما ينتقل الجهاز المصاحب إلى خارج نطاق البلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة أو يتم إنهاء اتصال البلوتوث.
- تتم إدارة حالة ربط
سيتلقّى التطبيق رد اتصال استنادًا إلى مجموعة متنوعة من
DevicePresenceEvent.للحصول على التفاصيل، يُرجى الاطّلاع على
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceEvent().
