Auf Geräten mit Android 8.0 (API-Ebene 26) und höher wird bei der Kopplung von Companion-Geräten im Namen Ihrer App ein Bluetooth- oder WLAN-Scan von Geräten in der Nähe durchgeführt, ohne dass die Berechtigung ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION erforderlich ist. So wird der Datenschutz für Nutzer maximiert. Mit dieser Methode können Sie die Ersteinrichtung des Begleitgeräts, z. B. einer BLE-fähigen Smartwatch, vornehmen. Außerdem müssen die Standortdienste aktiviert sein, damit das Companion-Gerät gekoppelt werden kann.
Durch die Kopplung eines Begleitgeräts werden keine Verbindungen hergestellt und kein kontinuierliches Scannen aktiviert. Apps können Bluetooth- oder WLAN-Verbindungs-APIs verwenden, um Verbindungen herzustellen.
Nachdem das Gerät gekoppelt wurde, kann es die Berechtigungen REQUEST_COMPANION_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND und REQUEST_COMPANION_USE_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND verwenden, um die App im Hintergrund zu starten. Apps können auch die Berechtigung REQUEST_COMPANION_START_FOREGROUND_SERVICES_FROM_BACKGROUND verwenden, um einen Dienst im Vordergrund aus dem Hintergrund zu starten.
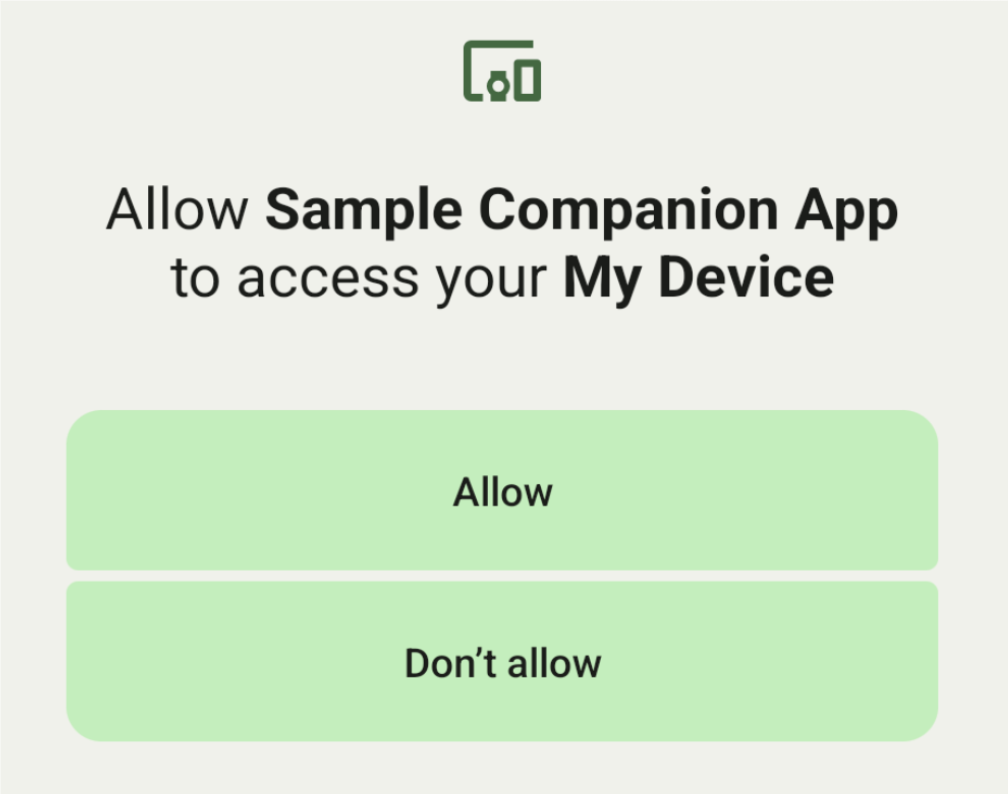
Ein Nutzer kann ein Gerät aus einer Liste auswählen und der App Berechtigungen für den Zugriff auf das Gerät erteilen. Diese Berechtigungen werden widerrufen, wenn Sie die App deinstallieren oder disassociate() aufrufen.
Die Companion-App ist dafür verantwortlich, ihre eigenen Verknüpfungen zu löschen, wenn der Nutzer sie nicht mehr benötigt, z. B. wenn er sich abmeldet oder verknüpfte Geräte entfernt.
Begleitgerätkopplung implementieren
In diesem Abschnitt wird beschrieben, wie Sie die CompanionDeviceManager verwenden, um Ihre App über Bluetooth, BLE und WLAN mit Begleitgeräten zu koppeln.
Begleitgeräte angeben
Das folgende Codebeispiel zeigt, wie Sie das Flag <uses-feature> einer Manifestdatei hinzufügen. Dadurch wird dem System mitgeteilt, dass Ihre App Begleitgeräte einrichten möchte.
<uses-feature android:name="android.software.companion_device_setup"/>
Geräte nach DeviceFilter auflisten
Sie können alle Companion-Geräte in Reichweite anzeigen, die dem von Ihnen angegebenen DeviceFilter entsprechen (siehe Abbildung 1). Wenn Sie das Scannen auf ein Gerät beschränken möchten, können Sie setSingleDevice() auf true setzen (siehe Abbildung 2).
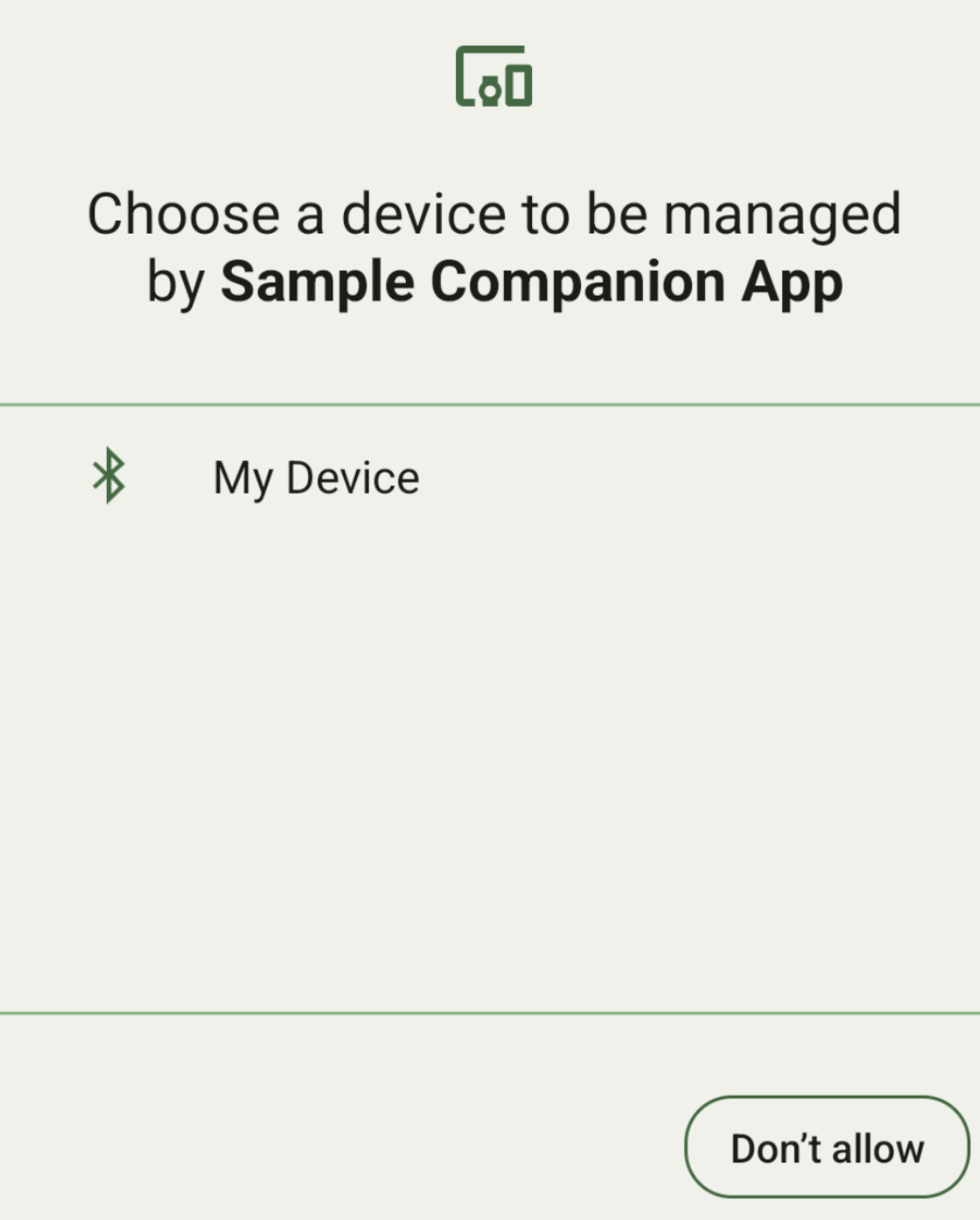
Die folgenden Unterklassen von DeviceFilter können in AssociationRequest angegeben werden:
Alle drei Unterklassen haben Builder, die die Konfiguration von Filtern vereinfachen.
Im folgenden Beispiel sucht ein Gerät nach einem Bluetooth-Gerät mit einem BluetoothDeviceFilter.
Kotlin
val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build()
Java
BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build();
Legen Sie ein DeviceFilter auf ein AssociationRequest fest, damit CompanionDeviceManager ermitteln kann, nach welchen Gerätetypen gesucht werden soll.
Kotlin
val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build()
Java
AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build();
Nachdem Ihre App ein AssociationRequest initialisiert hat, führen Sie die Funktion associate() für das CompanionDeviceManager aus. Die Funktion associate() verwendet ein AssociationRequest und ein Callback.
Die Callback gibt eine IntentSender in der onAssociationPending zurück, wenn CompanionDeviceManager ein Gerät findet und ein Dialogfeld für die Einwilligung des Nutzers angezeigt werden kann.
Nachdem der Nutzer das Gerät bestätigt hat, wird ein AssociationInfo des Geräts in onAssociationCreated zurückgegeben.
Wenn Ihre App keine Geräte findet, gibt der Callback onFailure mit einer Fehlermeldung zurück.
Auf Geräten mit Android 13 (API‑Level 33) und höher gilt Folgendes:
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // An association is created. } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } })
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // An association is created. } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // To handle the failure. });
Auf Geräten mit Android 12L (API‑Level 32) oder niedriger (eingestellt):
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } }, null)
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // To handle the failure. } }, null);
Das Ergebnis der Nutzerauswahl wird an das Fragment in der onActivityResult() Ihrer Aktivität zurückgesendet. Sie können dann auf das ausgewählte Gerät zugreifen.
Wenn der Nutzer ein Bluetooth-Gerät auswählt, wird ein BluetoothDevice erwartet.
Wenn der Nutzer ein Bluetooth LE-Gerät auswählt, wird eine android.bluetooth.le.ScanResult erwartet.
Wenn der Nutzer ein WLAN-Gerät auswählt, erwarte ein android.net.wifi.ScanResult.
Kotlin
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } }
Java
@Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } }
Vollständiges Beispiel ansehen:
Auf Geräten mit Android 13 (API‑Level 33) und höher gilt Folgendes:
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } val mBluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter by lazy { val java = BluetoothManager::class.java getSystemService(java)!!.adapter } val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. var associationId: int = associationInfo.id var macAddress: MacAddress = associationInfo.deviceMacAddress } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } ) override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // do not include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. int associationId = associationInfo.getId(); MacAddress macAddress = associationInfo.getDeviceMacAddress(); } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // Handle the failure. }); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
Auf Geräten mit Android 12L (API‑Level 32) oder niedriger (eingestellt):
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } }, null) } override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // don't include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { // failed to send the intent } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // handle failure to find the companion device } }, null); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
Profile für Begleitgeräte
Unter Android 12 (API-Level 31) und höher können Companion-Apps, die Geräte wie Smartwatches verwalten, Companion-Geräteprofile verwenden, um die Einrichtung zu vereinfachen. Dazu werden beim Koppeln die erforderlichen Berechtigungen erteilt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Companion Device Profiles.
Companion-Apps aktiv lassen
Ab Android 16 (API-Level 36)
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence(String)
und
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceAppeared()
wurden eingestellt.
Sie sollten
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence (ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)verwenden, um die Bindung Ihrer implementiertenCompanionDeviceServiceautomatisch zu verwalten.- Der Bindungsstatus Ihres
CompanionDeviceServicewird automatisch anhand des Anwesenheitsstatus des zugehörigen Companion-Geräts verwaltet:- Der Dienst wird gebunden, wenn sich das Companion-Gerät in BLE-Reichweite befindet oder über Bluetooth verbunden ist.
- Die Bindung an den Dienst wird aufgehoben, wenn sich das Companion-Gerät außerhalb der BLE-Reichweite befindet oder die Bluetooth-Verbindung beendet wird.
- Der Bindungsstatus Ihres
Die App erhält einen Callback basierend auf verschiedenen
DevicePresenceEvent.Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceEvent().
