Halaman ini menjelaskan cara SDK pihak ketiga dapat mengintegrasikan penginstalan inline, fitur pengujian baru untuk Google Play yang menampilkan detail produk aplikasi Google Play dalam antarmuka setengah layar. Instalasi sebaris memungkinkan pengguna merasakan alur instalasi aplikasi yang lancar tanpa meninggalkan konteks aplikasi.
Developer SDK pihak ketiga dapat mengintegrasikan fitur penginstalan inline ke dalam SDK mereka untuk memungkinkan developer aplikasi yang menggunakan SDK tersebut mengakses penginstalan inline untuk aplikasi mereka.
Persyaratan
Agar antarmuka setengah lembar instalasi sebaris muncul di aplikasi:
- Versi minimum Google Play harus 40.4.
- Level API Android harus 23 atau lebih tinggi.
Arsitektur proses
Arsitektur proses instalasi sebaris ditunjukkan pada gambar berikut:
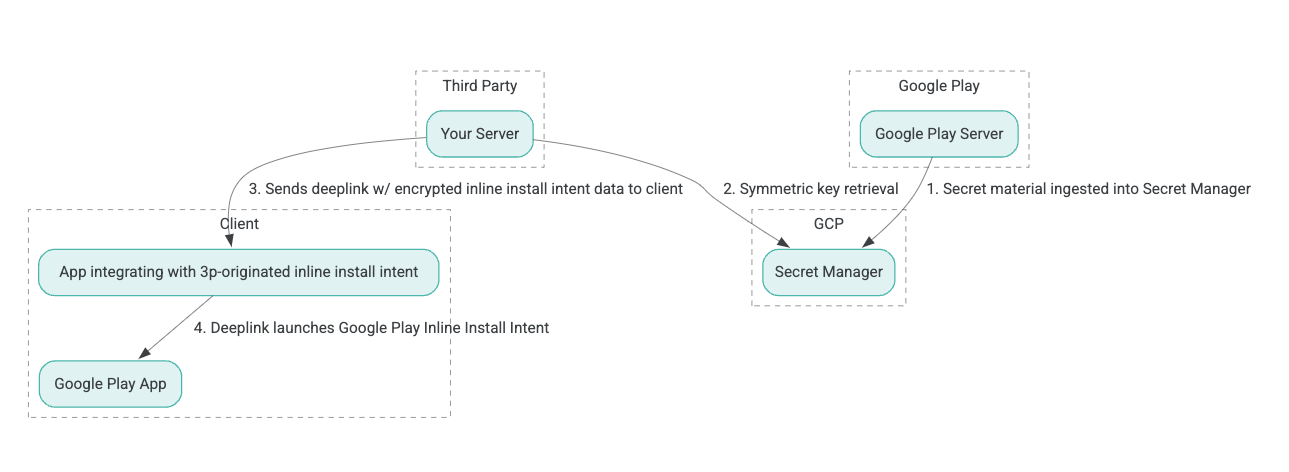
- Server Google Play membuat kunci enkripsi Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD) dan memasukkan kunci tersebut ke instance Secret Manager Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Integrator pihak ketiga mengambil kunci AEAD dari GCP Secret Manager.
- Integrator pihak ketiga mengenkripsi data
Intentpenginstalan inline, membuat ciphertext yang diteruskan dalam deep link yang digunakan untuk memanggil intent penginstalan inline, dan mengirim deep link ke klien dalam respons. - Saat deep link diikuti, aplikasi Google Play akan menangani intent.
Untuk mengonfigurasi SDK pihak ketiga untuk menggunakan proses instalasi sebaris, selesaikan langkah-langkah berikut.
Membuat akun layanan di Project Google Cloud
Pada langkah ini, Anda menyiapkan akun layanan menggunakan Google Cloud Console.
- Siapkan Project Google Cloud:
- Buat organisasi Google Cloud. Saat Anda membuat akun Google Workspace atau Cloud Identity dan mengaitkannya dengan nama domain Anda, sumber daya organisasi akan dibuat secara otomatis. Untuk detailnya, lihat Membuat dan mengelola sumber daya organisasi.
- Masuk ke GCP Console menggunakan akun Google Cloud yang dibuat pada langkah sebelumnya, lalu buat proyek Google Cloud. Untuk detailnya, lihat Membuat proyek Google Cloud.
- Buat akun layanan di proyek Google Cloud yang dibuat. Akun layanan digunakan sebagai Google Cloud Identity untuk mengakses kunci simetris atas nama server Anda. Untuk detailnya, lihat Membuat akun layanan.
- Gunakan ID Pelanggan Google Workspace (GWCID) / ID Dasher yang sama yang dimasukkan pada formulir minat.
- Buat dan unduh kunci pribadi akun layanan tersebut.
- Buat kunci untuk akun layanan tersebut. Untuk detailnya, lihat Membuat kunci akun layanan.
- Unduh kunci akun layanan dan simpan agar dapat diakses di server Anda, karena kunci tersebut digunakan untuk autentikasi untuk mengakses sumber daya Google Cloud untuk kunci simetris. Untuk detailnya, lihat Mendapatkan kunci akun layanan.
Ambil kredensial
Pada langkah ini, Anda mengambil kunci simetris dari Secret Manager dan menyimpannya dengan aman (misalnya, dalam file JSON) di penyimpanan server Anda sendiri. Kunci ini digunakan untuk menghasilkan ciphertext data instalasi sebaris.
Nilai secret_id/secretId merujuk pada nama rahasia di dalam Secret Manager; nama ini dibuat dengan menambahkan hsdp-3p-key- ke nilai sdk_id yang disediakan Play. Misalnya, jika sdk_id adalah abc, nama rahasianya adalah hsdp-3p-key-abc.
Versi rahasia diperbarui setiap minggu pada hari Selasa pukul 2 siang UTC. Kunci terbaru kedua terus berfungsi hingga rotasi berikutnya, dan materi kunci harus diambil dan disimpan setiap minggu.
Contoh Python
Contoh kode berikut menggunakan token akses yang disimpan dalam file JSON untuk mengakses materi kunci di GCP Secret Manager dan mencetaknya ke konsol.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
from google.cloud import secretmanager
from google.oauth2 import service_account
import google_crc32c
# Create a service account key file.
service_account_key_file = "<json key file of the service account>"
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(service_account_key_file)
# Create the Secret Manager client.
client = secretmanager.SecretManagerServiceClient(
credentials=credentials
)
# Build the resource name of the secret version.
name = f"projects/prod-play-hsdp-3p-caller-auth/secrets/<secret_id>/versions/latest"
# Access the secret version.
response = client.access_secret_version(request={"name": name})
# Verify payload checksum.
crc32c = google_crc32c.Checksum()
crc32c.update(response.payload.data)
if response.payload.data_crc32c != int(crc32c.hexdigest(), 16):
print("Data corruption detected.")
# A keyset created with "tinkey create-keyset --key-template=AES256_GCM". Note
# that this keyset has the secret key information in cleartext.
keyset = response.payload.data.decode("UTF-8")
# WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment. Please store it
# in a secure storage.
with open('<key file name>', 'w') as f:
f.write(keyset)
Contoh Java
Contoh kode berikut menggunakan token akses yang disimpan dalam file JSON untuk mengakses materi utama di GCP Secret Manager dan menuliskannya ke file JSON.
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.api.gax.core.CredentialsProvider;
import com.google.api.gax.core.FixedCredentialsProvider;
import com.google.auth.oauth2.ServiceAccountCredentials;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.AccessSecretVersionResponse;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceClient;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceSettings;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretVersionName;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.zip.CRC32C;
import java.util.zip.Checksum;
/** */
final class ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide {
private ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
accessSecretVersion();
}
public static void accessSecretVersion() throws IOException {
// TODO(developer): Replace these variables before running the sample.
String projectId = "projectId";
String secretId = "secretId";
String versionId = "versionId";
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath = "path/to/credentials.json";
String secretMaterialOutputPath = "path/to/secret.json";
accessSecretVersion(
projectId, secretId, versionId, accessTokenPrivateKeyPath, secretMaterialOutputPath);
}
// Access the payload for the given secret version if one exists. The version
// can be a version number as a string (e.g. "5") or an alias (e.g. "latest").
public static void accessSecretVersion(
String projectId,
String secretId,
String versionId,
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath,
String secretMaterialOutputPath)
throws IOException {
// We can explicitly instantiate the SecretManagerServiceClient (below) from a json file if we:
// 1. Create a CredentialsProvider from a FileInputStream of the JSON file,
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider =
FixedCredentialsProvider.create(
ServiceAccountCredentials.fromStream(new FileInputStream(accessTokenPrivateKeyPath)));
// 2. Build a SecretManagerService Settings object from that credentials provider, and
SecretManagerServiceSettings secretManagerServiceSettings =
SecretManagerServiceSettings.newBuilder()
.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.build();
// 3. Initialize client that will be used to send requests by passing the settings object to
// create(). This client only needs to be created once, and can be reused for multiple requests.
// After completing all of your requests, call the "close" method on the client to safely clean
// up any remaining background resources.
try (SecretManagerServiceClient client =
SecretManagerServiceClient.create(secretManagerServiceSettings)) {
SecretVersionName secretVersionName = SecretVersionName.of(projectId, secretId, versionId);
// Access the secret version.
AccessSecretVersionResponse response = client.accessSecretVersion(secretVersionName);
// Verify checksum. The used library is available in Java 9+.
// If using Java 8, you may use the following:
// https://github.com/google/guava/blob/e62d6a0456420d295089a9c319b7593a3eae4a83/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/Hashing.java#L395
byte[] data = response.getPayload().getData().toByteArray();
Checksum checksum = new CRC32C();
checksum.update(data, 0, data.length);
if (response.getPayload().getDataCrc32C() != checksum.getValue()) {
System.out.printf("Data corruption detected.");
return;
}
String payload = response.getPayload().getData().toStringUtf8();
// Print the secret payload.
//
// WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment - this
// snippet is showing how to access the secret material.
System.out.printf("Plaintext: %s\n", payload);
// Write the JSON secret material payload to a json file
try (PrintWriter out =
new PrintWriter(Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get(secretMaterialOutputPath), UTF_8))) {
out.write(payload);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Menetapkan Kredensial Default Aplikasi
Jika Anda tidak ingin menggunakan CredentialsProvider untuk meneruskan kunci privat ke file JSON dalam implementasi Java, Anda dapat mengubah implementasinya dengan menetapkan Kredensial Default Aplikasi (ADC):
- Beri tahu library klien tempat untuk menemukan kunci akun layanan.
- Tambahkan dependensi Maven ke project Java.
- Panggil
SecretManagerServiceClient.create(), yang mengambil autentikasi secara otomatis (karena langkah 1).
Langkah-langkah ini mengubah implementasi Java dengan:
- Menghilangkan kebutuhan untuk membuat objek
CredentialsProviderdanSecretManagerServiceSettings. - Mengubah panggilan ke
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()agar tidak menyertakan argumen.
Buat ciphertext dan hasilkan tautan dalam
Pada langkah ini, Anda menggunakan pustaka kriptografi Tink untuk membuat enifd (ciphertext InlineInstallData) dari objek protobuf InlineInstallData.
Proto InlineInstallData didefinisikan sebagai berikut:
syntax = "proto2";
package hsdpexperiments;
option java_package = "com.google.hsdpexperiments";
option java_multiple_files = true;
// InlineInstallData is used by 3p auth callers to generate "encrypted inline
// flow data" (enifd) which is decrypted in PGS to verify authenticity and
// freshness.
message InlineInstallData {
// The timestamp which indicates the time encrypted data is generated.
// Used to validate freshness (i.e. generation time in past 4 hours).
// Required.
optional int64 timestamp_ms = 1;
// The docid of the app that we want to open inline install page for.
// This is the package name.
// Required.
optional string target_package_name = 2;
// This is the name of the app requesting the ad from Google Ad Serving
// system.
// Required.
optional string caller_package_name = 3;
// This is the advertising id that will be collected by 3P Ad SDKs.
// Optional.
optional string advertising_id = 4;
// This is used to indicate the network from where the inline install was
// requested.
// Required.
optional string ad_network_id = 5;
}
Pada langkah ini Anda juga membuat URL tautan dalam menggunakan parameter berikut:
| Kolom | Deskripsi | Wajib |
|---|---|---|
| id | Nama paket aplikasi yang akan diinstal. | Ya |
| sisipan | Tetapkan ke true jika setengah lembar penginstalan sebaris diminta; jika false, maksudnya tautan dalam ke Google Play. |
Ya |
| enifd | ID terenkripsi untuk SDK pihak ketiga. | Ya |
| lft | Pengenal internal. | Ya |
| 3pAuthCallerId | Pengidentifikasi SDK. | Ya |
| listingan | Parameter opsional untuk menentukan target untuk cantuman toko khusus. | Tidak |
| referensi | String pelacakan referrer opsional. | Tidak |
Contoh Python
Perintah berikut menghasilkan kode Python dari InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --python_out=.
Kode contoh Python berikut membangun InlineInstallData dan mengenkripsinya dengan kunci simetris untuk membuat ciphertext:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
import base64
import time
import inline_install_data_pb2 as InlineInstallData
import tink
from tink import aead
from tink import cleartext_keyset_handle
# Read the stored symmetric key.
with open("example3psecret.json", "r") as f:
keyset = f.read()
"""Encrypt and decrypt using AEAD."""
# Register the AEAD key managers. This is needed to create an Aead primitive later.
aead.register()
# Create a keyset handle from the cleartext keyset in the previous
# step. The keyset handle provides abstract access to the underlying keyset to
# limit access of the raw key material. WARNING: In practice, it is unlikely
# you will want to use a cleartext_keyset_handle, as it implies that your key
# material is passed in cleartext, which is a security risk.
keyset_handle = cleartext_keyset_handle.read(tink.JsonKeysetReader(keyset))
# Retrieve the Aead primitive we want to use from the keyset handle.
primitive = keyset_handle.primitive(aead.Aead)
inlineInstallData = InlineInstallData.InlineInstallData()
inlineInstallData.timestamp_ms = int(time.time() * 1000)
inlineInstallData.target_package_name = "x.y.z"
inlineInstallData.caller_package_name = "a.b.c"
inlineInstallData.ad_network_id = "<sdk_id>"
# Use the primitive to encrypt a message. In this case the primary key of the
# keyset will be used (which is also the only key in this example).
ciphertext = primitive.encrypt(inlineInstallData.SerializeToString(), b'<sdk_id>')
print(f"InlineInstallData Ciphertext: {ciphertext}")
# Base64 Encoded InlineInstallData Ciphertext
enifd = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(ciphertext).decode('utf-8')
print(enifd)
# Deeplink
print(f"https://play.google.com/d?id={inlineInstallData.target_package_name}\&inline=true\&enifd={enifd}\&lft=1\&3pAuthCallerId={inlineInstallData.ad_network_id}")
Jalankan skrip Python dengan menjalankan perintah berikut:
python <file_name>.py
Contoh Java
Perintah berikut menghasilkan kode Java dari InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --java_out=.
Contoh kode Java berikut membuat InlineInstallData dan mengenkripsinya
dengan kunci simetris untuk membuat ciphertext:
package com.google.hsdpexperiments;
import static com.google.common.io.BaseEncoding.base64Url;
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.common.flags.Flag;
import com.google.common.flags.FlagSpec;
import com.google.common.flags.Flags;
import com.google.crypto.tink.Aead;
import com.google.crypto.tink.InsecureSecretKeyAccess;
import com.google.crypto.tink.KeysetHandle;
import com.google.crypto.tink.TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat;
import com.google.crypto.tink.aead.AeadConfig;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.Security;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.conscrypt.Conscrypt;
/** info on encryption in https://github.com/google/tink#learn-more */
final class ThirdPartyEnifdGuide {
@FlagSpec(
name = "third_party_id",
help = "the identifier associated with the 3p for which to generate the enifd")
private static final Flag<String> thirdPartyAuthCallerId = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "package_name", help = "the package name of the target app")
private static final Flag<String> packageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "caller_package_name", help = "the package name of the caller app")
private static final Flag<String> callerPackageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "secret_filename", help = "the path to the json file with the secret material")
private static final Flag<String> secretFilename = Flag.value("");
private ThirdPartyEnifdGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// parse flags
Flags.parse(args);
// File keyFile = new File(args[0]);
Path keyFile = Paths.get(secretFilename.get());
// Create structured inline flow data
InlineInstallData idrp =
InlineInstallData.newBuilder()
.setTargetPackageName(packageName.get())
.setCallerPackageName(callerPackageName.get())
.setTimestampMs(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setAdNetworkId(thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get())
.build();
// we can print this out here to make sure it's well formatted, this will help debug
System.out.println(idrp.toString());
// Register all AEAD key types with the Tink runtime.
Conscrypt.checkAvailability();
Security.addProvider(Conscrypt.newProvider());
AeadConfig.register();
// Read AEAD key downloaded from secretmanager into keysethandle
KeysetHandle handle =
TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat.parseKeyset(
new String(Files.readAllBytes(keyFile), UTF_8), InsecureSecretKeyAccess.get());
// Generate enifd using tink library
Aead aead = handle.getPrimitive(Aead.class);
byte[] plaintext = idrp.toByteArray();
byte[] ciphertext = aead.encrypt(plaintext, thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get().getBytes(UTF_8));
String enifd = base64Url().omitPadding().encode(ciphertext);
// Build deeplink, escaping ampersands (TODO: verify this is necessary while testing e2e)
String deeplink =
"https://play.google.com/d?id="
+ packageName.get()
+ "\\&inline=true\\&enifd="
+ enifd
+ "\\&lft=1\\&3pAuthCallerId="
+ thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get();
System.out.println(deeplink);
}
}
Terakhir, buat program Java menjadi biner dan panggil menggunakan kode berikut:
path/to/binary/ThirdPartyEnifdGuide --secret_filename=path/to/jsonfile/example3psecret.json --package_name=<package_name_of_target_app> --third_party_id=<3p_caller_auth_id>
- Bendera
secret_filenamemenentukan jalur ke file JSON yang berisi materi rahasia. - Bendera
package_nameadalah ID dokumen aplikasi target. - Flag
third_party_iddigunakan untuk menentukan ID autentikasi pemanggil pihak ketiga (yaitu,<sdk_id>).
Luncurkan maksud Instalasi Inline
Untuk menguji tautan dalam yang dibuat selama langkah sebelumnya, hubungkan perangkat Android (pastikan USB debugging diaktifkan) ke stasiun kerja yang telah menginstal ADB dan jalankan perintah berikut:
adb shell am start "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
Dalam kode klien, kirim intent menggunakan salah satu metode berikut (Kotlin atau Java).
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
val deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending")
intent.data = Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl)
val packageManager = context.getPackageManager()
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0)
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
String id = "exampleAppToBeInstalledId";
String deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>";
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending");
intent.setData(Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl));
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Lampiran
Bagian berikut memberikan panduan tambahan pada kasus penggunaan tertentu.
Menyiapkan lingkungan Python
Untuk menjalankan kode contoh Python, atur lingkungan Python di stasiun kerja Anda dan instal dependensi yang diperlukan.
Siapkan lingkungan Python:
Instal python3.11 (jika sudah terpasang, lewati langkah ini):
sudo apt install python3.11Instal pip:
sudo apt-get install pipInstal
virtualenv:sudo apt install python3-virtualenvBuat lingkungan virtual (diperlukan untuk dependensi Tink):
virtualenv inlineinstall --python=/usr/bin/python3.11
Masuk ke lingkungan virtual:
source inlineinstall/bin/activatePerbarui pip:
python -m pip install --upgrade pipInstal dependensi yang diperlukan:
Instal Tink:
pip install tinkInstal crc32c Google:
pip install google-crc32cInstal Secret Manager:
pip install google-cloud-secret-managerInstal kompiler protobuf:
sudo apt install protobuf-compiler
Pembuatan enifd C++
Berikut ini adalah contoh C++ yang telah kami tulis dan validasi secara internal untuk menghasilkan enifd.
Pembuatan enifd dapat dilakukan menggunakan kode C++ sebagai berikut:
// A command-line example for using Tink AEAD w/ key template aes128gcmsiv to
// encrypt an InlineInstallData proto.
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "<path_to_protoc_output>/inline_install_data.proto.h"
#include "absl/flags/flag.h"
#include "absl/flags/parse.h"
#include "absl/strings/escaping.h"
#include "absl/strings/string_view.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_config.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_key_templates.h"
#include "tink/cc/config/global_registry.h"
#include "tink/cc/examples/util/util.h"
#include "tink/cc/keyset_handle.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/status.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/statusor.h"
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, keyset_filename, "",
"Keyset file (downloaded from secretmanager) in JSON format");
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, associated_data, "",
"Associated data for AEAD (default: empty");
namespace {
using ::crypto::tink::Aead;
using ::crypto::tink::AeadConfig;
using ::crypto::tink::KeysetHandle;
using ::crypto::tink::util::Status;
using ::crypto::tink::util::StatusOr;
} // namespace
namespace tink_cc_examples {
// AEAD example CLI implementation.
void AeadCli(const std::string& keyset_filename,
absl::string_view associated_data) {
Status result = AeadConfig::Register();
if (!result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to register AeadConfig";
return;
}
// Read the keyset from file.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<KeysetHandle>> keyset_handle =
ReadJsonCleartextKeyset(keyset_filename);
if (!keyset_handle.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to read json keyset";
return;
}
// Get the primitive.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<Aead>> aead =
(*keyset_handle)
->GetPrimitive<crypto::tink::Aead>(
crypto::tink::ConfigGlobalRegistry());
if (!aead.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to get primitive";
return;
}
// Instantiate the enifd.
hsdpexperiments::InlineInstallData iid;
iid.set_timestamp_ms(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch())
.count());
iid.set_target_package_name("<TARGET_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_caller_package_name("<CALLER_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_ad_network_id("<SDK_ID>");
// Compute the output.
StatusOr<std::string> encrypt_result =
(*aead)->Encrypt(iid.SerializeAsString(), associated_data);
if (!encrypt_result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to encrypt Inline Install Data";
return;
}
const std::string& output = encrypt_result.value();
std::string enifd;
absl::WebSafeBase64Escape(output, &enifd);
std::clog << "enifd: " << enifd << '\n';
}
} // namespace tink_cc_examples
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
absl::ParseCommandLine(argc, argv);
std::string keyset_filename = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_keyset_filename);
std::string associated_data = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_associated_data);
std::clog << "Using keyset from file " << keyset_filename
<< " to AEAD-encrypt inline install data with associated data '"
<< associated_data << "'." << '\n';
tink_cc_examples::AeadCli(keyset_filename, associated_data);
return 0;
}
Kode ini diadaptasi dari contoh yang dapat ditemukan di dokumen Tink.
