App-Leisten sind Container oben oder unten auf dem Bildschirm, über die Nutzer auf wichtige Funktionen und Navigationselemente zugreifen können:
Eingeben |
Darstellung |
Zweck |
|---|---|---|
| Obere App-Leiste | Oben auf dem Bildschirm. |
Bietet Zugriff auf wichtige Aufgaben und Informationen. Enthält in der Regel einen Titel, wichtige Aktionselemente und bestimmte Navigationselemente. |
| Untere App-Leiste | Unten auf dem Bildschirm. |
Enthält in der Regel die wichtigsten Navigationselemente. Sie können Zugriff auf andere Aktionen gewähren, z. B. über eine schwebende Aktionsschaltfläche. |
Versionskompatibilität
Für diese Implementierung muss das minSDK Ihres Projekts auf API-Level 21 oder höher festgelegt sein.
Abhängigkeiten
Obere App-Leiste implementieren
Der folgende Code zeigt Implementierungen für die vier Arten von oberen App-Leisten, einschließlich verschiedener Beispiele dafür, wie Sie das Scrollverhalten steuern können.
- Kleine obere App-Leiste
- Mitte der oberen App-Leiste
- Mittlere obere App-Leiste
- Große obere App-Leiste
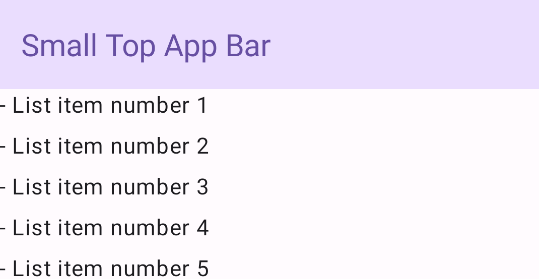
Kleine obere App-Leiste
Verwenden Sie das TopAppBar-Element, um eine kleine App-Leiste oben zu erstellen. Dies ist die einfachste App-Leiste, die in diesem Beispiel nur einen Titel enthält.
Im folgenden Beispiel wird TopAppBar kein Wert für scrollBehavior übergeben. Daher reagiert die obere App-Leiste nicht auf das Scrollen der inneren Inhalte.
Ergebnis
Zentriert ausgerichtete obere App-Leiste
Die zentrierte obere App-Leiste entspricht der kleinen App-Leiste, mit der Ausnahme, dass der Titel in der Mitte der Komponente zentriert ist. Verwenden Sie dazu die spezielle CenterAlignedTopAppBar-Komponente.
In diesem Beispiel wird enterAlwaysScrollBehavior() verwendet, um den Wert abzurufen, der für scrollBehavior übergeben wird. Die Leiste wird minimiert, wenn der Nutzer im inneren Inhalt des Scaffolds scrollt.
Ergebnis

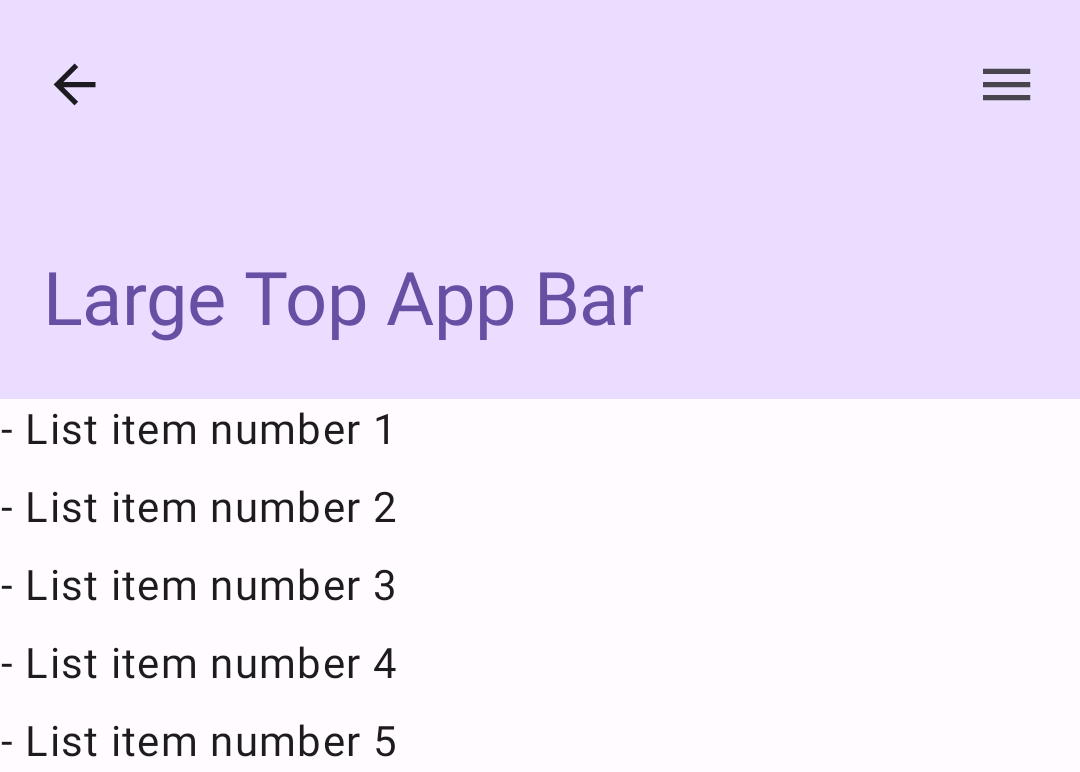
Obere App-Leiste (mittel)
Bei der mittleren oberen App-Leiste wird der Titel unter zusätzlichen Symbolen platziert. Verwenden Sie zum Erstellen MediumTopAppBar composable.
Wie im vorherigen Code wird in diesem Beispiel enterAlwaysScrollBehavior() verwendet, um den Wert abzurufen, der für scrollBehavior übergeben wird.
Ergebnis
enterAlwaysScrollBehavior zeigtGroße obere App-Leiste
Eine große obere App-Leiste ähnelt der mittleren, hat aber einen größeren Abstand zwischen dem Titel und den Symbolen und nimmt insgesamt mehr Platz auf dem Bildschirm ein. Verwenden Sie dazu das LargeTopAppBar-Element.
In diesem Beispiel wird exitUntilCollapsedScrollBehavior() verwendet, um den Wert abzurufen, der für scrollBehavior übergeben wird. Die Leiste wird minimiert, wenn der Nutzer im inneren Inhalt des Scaffolds scrollt, und maximiert, wenn er zum Ende des inneren Inhalts scrollt.
Ergebnis
Untere App-Leiste implementieren
Verwenden Sie zum Erstellen einer unteren App-Leiste das BottomAppBar-Element, das dem Element für die obere App-Leiste ähnelt.
Sie übergeben die folgenden Schlüsselparameter für Composeables:
actions: Eine Reihe von Symbolen, die links in der Leiste angezeigt werden. Dies sind in der Regel entweder wichtige Aktionen für den jeweiligen Bildschirm oder Navigationselemente.floatingActionButton: Die unverankerte Aktionsschaltfläche, die rechts in der Leiste angezeigt wird.
Ergebnis

Wichtige Fakten
- Sie übergeben App-Leisten in der Regel an das
Scaffold-Komposit, das bestimmte Parameter zum Empfangen hat. Die Composeables, die Sie zum Implementieren von oberen App-Leisten verwenden, haben gemeinsame Schlüsselparameter:
title: Der Text, der in der App-Leiste angezeigt wird.navigationIcon: Das primäre Navigationssymbol, das links neben der App-Leiste angezeigt wird.actions: Symbole, über die Nutzer auf wichtige Aktionen zugreifen können, die rechts neben der App-Leiste angezeigt werden.scrollBehavior: Bestimmt, wie die obere App-Leiste auf das Scrollen des Inhalts des Scaffolds reagiert.colors: Bestimmt, wie die App-Leiste angezeigt wird.
Sie können festlegen, wie die App-Leiste reagiert, wenn der Nutzer im inneren Inhalt des Scaffolds scrollt. Erstellen Sie dazu eine Instanz von
TopAppBarScrollBehaviorund übergeben Sie sie der oberen App-Leiste für den ParameterscrollBehavior. Es gibt drei Arten vonTopAppBarScrollBehavior:enterAlwaysScrollBehavior: Wenn der Nutzer den inneren Inhalt des Scaffolds maximiert, wird die obere App-Leiste minimiert. Die App-Leiste wird maximiert, wenn der Nutzer den inneren Inhalt nach unten zieht.exitUntilCollapsedScrollBehavior: Ähnlich wie beienterAlwaysScrollBehavior, wobei sich die App-Leiste auch maximiert, wenn der Nutzer das Ende des inneren Inhalts des Scaffolds erreicht.pinnedScrollBehavior: Die App-Leiste bleibt an Ort und Stelle und reagiert nicht auf Scrollen.
Sammlungen, die diesen Leitfaden enthalten
Dieser Leitfaden ist Teil der folgenden ausgewählten Sammlungen von Kurzanleitungen, die allgemeinere Ziele der Android-Entwicklung abdecken: