Com o GnssLogger v3.1, os usuários podem conferir e analisar dados GNSS brutos na tela Medições.
Esta é a tela Medições, seguida de algumas dicas e truques para aproveitar ao máximo esses dados:
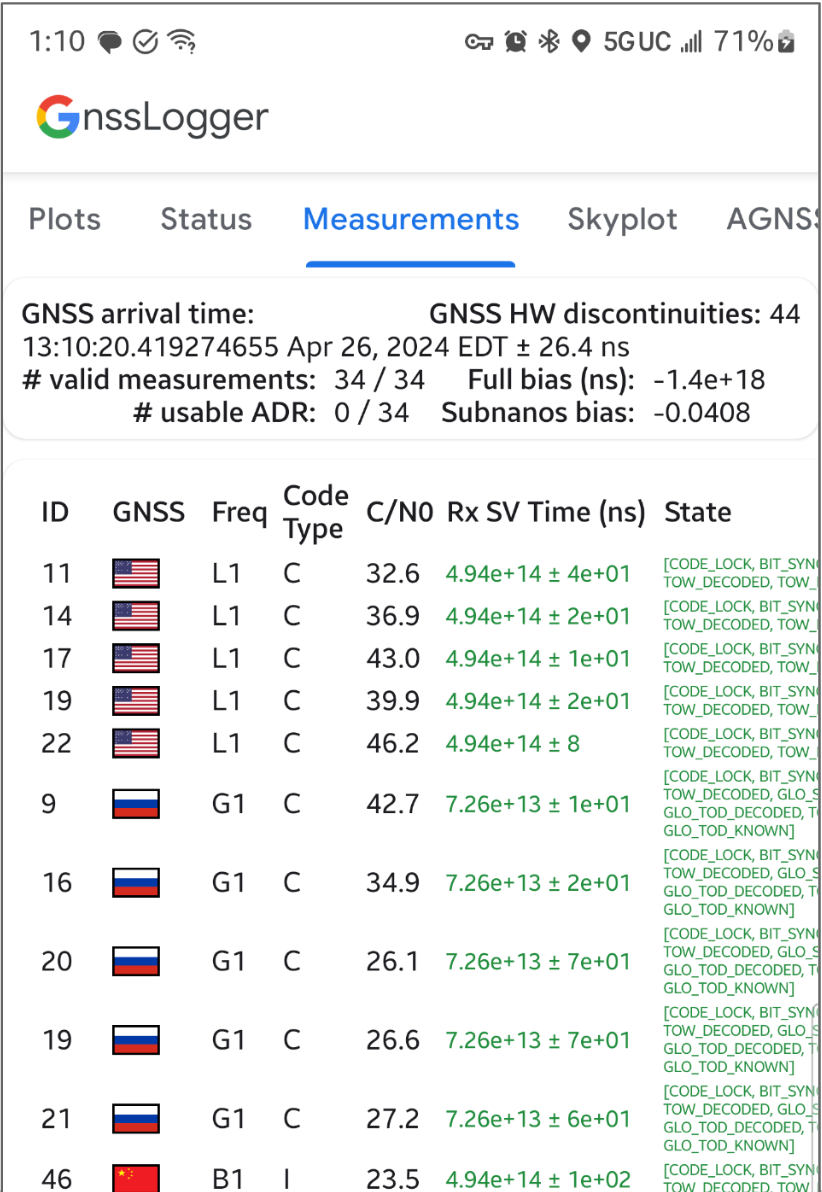
No card de cima:
- O canto superior esquerdo mostra os dados do relógio GNSS (correspondentes a
GnssClock). - No canto superior direito, é mostrada a contagem de descontinuidades de hardware (HW) do GNSS (de
GnssClock.getHardwareClockDiscontinuityCount), que ajuda a determinar se o ciclo de trabalho está ativado ou desativado. Quando esse contador aumenta, ele indica que houve uma interrupção na observação contínua dos sinais do GNSS (por exemplo, o ciclo de trabalho está ativado). Mais abaixo, o card mostra informações agregadas de todas as medições:- # medições válidas: para que uma medição seja considerada válida, as flags
STATE_CODE_LOCKeSTATE_TOW_KNOWNouSTATE_TOW_DECODEDprecisam ser definidas emGnssMeasurement.getState. - # intervalo delta acumulado utilizável (ADR, na sigla em inglês) — Para que o ADR, ou fase da operadora, seja
considerado utilizável para posicionamento, a flag
ADR_STATE_VALIDprecisa ser definida, e nem a flagADR_STATE_RESETnem aADR_STATE_CYCLE_SLIPpodem ser definidas emGnssMeasurement.getAccumulatedDeltaRangeState.
- # medições válidas: para que uma medição seja considerada válida, as flags
Se o dispositivo sempre informar 0 ADR utilizável, mesmo em céu aberto com ciclo de trabalho desativado, isso indica que ele não oferece suporte a medições de fase de portador que podem ser usadas para GNSS de alta precisão.
No card de baixo, cada linha representa um GnssMeasurement individual.
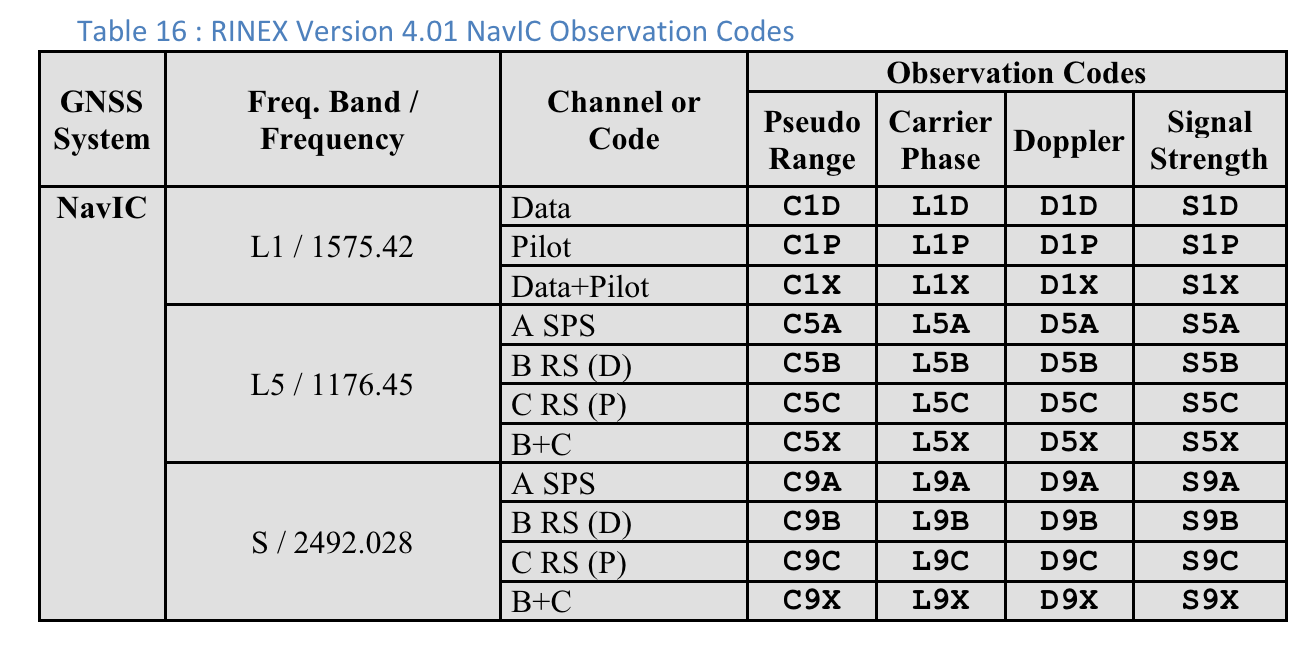
- A coluna Tipo de código mostra o tipo exato de sinal GNSS usando os tipos de código definidos no RINEX 4.01. Por exemplo, os sinais do GPS L1 com o tipo de código "C" representam L1 C/A, conforme indicado pela última letra no código de três caracteres nas tabelas RINEX. O GPS L5 Q também teria um tipo de código "Q". Consulte as tabelas de outras constelações do GNSS no final deste documento para referência.
- Na coluna Rx SV Time (ns), o texto fica verde se a medição for válida.
- Na coluna Estado, o estado também é verde se a medição for válida. O estado mostra uma versão legível por humanos das flags binárias definidas no campo GnssMeasurement.getState().
Envie feedback sobre novos recursos usando nosso Issue Tracker público.
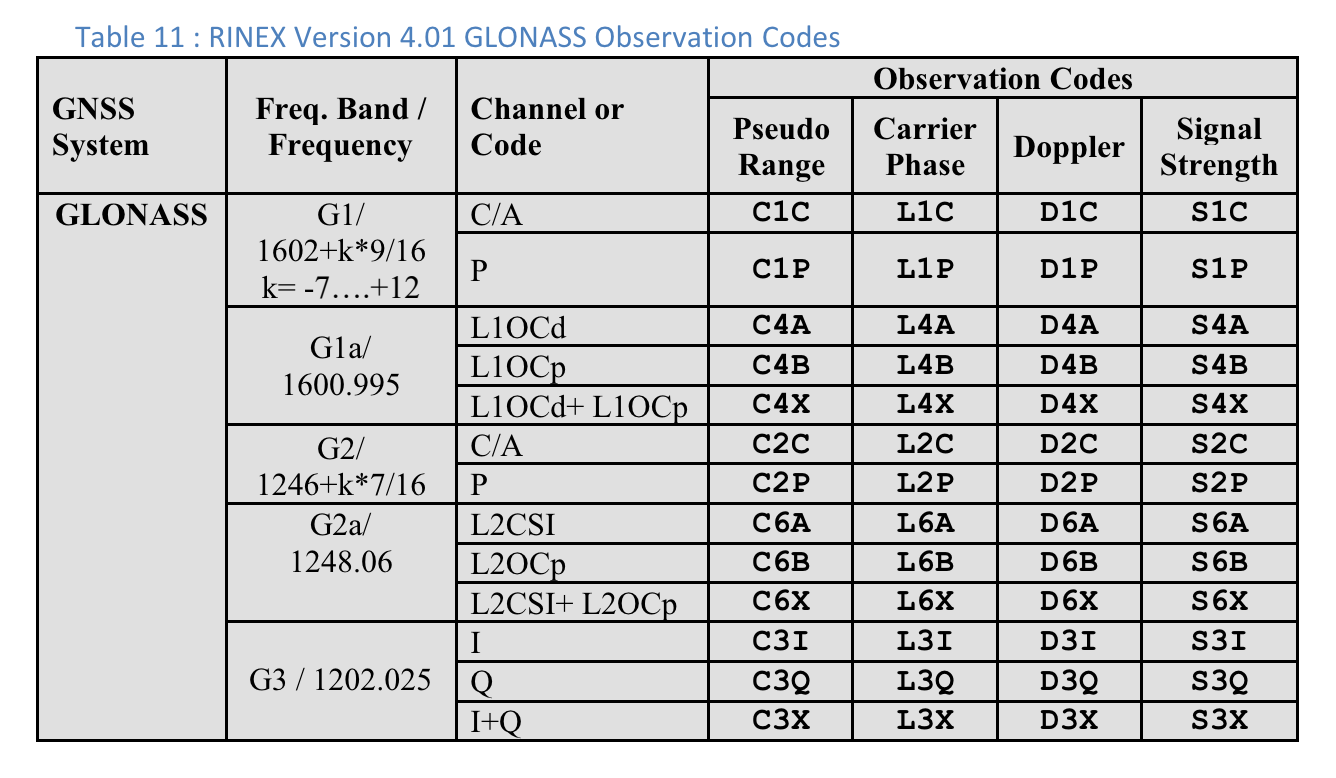
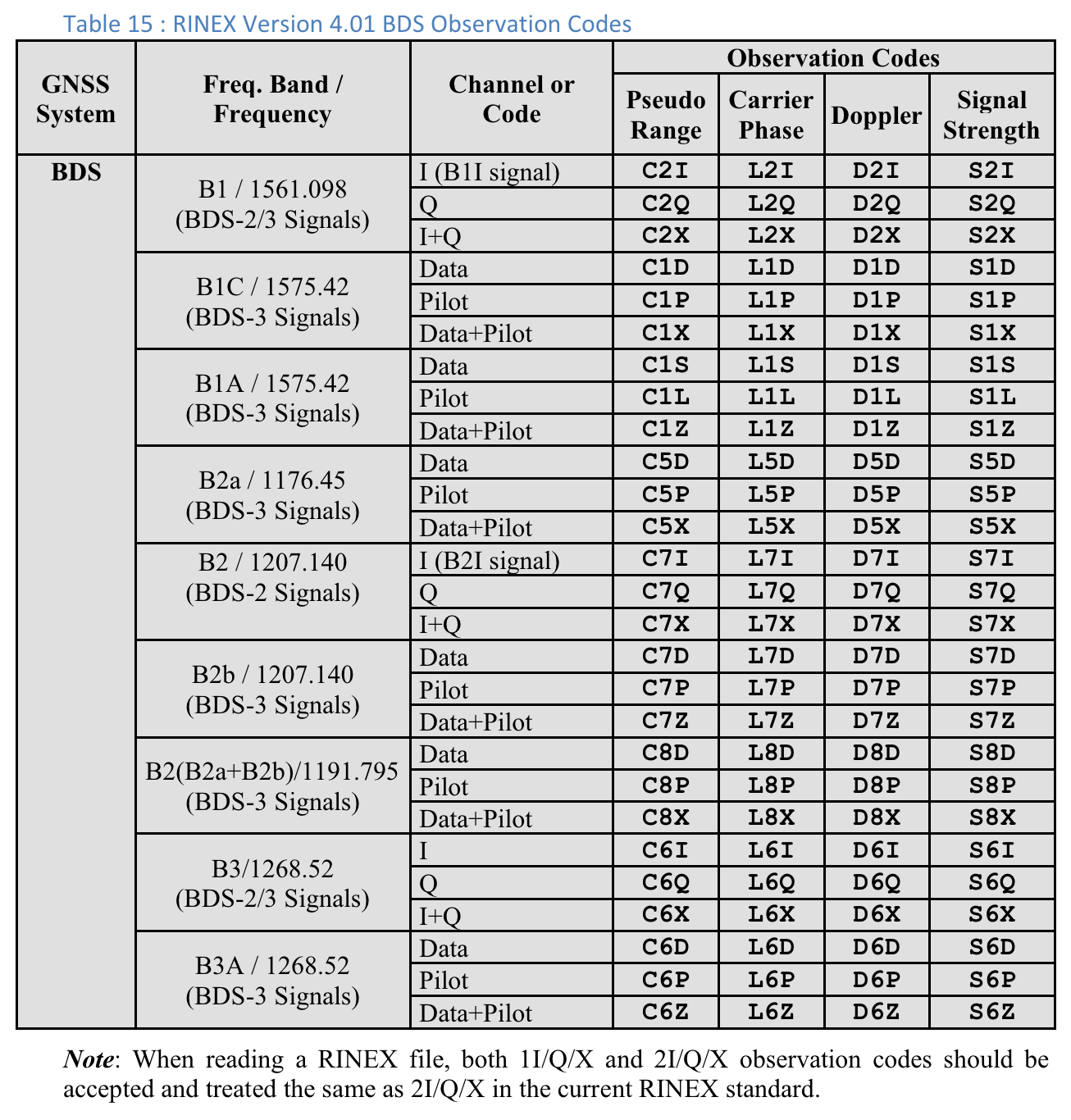
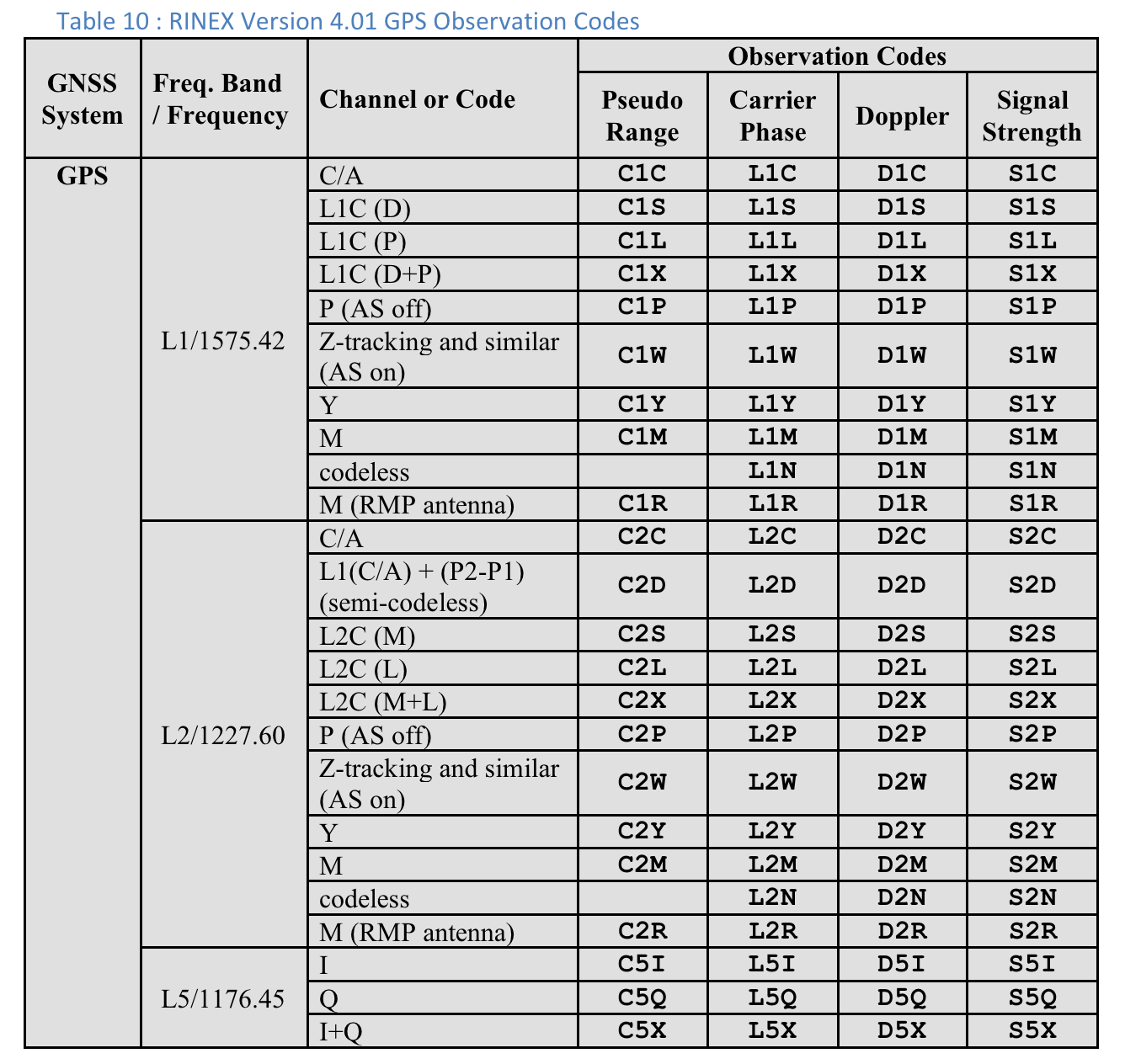
Tabela 10 : códigos de observação do GPS do RINEX, versão 4.01
Para cada medição, o "Tipo de código" mostrado é a última letra do valor "Pseudorange" definido na especificação RINEX 4.01 para o sistema GNSS relevante e a frequência do portador. Por exemplo, "C" é usado para GPS L1 [C/A], enquanto "Q" é usado para GPS L5 Q.
Os usuários podem rolar para a direita para conferir outras colunas de cada medição:
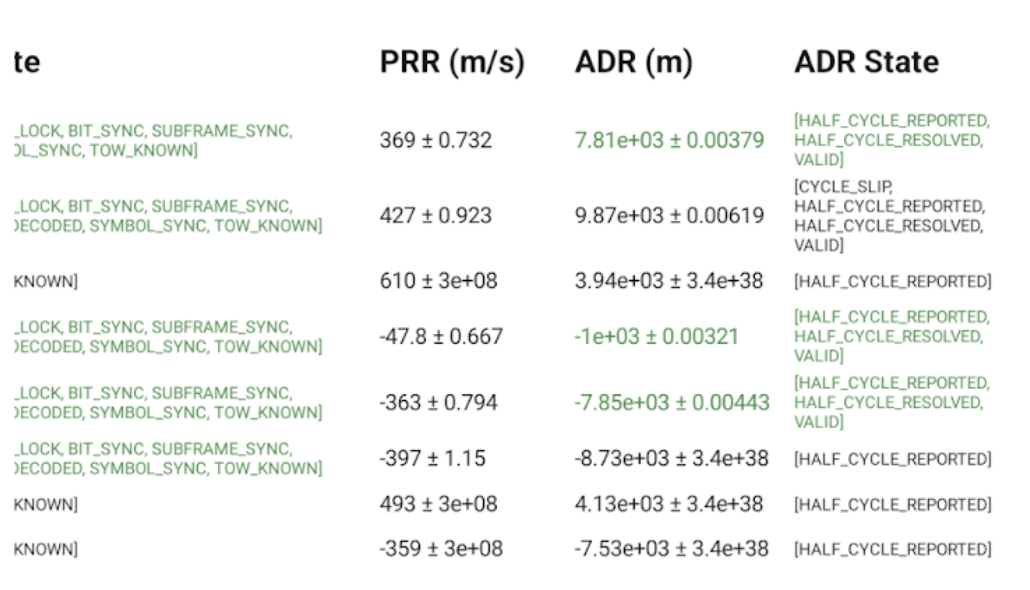
- PRR é a taxa de pseudo-alcance em metros por segundo de GnssMeasurement.getPseudorangeRateMetersPerSecond().
- A coluna ADR State mostra a versão legível por humanos das flags de bit definidas na coluna GnssMeasurement.getAccumulatedDeltaRangeState(). Se o ADR puder ser usado para posicionamento, o texto nos campos ADR (m) e Estado do ADR será verde.
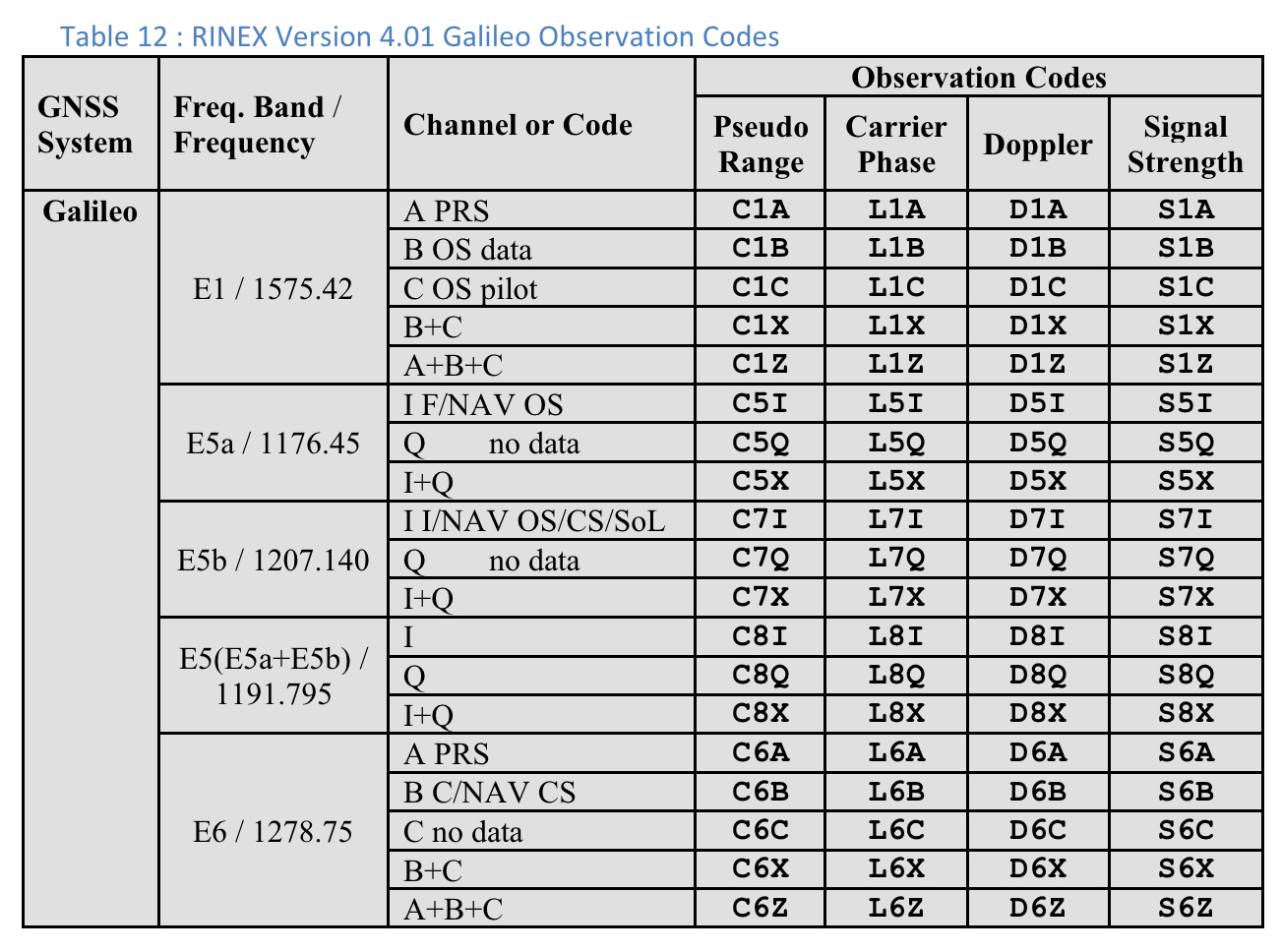
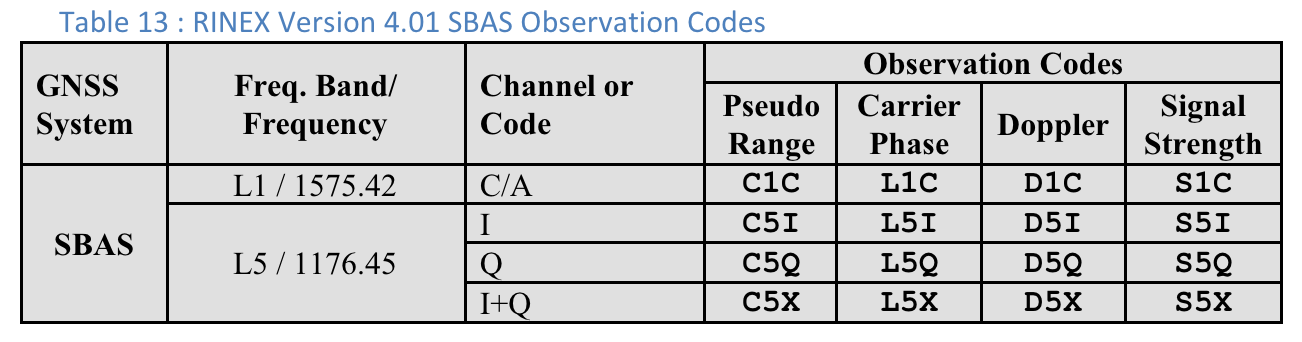
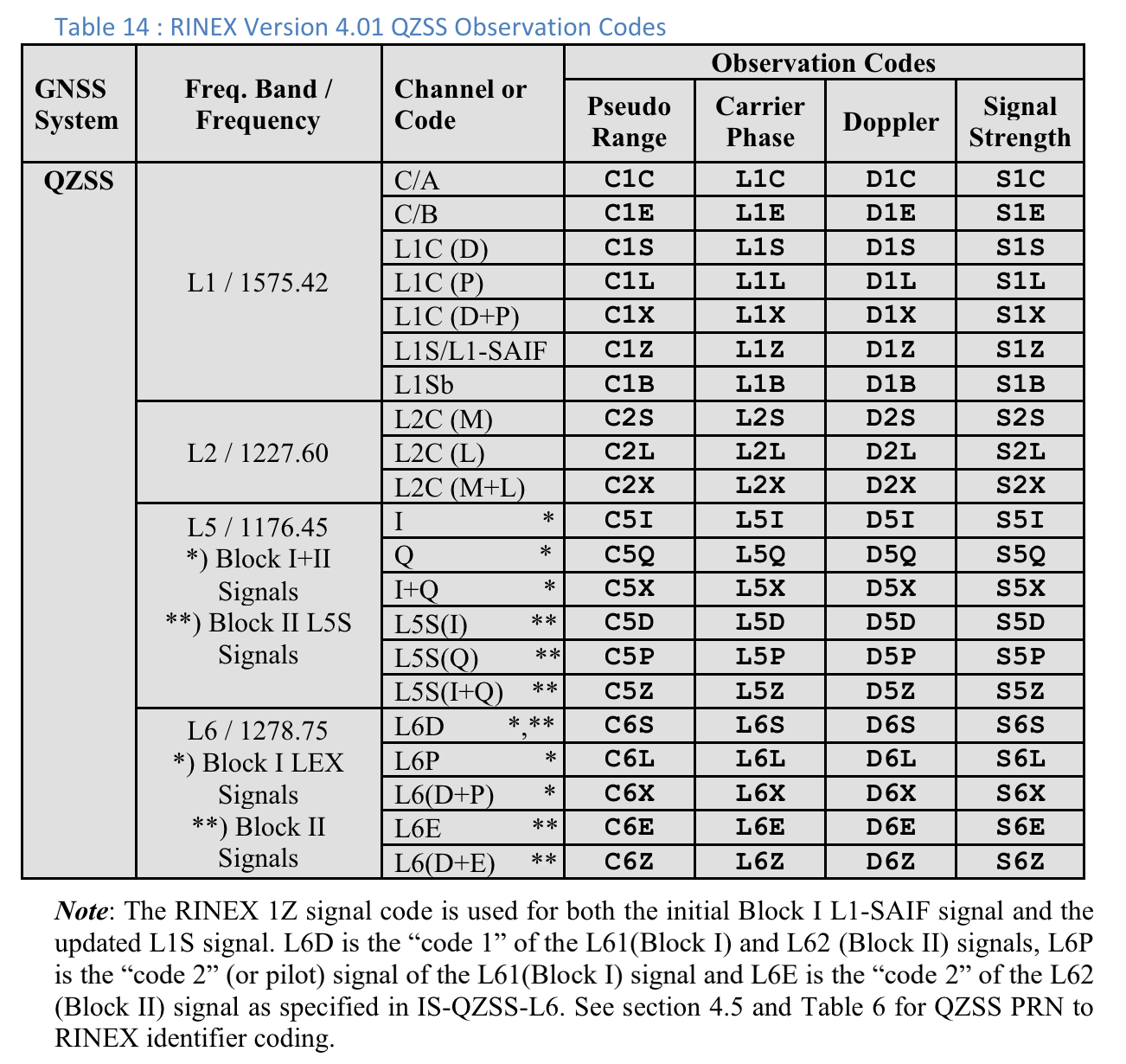
Códigos de observação RINEX 4.01
A última das três letras nos códigos de observação RINEX na coluna Pseudo Range é o valor Code type mostrado na tela Measurements no GnssLogger.
Confira a seguir as tabelas da especificação RINEX 4.01 para sua conveniência. Consulte a especificação completa para mais detalhes.