Em dispositivos com Android 8.0 (API de nível 26) e versões mais recentes, o pareamento de dispositivos complementares executa uma busca por Bluetooth ou Wi-Fi de dispositivos próximos em nome do seu app sem exigir a permissão ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. Isso ajuda a maximizar as proteções de privacidade do usuário. Use esse método para
fazer a configuração inicial do dispositivo complementar, como um smartwatch
compatível com BLE. Além disso, o pareamento de dispositivos complementares exige que os Serviços de localização estejam ativados.
O pareamento de dispositivos complementares não cria conexões por conta própria nem ativa a leitura contínua. Os apps podem usar APIs de conectividade Bluetooth ou Wi-Fi para estabelecer conexões.
Depois que o dispositivo é pareado, ele pode usar as permissões
REQUEST_COMPANION_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND
e
REQUEST_COMPANION_USE_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND
para iniciar o app em segundo plano. Os apps também podem usar a permissão
REQUEST_COMPANION_START_FOREGROUND_SERVICES_FROM_BACKGROUND
para iniciar um serviço em primeiro plano em segundo plano.
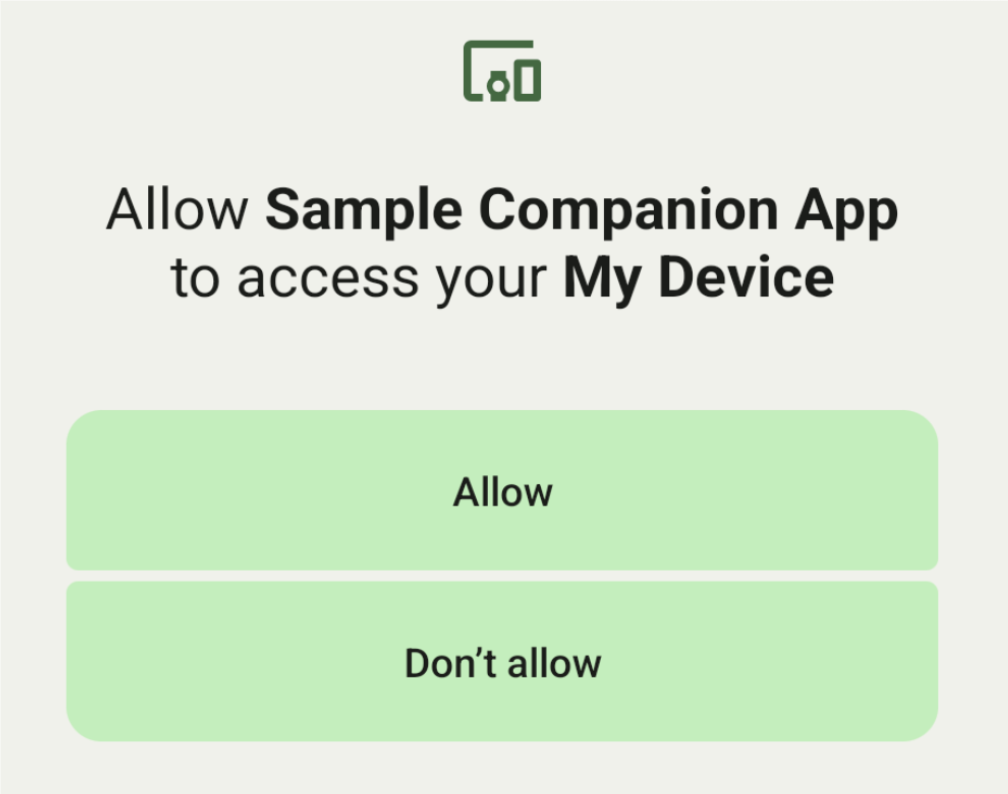
Um usuário pode selecionar um dispositivo em uma lista e conceder ao app permissões para acessar
o dispositivo. Essas permissões são revogadas se você desinstalar o app ou chamar
disassociate().
O app complementar é responsável por limpar as próprias associações se o usuário
não precisar mais delas, como quando ele faz logout ou remove dispositivos vinculados.
Implementar o pareamento de dispositivo complementar
Nesta seção, explicamos como usar o CompanionDeviceManager para parear seu
app com dispositivos complementares por Bluetooth, BLE e Wi-Fi.
Especificar dispositivos complementares
O exemplo de código a seguir mostra como adicionar a flag
<uses-feature> a um
arquivo de manifesto. Isso informa ao sistema que o app pretende configurar dispositivos
complementares.
<uses-feature android:name="android.software.companion_device_setup"/>
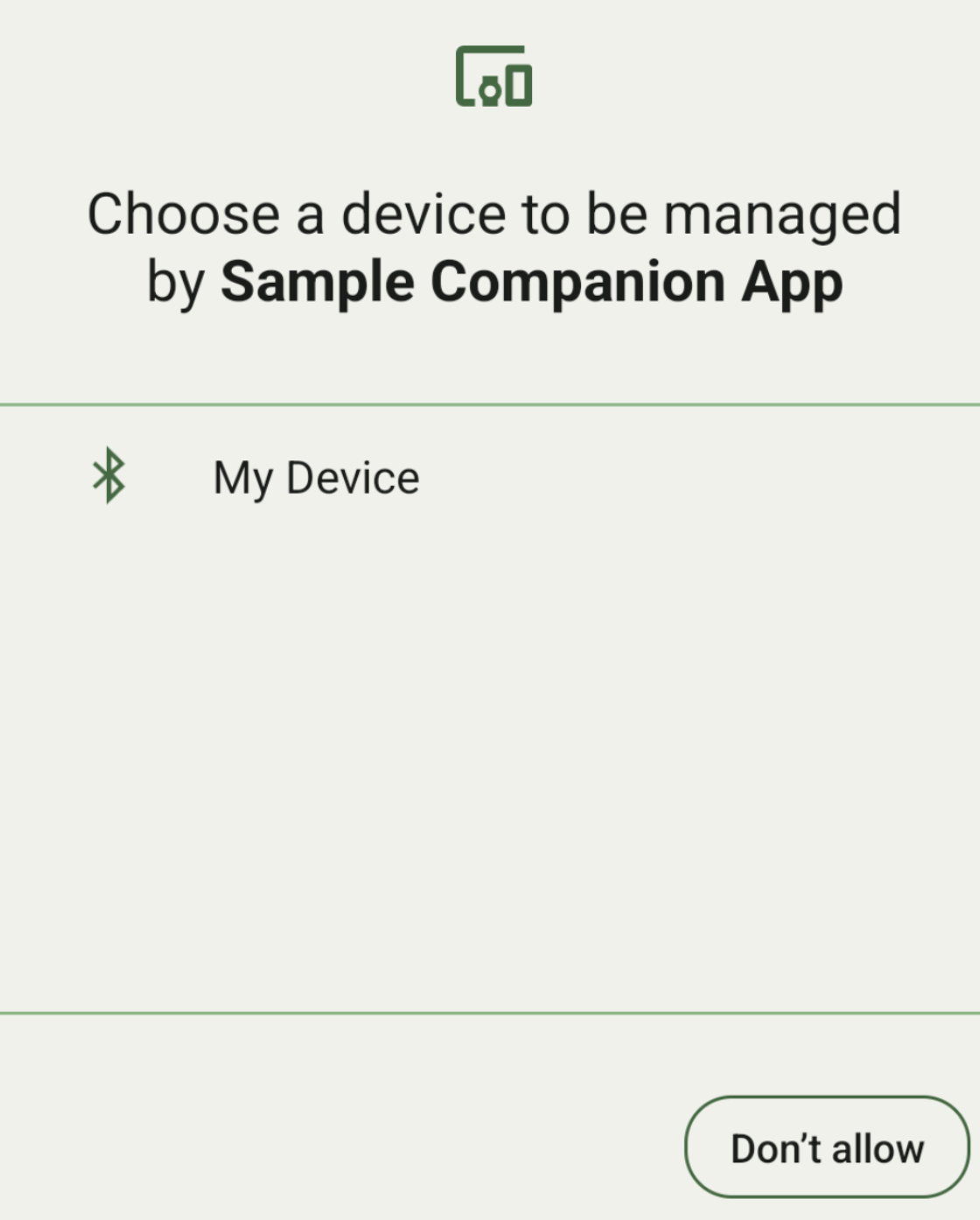
Listar dispositivos por DeviceFilter
É possível mostrar todos os dispositivos complementares no alcance que correspondem ao
DeviceFilter
fornecido (mostrado na Figura 1). Se quiser limitar a verificação a apenas um
dispositivo, você pode
setSingleDevice()
para true (mostrado na figura 2).
Estas são as subclasses de DeviceFilter que podem ser especificadas em AssociationRequest:
Todas as três subclasses têm criadores que simplificam a configuração de filtros.
No exemplo a seguir, um dispositivo procura um dispositivo Bluetooth com um
BluetoothDeviceFilter.
Kotlin
val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build()
Java
BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build();
Defina um DeviceFilter como um AssociationRequest para que o
CompanionDeviceManager possa determinar que tipo de dispositivos procurar.
Kotlin
val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build()
Java
AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build();
Depois que o app inicializar um AssociationRequest, execute a função
associate()
no CompanionDeviceManager. A função associate() usa um AssociationRequest e um Callback.
O Callback retorna um
IntentSender no
onAssociationPending quando CompanionDeviceManager localiza um dispositivo
e ele está pronto para iniciar uma caixa de diálogo de consentimento do usuário.
Depois que o usuário confirma o dispositivo, um AssociationInfo
do dispositivo é retornado em onAssociationCreated.
Se o app não encontrar nenhum dispositivo, o callback vai retornar onFailure
com uma mensagem de erro.
Em dispositivos com o Android 13 (nível 33 da API) e versões mais recentes:
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // An association is created. } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } })
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // An association is created. } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // To handle the failure. });
Em dispositivos com Android 12L (nível 32 da API) ou anterior (descontinuado):
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } }, null)
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // To handle the failure. } }, null);
O resultado da seleção do usuário é enviado de volta ao fragmento no
onActivityResult()
da sua atividade. Em seguida, acesse o dispositivo selecionado.
Quando o usuário selecionar um dispositivo Bluetooth, espere um
BluetoothDevice.
Quando o usuário selecionar um dispositivo Bluetooth LE, espere um
android.bluetooth.le.ScanResult.
Quando o usuário selecionar um dispositivo Wi-Fi, espere um
android.net.wifi.ScanResult.
Kotlin
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } }
Java
@Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } }
Confira o exemplo completo:
Em dispositivos com o Android 13 (nível 33 da API) e versões mais recentes:
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } val mBluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter by lazy { val java = BluetoothManager::class.java getSystemService(java)!!.adapter } val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. var associationId: int = associationInfo.id var macAddress: MacAddress = associationInfo.deviceMacAddress } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } ) override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // do not include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. int associationId = associationInfo.getId(); MacAddress macAddress = associationInfo.getDeviceMacAddress(); } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // Handle the failure. }); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
Em dispositivos com Android 12L (nível 32 da API) ou anterior (descontinuado):
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } }, null) } override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // don't include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { // failed to send the intent } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // handle failure to find the companion device } }, null); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
Perfis de dispositivos complementares
No Android 12 (nível 31 da API) e versões mais recentes, apps complementares que gerenciam dispositivos como relógios podem usar perfis de dispositivos complementares para simplificar o processo de configuração concedendo as permissões necessárias durante o pareamento. Para mais informações, consulte Perfis de dispositivos complementares.
Manter os apps Companion ativados
A partir do Android 16 (nível 36 da API),
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence(String)
e
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceAppeared()
foram descontinuadas.
Use
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence (ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)para gerenciar automaticamente a vinculação doCompanionDeviceServiceimplementado.- O estado de vinculação do seu
CompanionDeviceServiceé gerenciado automaticamente com base no status de presença do dispositivo complementar associado:- O serviço é vinculado quando o dispositivo complementar está dentro do alcance do BLE ou conectado por Bluetooth.
- O serviço é desvinculado quando o dispositivo complementar sai do alcance do BLE ou a conexão Bluetooth é encerrada.
- O estado de vinculação do seu
O app recebe um callback com base em várias
DevicePresenceEvent.Para mais detalhes, consulte
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceEvent().
