Pada perangkat yang menjalankan Android 8.0 (level API 26) dan yang lebih tinggi, penyambungan perangkat pendamping melakukan pemindaian Bluetooth atau Wi-Fi pada perangkat di sekitar atas nama aplikasi Anda tanpa memerlukan izin ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. Hal ini membantu memaksimalkan perlindungan privasi pengguna. Gunakan metode ini untuk melakukan konfigurasi awal perangkat pendamping, seperti smartwatch yang kompatibel dengan BLE. Selain itu, penyambungan perangkat pendamping mengharuskan Layanan Lokasi diaktifkan.
Penyambungan perangkat pendamping tidak membuat koneksi dengan sendirinya atau mengaktifkan pemindaian berkelanjutan. Aplikasi dapat menggunakan API konektivitas Bluetooth atau Wi-Fi untuk membuat koneksi.
Setelah perangkat disambungkan, perangkat dapat menggunakan izin
REQUEST_COMPANION_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND
dan
REQUEST_COMPANION_USE_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND
untuk memulai aplikasi dari latar belakang. Aplikasi juga dapat menggunakan izin
REQUEST_COMPANION_START_FOREGROUND_SERVICES_FROM_BACKGROUND
untuk memulai layanan latar depan dari latar belakang.
Pengguna dapat memilih perangkat dari daftar dan memberikan izin aplikasi untuk mengakses perangkat. Izin ini dicabut jika Anda meng-uninstal aplikasi atau memanggil
disassociate().
Aplikasi pendamping bertanggung jawab untuk menghapus asosiasinya sendiri jika pengguna tidak memerlukannya lagi, seperti saat pengguna logout atau menghapus perangkat yang terikat.
Menerapkan penyambungan perangkat pendamping
Bagian ini menjelaskan cara menggunakan CompanionDeviceManager untuk menyambungkan aplikasi Anda dengan perangkat pendamping melalui Bluetooth, BLE, dan Wi-Fi.
Menentukan perangkat pendamping
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara menambahkan tanda
<uses-feature> ke file
manifes. Hal ini memberi tahu sistem bahwa aplikasi Anda bermaksud menyiapkan perangkat pendamping.
<uses-feature android:name="android.software.companion_device_setup"/>
Mencantumkan perangkat menurut DeviceFilter
Anda dapat menampilkan semua perangkat pendamping dalam jangkauan yang cocok dengan
DeviceFilter
yang Anda berikan (ditampilkan pada gambar 1). Jika ingin membatasi pemindaian hanya ke satu perangkat, Anda dapat
setSingleDevice()
ke true (ditunjukkan pada gambar 2).
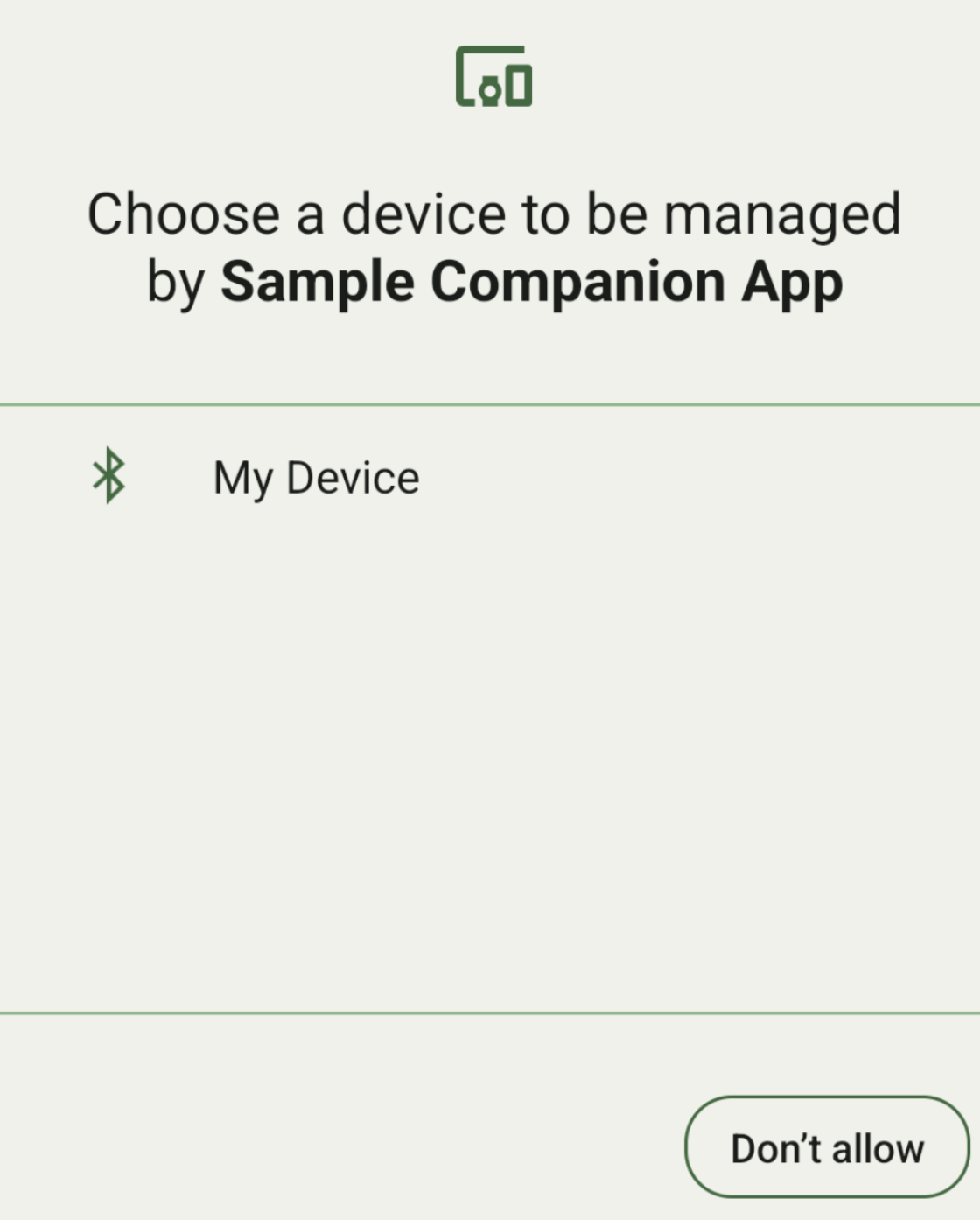
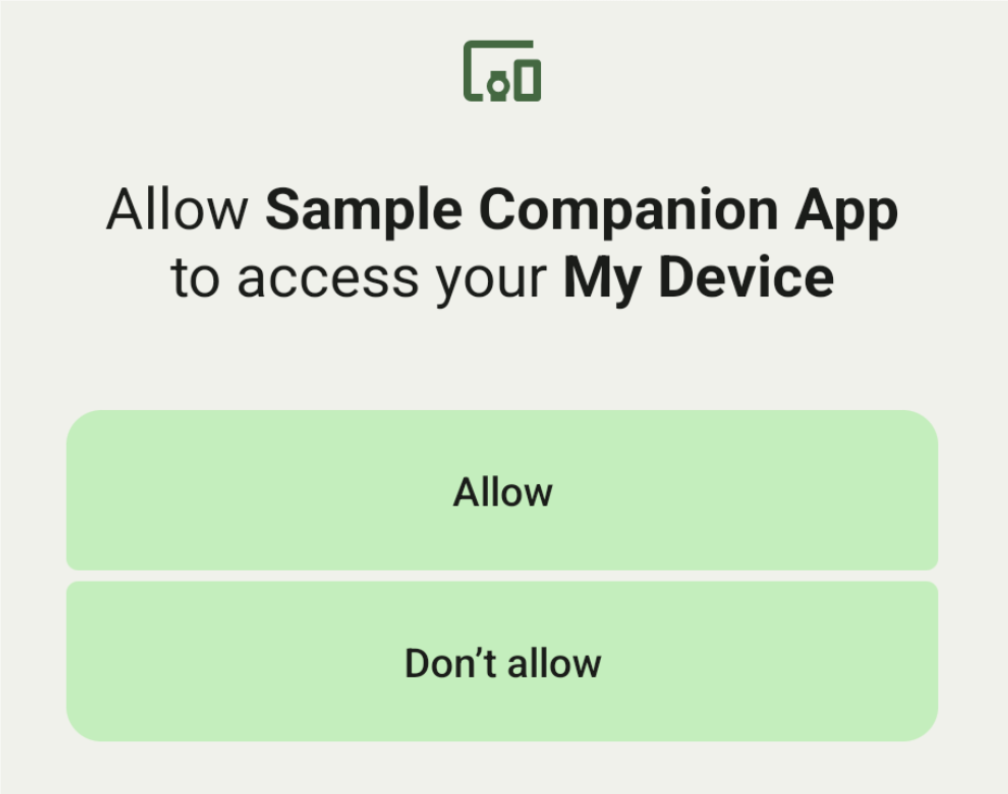
Berikut adalah subclass DeviceFilter yang dapat ditentukan dalam AssociationRequest:
Ketiga subclass memiliki builder yang menyederhanakan konfigurasi filter.
Dalam contoh berikut, perangkat memindai perangkat Bluetooth dengan
BluetoothDeviceFilter.
Kotlin
val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build()
Java
BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build();
Tetapkan DeviceFilter ke AssociationRequest sehingga
CompanionDeviceManager dapat menentukan jenis perangkat yang akan dicari.
Kotlin
val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build()
Java
AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build();
Setelah aplikasi Anda menginisialisasi AssociationRequest, jalankan fungsi
associate()
pada CompanionDeviceManager. Fungsi associate()
mengambil AssociationRequest dan Callback.
Callback menampilkan
IntentSender di
onAssociationPending saat CompanionDeviceManager menemukan perangkat
dan siap meluncurkan dialog izin pengguna.
Setelah pengguna mengonfirmasi perangkat, AssociationInfo
perangkat akan ditampilkan di onAssociationCreated.
Jika aplikasi Anda tidak menemukan perangkat, callback akan menampilkan onFailure
dengan pesan error.
Pada perangkat yang menjalankan Android 13 (level API 33) dan yang lebih tinggi:
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // An association is created. } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } })
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // An association is created. } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // To handle the failure. });
Di perangkat yang menjalankan Android 12L (level API 32) atau yang lebih rendah (tidak digunakan lagi):
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } }, null)
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // To handle the failure. } }, null);
Hasil pilihan pengguna dikirim kembali ke fragmen di
onActivityResult()
aktivitas Anda. Kemudian, Anda dapat mengakses perangkat yang dipilih.
Saat pengguna memilih perangkat Bluetooth, harapkan
BluetoothDevice.
Saat pengguna memilih perangkat Bluetooth LE, harapkan
android.bluetooth.le.ScanResult.
Saat pengguna memilih perangkat Wi-Fi, harapkan
android.net.wifi.ScanResult.
Kotlin
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } }
Java
@Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } }
Lihat contoh lengkapnya:
Pada perangkat yang menjalankan Android 13 (level API 33) dan yang lebih tinggi:
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } val mBluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter by lazy { val java = BluetoothManager::class.java getSystemService(java)!!.adapter } val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. var associationId: int = associationInfo.id var macAddress: MacAddress = associationInfo.deviceMacAddress } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } ) override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // do not include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. int associationId = associationInfo.getId(); MacAddress macAddress = associationInfo.getDeviceMacAddress(); } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // Handle the failure. }); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
Di perangkat yang menjalankan Android 12L (level API 32) atau yang lebih rendah (tidak digunakan lagi):
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } }, null) } override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // don't include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { // failed to send the intent } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // handle failure to find the companion device } }, null); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
Profil perangkat pendamping
Di Android 12 (level API 31) dan yang lebih tinggi, aplikasi pendamping yang mengelola perangkat seperti smartwatch dapat menggunakan profil perangkat pendamping untuk menyederhanakan proses penyiapan dengan memberikan izin yang diperlukan saat menyambungkan. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, lihat Profil Perangkat Pendamping.
Menjaga aplikasi pendamping tetap aktif
Mulai dari Android 16 (level API 36),
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence(String)
dan
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceAppeared()
tidak digunakan lagi.
Anda harus menggunakan
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence (ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)untuk mengelola bindingCompanionDeviceServiceyang diterapkan secara otomatis.- Status pengikatan
CompanionDeviceServiceAnda dikelola secara otomatis berdasarkan status kehadiran perangkat pendamping yang terkait:- Layanan ini terikat saat perangkat pendamping berada dalam jangkauan BLE atau terhubung menggunakan Bluetooth.
- Layanan menjadi tidak terikat saat perangkat pendamping bergerak keluar dari jangkauan BLE atau koneksi Bluetooth-nya dihentikan.
- Status pengikatan
Aplikasi akan menerima callback berdasarkan berbagai
DevicePresenceEvent.Untuk detailnya, lihat
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceEvent().

