これまでのリリースと同様、Android 16 には、アプリに影響する可能性がある動作変更が含まれています。下記の動作変更は、Android 16 以上をターゲットとするアプリにのみ適用されます。アプリが Android 16 以上をターゲットとする場合は、必要に応じてアプリを変更し、下記の動作に適切に対応できるようにしてください。
アプリの targetSdkVersion に関係なく、Android 16 で実行されるすべてのアプリに影響する動作変更のリストも必ずご確認ください。
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、より一貫性があり直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するために、以下の変更が加えられています。
エッジ ツー エッジのオプトアウトの廃止
Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリに対しては、Android 15 でエッジツーエッジが強制適用されますが、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement を true に設定することで、アプリでオプトアウトできます。Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとするアプリの場合、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement は非推奨で無効になっています。アプリでエッジツーエッジをオプトアウトすることはできません。
- アプリが Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとし、Android 15 デバイスで実行されている場合、
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementは引き続き機能します。 - アプリが Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとし、Android 16 デバイスで実行されている場合、
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementは無効になります。
Android 16 ベータ版 3 でテストするには、アプリがエッジ ツー エッジに対応していることを確認し、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement の使用をすべて削除して、Android 15 デバイスでもアプリがエッジ ツー エッジに対応するようにします。エッジツーエッジをサポートするには、Compose と ビューのガイダンスをご覧ください。
予測型「戻る」に移行またはオプトアウトが必要
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher and running on an
Android 16 or higher device, the predictive back system animations
(back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity) are enabled by default.
Additionally, onBackPressed is not called and
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK is not dispatched anymore.
If your app intercepts the back event and you haven't migrated to predictive
back yet, update your app to use supported back navigation APIs. or
temporarily opt out by setting the
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback attribute to false in the
<application> or <activity> tag of your app's AndroidManifest.xml file.
Elegant フォント API の非推奨と無効化
Apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) have the
elegantTextHeight
TextView attribute set to true by
default, replacing the compact font with one that is much more readable. You
could override this by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to false.
Android 16 deprecates the
elegantTextHeight attribute,
and the attribute will be ignored once your app targets Android 16. The "UI
fonts" controlled by these APIs are being discontinued, so you should adapt any
layouts to ensure consistent and future proof text rendering in Arabic, Lao,
Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu or Thai.
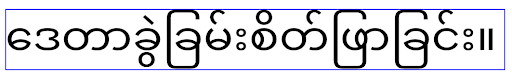
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
14 (API level 34) and lower, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35)
that overrode the default by setting the elegantTextHeight
attribute to false.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
16, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) that didn't override the
default by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to
false.コア機能
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、Android システムのさまざまなコア機能を変更または拡張する次の変更が含まれています。
固定レートの勤務スケジュールの最適化
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、大画面デバイスに表示されるアプリについて、次のように変更されています。
アダプティブ レイアウト
Android アプリは、さまざまなデバイス(スマートフォン、タブレット、折りたたみ式デバイス、デスクトップ、自動車、テレビなど)と大画面のウィンドウ モード(分割画面やデスクトップ ウィンドウなど)で実行されるため、デベロッパーは、デバイスの向きに関係なく、あらゆる画面とウィンドウ サイズに適応する Android アプリを構築する必要があります。画面の向きやサイズ変更の制限などのパラダイムは、今日のマルチデバイス環境では制限が厳しすぎます。
画面の向き、サイズ変更、アスペクト比の制限を無視する
Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとするアプリの場合、Android 16 では、システムが画面の向き、サイズ変更、アスペクト比の制限を管理する方法が変更されています。最小幅が 600dp 以上のディスプレイでは、この制限は適用されなくなります。また、アプリは、アスペクト比やユーザーが選択した画面の向きに関係なく、ディスプレイ ウィンドウ全体に表示されます。ピラーボックス表示は使用されません。
この変更により、新しい標準のプラットフォーム動作が導入されます。Android は、アプリがさまざまな画面の向き、表示サイズ、アスペクト比に適応することが期待されるモデルに移行しています。固定の画面の向きやサイズ変更の制限などの制約は、アプリの適応性を妨げるため、可能な限り優れたユーザー エクスペリエンスを提供するために、アプリを適応性のあるものにすることをおすすめします。
アプリの互換性フレームワークを使用して UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT 互換性フラグを有効にすることで、この動作をテストすることもできます。
一般的な破壊的変更
向き、サイズ変更、アスペクト比の制限を無視すると、一部のデバイスでアプリの UI に影響する可能性があります。特に、縦向きでロックされた小さなレイアウト用に設計された要素に影響する可能性があります。たとえば、レイアウトの引き伸ばし、画面外のアニマーションやコンポーネントなどの問題が発生する可能性があります。アスペクト比や画面の向きについて想定すると、アプリの視覚的な問題が発生する可能性があります。これらの問題を回避し、アプリの適応型動作を改善する方法について詳細をご覧ください。
デバイスの回転を許可すると、アクティビティの再作成が増え、適切に保存されなかった場合にユーザーの状態が失われる可能性があります。UI の状態を正しく保存する方法については、UI の状態を保存するをご覧ください。
実装の詳細
次のマニフェスト属性とランタイム API は、大画面デバイスで全画面モードとマルチウィンドウ モードの両方で無視されます。
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
screenOrientation、setRequestedOrientation()、getRequestedOrientation() の次の値は無視されます。
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
ディスプレイのサイズ変更に関しては、android:resizeableActivity="false"、android:minAspectRatio、android:maxAspectRatio は効果がありません。
Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとするアプリの場合、大画面ではアプリの向き、サイズ変更、アスペクト比の制約はデフォルトで無視されますが、完全に準備ができていないすべてのアプリは、オプトアウトすることでこの動作を一時的にオーバーライドできます(これにより、互換モードに置かれるという以前の動作になります)。
例外
Android 16 の画面の向き、サイズ変更、アスペクト比の制限は、次の状況では適用されません。
- ゲーム(
android:appCategoryフラグに基づく) - ユーザーがデバイスのアスペクト比設定でアプリのデフォルトの動作を明示的に有効にしている
sw600dpより小さい画面
一時的にオプトアウトする
特定のアクティビティをオプトアウトするには、PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY マニフェスト プロパティを宣言します。
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
アプリの多くの部分が Android 16 に対応していない場合は、アプリケーション レベルで同じプロパティを適用して、完全にオプトアウトできます。
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
健康&フィットネス
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、健康とフィットネスのデータに関連する以下の変更が加えられました。
健康とフィットネスの権限
Android 16(API レベル 36)以上をターゲットとするアプリの場合、BODY_SENSORS 権限は、ヘルスコネクトでも使用される android.permissions.health の下でより細かい権限を使用します。Android 16 以降、これまで BODY_SENSORS または BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND を必要としていた API はすべて、対応する android.permissions.health 権限が必要となります。これは、次のデータタイプ、API、フォアグラウンド サービスのタイプに影響します。
- Wear OS のヘルスサービス
HEART_RATE_BPM - Android Sensor Manager の
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - Wear OS の
ProtoLayoutからheartRateAccuracyとheartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH:BODY_SENSORSの代わりに、それぞれのandroid.permission.health権限が必要
アプリがこれらの API を使用する場合は、それぞれ詳細な権限をリクエストする必要があります。
- 心拍数、血中酸素ウェルネス、皮膚温の使用中のモニタリングの場合:
android.permissions.healthの詳細な権限をリクエストします(BODY_SENSORSではなくREAD_HEART_RATEなど)。 - バックグラウンド センサーへのアクセスの場合:
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDではなくREAD_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDをリクエストします。
これらの権限は、健康、フィットネス、ウェルネス データ用の Android データストアである ヘルスコネクトからのデータの読み取りアクセスを保護する権限と同じです。
モバイルアプリ
READ_HEART_RATE などのきめ細かい権限を使用するように移行するモバイルアプリは、アプリのプライバシー ポリシーを表示するためにアクティビティを宣言する必要もあります。これはヘルスコネクトと同じ要件です。
接続
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、Bluetooth スタックに次の変更が加えられて、周辺機器との接続が改善されています。
ボンドの損失と暗号化の変更を処理する新しいインテントの追加
As part of the Improved bond loss handling, Android 16 also introduces 2 new intents to provide apps with greater awareness of bond loss and encryption changes.
Apps targeting Android 16 can now:
- Receive an
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent when remote bond loss is detected, allowing them to provide more informative user feedback and take appropriate actions. - Receive an
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent whenever encryption status of the link changes. This includes encryption status change, encryption algorithm change, and encryption key size change. Apps must consider the bond restored if the link is successfully encrypted upon receivingACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent later.
If your app currently uses custom mechanisms for bond loss handling, migrate to
the new intent ACTION_KEY_MISSING to detect and manage bond loss
events. We recommend your app guide the user to confirm the remote device is in
range before initiating device forgetting and re-pairing.
Moreover, if a device disconnects after ACTION_KEY_MISSING intent
is received, your app should be mindful about reconnecting to the device as that
device may no longer be bonded with the system.
Bluetooth ボンディングを削除する新しい方法
Android 16 をターゲットとするすべてのアプリで、CompanionDeviceManager の公開 API を使用して Bluetooth デバイスのペア設定を解除できるようになりました。コンパニオン デバイスが CDM の関連付けとして管理されている場合、アプリは、関連付けられたデバイスで新しい removeBond(int) API を使用して、Bluetooth の接続解除をトリガーできます。アプリは、Bluetooth デバイスのブロードキャスト イベント ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED をリッスンすることで、ボンディング状態の変化をモニタリングできます。
セキュリティ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、セキュリティが次のように変更されています。
MediaStore バージョンのロックダウン
Android 16 以降をターゲットとするアプリの場合、MediaStore#getVersion() はアプリごとに一意になります。これにより、バージョン文字列から識別プロパティが削除され、フィンガープリント手法の不正使用と使用が防止されます。アプリでは、このバージョンの形式について前提条件を設定しないでください。アプリは、この API を使用する際にバージョンの変更をすでに処理している必要があります。ほとんどの場合、デベロッパーがこの API の対象範囲を超える追加情報を推測しようとしない限り、現在の動作を変更する必要はありません。
Safer Intents
The Safer Intents feature is a multi-phase security initiative designed to improve the security of Android's intent resolution mechanism. The goal is to protect apps from malicious actions by adding checks during intent processing and filtering intents that don't meet specific criteria.
In Android 15 the feature focused on the sending app, now with Android 16, shifts control to the receiving app, allowing developers to opt-in to strict intent resolution using their app manifest.
Two key changes are being implemented:
Explicit Intents Must Match the Target Component's Intent Filter: If an intent explicitly targets a component, it should match that component's intent filter.
Intents Without an Action Cannot Match any Intent Filter: Intents that don't have an action specified shouldn't be resolved to any intent filter.
These changes only apply when multiple apps are involved and don't affect intent handling within a single app.
Impact
The opt-in nature means that developers must explicitly enable it in their app manifest for it to take effect. As a result, the feature's impact will be limited to apps whose developers:
- Are aware of the Safer Intents feature and its benefits.
- Actively choose to incorporate stricter intent handling practices into their apps.
This opt-in approach minimizes the risk of breaking existing apps that may rely on the current less-secure intent resolution behavior.
While the initial impact in Android 16 may be limited, the Safer Intents initiative has a roadmap for broader impact in future Android releases. The plan is to eventually make strict intent resolution the default behavior.
The Safer Intents feature has the potential to significantly enhance the security of the Android ecosystem by making it more difficult for malicious apps to exploit vulnerabilities in the intent resolution mechanism.
However, the transition to opt-out and mandatory enforcement must be carefully managed to address potential compatibility issues with existing apps.
Implementation
Developers need to explicitly enable stricter intent matching using the
intentMatchingFlags attribute in their app manifest.
Here is an example where the feature is opt-in for the entire app,
but disabled/opt-out on a receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
More on the supported flags:
| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Enforces stricter matching for incoming intents |
| none | Disables all special matching rules for incoming intents. When specifying multiple flags, conflicting values are resolved by giving precedence to the "none" flag |
| allowNullAction | Relaxes the matching rules to allow intents without an action to match. This flag to be used in conjunction with "enforceIntentFilter" to achieve a specific behavior |
Testing and Debugging
When the enforcement is active, apps should function correctly if the intent
caller has properly populated the intent.
However, blocked intents will trigger warning log messages like
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" and "Access blocked:"
with the tag "PackageManager."
This indicates a potential issue that could impact the app and requires
attention.
Logcat filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
プライバシー
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、プライバシーに関する次の変更が行われています。
ローカル ネットワークへのアクセス権
Devices on the LAN can be accessed by any app that has the INTERNET permission.
This makes it easy for apps to connect to local devices but it also has privacy
implications such as forming a fingerprint of the user, and being a proxy for
location.
The Local Network Protections project aims to protect the user's privacy by gating access to the local network behind a new runtime permission.
Release plan
This change will be deployed between two releases, 25Q2 and TBD respectively. It is imperative that developers follow this guidance for 25Q2 and share feedback because these protections will be enforced at a later Android release. Moreover, they will need to update scenarios which depend on implicit local network access by using the following guidance and prepare for user rejection and revocation of the new permission.
Impact
At the current stage, LNP is an opt-in feature which means only the apps that opt in will be affected. The goal of the opt-in phase is for app developers to understand which parts of their app depend on implicit local network access such that they can prepare to permission guard them for the next release.
Apps will be affected if they access the user's local network using:
- Direct or library use of raw sockets on local network addresses (e.g. mDNS or SSDP service discovery protocol)
- Use of framework level classes that access the local network (e.g. NsdManager)
Traffic to and from a local network address requires local network access permission. The following table lists some common cases:
| App Low Level Network Operation | Local Network Permission Required |
|---|---|
| Making an outgoing TCP connection | yes |
| Accepting incoming TCP connections | yes |
| Sending a UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
| Receiving an incoming UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
These restrictions are implemented deep in the networking stack, and thus they apply to all networking APIs. This includes sockets created in native or managed code, networking libraries like Cronet and OkHttp, and any APIs implemented on top of those. Trying to resolve services on the local network (i.e. those with a .local suffix) will require local network permission.
Exceptions to the rules above:
- If a device's DNS server is on a local network, traffic to or from it (at port 53) doesn't require local network access permission.
- Applications using Output Switcher as their in-app picker won't need local network permissions (more guidance to come in 2025Q4).
Developer Guidance (Opt-in)
To opt into local network restrictions, do the following:
- Flash the device to a build with 25Q2 Beta 3 or later.
- Install the app to be tested.
Toggle the Appcompat flag in adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Reboot The device
Now your app's access to the local network is restricted and any attempt to access the local network will lead to socket errors. If you are using APIs that perform local network operations outside of your app process (ex: NsdManager), they won't be impacted during the opt-in phase.
To restore access, you must grant your app permission to NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Ensure the app declares the
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESpermission in its manifest. - Go to Settings > Apps > [Application Name] > Permissions > Nearby devices > Allow.
Now your app's access to the local network should be restored and all your scenarios should work as they did prior to opting the app in.
Once enforcement for local network protection begins, here is how the app network traffic will be impacted.
| Permission | Outbound LAN Request | Outbound/Inbound Internet Request | Inbound LAN Request |
|---|---|---|---|
| Granted | Works | Works | Works |
| Not Granted | Fails | Works | Fails |
Use the following command to toggle-off the App-Compat flag
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Errors
Errors arising from these restrictions will be returned to the calling socket whenever it invokes send or a send variant to a local network address.
Example errors:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Local Network Definition
A local network in this project refers to an IP network that utilizes a broadcast-capable network interface, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet, but excludes cellular (WWAN) or VPN connections.
The following are considered local networks:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Directly-connected routes
- Stub networks like Thread
- Multiple-subnets (TBD)
Additionally, both multicast addresses (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) and the IPv4 broadcast address (255.255.255.255) are classified as local network addresses.
アプリ所有の写真
Android 16 以降を搭載したデバイスで、SDK 36 以降をターゲットとするアプリから写真と動画の権限を求めるメッセージが表示された場合、選択したメディアへのアクセスを制限することを選択したユーザーには、アプリが所有する写真が写真選択ツールで事前選択された状態で表示されます。ユーザーは、これらの事前選択された項目の選択を解除できます。これにより、それらの写真と動画へのアプリのアクセス権が取り消されます。

