이전 버전과 마찬가지로 Android 15에는 앱에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 동작 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다. 다음 동작 변경사항은 Android 15 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱에만 적용됩니다. 앱이 Android 15 이상을 타겟팅한다면 이러한 동작을 올바르게 지원하도록 앱을 수정해야 합니다(적용되는 경우).
앱의 targetSdkVersion과 관계없이 Android 15에서 실행되는 모든 앱에 영향을 미치는 동작 변경사항 목록도 검토해야 합니다.
핵심 기능
Android 15는 Android 시스템의 다양한 핵심 기능을 수정하거나 확장합니다.
포그라운드 서비스 변경사항
We are making the following changes to foreground services with Android 15.
- Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
- New media processing foreground service type
- Restrictions on
BOOT_COMPLETEDbroadcast receivers launching foreground services - Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOWpermission
Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
Android 15에서는 Android 15 (API 수준 35) 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱의 dataSync에 새로운 제한 시간 동작을 도입합니다. 이 동작은 새 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스 유형에도 적용됩니다.
시스템은 앱의 dataSync 서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간 동안 실행되도록 허용합니다. 그 후에는 실행 중인 서비스의 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 메서드 (Android 15에서 도입됨)를 호출합니다. 이때 서비스는 Service.stopSelf()를 호출할 수 있는 몇 초의 시간을 갖습니다. Service.onTimeout()가 호출되면 서비스는 더 이상 포그라운드 서비스로 간주되지 않습니다. 서비스가 Service.stopSelf()를 호출하지 않으면 시스템에서 내부 예외를 발생시킵니다. 예외는 다음 메시지와 함께 Logcat에 로깅됩니다.
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
이 동작 변경과 관련된 문제를 방지하려면 다음 중 하나 이상을 실행하세요.
- 서비스가 새
Service.onTimeout(int, int)메서드를 구현하도록 합니다. 앱이 콜백을 수신하면 몇 초 이내에stopSelf()를 호출해야 합니다. 앱을 즉시 중지하지 않으면 시스템에서 실패를 생성합니다. - 앱의
dataSync서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간 넘게 실행되지 않도록 합니다 (사용자가 앱과 상호작용하여 타이머를 재설정하는 경우 제외). - 직접적인 사용자 상호작용의 결과로만
dataSync포그라운드 서비스를 시작합니다. 서비스가 시작될 때 앱이 포그라운드에 있으므로 앱이 백그라운드로 전환된 후 6시간 동안 서비스가 계속 실행됩니다. dataSync포그라운드 서비스를 사용하는 대신 대체 API를 사용하세요.
앱의 dataSync 포그라운드 서비스가 지난 24시간 동안 6시간 동안 실행된 경우 사용자가 앱을 포그라운드로 가져와 (타이머 재설정) 않는 한 다른 dataSync 포그라운드 서비스를 시작할 수 없습니다. 다른 dataSync 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하려고 하면 시스템에서 '포그라운드 서비스 유형 dataSync의 시간 제한이 이미 소진됨'과 같은 오류 메시지와 함께 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException를 발생시킵니다.
테스트
앱 동작을 테스트하려면 앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않더라도 (앱이 Android 15 기기에서 실행되는 경우) 데이터 동기화 시간 제한을 사용 설정할 수 있습니다. 제한 시간을 사용 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
제한에 도달할 때 앱이 어떻게 동작하는지 더 쉽게 테스트할 수 있도록 제한 시간도 조정할 수 있습니다. 새 제한 시간을 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
New media processing foreground service type
Android 15에서는 새로운 포그라운드 서비스 유형인 mediaProcessing가 도입되었습니다. 이 서비스 유형은 미디어 파일 트랜스코딩과 같은 작업에 적합합니다. 예를 들어 미디어 앱에서 오디오 파일을 다운로드한 후 재생하기 전에 다른 형식으로 변환해야 할 수 있습니다. mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스를 사용하여 앱이 백그라운드에 있는 동안에도 전환이 계속되도록 할 수 있습니다.
시스템은 앱의 mediaProcessing 서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간 동안 실행되도록 허용합니다. 그 후에는 실행 중인 서비스의 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 메서드 (Android 15에서 도입됨)를 호출합니다. 현재 서비스는 몇 초 동안 Service.stopSelf()를 호출할 수 있습니다. 서비스가 Service.stopSelf()를 호출하지 않으면 시스템에서 내부 예외가 발생합니다. 예외는 다음 메시지와 함께 Logcat에 로깅됩니다.
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
예외가 적용되지 않도록 하려면 다음 중 하나를 수행하세요.
- 서비스가 새
Service.onTimeout(int, int)메서드를 구현하도록 합니다. 앱이 콜백을 수신하면 몇 초 내에stopSelf()를 호출해야 합니다. 앱을 즉시 중지하지 않으면 시스템에서 실패를 생성합니다. - 사용자가 앱과 상호작용하여 타이머를 재설정하지 않는 한 앱의
mediaProcessing서비스가 24시간 동안 총 6시간을 초과하여 실행되지 않아야 합니다. - 직접적인 사용자 상호작용의 결과로만
mediaProcessing포그라운드 서비스를 시작합니다. 서비스가 시작될 때 앱이 포그라운드에 있으므로 앱이 백그라운드로 전환된 후 6시간 동안 서비스가 계속 실행됩니다. mediaProcessing포그라운드 서비스를 사용하는 대신 WorkManager와 같은 대체 API를 사용하세요.
앱의 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스가 지난 24시간 동안 6시간 동안 실행된 경우 사용자가 앱을 포그라운드로 가져와 (타이머 재설정) 않는 한 다른 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스를 시작할 수 없습니다. 다른 mediaProcessing 포그라운드 서비스를 시작하려고 하면 시스템에서 '포그라운드 서비스 유형 mediaProcessing의 시간 제한이 이미 소진되었습니다'와 같은 오류 메시지와 함께 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException을 발생시킵니다.
mediaProcessing 서비스 유형에 관한 자세한 내용은 Android 15의 포그라운드 서비스 유형 변경사항: 미디어 처리를 참고하세요.
테스트
앱의 동작을 테스트하려면 앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않더라도 (앱이 Android 15 기기에서 실행되는 경우) 미디어 처리 시간 제한을 사용 설정할 수 있습니다. 제한 시간을 사용 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
제한에 도달할 때 앱이 어떻게 동작하는지 더 쉽게 테스트할 수 있도록 제한 시간도 조정할 수 있습니다. 새 제한 시간을 설정하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Restrictions on BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast receivers launching foreground services
출시되는 broadcast receiver BOOT_COMPLETED개에 새로운 제한사항이 있습니다.
포그라운드 서비스가 될 수 있습니다 BOOT_COMPLETED 수신기는 다음 유형의 포그라운드 서비스를 실행할 수 없습니다.
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(이 제한은 이후microphone부터 적용되었음 Android 14)
BOOT_COMPLETED 수신기가 이러한 유형의 포그라운드를 실행하려고 하는 경우
시스템에서 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException을 발생시킵니다.
테스트
앱의 동작을 테스트하기 위해
앱이 Android 15를 타겟팅하지 않음 (앱이 Android 15
기기). 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
기기를 다시 시작하지 않고 BOOT_COMPLETED 브로드캐스트를 전송하려면 다음 안내를 따르세요.
다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission
Previously, if an app held the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission, it could launch
a foreground service even if the app was currently in the background (as
discussed in exemptions from background start restrictions).
If an app targets Android 15, this exemption is now narrower. The app now needs
to have the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission and also have a visible overlay
window. That is, the app needs to first launch a
TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY window and the window
needs to be visible before you start a foreground service.
If your app attempts to start a foreground service from the background without
meeting these new requirements (and it does not have some other exemption), the
system throws ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
If your app declares the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission
and launches foreground services from the background, it may be affected by this
change. If your app gets a ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, check
your app's order of operations and make sure your app already has an active
overlay window before it attempts to start a foreground service from the
background. You can check if your overlay window is currently visible
by calling View.getWindowVisibility(), or you
can override View.onWindowVisibilityChanged()
to get notified whenever the visibility changes.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable these new restrictions even if your
app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). To enable these new restrictions on starting foreground services
from the background, run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
앱이 방해 금지 모드의 전역 상태를 수정할 수 있는 시점 변경
Apps that target Android 15 (API level 35) and higher can no longer change the
global state or policy of Do Not Disturb (DND) on a device (either by modifying
user settings, or turning off DND mode). Instead, apps must contribute an
AutomaticZenRule, which the system combines into a global policy with the
existing most-restrictive-policy-wins scheme. Calls to existing APIs that
previously affected global state (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) result in the creation or update of an implicit
AutomaticZenRule, which is toggled on and off depending on the call-cycle of
those API calls.
Note that this change only affects observable behavior if the app is calling
setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) and expects that call to
deactivate an AutomaticZenRule that was previously activated by their owners.
OpenJDK API 변경사항
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
Some of these changes can affect app compatibility for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35):
Changes to string formatting APIs: Validation of argument index, flags, width, and precision are now more strict when using the following
String.format()andFormatter.format()APIs:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
For example, the following exception is thrown when an argument index of 0 is used (
%0in the format string):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0In this case, the issue can be fixed by using an argument index of 1 (
%1in the format string).Changes to component type of
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): When usingArrays.asList(...).toArray(), the component type of the resulting array is now anObject—not the type of the underlying array's elements. So the following code throws aClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();For this case, to preserve
Stringas the component type in the resulting array, you could useCollection.toArray(Object[])instead:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Changes to language code handling: When using the
LocaleAPI, language codes for Hebrew, Yiddish, and Indonesian are no longer converted to their obsolete forms (Hebrew:iw, Yiddish:ji, and Indonesian:in). When specifying the language code for one of these locales, use the codes from ISO 639-1 instead (Hebrew:he, Yiddish:yi, and Indonesian:id).Changes to random int sequences: Following the changes made in https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, the following
Random.ints()methods now return a different sequence of numbers than theRandom.nextInt()methods do:Generally, this change shouldn't result in app-breaking behavior, but your code shouldn't expect the sequence generated from
Random.ints()methods to matchRandom.nextInt().
The new SequencedCollection API can affect your app's compatibility
after you update compileSdk in your app's build configuration to use
Android 15 (API level 35):
Collision with
MutableList.removeFirst()andMutableList.removeLast()extension functions inkotlin-stdlibThe
Listtype in Java is mapped to theMutableListtype in Kotlin. Because theList.removeFirst()andList.removeLast()APIs have been introduced in Android 15 (API level 35), the Kotlin compiler resolves function calls, for examplelist.removeFirst(), statically to the newListAPIs instead of to the extension functions inkotlin-stdlib.If an app is re-compiled with
compileSdkset to35andminSdkset to34or lower, and then the app is run on Android 14 and lower, a runtime error is thrown:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;The existing
NewApilint option in Android Gradle Plugin can catch these new API usages../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()To fix the runtime exception and lint errors, the
removeFirst()andremoveLast()function calls can be replaced withremoveAt(0)andremoveAt(list.lastIndex)respectively in Kotlin. If you're using Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 or higher, it also provides a quick fix option for these errors.Consider removing
@SuppressLint("NewApi")andlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }if the lint option has been disabled.Collision with other methods in Java
New methods have been added into the existing types, for example,
ListandDeque. These new methods might not be compatible with the methods with the same name and argument types in other interfaces and classes. In the case of a method signature collision with incompatibility, thejavaccompiler outputs a build-time error. For example:Example error 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListExample error 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorExample error 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorTo fix these build errors, the class implementing these interfaces should override the method with a compatible return type. For example:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
보안
Android 15에는 악성 앱으로부터 앱과 사용자를 보호하기 위해 시스템 보안을 강화하는 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
제한된 TLS 버전
Android 15 restricts the usage of TLS versions 1.0 and 1.1. These versions had previously been deprecated in Android, but are now disallowed for apps targeting Android 15.
보안 백그라운드 활동 실행
Android 15 protects users from malicious apps and gives them more control over their devices by adding changes that prevent malicious background apps from bringing other apps to the foreground, elevating their privileges, and abusing user interaction. Background activity launches have been restricted since Android 10 (API level 29).
Other changes
- Change
PendingIntentcreators to block background activity launches by default. This helps prevent apps from accidentally creating aPendingIntentthat could be abused by malicious actors. - Don't bring an app to the foreground unless the
PendingIntentsender allows it. This change aims to prevent malicious apps from abusing the ability to start activities in the background. By default, apps are not allowed to bring the task stack to the foreground unless the creator allows background activity launch privileges or the sender has background activity launch privileges. - Control how the top activity of a task stack can finish its task. If the top activity finishes a task, Android will go back to whichever task was last active. Moreover, if a non-top activity finishes its task, Android will go back to the home screen; it won't block the finish of this non-top activity.
- Prevent launching arbitrary activities from other apps into your own task. This change prevents malicious apps from phishing users by creating activities that appear to be from other apps.
- Block non-visible windows from being considered for background activity launches. This helps prevent malicious apps from abusing background activity launches to display unwanted or malicious content to users.
더 안전한 인텐트
Android 15 introduces StrictMode for
intents.
In order to see detailed logs about Intent usage violations, use following
method:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
사용자 경험 및 시스템 UI
Android 15에는 더 일관되고 직관적인 사용자 환경을 만들기 위한 몇 가지 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
창 인셋 변경
There are two changes related to window insets in Android 15: edge-to-edge is enforced by default, and there are also configuration changes, such as the default configuration of system bars.
더 넓은 화면 적용
Apps are edge-to-edge by default on devices running Android 15 if the app is targeting Android 15 (API level 35).
This is a breaking change that might negatively impact your app's UI. The changes affect the following UI areas:
- Gesture handle navigation bar
- Transparent by default.
- Bottom offset is disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare deprecated and don't affect gesture navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedcontinue to have no effect on gesture navigation.
- 3-button navigation
- Opacity set to 80% by default, with color possibly matching the window background.
- Bottom offset disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare set to match the window background by default. The window background must be a color drawable for this default to apply. This API is deprecated but continues to affect 3-button navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedis true by default, which adds an 80% opaque background across 3-button navigation.
- Status bar
- Transparent by default.
- The top offset is disabled so content draws behind the status bar unless insets are applied.
setStatusBarColorandR.attr#statusBarColorare deprecated and have no effect on Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedare deprecated but still have an effect on Android 15.
- Display cutout
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeof non-floating windows must beLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVER, andDEFAULTare interpreted asALWAYSso that users don't see a black bar caused by the display cutout and appear edge-to-edge.
The following example shows an app before and after targeting Android 15 (API level 35), and before and after applying insets. This example is not comprehensive, this might appear differently on Android Auto.
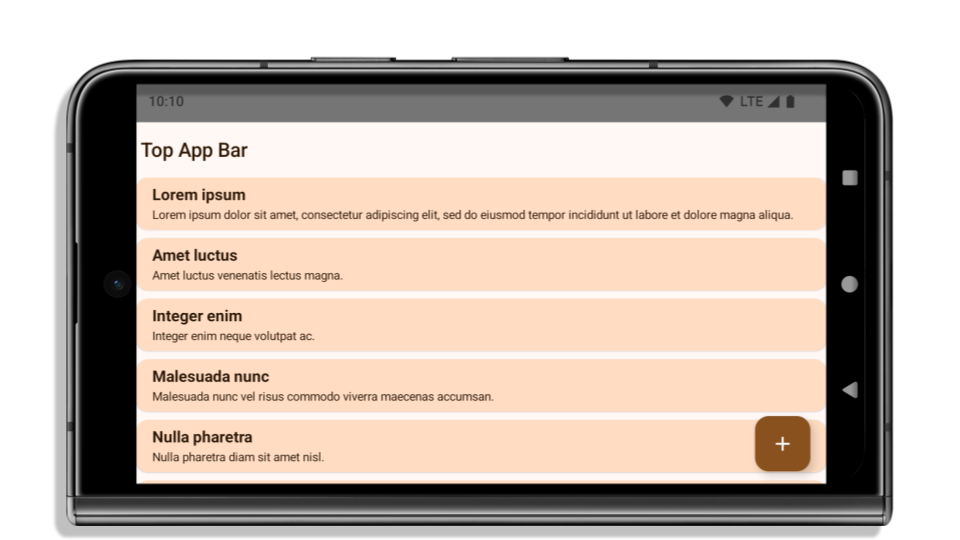

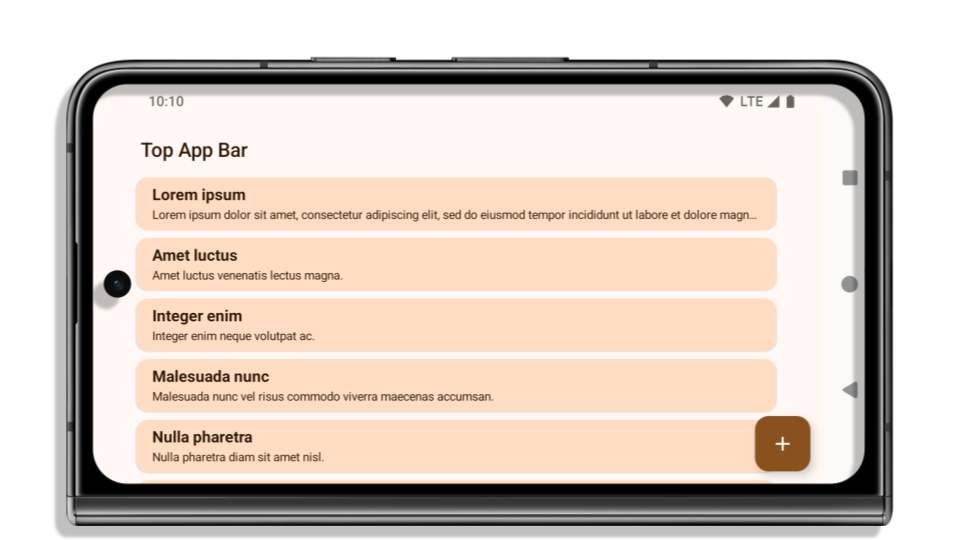
What to check if your app is already edge-to-edge
If your app is already edge-to-edge and applies insets, you are mostly unimpacted, except in the following scenarios. However, even if you think you aren't impacted, we recommend you test your app.
- You have a non-floating window, such as an
Activitythat usesSHORT_EDGES,NEVERorDEFAULTinstead ofLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. If your app crashes on launch, this might be due to your splashscreen. You can either upgrade the core splashscreen dependency to 1.2.0-alpha01 or later or setwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - There might be lower-traffic screens with occluded UI. Verify these
less-visited screens don't have occluded UI. Lower-traffic screens include:
- Onboarding or sign-in screens
- Settings pages
What to check if your app is not already edge-to-edge
If your app is not already edge-to-edge, you are most likely impacted. In addition to the scenarios for apps that are already edge-to-edge, you should consider the following:
- If your app uses Material 3 Components (
androidx.compose.material3) in compose, such asTopAppBar,BottomAppBar, andNavigationBar, these components are likely not impacted because they automatically handle insets. - If your app is using Material 2 Components (
androidx.compose.material) in Compose, these components don't automatically handle insets. However, you can get access to the insets and apply them manually. In androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 and later, use thewindowInsetsparameter to apply the insets manually forBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigation, andNavigationRail. Likewise, use thecontentWindowInsetsparameter forScaffold. - If your app uses views and Material Components
(
com.google.android.material), most views-based Material Components such asBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailView, orNavigationView, handle insets and require no additional work. However, you need to addandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"if usingAppBarLayout. - For custom composables, apply the insets manually as padding. If your
content is within a
Scaffold, you can consume insets using theScaffoldpadding values. Otherwise, apply padding using one of theWindowInsets. - If your app is using views and
BottomSheet,SideSheetor custom containers, apply padding usingViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ForRecyclerView, apply padding using this listener and also addclipToPadding="false".
What to check if your app must offer custom background protection
If your app must offer custom background protection to 3-button navigation or
the status bar, your app should place a composable or view behind the system bar
using WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() to get the 3-button
navigation bar height or WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Additional edge-to-edge resources
See the Edge to Edge Views and Edge to Edge Compose guides for additional considerations on applying insets.
Deprecated APIs
The following APIs are deprecated but not disabled:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
The following APIs are deprecated and disabled:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
안정적인 구성
If your app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or higher, Configuration no
longer excludes the system bars. If you use the screen size in the
Configuration class for layout calculation, you should replace it with better
alternatives like an appropriate ViewGroup, WindowInsets, or
WindowMetricsCalculator depending on your need.
Configuration has been available since API 1. It is typically obtained from
Activity.onConfigurationChanged. It provides information like window density,
orientation, and sizes. One important characteristic about the window sizes
returned from Configuration is that it previously excluded the system bars.
The configuration size is typically used for resource selection, such as
/res/layout-h500dp, and this is still a valid use case. However, using it for
layout calculation has always been discouraged. If you do so, you should move
away from it now. You should replace the use of Configuration with something
more suitable depending on your use case.
If you use it to calculate the layout, use an appropriate ViewGroup, such as
CoordinatorLayout or ConstraintLayout. If you use it to determine the height
of the system navbar, use WindowInsets. If you want to know the current size
of your app window, use computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
The following list describes the fields affected by this change:
Configuration.screenWidthDpandscreenHeightDpsizes no longer exclude the system bars.Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpis indirectly affected by changes toscreenWidthDpandscreenHeightDp.Configuration.orientationis indirectly affected by changes toscreenWidthDpandscreenHeightDpon close-to-square devices.Display.getSize(Point)is indirectly affected by the changes inConfiguration. This was deprecated beginning in API level 30.Display.getMetrics()has already worked like this since API level 33.
elegantTextHeight 속성이 기본적으로 true로 설정됨
For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), the
elegantTextHeight TextView attribute
becomes true by default, replacing the compact font used by default with some
scripts that have large vertical metrics with one that is much more readable.
The compact font was introduced to prevent breaking layouts; Android 13 (API
level 33) prevents many of these breakages by allowing the text layout to
stretch the vertical height utilizing the fallbackLineSpacing
attribute.
In Android 15, the compact font still remains in the system, so your app can set
elegantTextHeight to false to get the same behavior as before, but it is
unlikely to be supported in upcoming releases. So, if your app supports the
following scripts: Arabic, Lao, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam,
Odia, Telugu or Thai, test your app by setting elegantTextHeight to true.
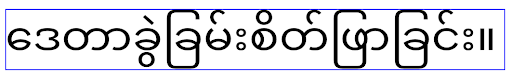
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 14 (API level 34) and lower.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 15.복잡한 글자 모양의 TextView 너비 변경
In previous versions of Android, some cursive fonts or languages that have
complex shaping might draw the letters in the previous or next character's area.
In some cases, such letters were clipped at the beginning or ending position.
Starting in Android 15, a TextView allocates width for drawing enough space
for such letters and allows apps to request extra paddings to the left to
prevent clipping.
Because this change affects how a TextView decides the width, TextView
allocates more width by default if the app targets Android 15 (API level 35) or
higher. You can enable or disable this behavior by calling the
setUseBoundsForWidth API on TextView.
Because adding left padding might cause a misalignment for existing layouts, the
padding is not added by default even for apps that target Android 15 or higher.
However, you can add extra padding to preventing clipping by calling
setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang.
The following examples show how these changes can improve text layout for some fonts and languages.

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
EditText의 언어 인식 기본 행 높이
In previous versions of Android, the text layout stretched the height of the
text to meet the line height of the font that matched the current locale. For
example, if the content was in Japanese, because the line height of the Japanese
font is slightly larger than the one of a Latin font, the height of the text
became slightly larger. However, despite these differences in line heights, the
EditText element was sized uniformly, regardless
of the locale being used, as illustrated in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText is the same, even though these languages
have different line heights from each other.For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), a minimum line height is now
reserved for EditText to match the reference font for the specified Locale, as
shown in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText now includes space to accommodate the
default line height for these languages' fonts.If needed, your app can restore the previous behavior by specifying the
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum attribute
to false, and your app can set custom minimum vertical metrics using the
setMinimumFontMetrics API in Kotlin and Java.
카메라 및 미디어
Android 15에서는 Android 15 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱의 카메라 및 미디어 동작이 다음과 같이 변경됩니다.
오디오 포커스 요청 제한사항
Apps that target Android 15 (API level 35) must be the top app or running a
foreground service in order to request audio focus. If an app
attempts to request focus when it does not meet one of these requirements, the
call returns AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
You can learn more about audio focus at Manage audio focus.
업데이트된 비 SDK 제한사항
Android 15 includes updated lists of restricted non-SDK interfaces based on collaboration with Android developers and the latest internal testing. Whenever possible, we make sure that public alternatives are available before we restrict non-SDK interfaces.
If your app does not target Android 15, some of these changes might not immediately affect you. However, while it's possible for your app to access some non-SDK interfaces depending on your app's target API level, using any non-SDK method or field always carries a high risk of breaking your app.
If you are unsure if your app uses non-SDK interfaces, you can test your app to find out. If your app relies on non-SDK interfaces, you should begin planning a migration to SDK alternatives. Nevertheless, we understand that some apps have valid use cases for using non-SDK interfaces. If you can't find an alternative to using a non-SDK interface for a feature in your app, you should request a new public API.
To learn more about the changes in this release of Android, see Updates to non-SDK interface restrictions in Android 15. To learn more about non-SDK interfaces generally, see Restrictions on non-SDK interfaces.
