หลังจากทำความเข้าใจวิธีจัดการรูปร่างต่างๆ ของนาฬิกาแล้ว ให้ตัดสินใจว่าต้องการใช้แพลตฟอร์มใด
เลย์เอาต์แอปที่พบได้ทั่วไปมีดังนี้
- หน้าจอเดียว (ง่ายที่สุด): องค์ประกอบ UI จะแสดงเฉพาะสิ่งที่มองเห็นได้พร้อมกันโดยไม่ต้องเลื่อน
- คอนเทนเนอร์แนวตั้ง (พบบ่อยที่สุด): เนื้อหาอยู่นอกส่วนที่มองเห็นได้ของหน้าจอและเข้าถึงได้โดยเลื่อน
- ตัวเลือกอื่นๆ ได้แก่ รายการ การเลื่อนหน้า หรือการปัด 2 มิติ
เราได้อธิบายประเภทเลย์เอาต์เหล่านี้ไว้ในส่วนต่อไปนี้ คุณใช้เลย์เอาต์หลายประเภทผสมผสานกันได้หากต้องการใช้หน้าจอหลายหน้าจอ
หมายเหตุ: สำหรับกิจกรรม ให้รับค่าจาก ComponentActivity หรือ FragmentActivity (หากใช้ข้อมูลโค้ด)
กิจกรรมประเภทอื่นๆ ใช้องค์ประกอบ UI สำหรับอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่โดยเฉพาะซึ่งคุณไม่จําเป็นต้องใช้ใน Wear OS
หน้าจอเดียว
ผู้ใช้จะเห็นองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดในหน้าจอเดียวโดยไม่ต้องเลื่อน ซึ่งหมายความว่าคุณใส่องค์ประกอบได้เพียงไม่กี่รายการ

รูปที่ 1 ตัวอย่างเลย์เอาต์หน้าจอเดียว
หน้าจอเดียวเหมาะที่จะใช้ร่วมกับ
BoxInsetLayout
ร่วมกับ
ConstraintLayout
เพื่อจัดเรียงองค์ประกอบ
คอนเทนเนอร์แนวตั้ง
คอนเทนเนอร์แนวตั้งเป็นเลย์เอาต์แอปประเภทที่พบบ่อยที่สุด เนื้อหาบางอย่างอาจไม่แสดงบนหน้าจอ แต่เข้าถึงได้โดยเลื่อน
รูปที่ 2 แสดงเลย์เอาต์แอปที่สมบูรณ์หลายรายการ ซึ่งจะเห็นเนื้อหาเพียงบางส่วนบนหน้าจอทรงกลมของนาฬิกา ในตัวอย่างนี้ เนื้อหาหลักจะอยู่ในส่วนด้านบนของคอนเทนเนอร์ และเส้นทางของผู้ใช้ที่สําคัญ (CUJ) และการตั้งค่าอื่นๆ จะอยู่ที่ด้านล่าง ซึ่งเป็นแนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำสำหรับการจัดวางเนื้อหา
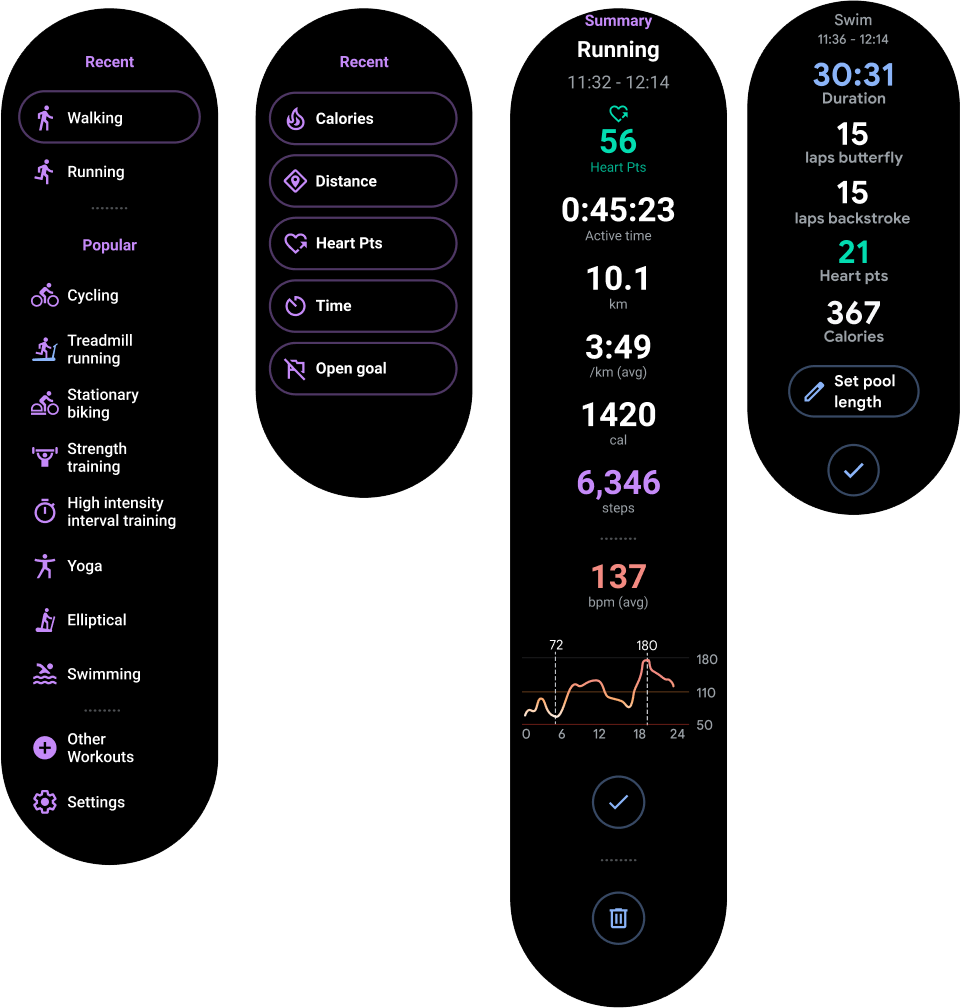
รูปที่ 2 ตัวอย่างเลย์เอาต์คอนเทนเนอร์แนวตั้ง
อย่าใช้ BoxInsetLayout ซึ่งต่างจากเลย์เอาต์แอปแบบหน้าจอเดียว แต่ให้ใช้ ConstraintLayout ใน NestedScrollView แทน
วางวิดเจ็ตที่เหมาะกับแอปของคุณมากที่สุดใน ConstraintLayout วิธีนี้ช่วยให้คุณใช้ประโยชน์จากพื้นที่ว่างด้านข้างของจอแสดงผลแบบวงกลมได้
รูปที่ 3 เนื้อหาใน ConstraintLayout ภายใน NestedScrollView
ตรวจสอบว่าเนื้อหาที่ด้านบนและด้านล่างของคอนเทนเนอร์แนวตั้งมีขนาดเล็กพอที่จะใส่ที่ด้านบนและด้านล่างของจอแสดงผลแบบวงกลมได้ ดังตัวอย่างในรูปที่ 3
หมายเหตุ:
หากเป็นไปได้ ให้เพิ่มตัวบ่งชี้การเลื่อนลงใน NestedScrollView โดยการตั้งค่า android:scrollbars="vertical" ใน XML วิธีนี้ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ทราบว่ามีเนื้อหาเพิ่มเติมให้รับชมและช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ทราบว่ากำลังดูเนื้อหาส่วนใดอยู่
ตัวเลือกอื่นๆ สำหรับเลย์เอาต์แอป
-
รายการ: แสดงชุดข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ด้วยวิดเจ็ต
WearableRecyclerViewที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับแพลตฟอร์มอุปกรณ์ที่สวมใส่ได้ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่สร้างรายการใน Wear OS - การเลื่อนแนวนอน: สำหรับกรณีการใช้งานที่มีหน้าจอพี่น้องหลายหน้าจอ ให้ใช้การปัดแนวนอน หากใช้การเลื่อนหน้าแนวนอน คุณต้องรองรับการปัดเพื่อปิดที่ขอบด้านซ้าย
- การเลื่อน 2 มิติ: สำหรับกรณีการใช้งานอย่างแผนที่ ผู้ใช้สามารถลากเพื่อเลื่อนไปยังทิศทางต่างๆ ได้ เปิดใช้การปัดเพื่อปิดหากกิจกรรมของคุณกินพื้นที่ทั้งหน้าจอ

