بعد از اینکه نحوه برخورد با اشکال مختلف ساعت را فهمیدید، تصمیم بگیرید که از کدام سطح استفاده کنید.
طرح بندی برنامه های رایج شامل موارد زیر است:
- تک صفحه (ساده ترین): عناصر رابط کاربری محدود به مواردی هستند که در یک زمان بدون پیمایش قابل مشاهده است.
- ظرف عمودی (متداول ترین): محتوا فراتر از قسمت قابل مشاهده صفحه وجود دارد و با پیمایش قابل دسترسی است.
- گزینههای دیگر: فهرستها، صفحهبندی، یا حرکت دوبعدی.
این انواع چیدمان در بخش های بعدی توضیح داده شده است. در صورت نیاز به چند صفحه نمایش می توانید از ترکیبی از انواع طرح بندی استفاده کنید.
توجه: برای فعالیت خود، از یک ComponentActivity یا اگر از Fragment استفاده می کنید، از یک FragmentActivity ارث ببرید. سایر انواع فعالیتها از عناصر رابط کاربری مخصوص موبایل استفاده میکنند که برای Wear OS به آنها نیاز ندارید.
تک صفحه نمایش
کاربر تمام عناصر را در یک صفحه بدون پیمایش می بیند. این به این معنی است که شما می توانید فقط تعداد کمی از عناصر را وارد کنید.

شکل 1. نمونه ای از طرح بندی تک صفحه.
صفحههای منفرد با BoxInsetLayout در ترکیب با ConstraintLayout به خوبی کار میکنند تا عناصر شما را مرتب کنند.
ظرف عمودی
ظرف عمودی رایج ترین نوع طرح بندی برنامه است. برخی از محتواها روی صفحه نمایش قابل مشاهده نیستند، اما با پیمایش قابل دسترسی هستند.
شکل 2 چندین طرح بندی کامل اپلیکیشن را نشان می دهد که در آن تنها بخشی از محتوا را می توان در صفحه دایره ای ساعت مشاهده کرد. در این مثالها، محتوای اصلی در قسمت بالای کانتینر است و سایر سفرهای کاربر حیاتی (CUJ) و تنظیمات در پایین هستند. این بهترین روش برای چیدمان محتوا است.
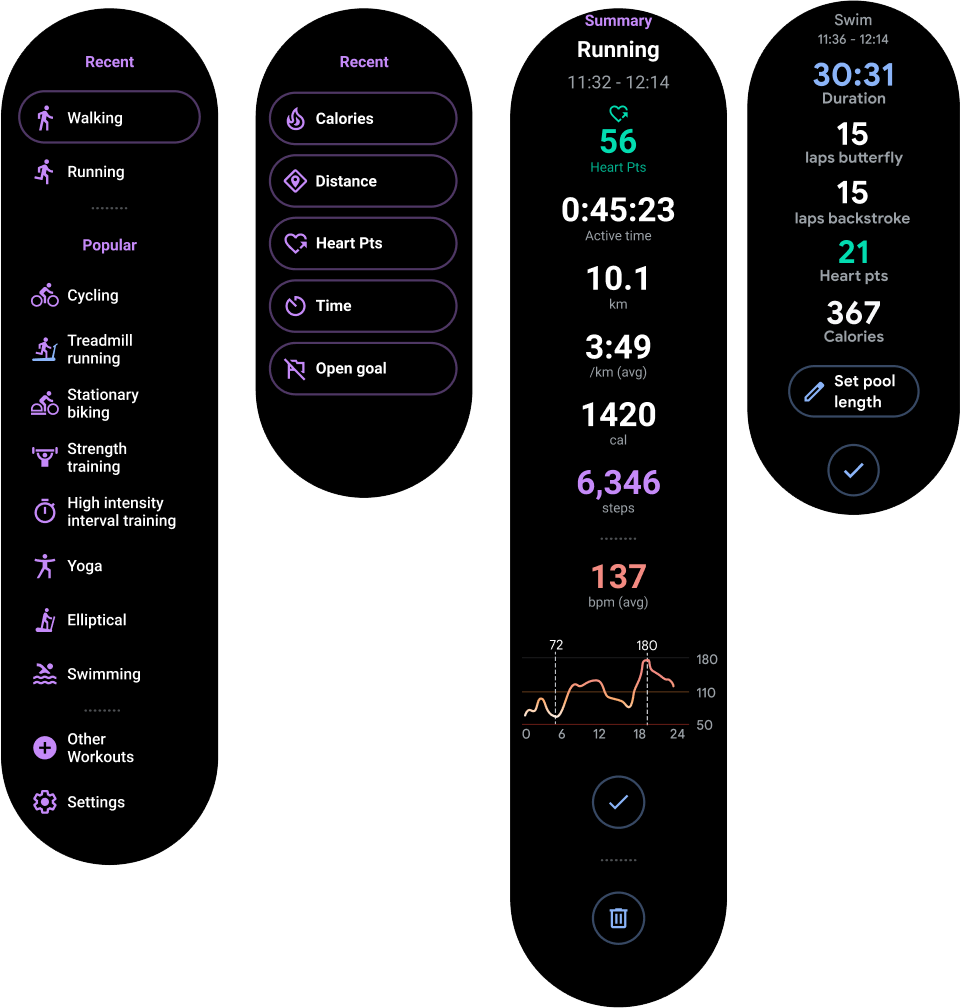
شکل 2. نمونه هایی از طرح بندی ظروف عمودی.
برخلاف طرحبندی برنامههای تک صفحه، از BoxInsetLayout استفاده نکنید. در عوض، از یک ConstraintLayout در داخل NestedScrollView استفاده کنید. در داخل ConstraintLayout ، ویجتهایی را قرار دهید که بیشترین حس را برای برنامه شما دارند. این به شما امکان می دهد از فضای اضافی در کناره های یک صفحه نمایش دایره ای استفاده کنید.
شکل 3. محتوا در یک ConstraintLayout در داخل NestedScrollView .
اطمینان حاصل کنید که محتوای بالا و پایین ظرف عمودی شما به اندازه کافی کوچک است که در بالا و پایین یک نمایشگر دایره ای قرار گیرد، مانند مثال در شکل 3.
توجه: در صورت امکان، با تنظیم android:scrollbars="vertical" در XML، یک نشانگر اسکرول به NestedScrollView خود اضافه کنید. این به کاربران کمک میکند بفهمند که محتوای بیشتری در دسترس است و به آنها کمک میکند ببینند در رابطه با همه محتوا کجا هستند.
گزینه های دیگر برای طرح بندی برنامه ها
- فهرستها : مجموعههای بزرگی از دادهها را با ویجت
WearableRecyclerViewبهینهسازی شده برای سطوح پوشیدنی نمایش میدهد. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به ایجاد لیست در Wear OS مراجعه کنید. - صفحهبندی افقی : برای موارد استفاده با صفحهنمایش خواهر و برادر متعدد، از کش رفتن افقی استفاده کنید. اگر از صفحهبندی افقی استفاده میکنید، باید از Swipe to Dimiss برای لبه چپ پشتیبانی کنید.
- پاننگ دو بعدی : برای موارد استفاده مانند نقشه ها، کاربران می توانند برای حرکت در جهات مختلف بکشند . اگر فعالیت شما کل صفحه را اشغال می کند ، تند کشیدن برای رد کردن را فعال کنید.


