內容供應器可協助應用程式管理自行儲存資料或由其他應用程式儲存的資料存取權,並提供與其他應用程式共用資料的方式。這些 API 能封裝資料,並提供定義資料安全性的機制。內容供應器是標準介面,可將某項程序中的資料與在其他程序中執行的程式碼連結在一起。
實作內容供應器有許多好處。最重要的是,您可以設定內容供應器,讓其他應用程式安全地存取及修改應用程式資料,如圖 1 所示。
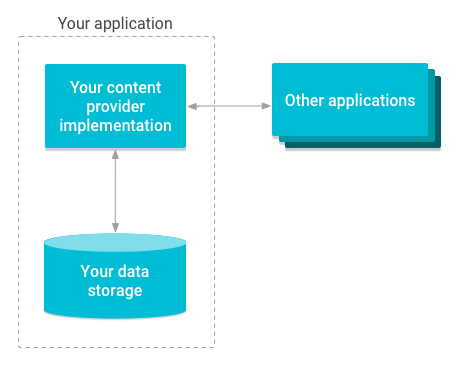
圖 1 內容供應器管理儲存空間存取權的總覽圖表。
如果您打算分享資料,請使用內容供應器。如果您不打算共用資料,可以不使用資料,但您可以選擇這樣做,因為它們提供抽象化機制,可讓您修改應用程式資料儲存空間實作,而不影響其他需要存取您的資料的應用程式。
在這種情況下,只有內容供應器會受到影響,不影響存取該內容的應用程式。例如您可以更換 SQLite 資料庫以進行替代儲存空間,如圖 2 所示。
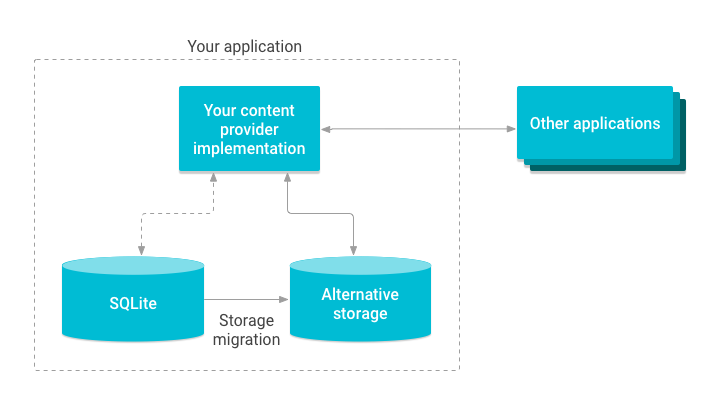
圖 2. 插圖:遷移內容供應器儲存空間。
許多其他類別依賴 ContentProvider 類別:
如果您使用上述任一類別,就必須在應用程式中實作內容供應器。使用同步轉換介面架構時,您也可以建立虛設常式內容供應器做為替代方案。詳情請參閱「建立虛設常式內容供應器」。此外,在下列情況下,您需要自己的內容供應器:
- 在應用程式中實作自訂搜尋建議。
- 向小工具公開應用程式資料。
- 從您的應用程式複製複雜的資料或檔案,並貼到其他應用程式。
Android 架構包含管理音訊、影片、圖片和個人聯絡資訊等資料的內容供應器。您可以在 android.provider
套件的參考說明文件中查看其中幾項設定。但在某些情況下,所有 Android 應用程式都可以存取這些供應器。
內容供應器可用來管理各種資料儲存來源的存取權,包括結構化資料 (例如 SQLite 關聯資料庫) 或非結構化資料 (例如圖片檔)。如要進一步瞭解 Android 可用的儲存空間類型,請參閱「資料與檔案儲存空間總覽」和「 設計資料儲存空間」。
內容供應器的優點
內容供應器提供精細的控制選項,讓你控管資料存取權限。您可以選擇僅存取應用程式中的內容供應器、授予大量存取其他應用程式的資料權限,或是設定不同的讀取和寫入資料權限。如要進一步瞭解如何安全地使用內容供應器,請參閱 資料儲存的安全性提示和 內容供應器權限。
您可以使用內容供應器來簡化在應用程式中存取不同資料來源的詳細資料。例如,您的應用程式可能會將結構化記錄儲存在 SQLite 資料庫,以及影片和音訊檔案。您可以使用內容供應器存取所有資料。
此外,CursorLoader 物件仰賴內容供應器執行非同步查詢,然後將結果傳回應用程式的 UI 層。如要進一步瞭解如何使用 CursorLoader 在背景載入資料,請參閱「
載入器」。
以下主題會進一步說明內容供應者:
- 內容供應器基礎知識
- 如何使用現有的內容供應器存取及更新資料。
- 建立內容供應器
- 如何設計及實作自己的內容供應器。
- 日曆提供者總覽
- 如何存取 Android 平台中的日曆供應程式。
- 聯絡人提供者
- 如何存取 Android 平台的聯絡人供應程式。
