Sobre la base de las APIs de Descubrimiento de dispositivos y Conexión segura, la La API de Sessions proporciona una poderosa abstracción para compilar apps multidispositivo fluidas experiencias. Una sesión representa una experiencia del usuario de la aplicación que se puede se transfieren y comparten entre dispositivos.
La API de Sessions también se basa en la noción de identidad experiencias representadas por los casos de uso de transferencia y uso compartido de sesiones respectivamente. En el siguiente diagrama, se ilustran las sesiones en un nivel alto:
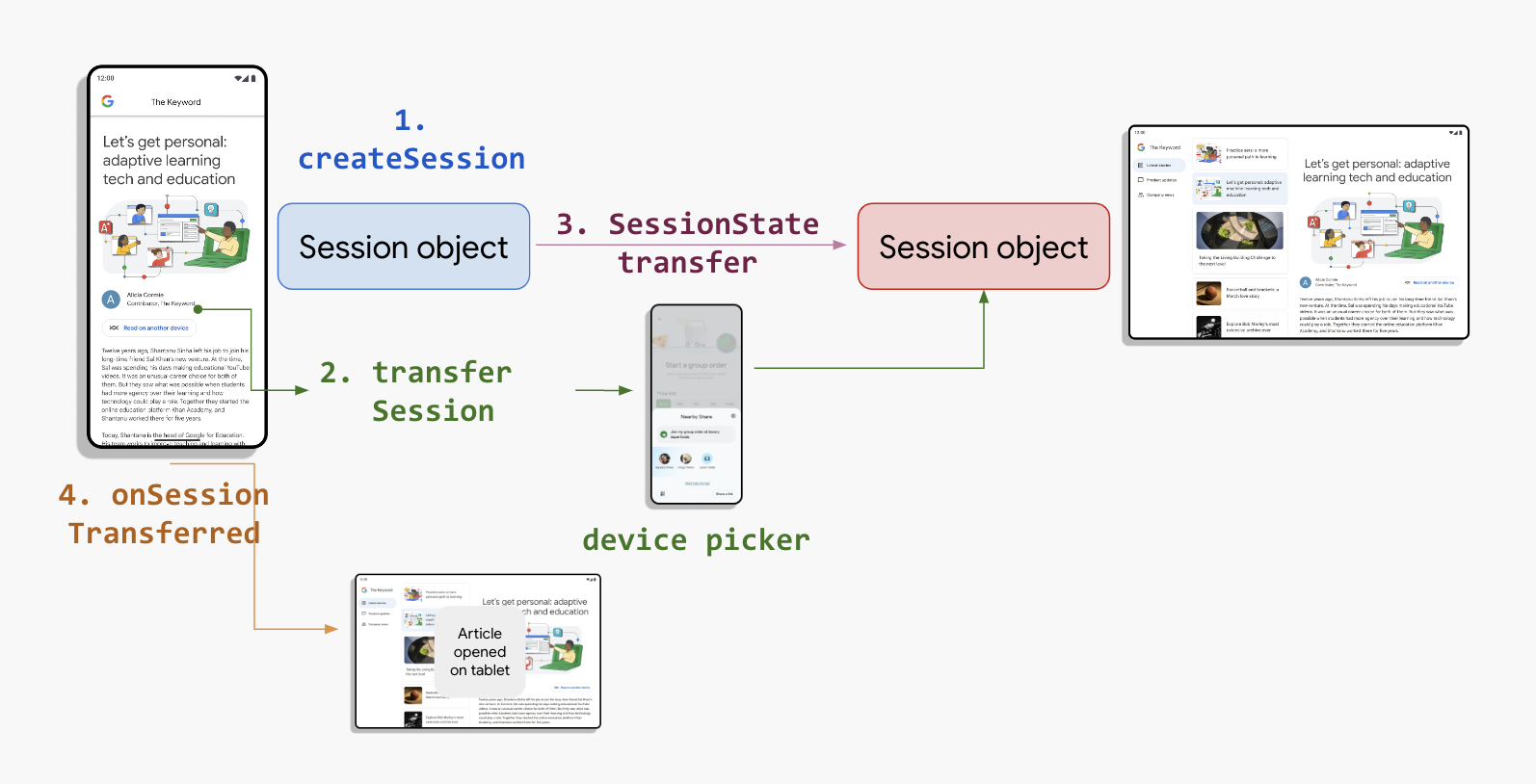
Crea y transfiere una sesión
La API de Sessions distingue entre el dispositivo de origen y el receptor. El dispositivo de origen crea la sesión y busca un que puede manejar la sesión. El usuario del dispositivo de origen selecciona un dispositivo de la lista proporcionada por el diálogo del sistema. Una vez que el usuario selecciona el dispositivo receptor, la sesión de origen se transfiere y se quita desde el dispositivo de origen.
Para transferir la sesión, primero debes crearla con los siguientes comandos: parámetros:
- Una etiqueta de sesión de aplicación, un identificador que te permite diferenciar entre varias sesiones en tu app.
Luego, inicia la transferencia con los siguientes parámetros:
- Un objeto
DeviceFilterpara filtrar los dispositivos que pueden controlar la sesión - Un objeto de devolución de llamada que implementa
OriginatingSessionStateCallback
En el dispositivo de origen, crea una sesión con el siguiente ejemplo:
Kotlin
private val HELLO_WORLD_TRANSFER_ACTION = "hello_world_transfer" private lateinit var originatingSession: OriginatingSession private lateinit var sessions: Sessions override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) sessions = Sessions.create(context = this) } suspend fun transferSession() { val sessionId = sessions.createSession( ApplicationSessionTag("hello_world_transfer"), ) originatingSession = sessions.transferSession( sessionId, StartComponentRequest.Builder() .setAction(HELLO_WORLD_TRANSFER_ACTION) .setReason("Transfer reason here") .build(), emptyList(), HelloWorldTransferSessionStateCallback() ) }
Java
private static final String HELLO_WORLD_TRANSFER_ACTION = "hello_world_transfer"; private OriginatingSession originatingSession; private Sessions sessions; @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); sessions = Sessions.create(/* context= */ this); } public void transferSession() { SessionId sessionId = sessions.createSession(new ApplicationSessionTag("hello_world_transfer")); ListenableFuture<OriginatingSession> originatingSessionFuture = sessions.transferSessionFuture( sessionId, new StartComponentRequest.Builder() .setAction(HELLO_WORLD_TRANSFER_ACTION) .setReason("Transfer reason here") .build(), Collections.emptyList(), new HelloWorldTransferSessionStateCallback()); Futures.addCallback( originatingSessionFuture, new FutureCallback<>() { @Override public void onSuccess(OriginatingSession result) { // Do nothing, handled in HelloWorldTransferSessionStateCallback originatingSession = result; } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { Log.d(TAG, "onFailure called for transferSessionFuture", t); } }, mainExecutor); }
A continuación, define la devolución de llamada de la sesión en el dispositivo de origen:
Kotlin
private inner class HelloWorldTransferSessionStateCallback : OriginatingSessionStateCallback { override fun onConnected(sessionId: SessionId) { val startupRemoteConnection = originatingSession.getStartupRemoteConnection() lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed { startupRemoteConnection.send("hello, world".toByteArray(UTF_8)) startupRemoteConnection.registerReceiver( object : SessionConnectionReceiver { override fun onMessageReceived(participant: SessionParticipant, payload: ByteArray) { val ok = payload.contentEquals("ok".toByteArray(UTF_8)) Log.d(TAG, "Session transfer initialized. ok=$ok") } } ) } } override fun onSessionTransferred(sessionId: SessionId) { Log.d(TAG, "Transfer done.") } override fun onTransferFailure(sessionId: SessionId, exception: SessionException) { // Handle error } }
Java
private class HelloWorldTransferSessionStateCallback implements OriginatingSessionStateCallback { @Override public void onConnected(SessionId sessionId) { SessionRemoteConnection startupRemoteConnection = originatingSession.getStartupRemoteConnection(); Futures.addCallback( startupRemoteConnection.sendFuture("hello, world".getBytes()), new FutureCallback<>() { @Override public void onSuccess(Void result) { Log.d(TAG, "Successfully sent initialization message"); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { Log.d(TAG, "Failed to send initialization message", t); } }, mainExecutor); } @Override public void onSessionTransferred(SessionId sessionId) { Log.d(TAG, "Transfer done."); } @Override public void onTransferFailure(SessionId sessionId, SessionException exception) { // Handle error } }
Una vez que se inicia la transferencia de la sesión, el dispositivo receptor recibe una devolución de llamada
en el método onNewIntent(intent: Intent). Los datos de la intent contienen todo
necesario para transferir la sesión.
Para completar la transferencia en el dispositivo receptor, haz lo siguiente:
Kotlin
private lateinit var sessions: Sessions override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) sessions = Sessions.create(context = this) } override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent) { super.onNewIntent(intent) lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed { val receivingSession = sessions.getReceivingSession(intent, HelloWorldReceivingSessionStateCallback()) // Get info from receiving device and init. val startupRemoteConnection = receivingSession.getStartupRemoteConnection() startupRemoteConnection.registerReceiver( object : SessionConnectionReceiver { override fun onMessageReceived(participant: SessionParticipant, payload: ByteArray) { lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed { val transferInfo = String(payload) startupRemoteConnection.send("ok".toByteArray(UTF_8)) // Complete transfer. Log.d(TAG, "Transfer info: " + transferInfo) receivingSession.onComplete() } } } ) } } private inner class HelloWorldReceivingSessionStateCallback : ReceivingSessionStateCallback { override fun onTransferFailure(sessionId: SessionId, exception: SessionException) { // Handle error } }
Java
private Sessions sessions; @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); sessions = Sessions.create(/* context= */ this); } @Override public void onNewIntent(Intent intent) { super.onNewIntent(intent); ListenableFuture<ReceivingSession> receivingSessionFuture = sessions.getReceivingSessionFuture(intent, new HelloWorldReceivingSessionStateCallback()); ListenableFuture<Void> registerReceiverFuture = Futures.transform( receivingSessionFuture, receivingSession -> { SessionRemoteConnection startupRemoteConnection = receivingSession.getStartupRemoteConnection(); SessionConnectionReceiver receiver = (participant, payload) -> { Log.d( TAG, "Successfully received initialization message of size: " + payload.length); applicationInitialization(receivingSession, payload); }; startupRemoteConnection.registerReceiver(receiver); return null; }, mainExecutor); Futures.addCallback( registerReceiverFuture, new FutureCallback<Void>() { @Override public void onSuccess(Void unused) { Log.d(TAG, "Connection receiver registerd successfully"); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { Log.w(TAG, "Failed to register connection receiver", t); } }, mainExecutor); } private void applicationInitialization(ReceivingSession receivingSession, byte[] initMessage) { ListenableFuture<SessionId> disconnectFuture = Futures.transform( receivingSession.onCompleteFuture(), sessionId -> { Log.d(TAG, "Succeeded to complete receive transfer for: " + sessionId); return sessionId; }, mainExecutor); Futures.addCallback( disconnectFuture, new FutureCallback<SessionId>() { @Override public void onSuccess(SessionId result) { Log.d(TAG, "Succeeded to remove the old session: " + result); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { Log.d(TAG, "Failed to remove the old session, which is now orphaned", t); } }, mainExecutor); } private static class HelloWorldReceivingSessionStateCallback implements ReceivingSessionStateCallback { @Override public void onTransferFailure(SessionId sessionId, SessionException exception) { // Handle error } }
Ahora el dispositivo receptor puede continuar con la experiencia del usuario.
Comparte una sesión
Al compartir una sesión, puedes invitar a otras personas cercanas a participar en un grupo. experiencia, por ejemplo,
- Comparte una ubicación en el mapa como pasajero directamente con el automóvil de tu amigo.
- Comparte tu ruta dominical en bicicleta con las personas con las que andas en bici.
- Recoge artículos para un pedido de comida grupal sin tener que pasar el teléfono.
- Vota en grupo por el próximo programa de TV para mirarlo juntos.
Cuando un usuario elige compartir una sesión con otro dispositivo, el dispositivo de origen El dispositivo busca y presenta los dispositivos que pueden unirse a la sesión y el el usuario selecciona los dispositivos receptores. La aplicación solicita al usuario dispositivo receptor para unirse a la sesión desde el dispositivo de origen. Un receptor al dispositivo se le otorga una sesión secundaria para que interactúe con la sesión en el dispositivo de origen. Las aplicaciones también pueden agregar participantes adicionales a sus sesión compartida en curso.
El proceso para compartir una sesión es similar al de transferir una sesión,
pero, en lugar de llamar a transferSession, llama a shareSession. El otro
las diferencias
en los métodos de devolución de llamada del estado de la sesión.
Kotlin
// Originating side. private val HELLO_WORLD_SHARE_ACTION = "hello_world_share" private var activePrimarySession: PrimarySession? = null private lateinit var sessions: Sessions override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) sessions = Sessions.create(context = this) } suspend fun shareSession() { val sessionId = sessions.createSession(ApplicationSessionTag("hello_world_share")) activePrimarySession = sessions.shareSession( sessionId, StartComponentRequest.Builder() .setAction(HELLO_WORLD_SHARE_ACTION) .setReason("Share reason here") .build(), emptyList(), HelloWorldShareSessionStateCallback(), ) } private inner class HelloWorldShareSessionStateCallback : PrimarySessionStateCallback { override fun onShareInitiated(sessionId: SessionId, numPotentialParticipants: Int) { // Custom logic here for when n devices can potentially join. // e.g. if there were 0, cancel/error if desired, // if non-0 maybe spin until numPotentialParticipants join etc. } override fun onParticipantJoined(sessionId: SessionId, participant: SessionParticipant) { // Custom join logic here lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed { // Example logic: send only to the participant who just joined. val connection = checkNotNull(activePrimarySession).getSecondaryRemoteConnectionForParticipant(participant) connection.send("Initing hello, world.".toByteArray(UTF_8)) connection.registerReceiver( object : SessionConnectionReceiver { override fun onMessageReceived(participant: SessionParticipant, payload: ByteArray) { val ok = payload.contentEquals("ok".toByteArray(UTF_8)) Log.d(TAG, "Session share initialized. ok=$ok") // Example logic: broadcast to all participants, including the one // that just joined. lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed { checkNotNull(activePrimarySession) .broadcastToSecondaries("hello, all.".toByteArray(UTF_8)) } } } ) } } override fun onParticipantDeparted(sessionId: SessionId, participant: SessionParticipant) { // Custom leave logic here. } override fun onPrimarySessionCleanup(sessionId: SessionId) { // Custom cleanup logic here. activePrimarySession = null } override fun onShareFailureWithParticipant( sessionId: SessionId, exception: SessionException, participant: SessionParticipant ) { // Handle error } }
Java
// Originating side private static final String HELLO_WORLD_SHARE_ACTION = "hello_world_share"; @Nullable private PrimarySession activePrimarySession = null; private Sessions sessions; @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); sessions = Sessions.create(/* context= */ this); } private void shareSession() { SessionId sessionId = sessions.createSession(new ApplicationSessionTag("hello_world_share")); ListenableFuture<PrimarySession> shareSessionFuture = sessions.shareSessionFuture( sessionId, new StartComponentRequest.Builder() .setAction(HELLO_WORLD_SHARE_ACTION) .setReason("Share reason here") .build(), Collections.emptyList(), new HelloWorldShareSessionStateCallback()); Futures.addCallback( shareSessionFuture, new FutureCallback<PrimarySession>() { @Override public void onSuccess(PrimarySession primarySession) { activePrimarySession = primarySession; } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { Log.d(TAG, "Failed to share session", t); } }, mainExecutor); } private class HelloWorldShareSessionStateCallback implements PrimarySessionStateCallback { @Override public void onShareInitiated(SessionId sessionId, int numPotentialParticipants) { // Custom logic here for when n devices can potentially join. // e.g. if there were 0, cancel/error if desired, // if non-0 maybe spin until numPotentialParticipants join etc. } @Override public void onParticipantJoined(SessionId sessionId, SessionParticipant participant) { PrimarySession joinedSession = activePrimarySession; if (joinedSession == null) { return; } SessionRemoteConnection connection = joinedSession.getSecondaryRemoteConnectionForParticipant(participant); Futures.addCallback( connection.sendFuture("Initiating hello, world.".getBytes()), new FutureCallback<Void>() { @Override public void onSuccess(Void result) { // Send successful. } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { // Failed to send. } }, mainExecutor); connection.registerReceiver( new SessionConnectionReceiver() { @Override public void onMessageReceived(SessionParticipant participant, byte[] payload) { boolean ok = new String(payload, UTF_8).equals("ok"); Log.d(TAG, "Session share initialized. ok=" + ok); // Example logic: broadcast to all participants, including the one // that just joined. Futures.addCallback( joinedSession.broadcastToSecondariesFuture("hello, all.".getBytes()), new FutureCallback<Void>() { @Override public void onSuccess(Void result) { // Broadcast successful. } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { // Failed to broadcast hello world. } }, mainExecutor); } }); } @Override public void onParticipantDeparted(SessionId sessionId, SessionParticipant participant) { // Custom leave logic here. } @Override public void onPrimarySessionCleanup(SessionId sessionId) { // Custom cleanup logic here. activePrimarySession = null; } @Override public void onShareFailureWithParticipant( SessionId sessionId, SessionException exception, SessionParticipant participant) { // Custom error handling logic here. } }
En el lado receptor:
Kotlin
// Receiving side. override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent) { super.onNewIntent(intent) lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed { val secondarySession = sessions.getSecondarySession(intent, HelloWorldSecondaryShareSessionStateCallback()) val remoteConnection = secondarySession.getDefaultRemoteConnection() remoteConnection.registerReceiver( object : SessionConnectionReceiver { override fun onMessageReceived(participant: SessionParticipant, payload: ByteArray) { Log.d(TAG, "Payload received: ${String(payload)}") } } ) } } private inner class HelloWorldSecondaryShareSessionStateCallback : SecondarySessionStateCallback { override fun onSecondarySessionCleanup(sessionId: SessionId) { // Custom cleanup logic here. } }
Java
// Receiving side. @Override public void onNewIntent(Intent intent) { super.onNewIntent(intent); sessions = Sessions.create(this); ListenableFuture<SecondarySession> secondarySessionFuture = sessions.getSecondarySessionFuture( intent, new HelloWorldSecondaryShareSessionStateCallback()); Futures.addCallback( secondarySessionFuture, new FutureCallback<SecondarySession>() { @Override public void onSuccess(SecondarySession secondarySession) { SessionRemoteConnection remoteConnection = secondarySession.getDefaultRemoteConnection(); remoteConnection.registerReceiver( new SessionConnectionReceiver() { @Override public void onMessageReceived(SessionParticipant participant, byte[] payload) { Log.d(TAG, "Payload received: " + new String(payload, UTF_8)); } }); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { // Handle error. } }, mainExecutor); } private static class HelloWorldSecondaryShareSessionStateCallback implements SecondarySessionStateCallback { @Override public void onSecondarySessionCleanup(SessionId sessionId) { // Custom cleanup logic here. } }
