مؤلفه Dialog پیامهای پاپآپ را نمایش میدهد یا ورودی کاربر را در لایهای بالای محتوای اصلی برنامه درخواست میکند. این یک تجربه رابط کاربری وقفهای ایجاد میکند تا توجه کاربر را به خود جلب کند.
از جمله موارد استفاده برای دیالوگ موارد زیر است:
- تأیید عملکرد کاربر، مانند هنگام حذف یک فایل.
- درخواست ورودی کاربر، مانند برنامه فهرست کارها.
- ارائه فهرستی از گزینهها برای انتخاب کاربر، مانند انتخاب کشور در تنظیمات نمایه.
این موضوع پیاده سازی های زیر را ارائه می دهد:
سازگاری نسخه
این پیاده سازی مستلزم آن است که minSDK پروژه شما روی سطح API 21 یا بالاتر تنظیم شود.
وابستگی ها
یک گفتگوی هشدار ایجاد کنید
AlertDialog composable یک API مناسب برای ایجاد یک گفتگو با موضوع طراحی مواد ارائه می دهد. مثال زیر دو دکمه را در یک گفتگوی هشدار اجرا می کند، یکی که گفتگو را رد می کند و دیگری که درخواست آن را تایید می کند:
این پیاده سازی مستلزم یک composable والد است که آرگومان های قابل ترکیب را به این ترتیب به فرزند ارسال می کند:
نتایج
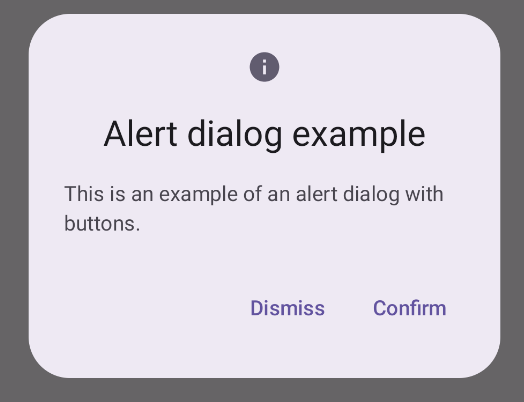
نکات کلیدی
AlertDialog دارای پارامترهای خاصی برای مدیریت عناصر خاصی از گفتگو است. از جمله موارد زیر است:
-
title: متنی که در بالای دیالوگ ظاهر می شود. -
text: متنی که در مرکز گفتگو ظاهر می شود. -
icon: گرافیکی که در بالای دیالوگ ظاهر می شود. -
onDismissRequest: تابعی که وقتی کاربر دیالوگ را رد می کند، مثلاً با ضربه زدن در خارج از آن، فراخوانی می شود. -
dismissButton: قابل ترکیب که به عنوان دکمه رد کردن عمل می کند. confirmButton: قابل ترکیب که به عنوان دکمه تایید عمل می کند.هنگامی که کاربر روی هر یک از دکمه ها کلیک می کند، گفتگو بسته می شود. وقتی کاربر تأیید را کلیک می کند، تابعی را فراخوانی می کند که تأیید را نیز کنترل می کند. در این مثال، آن توابع
onDismissRequest()وonConfirmRequest()هستند.در مواردی که گفتگوی شما به مجموعه پیچیده تری از دکمه ها نیاز دارد، ممکن است از استفاده از
Dialogcomposable و پر کردن آن به شیوه ای آزادتر بهره مند شوید.
یک دیالوگ ایجاد کنید
Dialog یک ترکیب اولیه است که هیچ گونه استایل یا جایگاه های از پیش تعریف شده ای برای محتوا ارائه نمی دهد. این یک ظرف ساده است که باید آن را با ظرفی مانند Card پر کنید. در زیر برخی از پارامترهای کلیدی یک دیالوگ آمده است:
-
onDismissRequest: زمانی که کاربر کادر گفتگو را می بندد، لامبدا فراخوانی می شود. -
properties: نمونه ای ازDialogPropertiesکه فضای بیشتری را برای سفارشی سازی فراهم می کند.
یک گفتگوی اساسی ایجاد کنید
مثال زیر یک پیاده سازی اساسی از Dialog composable است. توجه داشته باشید که از یک Card به عنوان ظرف ثانویه استفاده می کند. بدون Card ، جزء Text به تنهایی بالای محتوای اصلی برنامه ظاهر میشود.
نتیجه
توجه داشته باشید که وقتی کادر گفتگو باز است، محتوای اصلی برنامه در زیر آن تیره و خاکستری به نظر می رسد:

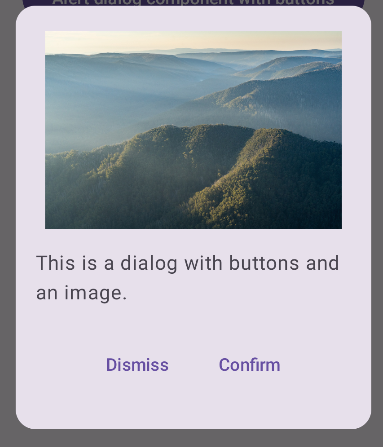
یک گفتگوی پیشرفته ایجاد کنید
زیر یک پیاده سازی پیشرفته تر از Dialog composable است. در این مورد، کامپوننت به صورت دستی یک رابط مشابه با مثال قبلی AlertDialog پیاده سازی می کند.
نتیجه
مجموعه هایی که حاوی این راهنما هستند
این راهنما بخشی از مجموعههای راهنمای Quick Guide است که اهداف توسعه Android گستردهتری را پوشش میدهد:
نمایش متن

درخواست ورودی کاربر




