در طراحی متریال، داربست یک ساختار اساسی است که یک پلت فرم استاندارد شده برای رابط های کاربری پیچیده فراهم می کند. بخشهای مختلف رابط کاربری، مانند نوارهای برنامه و دکمههای عمل شناور را در کنار هم نگه میدارد و به برنامهها ظاهر و احساسی منسجم میدهد.
سازگاری نسخه
این پیاده سازی مستلزم آن است که minSDK پروژه شما روی سطح API 21 یا بالاتر تنظیم شود.
وابستگی ها
یک داربست ایجاد کنید
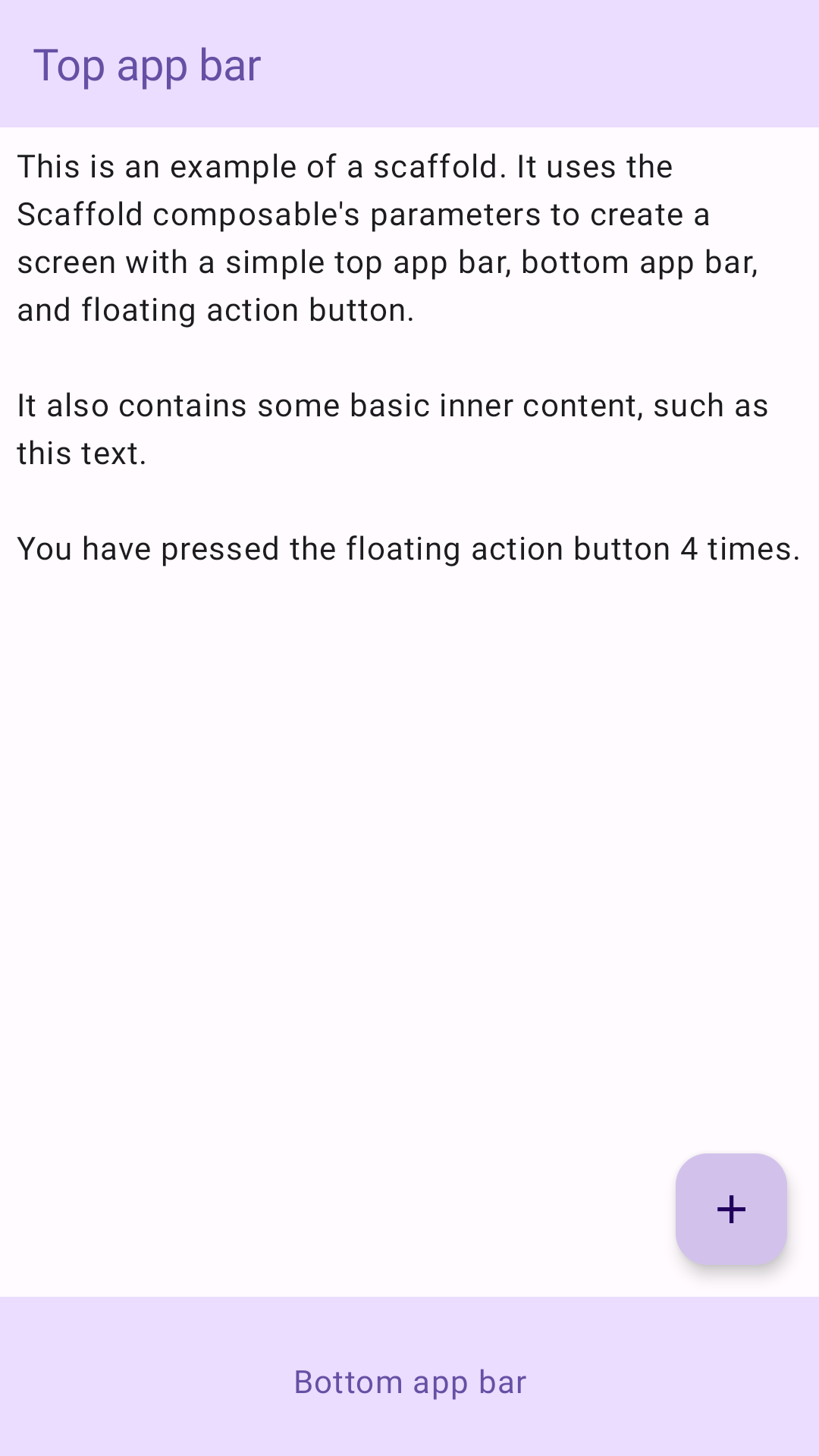
مثال زیر یک مثال کامل از نحوه پیاده سازی Scaffold را ارائه می دهد. این شامل یک نوار برنامه بالا، نوار برنامه پایین و یک دکمه عمل شناور است که با وضعیت داخلی Scaffold تعامل دارد.
نتایج
نکات کلیدی
Scaffold composable یک API ساده ارائه می دهد که می توانید از آن برای جمع آوری سریع ساختار برنامه خود مطابق با دستورالعمل های طراحی متریال استفاده کنید. Scaffold چندین ترکیب پذیر را به عنوان پارامتر می پذیرد. از جمله موارد زیر است:
-
topBar: نوار برنامه در بالای صفحه. -
bottomBar: نوار برنامه در پایین صفحه. -
floatingActionButton: دکمهای که روی گوشه سمت راست پایین صفحه قرار میگیرد و میتوانید از آن برای نمایش اقدامات کلیدی استفاده کنید.
برای مثالهای دقیقتر در مورد نحوه اجرای هر دو نوار برنامه بالا و پایین، به صفحه نوار برنامه مراجعه کنید.
همچنین میتوانید محتوای Scaffold را همانطور که به ظروف دیگر منتقل میکنید ارسال کنید. یک مقدار innerPadding را به content lambda ارسال میکند که میتوانید از آن در composableهای فرزند استفاده کنید.
مجموعه هایی که حاوی این راهنما هستند
این راهنما بخشی از مجموعههای راهنمای Quick Guide است که اهداف توسعه Android گستردهتری را پوشش میدهد:
یک داربست صفحه اصلی ایجاد کنید




