Android 16 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた新しい機能と API が導入されました。以下のセクションでは、これらの機能の概要を説明し、関連する API を使い始めるうえで役立つ情報を提供します。
新しい API、変更された API、削除された API の一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。新しい API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。新しい API は、見つけやすいようにハイライト表示されています。また、プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する可能性がある領域も確認する必要があります。詳細については、次のページをご覧ください。
コア機能
Android には、Android システムのコア機能を拡張する新しい API が含まれています。
2025 年に 2 つの Android API をリリース
- This preview is for the next major release of Android with a planned launch in Q2 of 2025. This release is similar to all of our API releases in the past, where we can have planned behavior changes that are often tied to a targetSdkVersion.
- We're planning the major release a quarter earlier (Q2 rather than Q3 in prior years) to better align with the schedule of device launches across our ecosystem, so more devices can get the major release of Android sooner. With the major release coming in Q2, you'll need to do your annual compatibility testing a few months earlier than in previous years to make sure your apps are ready.
- We plan to have another release in Q4 of 2025 which also will include new developer APIs. The Q2 major release will be the only release in 2025 to include planned behavior changes that could affect apps.
In addition to new developer APIs, the Q4 minor release will pick up feature updates, optimizations, and bug fixes; it will not include any app-impacting behavior changes.
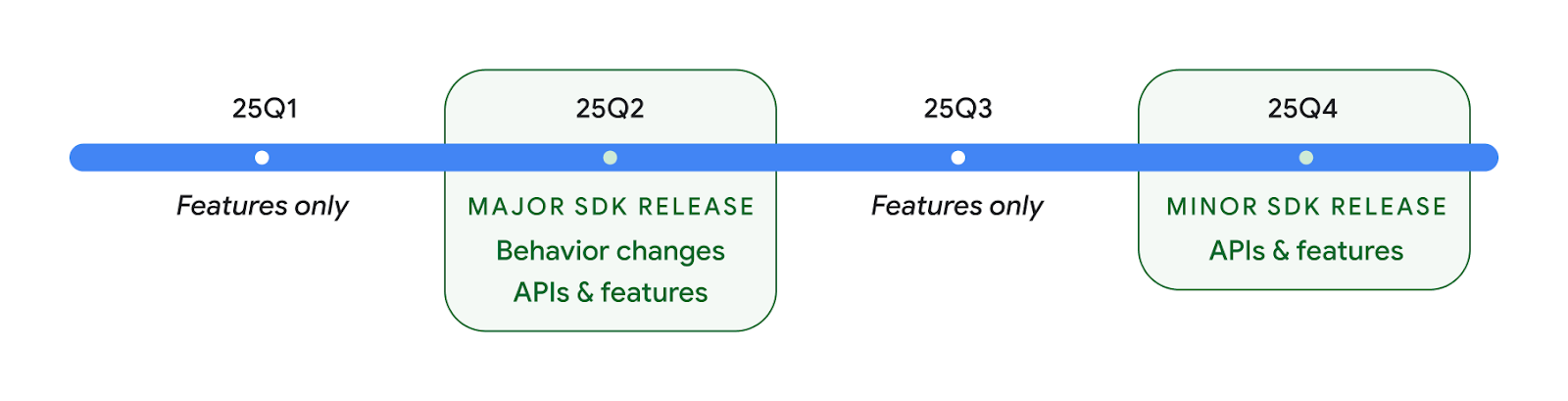
We'll continue to have quarterly Android releases. The Q1 and Q3 updates in-between the API releases will provide incremental updates to help ensure continuous quality. We're actively working with our device partners to bring the Q2 release to as many devices as possible.
Using new APIs with major and minor releases
Guarding a code block with a check for API level is done today using
the SDK_INT constant with
VERSION_CODES. This will continue
to be supported for major Android releases.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
The new SDK_INT_FULL
constant can be used for API checks against both major and minor versions with
the new VERSION_CODES_FULL
enumeration.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
You can also use the
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
method to get just the minor SDK version.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
These APIs have not yet been finalized and are subject to change, so please send us feedback if you have any concerns.
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16 では、アプリ デベロッパーとユーザーがニーズに合わせてデバイスを構成するための制御と柔軟性が向上しています。
進行状況を中心とした通知
Android 16 では、ユーザーが開始した、最初から最後までのジャーニーをシームレスに追跡できるように、進行状況重視の通知が導入されています。
Notification.ProgressStyle は、進行状況重視の通知を作成できる新しい通知スタイルです。主なユースケースには、乗車シェアリング、配達、ナビゲーションなどがあります。Notification.ProgressStyle クラス内で、ポイントとセグメントを使用して、ユーザー ジャーニー内の状態とマイルストーンを指定できます。
詳細については、進行状況重視の通知のドキュメント ページをご覧ください。
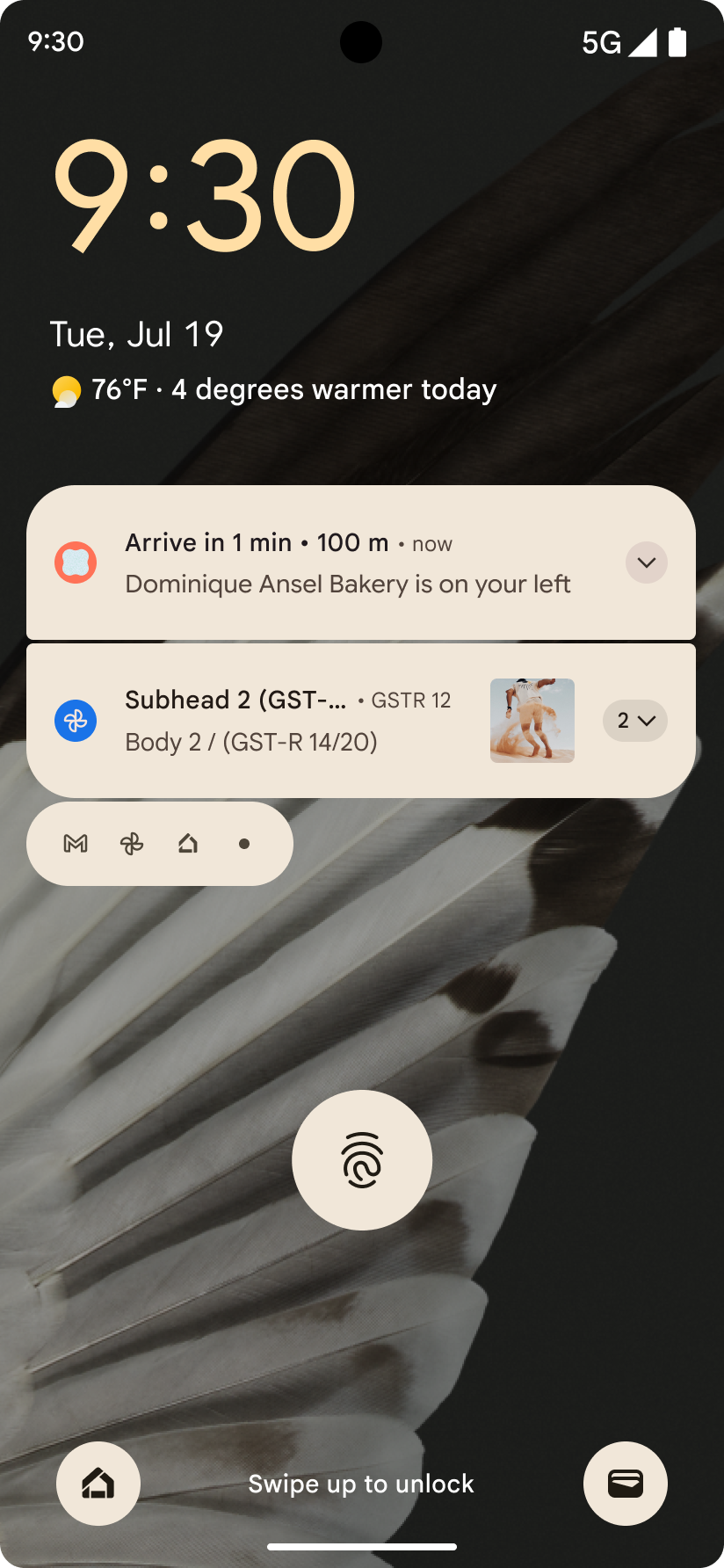
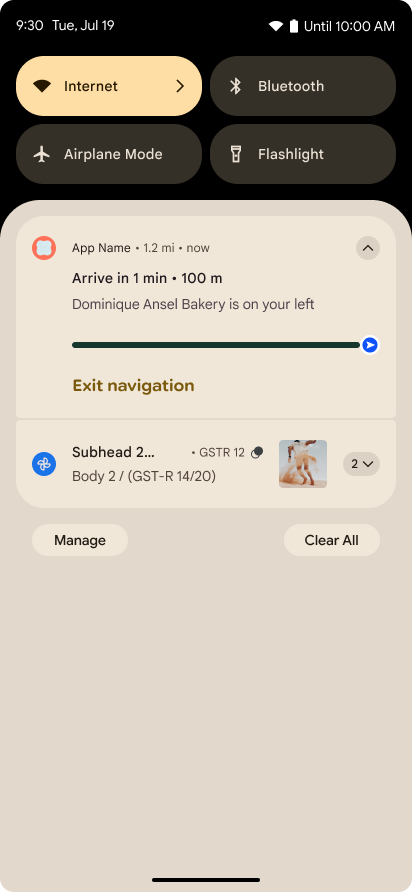
予測型「戻る」のアップデート
Android 16 では、ジェスチャー ナビゲーション(ホームに戻るアニメーションなど)で予測型「戻る」システム アニメーションを有効にするための新しい API が追加されました。新しい PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER に onBackInvokedCallback を登録すると、システムが「戻る」ナビゲーションを処理するたびに、通常の「戻る」ナビゲーション フローに影響を与えることなく、アプリが通常の onBackInvoked 呼び出しを受け取ることができます。
Android 16 では、finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() と moveTaskToBackCallback も追加されています。これらのコールバックを OnBackInvokedDispatcher に登録することで、システムは、戻るジェスチャーが呼び出されたときに特定の動作をトリガーし、対応する事前アニメーションを再生できます。
リッチ ハプティクス
Android は、誕生以来、触覚アクチュエータの制御を公開してきました。
Android 11 では、デバイス定義のセマンティック プリミティブの VibrationEffect.Compositions を介して、より高度なアクチュエータがサポートできる、より複雑なハプティクス エフェクトのサポートが追加されました。
Android 16 では、ハプティクス API が追加されました。これにより、アプリはデバイスの機能の違いを抽象化しながら、ハプティクス エフェクトの振幅と周波数の曲線を定義できます。
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
生産性を向上させるための取り組みのほとんどは、Android Studio、Jetpack Compose、Android Jetpack ライブラリなどのツールを中心に行われていますが、プラットフォームでビジョンを実現するための方法も常に探しています。
ライブ壁紙のコンテンツ処理
In Android 16, the live wallpaper framework is gaining a new content API to
address the challenges of dynamic, user-driven wallpapers. Currently, live
wallpapers incorporating user-provided content require complex, service-specific
implementations. Android 16 introduces
WallpaperDescription and
WallpaperInstance. WallpaperDescription lets you
identify distinct instances of a live wallpaper from the same service. For
example, a wallpaper that has instances on both the home screen and on the lock
screen may have unique content in both places. The wallpaper picker and
WallpaperManager use this metadata to better present
wallpapers to users, streamlining the process for you to create diverse and
personalized live wallpaper experiences.
パフォーマンスとバッテリー
Android 16 では、アプリに関する分析情報を収集するのに役立つ API が導入されています。
システム トリガー プロファイリング
ProfilingManager は Android 15 で追加されました。これにより、アプリは、フィールドの一般公開デバイスで Perfetto を使用してプロファイリング データの収集をリクエストできるようになりました。ただし、このプロファイリングはアプリから開始する必要があるため、起動や ANR などの重要なフローは、アプリでキャプチャするのが困難または不可能です。
これを支援するため、Android 16 では ProfilingManager にシステム トリガーのプロファイリングが導入されています。アプリは、コールド スタート reportFullyDrawn や ANR などの特定のトリガーのトレースを受信する関心を登録できます。これにより、システムはアプリに代わってトレースを開始および停止します。トレース完了後、結果はアプリのデータ ディレクトリに配信されます。
ApplicationStartInfo の開始コンポーネント
ApplicationStartInfo は Android 15 で追加されました。これにより、アプリはプロセスの開始理由、開始タイプ、開始時間、スロットリングなどの有用な診断データを確認できるようになりました。Android 16 では、起動をトリガーしたコンポーネントのタイプを区別するために getStartComponent() が追加されました。これは、アプリの起動フローを最適化する際に役立ちます。
ジョブのイントロスペクションの改善
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API は、ジョブが保留中である理由を返します。ただし、ジョブが保留状態になる理由は複数考えられます。
Android 16 では、新しい API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId) が導入されます。この API は、デベロッパーが設定した明示的な制約とシステムが設定した暗黙的な制約の両方により、ジョブが保留になっている理由を複数返します。
また、最近の制約変更のリストを返す JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId) も導入されます。
特に、特定のタスクの成功率が低下している場合や、特定のジョブの完了のレイテンシに関するバグがある場合は、API を使用してジョブが実行されない理由をデバッグすることをおすすめします。たとえば、バックグラウンドでのウィジェットの更新が失敗した場合や、アプリの起動前にプリフェッチ ジョブが呼び出されなかった場合です。
また、明示的に設定された制約ではなく、システム定義の制約が原因で特定のジョブが完了していないかどうかを把握するのにも役立ちます。
リフレッシュ レートの自動調整
Adaptive refresh rate (ARR), introduced in Android 15, enables the display refresh rate on supported hardware to adapt to the content frame rate using discrete VSync steps. This reduces power consumption while eliminating the need for potentially jank-inducing mode-switching.
Android 16 introduces hasArrSupport() and
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) while restoring
getSupportedRefreshRates() to make it easier for your apps to take
advantage of ARR. RecyclerView
1.4 internally supports ARR when it is settling from a fling or
smooth scroll, and we're continuing our work to add ARR
support into more Jetpack libraries. This frame rate article covers
many of the APIs you can use to set the frame rate so that your app can directly
use ARR.
ADPF のヘッドルーム API
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
ユーザー補助
Android 16 では、すべてのユーザーにアプリを提供するために役立つ新しいユーザー補助 API と機能が追加されています。
Accessibility API の改善
Android 16 adds additional APIs to enhance UI semantics that help improve consistency for users that rely on accessibility services, such as TalkBack.
Outline text for maximum text contrast
Users with low vision often have reduced contrast sensitivity, making it challenging to distinguish objects from their backgrounds. To help these users, Android 16 introduces outline text, replacing high contrast text, which draws a larger contrasting area around text to greatly improve legibility.
Android 16 contains new AccessibilityManager APIs to let
your apps check or register a listener to
see if this mode is enabled. This is primarily for UI Toolkits like Compose to
offer a similar visual experience. If you maintain a UI Toolkit library or your
app performs custom text rendering that bypasses the
android.text.Layout class then you can use this to know
when outline text is enabled.
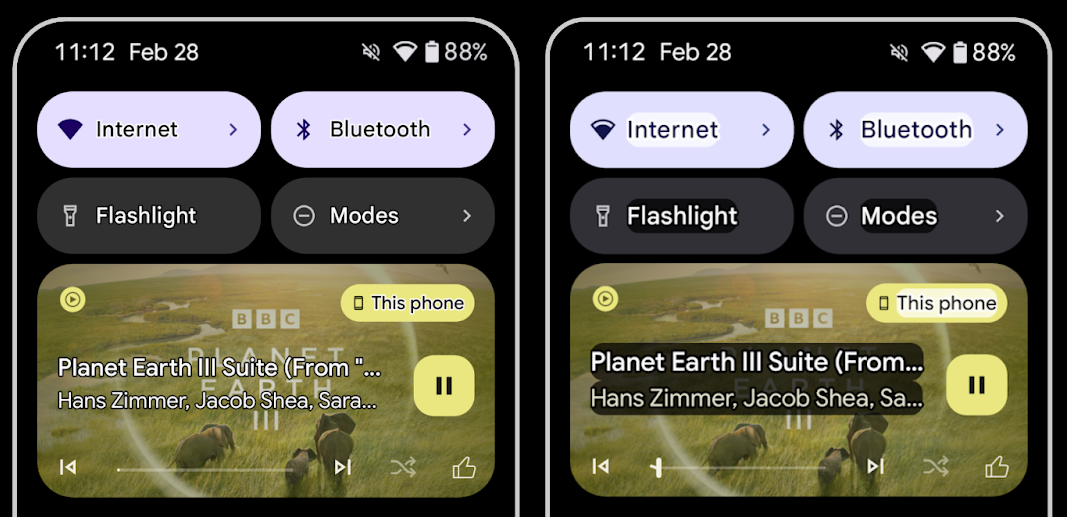
Duration added to TtsSpan
Android 16 extends TtsSpan with a TYPE_DURATION,
consisting of ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES,
and ARG_SECONDS. This lets you directly annotate time
duration, ensuring accurate and consistent text-to-speech output with services
like TalkBack.
Support elements with multiple labels
Android currently allows UI elements to derive their accessibility label from
another, and now offers the ability for multiple labels to be associated, a
common scenario in web content. By introducing a list-based API within
AccessibilityNodeInfo, Android can directly support these
multi-label relationships. As part of this change, we've deprecated
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy and
#getLabeledBy in favor of
#addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy, and
#getLabeledByList.
Improved support for expandable elements
Android 16 adds accessibility APIs that allow you to convey the expanded or
collapsed state of interactive elements, such as menus and expandable lists. By
setting the expanded state using setExpandedState and
dispatching TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
with a CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED content change type,
you can ensure that screen readers like TalkBack announce
state changes, providing a more intuitive and inclusive user experience.
Indeterminate ProgressBars
Android 16 adds RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, giving a way for
you to expose RangeInfo for both determinate and
indeterminate ProgressBar widgets, allowing services like
TalkBack to more consistently provide feedback for progress
indicators.
Tri-state CheckBox
The new AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked and setChecked(int)
methods in Android 16 now support a "partially checked" state in addition to
"checked" and "unchecked." This replaces the deprecated boolean
isChecked and setChecked(boolean).
Supplemental descriptions
When an accessibility service describes a ViewGroup, it
combines content labels from its child views. If you provide a
contentDescription for the ViewGroup, accessibility services assume you are
also overriding the description of non-focusable child views. This can be
problematic if you want to label things like a drop-down (for example, "Font
Family") while preserving the current selection for accessibility (for example,
"Roboto"). Android 16 adds setSupplementalDescription so
you can provide text that provides information about a ViewGroup without
overriding information from its children.
Required form fields
Android 16 adds setFieldRequired to
AccessibilityNodeInfo so apps can tell an accessibility
service that input to a form field is required. This is an important scenario
for users filling out many types of forms, even things as simple as a required
terms and conditions checkbox, helping users to consistently identify and
quickly navigate between required fields.
LEA 補聴器を使用した音声通話で、スマートフォンのマイクを入力として使用
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to switch between the built-in microphones on the hearing aids and the microphone on their phone for voice calls. This can be helpful in noisy environments or other situations where the hearing aid's microphones might not perform well.
LEA 補聴器の周囲の音の調整
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to adjust the volume of ambient sound that is picked up by the hearing aid's microphones. This can be helpful in situations where background noise is too loud or too quiet.
カメラ
Android 16 では、プロのカメラユーザー向けのサポートが強化され、ハイブリッド自動露出と、色温度と色合いの正確な調整が可能になります。新しいナイトモード インジケーターにより、アプリはナイトモードのカメラ セッションへの切り替えのタイミングを把握できます。新しい Intent アクションにより、モーション フォトを簡単に撮影できるようになりました。また、HEIC エンコードと ISO 21496-1 ドラフト標準の新しいパラメータのサポートにより、UltraHDR 画像の改善も継続して行っています。
ハイブリッド自動露出
Android 16 adds new hybrid auto-exposure modes to Camera2, allowing you to manually control specific aspects of exposure while letting the auto-exposure (AE) algorithm handle the rest. You can control ISO + AE, and exposure time + AE, providing greater flexibility compared to the current approach where you either have full manual control or rely entirely on auto-exposure.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
色温度と色合いを正確に調整
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





カメラの夜間モードのシーン検出
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
モーション フォトのキャプチャ インテント アクション
Android 16 adds standard Intent actions —
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE, and
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE — which request that
the camera application capture a motion photo and return
it.
You must either pass an extra EXTRA_OUTPUT to control
where the image will be written, or a Uri through
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). If you don't set a
ClipData, it will be copied there for you when calling
Context.startActivity(Intent).
ウルトラ HDR 画像の拡張

Android 16 continues our work to deliver dazzling image quality with UltraHDR
images. It adds support for UltraHDR images in the HEIC file
format. These images will get ImageFormat type
HEIC_ULTRAHDR and will contain an embedded gainmap similar
to the existing UltraHDR JPEG format. We're working on AVIF support for UltraHDR
as well, so stay tuned.
In addition, Android 16 implements additional parameters in UltraHDR from the ISO 21496-1 draft standard, including the ability to get and set the colorspace that gainmap math should be applied in, as well as support for HDR encoded base images with SDR gainmaps.
グラフィック
Android 16 には、AGSL を使用したカスタム グラフィック効果など、最新のグラフィックの改善が含まれています。
AGSL を使用したカスタム グラフィック効果
Android 16 adds RuntimeColorFilter and
RuntimeXfermode, allowing you to author complex effects like
Threshold, Sepia, and Hue Saturation and apply them to draw calls. Since Android
13, you've been able to use AGSL to create custom
RuntimeShaders that extend Shader. The new API
mirrors this, adding an AGSL-powered RuntimeColorFilter that
extends ColorFilter, and a Xfermode effect that
lets you implement AGSL-based custom compositing and blending between source and
destination pixels.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
接続
Android 16 では、プラットフォームがアップデートされ、アプリで最新の通信技術やワイヤレス技術を利用できるようになります。
セキュリティ強化による測距
Android 16 adds support for robust security features in Wi-Fi location on supported devices with Wi-Fi 6's 802.11az, allowing apps to combine the higher accuracy, greater scalability, and dynamic scheduling of the protocol with security enhancements including AES-256-based encryption and protection against MITM attacks. This allows it to be used more safely in proximity use cases, such as unlocking a laptop or a vehicle door. 802.11az is integrated with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, leveraging its infrastructure and capabilities for wider adoption and easier deployment.
汎用的な距離測定 API
Android 16 includes the new RangingManager, which provides
ways to determine the distance and angle on supported hardware between the local
device and a remote device. RangingManager supports the usage of a variety of
ranging technologies such as BLE channel sounding, BLE RSSI-based ranging, Ultra
Wideband, and Wi-Fi round trip time.
コンパニオン デバイス マネージャーのデバイスの存在
Android 16 では、コンパニオン アプリ サービスをバインドするための新しい API が導入されています。BLE が範囲内にあり、Bluetooth が接続されている場合はサービスがバインドされ、BLE が範囲外にあるか Bluetooth が接続されていない場合はサービスがバインド解除されます。アプリは、さまざまな DevicePresenceEvent に基づいて、新しい onDevicePresenceEvent() コールバックを受け取ります。詳しくは、'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)' をご覧ください。
メディア
Android 16 には、メディア エクスペリエンスを向上させるさまざまな機能が含まれています。
写真選択ツールの改善
写真選択ツールは、メディア ライブラリ全体ではなく、ローカル ストレージとクラウド ストレージの両方から選択した画像と動画にアプリがアクセスできるようにする、安全な組み込みツールです。Google システム アップデートを介したモジュラー システム コンポーネントと Google Play 開発者サービスを組み合わせて、Android 4.4(API レベル 19)以前に対応しています。統合に必要なコードは、関連する Android Jetpack ライブラリで数行のみです。
Android 16 では、写真選択ツールが次のように改善されています。
- 埋め込み写真選択ツール: アプリがビュー階層に写真選択ツールを埋め込むことを可能にする新しい API。これにより、アプリのより統合された部分のように感じながら、プロセスの分離を活用して、アプリが過度に広範な権限を必要とせずにユーザーがメディアを選択できるようにします。埋め込みの写真選択ツールを統合する場合は、プラットフォーム バージョン間の互換性を最大限に高め、統合を簡素化するために、今後リリースされる Android Jetpack ライブラリを使用することをおすすめします。
- 写真選択ツールでの Cloud Search: Android の写真選択ツールでクラウド メディア プロバイダからの検索を可能にする新しい API。写真選択ツールの検索機能は近日提供予定です。
高度なプロフェッショナル動画
Android 16 introduces support for the Advanced Professional Video (APV) codec which is designed to be used for professional level high quality video recording and post production.
The APV codec standard has the following features:
- Perceptually lossless video quality (close to raw video quality)
- Low complexity and high throughput intra-frame-only coding (without pixel domain prediction) to better support editing workflows
- Support for high bit-rate range up to a few Gbps for 2K, 4K and 8K resolution content, enabled by a lightweight entropy coding scheme
- Frame tiling for immersive content and for enabling parallel encoding and decoding
- Support for various chroma sampling formats and bit-depths
- Support for multiple decoding and re-encoding without severe visual quality degradation
- Support multi-view video and auxiliary video like depth, alpha, and preview
- Support for HDR10/10+ and user-defined metadata
A reference implementation of APV is provided through the OpenAPV project. Android 16 will implement support for the APV 422-10 Profile that provides YUV 422 color sampling along with 10-bit encoding and for target bitrates of up to 2Gbps.
プライバシー
Android 16 には、アプリ デベロッパーがユーザーのプライバシーを保護するのに役立つさまざまな機能が含まれています。
ヘルスコネクトの更新
ヘルスコネクトに ACTIVITY_INTENSITY が追加されました。これは、中程度および激しいアクティビティに関する世界保健機関のガイドラインに従って定義されたデータ型です。各レコードには、開始時間、終了時間、アクティビティの強度(中程度または激しい)が必要です。
ヘルスコネクトには、医療記録をサポートする更新された API も含まれています。これにより、アプリはユーザーの明示的な同意を得て、FHIR 形式の医療記録の読み取りと書き込みを行うことができます。
Android 版プライバシー サンドボックス
Android 16 incorporates the latest version of the Privacy Sandbox on Android, part of our ongoing work to develop technologies where users know their privacy is protected. Our website has more about the Privacy Sandbox on Android developer beta program to help you get started. Check out the SDK Runtime which allows SDKs to run in a dedicated runtime environment separate from the app they are serving, providing stronger safeguards around user data collection and sharing.
セキュリティ
Android 16 には、アプリのセキュリティを強化し、アプリのデータを保護するのに役立つ機能が含まれています。
キー共有 API
Android 16 adds APIs that support sharing access to
Android Keystore keys with other apps. The new
KeyStoreManager class supports
granting and revoking access to keys
by app uid, and includes an API for apps to access shared
keys.
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16 では、Android のフォーム ファクタを最大限に活用するためのサポートがアプリに提供されます。
テレビの画質と音質の標準化されたフレームワーク
The new MediaQuality
package in Android 16 exposes
a set of standardized APIs for access to audio and picture profiles and
hardware-related settings. This allows streaming apps to query profiles and
apply them to media dynamically:
- Movies mastered with a wider dynamic range require greater color accuracy to see subtle details in shadows and adjust to ambient light, so a profile that prefers color accuracy over brightness may be appropriate.
- Live sporting events are often mastered with a narrow dynamic range, but are often watched in daylight, so a profile that preferences brightness over color accuracy can give better results.
- Fully interactive content wants minimal processing to reduce latency, and wants higher frame rates, which is why many TV's ship with a game profile.
The API allows apps to switch between profiles and users to enjoy tuning supported TVs to best suit their content.
多言語対応
Android 16 では、デバイスが異なる言語で使用される場合のユーザー エクスペリエンスを補完する機能が追加されています。
縦書きテキスト
Android 16 adds low-level support for rendering and measuring text vertically to
provide foundational vertical writing support for library developers. This is
particularly useful for languages like Japanese that commonly use vertical
writing systems. A new flag,
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG,
has been added to the Paint class. When
this flag is set using
Paint.setFlags, Paint's
text measurement APIs will report vertical advances instead of horizontal
advances, and Canvas will draw text
vertically.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
測定単位のカスタマイズ
Users can now customize their measurement system in regional preferences within
Settings. The user preference is included as part of the locale code, so you can
register a BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED to handle locale configuration changes when
regional preferences change.
Using formatters can help match the local experience. For example, "0.5 in" in English (United States), is "12,7 mm" for a user who has set their phone to English (Denmark) or who uses their phone in English (United States) with the metric system as the measurement system preference.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & region.
