TableLayout یک ViewGroup است که عناصر View کودک را در سطرها و ستون ها نمایش می دهد.
توجه: برای عملکرد بهتر و پشتیبانی ابزار، در عوض باید طرح خود را با ConstraintLayout بسازید .
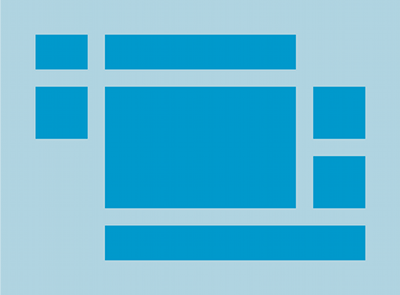
TableLayout فرزندان خود را در ردیف ها و ستون ها قرار می دهد. کانتینرهای TableLayout خطوط مرزی را برای سطرها، ستون ها یا سلول های خود نمایش نمی دهند. جدول به اندازه ردیفی که بیشترین سلول را دارد، ستون خواهد داشت. یک جدول می تواند سلول ها را خالی بگذارد. سلول ها می توانند چندین ستون را پوشش دهند، همانطور که در HTML می توانند. میتوانید با استفاده از فیلد span در کلاس TableRow.LayoutParams ، ستونها را پهن کنید.
توجه: سلول ها نمی توانند چندین ردیف را پوشش دهند.
اشیاء TableRow نماهای فرزند یک TableLayout هستند (هر TableRow یک ردیف را در جدول تعریف می کند). هر ردیف دارای صفر یا چند سلول است که هر کدام با هر نوع نمای دیگری تعریف می شوند. بنابراین، سلول های یک ردیف ممکن است از انواع مختلفی از اشیاء View، مانند اشیاء ImageView یا TextView تشکیل شده باشند. یک سلول همچنین ممکن است یک شی ViewGroup باشد (به عنوان مثال، می توانید TableLayout دیگری را به عنوان یک سلول تودرتو قرار دهید).
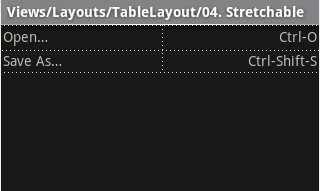
طرح نمونه زیر دارای دو ردیف و دو خانه در هر کدام است. اسکرین شات همراه نتیجه را با حاشیه های سلولی به صورت خطوط نقطه چین نشان می دهد (برای جلوه بصری اضافه شده است).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:stretchColumns="1"> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/table_layout_4_open" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="@string/table_layout_4_open_shortcut" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/table_layout_4_save" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="@string/table_layout_4_save_shortcut" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
ستونها را میتوان پنهان کرد، علامتگذاری کرد تا فضای صفحه نمایش را کشیده و پر کند، یا میتوان آنها را بهعنوان قابل انقباض علامتگذاری کرد تا ستون را مجبور به کوچک شدن کند تا زمانی که جدول به صفحه نمایش برسد. برای جزئیات بیشتر به مستندات TableLayout reference مراجعه کنید.
مثال
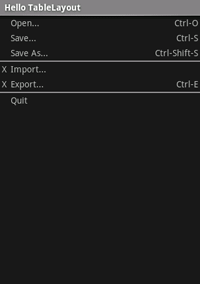
- پروژه جدیدی به نام HelloTableLayout را شروع کنید.
- فایل
res/layout/main.xmlباز کنید و موارد زیر را وارد کنید:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:stretchColumns="1"> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Open..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-O" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Save..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-S" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Save As..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-Shift-S" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <View android:layout_height="2dip" android:background="#FF909090" /> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="X" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Import..." android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="X" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Export..." android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="Ctrl-E" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <View android:layout_height="2dip" android:background="#FF909090" /> <TableRow> <TextView android:layout_column="1" android:text="Quit" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
توجه کنید که این چگونه به ساختار یک جدول HTML شباهت دارد. عنصر
TableLayoutمانند عنصر<table>HTML است.TableRowمانند یک عنصر><tr>>است. اما برای سلول ها، می توانید از هر نوع عنصرViewاستفاده کنید. در این مثال برای هر سلول ازTextViewاستفاده شده است. در بین برخی از ردیف ها، یکViewاصلی نیز وجود دارد که برای کشیدن یک خط افقی استفاده می شود. - مطمئن شوید که HelloTableLayout Activity شما این طرحبندی را در متد
onCreate()بارگیری میکند:کاتلین
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.main) }
جاوا
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); }
روش
setContentView(int)فایل طرحبندی را برایActivityبارگیری میکند، که توسط شناسه منبع مشخص شده است -R.layout.mainبه فایل طرحبندیres/layout/main.xmlاشاره دارد. - برنامه را اجرا کنید.
شما باید موارد زیر را ببینید: