As an open platform, Android offers choice. You can distribute your Android apps to users in any way you want, using any distribution approach or combination of approaches that meets your needs. From publishing in an app marketplace to serving your apps from a website or emailing them directly to users, you’re never locked into any particular distribution platform.
The process for building and packaging your apps for distribution is the same, regardless of how you distribute them. This saves you time and lets you automate parts of the process as needed. You can read Preparing for Release for more information.
The sections below highlight some of the alternatives for distributing your apps.
Distributing through an app marketplace
Usually, to reach the broadest possible audience, you’d distribute your apps through a marketplace, such as Google Play.
Google Play is the premier marketplace for Android apps and is particularly useful if you want to distribute your apps to a large global audience. However, you can distribute your apps through any app marketplace you want or use multiple marketplaces.
Unlike other forms of distribution, Google Play allows you to use the In-app Billing service and Licensing service. The In-app Billing service makes it easy to sell in-app products like game jewels or app feature upgrades. The Licensing service helps prevent unauthorized installation and use of your apps.
Distributing your apps by email
A quick and easy way to release your apps is to send them to users by email. To do this, you prepare the app for release, attach it to an email, and send it to a user. When the user opens your email on their Android-powered device, the Android system recognizes the APK and displays an Install Now button in the email message. Users can install your app by touching the button. Users need to opt in for installing unknown apps if they haven't already to proceed with the installation.
Distributing apps through email is convenient if you’re sending them to a few trusted users, as it provides few protections from piracy and unauthorized distribution; that is, anyone you send your apps to can simply forward them to others.
Distributing through a website
If you don't want to release your apps on a marketplace such as Google Play, you can make them available for download on your website or server, including on a private or enterprise server. To do this, first prepare your apps for release in the normal way, then host the release-ready APK files on your website and provide users with a download link. To install an app distributed in this way, users must opt-in for installing unknown apps.
User opt-in for installing unknown apps
Android protects users from inadvertent download and install of unknown apps, or apps from sources other than Google Play, which is trusted. Android blocks such installs until the user opts into allowing the installation of apps from other sources. The opt-in process depends on the version of Android running on the user's device:
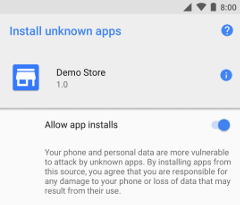
Figure 1: The Install unknown apps system settings screen, where users grant permission for a particular source to install unknown apps.
- On devices running Android 8.0 (API level 26) and higher, users must navigate to the Install unknown apps system settings screen to enable app installations from a particular location, as shown in Figure 1.
- On devices running Android 7.1.1 (API level 25) and lower, users should enable the Unknown sources system setting, found in Settings > Security on their devices.
In both cases, users need to complete the opt-in process before they can download and install unknown apps onto their devices.
