หน้านี้จะอธิบายว่า SDK ของบริษัทอื่นสามารถผสานรวมการติดตั้งแบบอินไลน์ ซึ่งเป็นฟีเจอร์การทดสอบใหม่สำหรับ Google Play ที่นำเสนอรายละเอียดผลิตภัณฑ์แอป Google Play ในอินเทอร์เฟซแบบแผ่นครึ่งได้อย่างไร การติดตั้งในบรรทัดช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ได้รับประสบการณ์การติดตั้งแอปที่ราบรื่นโดยไม่ต้องออกจากบริบทของแอป
นักพัฒนา SDK บุคคลที่สามสามารถผสานรวมฟีเจอร์การติดตั้งในบรรทัดเข้ากับ SDK ของตนเพื่อช่วยให้นักพัฒนาแอปที่ใช้ SDK เหล่านั้นเข้าถึงการติดตั้งในบรรทัดสำหรับแอปของตนได้
ข้อกำหนด
หากต้องการให้อินเทอร์เฟซครึ่งชีตของการติดตั้งแบบอินไลน์ปรากฏในแอป ให้ทำดังนี้
- เวอร์ชัน Google Play ขั้นต่ำต้องเป็น 40.4
- ระดับ API ของ Android จะต้องเป็น 23 หรือสูงกว่า
สถาปัตยกรรมกระบวนการ
สถาปัตยกรรมกระบวนการติดตั้งแบบอินไลน์แสดงในรูปต่อไปนี้:
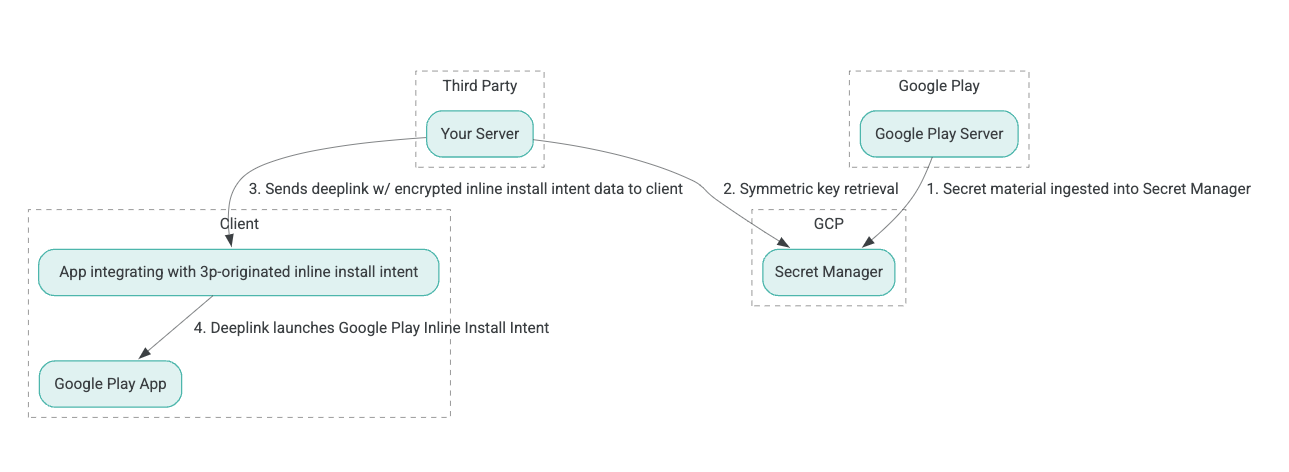
- เซิร์ฟเวอร์ของ Google Play จะสร้างคีย์การเข้ารหัส Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD) และส่งคีย์ไปยังอินสแตนซ์ Secret Manager ของ Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- ผู้รวมระบบบุคคลที่สามดึงคีย์ AEAD จาก GCP Secret Manager
- โปรแกรมผสานรวมบุคคลที่สามจะเข้ารหัสข้อมูลการติดตั้งในบรรทัด
Intentสร้างข้อความที่เข้ารหัสซึ่งส่งผ่านใน Deep Link ที่ใช้เรียกใช้ Intent การติดตั้งในบรรทัด และส่ง Deep Link ไปยังไคลเอ็นต์ในการตอบกลับ - เมื่อมีการคลิก Deep Link แอป Google Play จะจัดการ Intent
หากต้องการกำหนดค่า SDK ของบุคคลที่สามให้ใช้กระบวนการติดตั้งแบบอินไลน์ ให้ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้
สร้างบัญชีบริการใน Google Cloud Project
ในขั้นตอนนี้ คุณจะตั้งค่าบัญชีบริการโดยใช้ Google Cloud Console
- ตั้งค่าโครงการ Google Cloud:
- สร้างองค์กร Google Cloud เมื่อคุณสร้างบัญชี Google Workspace หรือ Cloud Identity และเชื่อมโยงกับชื่อโดเมนของคุณ ทรัพยากรขององค์กรจะถูกสร้างขึ้นโดยอัตโนมัติ สำหรับรายละเอียด โปรดดูที่การสร้างและการจัดการทรัพยากรขององค์กร
- เข้าสู่ระบบคอนโซล GCP โดยใช้บัญชี Google Cloud ที่สร้างไว้ในขั้นตอนก่อนหน้า จากนั้นสร้างโปรเจ็กต์ Google Cloud สำหรับรายละเอียด โปรดดูที่สร้างโครงการ Google Cloud
- สร้างบัญชีบริการในโครงการ Google Cloud ที่สร้างขึ้น ระบบจะใช้บัญชีบริการเป็นข้อมูลประจำตัวของ Google Cloud เพื่อเข้าถึงคีย์สมมาตรในนามของเซิร์ฟเวอร์ สำหรับรายละเอียด โปรดดูที่สร้างบัญชีบริการ
- ใช้รหัสลูกค้า Google Workspace (GWCID) / รหัส Dasher เดียวกันกับที่ ป้อนในแบบฟอร์มแสดงความสนใจ
- สร้างและดาวน์โหลดคีย์ส่วนตัวของบัญชีบริการนั้น
- สร้างคีย์สำหรับบัญชีบริการนั้น สำหรับรายละเอียด โปรดดูที่สร้างคีย์บัญชีบริการ
- ดาวน์โหลดคีย์บัญชีบริการและเก็บไว้ให้สามารถเข้าถึงได้บนเซิร์ฟเวอร์ของคุณ เนื่องจากคีย์นี้ใช้สำหรับการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์เพื่อเข้าถึงทรัพยากร Google Cloud สำหรับคีย์สมมาตร สำหรับรายละเอียด โปรดดูที่รับคีย์บัญชีบริการ
ดึงข้อมูลประจำตัว
ในขั้นตอนนี้ คุณจะดึงคีย์สมมาตรจาก Secret Manager และจัดเก็บไว้อย่างปลอดภัย (เช่น ในไฟล์ JSON) บนพื้นที่จัดเก็บเซิร์ฟเวอร์ของคุณเอง คีย์นี้ใช้เพื่อสร้างข้อมูลรหัสการติดตั้งแบบอินไลน์
ค่า secret_id/secretId อ้างอิงถึงชื่อความลับภายใน Secret Manager ชื่อนี้จะสร้างขึ้นโดยการเติม hsdp-3p-key- ลงในค่า sdk_id ที่ Play จัดเตรียมไว้ ตัวอย่างเช่น หาก sdk_id คือ abc ชื่อความลับจะเป็น hsdp-3p-key-abc
เวอร์ชันลับจะได้รับการอัปเดตทุกสัปดาห์ในวันอังคาร เวลา 14.00 น. UTC คีย์ใหม่ล่าสุดเป็นอันดับสองจะยังคงใช้งานได้จนกว่าจะถึงการหมุนเวียนรอบถัดไป และควรดึงข้อมูลคีย์มาและจัดเก็บใหม่เป็นประจำทุกสัปดาห์
ตัวอย่าง Python
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้ใช้โทเค็นการเข้าถึงที่เก็บไว้ในไฟล์ JSON เพื่อเข้าถึงข้อมูลคีย์ใน GCP Secret Manager และพิมพ์ไปยังคอนโซล
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
from google.cloud import secretmanager
from google.oauth2 import service_account
import google_crc32c
# Create a service account key file.
service_account_key_file = "<json key file of the service account>"
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(service_account_key_file)
# Create the Secret Manager client.
client = secretmanager.SecretManagerServiceClient(
credentials=credentials
)
# Build the resource name of the secret version.
name = f"projects/prod-play-hsdp-3p-caller-auth/secrets/<secret_id>/versions/latest"
# Access the secret version.
response = client.access_secret_version(request={"name": name})
# Verify payload checksum.
crc32c = google_crc32c.Checksum()
crc32c.update(response.payload.data)
if response.payload.data_crc32c != int(crc32c.hexdigest(), 16):
print("Data corruption detected.")
# A keyset created with "tinkey create-keyset --key-template=AES256_GCM". Note
# that this keyset has the secret key information in cleartext.
keyset = response.payload.data.decode("UTF-8")
# WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment. Please store it
# in a secure storage.
with open('<key file name>', 'w') as f:
f.write(keyset)
ตัวอย่าง Java
ตัวอย่างโค้ดต่อไปนี้ใช้โทเค็นการเข้าถึงที่เก็บไว้ในไฟล์ JSON เพื่อเข้าถึงเนื้อหาคีย์ใน GCP Secret Manager และเขียนลงในไฟล์ JSON
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.api.gax.core.CredentialsProvider;
import com.google.api.gax.core.FixedCredentialsProvider;
import com.google.auth.oauth2.ServiceAccountCredentials;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.AccessSecretVersionResponse;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceClient;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceSettings;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretVersionName;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.zip.CRC32C;
import java.util.zip.Checksum;
/** */
final class ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide {
private ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
accessSecretVersion();
}
public static void accessSecretVersion() throws IOException {
// TODO(developer): Replace these variables before running the sample.
String projectId = "projectId";
String secretId = "secretId";
String versionId = "versionId";
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath = "path/to/credentials.json";
String secretMaterialOutputPath = "path/to/secret.json";
accessSecretVersion(
projectId, secretId, versionId, accessTokenPrivateKeyPath, secretMaterialOutputPath);
}
// Access the payload for the given secret version if one exists. The version
// can be a version number as a string (e.g. "5") or an alias (e.g. "latest").
public static void accessSecretVersion(
String projectId,
String secretId,
String versionId,
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath,
String secretMaterialOutputPath)
throws IOException {
// We can explicitly instantiate the SecretManagerServiceClient (below) from a json file if we:
// 1. Create a CredentialsProvider from a FileInputStream of the JSON file,
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider =
FixedCredentialsProvider.create(
ServiceAccountCredentials.fromStream(new FileInputStream(accessTokenPrivateKeyPath)));
// 2. Build a SecretManagerService Settings object from that credentials provider, and
SecretManagerServiceSettings secretManagerServiceSettings =
SecretManagerServiceSettings.newBuilder()
.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.build();
// 3. Initialize client that will be used to send requests by passing the settings object to
// create(). This client only needs to be created once, and can be reused for multiple requests.
// After completing all of your requests, call the "close" method on the client to safely clean
// up any remaining background resources.
try (SecretManagerServiceClient client =
SecretManagerServiceClient.create(secretManagerServiceSettings)) {
SecretVersionName secretVersionName = SecretVersionName.of(projectId, secretId, versionId);
// Access the secret version.
AccessSecretVersionResponse response = client.accessSecretVersion(secretVersionName);
// Verify checksum. The used library is available in Java 9+.
// If using Java 8, you may use the following:
// https://github.com/google/guava/blob/e62d6a0456420d295089a9c319b7593a3eae4a83/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/Hashing.java#L395
byte[] data = response.getPayload().getData().toByteArray();
Checksum checksum = new CRC32C();
checksum.update(data, 0, data.length);
if (response.getPayload().getDataCrc32C() != checksum.getValue()) {
System.out.printf("Data corruption detected.");
return;
}
String payload = response.getPayload().getData().toStringUtf8();
// Print the secret payload.
//
// WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment - this
// snippet is showing how to access the secret material.
System.out.printf("Plaintext: %s\n", payload);
// Write the JSON secret material payload to a json file
try (PrintWriter out =
new PrintWriter(Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get(secretMaterialOutputPath), UTF_8))) {
out.write(payload);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ตั้งค่าข้อมูลรับรองเริ่มต้นของแอปพลิเคชัน
หากคุณไม่ต้องการใช้ CredentialsProvider เพื่อส่งคีย์ส่วนตัวไปยังไฟล์ JSON ในการใช้งาน Java คุณสามารถปรับเปลี่ยนการใช้งานได้โดยการตั้งค่า Application Default Credentials (ADC)
- บอกไลบรารีของไคลเอ็นต์ว่าจะค้นหาคีย์บัญชีบริการได้ที่ใด
- เพิ่มการอ้างอิง Maven ให้กับโครงการ Java
- โทร
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()ซึ่งจะรับการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์โดยอัตโนมัติ (เนื่องจากขั้นตอนที่ 1)
ขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ปรับเปลี่ยนการใช้งาน Java โดย:
- ขจัดความจำเป็นในการสร้างอ็อบเจ็กต์
CredentialsProviderและSecretManagerServiceSettings - การเปลี่ยนแปลงการเรียกไปที่
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()เพื่อไม่รวมอาร์กิวเมนต์
สร้างข้อความเข้ารหัสและสร้างลิงก์ลึก
ในขั้นตอนนี้ คุณใช้ไลบรารีการเข้ารหัส Tink เพื่อสร้าง enifd (ข้อความเข้ารหัส InlineInstallData) จากวัตถุ protobuf InlineInstallData
โปรโต InlineInstallData ถูกกำหนดดังต่อไปนี้:
syntax = "proto2";
package hsdpexperiments;
option java_package = "com.google.hsdpexperiments";
option java_multiple_files = true;
// InlineInstallData is used by 3p auth callers to generate "encrypted inline
// flow data" (enifd) which is decrypted in PGS to verify authenticity and
// freshness.
message InlineInstallData {
// The timestamp which indicates the time encrypted data is generated.
// Used to validate freshness (i.e. generation time in past 4 hours).
// Required.
optional int64 timestamp_ms = 1;
// The docid of the app that we want to open inline install page for.
// This is the package name.
// Required.
optional string target_package_name = 2;
// This is the name of the app requesting the ad from Google Ad Serving
// system.
// Required.
optional string caller_package_name = 3;
// This is the advertising id that will be collected by 3P Ad SDKs.
// Optional.
optional string advertising_id = 4;
// This is used to indicate the network from where the inline install was
// requested.
// Required.
optional string ad_network_id = 5;
}
ในขั้นตอนนี้ คุณยังสร้าง URL ลิงก์ลึกโดยใช้พารามิเตอร์เหล่านี้:
| ช่อง | คำอธิบาย | ต้องระบุ |
|---|---|---|
| id | ชื่อแพ็คเกจของแอปที่จะติดตั้ง | ใช่ |
| ในบรรทัด | ตั้งค่าเป็น true หากมีการร้องขอการติดตั้งแบบอินไลน์ครึ่งแผ่น หากเป็น false เจตนาจะลิงก์ลึกไปยัง Google Play |
ใช่ |
| เอนิฟดี | ตัวระบุที่เข้ารหัสสำหรับ 3P SDK | ใช่ |
| ซ้าย | ตัวระบุภายใน | ใช่ |
| รหัสผู้โทร 3pAuth | ตัวระบุ SDK | ใช่ |
| ข้อมูล | พารามิเตอร์ตัวเลือกในการระบุเป้าหมายสำหรับรายการร้านค้าที่กำหนดเอง | ไม่ |
| ผู้แนะนำ | สตริงการติดตาม referrer ที่เป็นทางเลือก | ไม่ |
ตัวอย่าง Python
คำสั่งต่อไปนี้จะสร้างโค้ด Python จาก InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --python_out=.
โค้ดตัวอย่าง Python ต่อไปนี้สร้าง InlineInstallData และเข้ารหัสด้วยคีย์แบบสมมาตรเพื่อสร้างข้อความที่เข้ารหัส
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
import base64
import time
import inline_install_data_pb2 as InlineInstallData
import tink
from tink import aead
from tink import cleartext_keyset_handle
# Read the stored symmetric key.
with open("example3psecret.json", "r") as f:
keyset = f.read()
"""Encrypt and decrypt using AEAD."""
# Register the AEAD key managers. This is needed to create an Aead primitive later.
aead.register()
# Create a keyset handle from the cleartext keyset in the previous
# step. The keyset handle provides abstract access to the underlying keyset to
# limit access of the raw key material. WARNING: In practice, it is unlikely
# you will want to use a cleartext_keyset_handle, as it implies that your key
# material is passed in cleartext, which is a security risk.
keyset_handle = cleartext_keyset_handle.read(tink.JsonKeysetReader(keyset))
# Retrieve the Aead primitive we want to use from the keyset handle.
primitive = keyset_handle.primitive(aead.Aead)
inlineInstallData = InlineInstallData.InlineInstallData()
inlineInstallData.timestamp_ms = int(time.time() * 1000)
inlineInstallData.target_package_name = "x.y.z"
inlineInstallData.caller_package_name = "a.b.c"
inlineInstallData.ad_network_id = "<sdk_id>"
# Use the primitive to encrypt a message. In this case the primary key of the
# keyset will be used (which is also the only key in this example).
ciphertext = primitive.encrypt(inlineInstallData.SerializeToString(), b'<sdk_id>')
print(f"InlineInstallData Ciphertext: {ciphertext}")
# Base64 Encoded InlineInstallData Ciphertext
enifd = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(ciphertext).decode('utf-8')
print(enifd)
# Deeplink
print(f"https://play.google.com/d?id={inlineInstallData.target_package_name}\&inline=true\&enifd={enifd}\&lft=1\&3pAuthCallerId={inlineInstallData.ad_network_id}")
ดำเนินการสคริปต์ Python โดยรันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
python <file_name>.py
ตัวอย่าง Java
คำสั่งต่อไปนี้จะสร้างโค้ด Java จาก InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --java_out=.
โค้ดตัวอย่าง Java ต่อไปนี้สร้าง InlineInstallData และเข้ารหัสด้วยคีย์สมมาตรเพื่อสร้างข้อความเข้ารหัส:
package com.google.hsdpexperiments;
import static com.google.common.io.BaseEncoding.base64Url;
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.common.flags.Flag;
import com.google.common.flags.FlagSpec;
import com.google.common.flags.Flags;
import com.google.crypto.tink.Aead;
import com.google.crypto.tink.InsecureSecretKeyAccess;
import com.google.crypto.tink.KeysetHandle;
import com.google.crypto.tink.TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat;
import com.google.crypto.tink.aead.AeadConfig;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.Security;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.conscrypt.Conscrypt;
/** info on encryption in https://github.com/google/tink#learn-more */
final class ThirdPartyEnifdGuide {
@FlagSpec(
name = "third_party_id",
help = "the identifier associated with the 3p for which to generate the enifd")
private static final Flag<String> thirdPartyAuthCallerId = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "package_name", help = "the package name of the target app")
private static final Flag<String> packageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "caller_package_name", help = "the package name of the caller app")
private static final Flag<String> callerPackageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "secret_filename", help = "the path to the json file with the secret material")
private static final Flag<String> secretFilename = Flag.value("");
private ThirdPartyEnifdGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// parse flags
Flags.parse(args);
// File keyFile = new File(args[0]);
Path keyFile = Paths.get(secretFilename.get());
// Create structured inline flow data
InlineInstallData idrp =
InlineInstallData.newBuilder()
.setTargetPackageName(packageName.get())
.setCallerPackageName(callerPackageName.get())
.setTimestampMs(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setAdNetworkId(thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get())
.build();
// we can print this out here to make sure it's well formatted, this will help debug
System.out.println(idrp.toString());
// Register all AEAD key types with the Tink runtime.
Conscrypt.checkAvailability();
Security.addProvider(Conscrypt.newProvider());
AeadConfig.register();
// Read AEAD key downloaded from secretmanager into keysethandle
KeysetHandle handle =
TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat.parseKeyset(
new String(Files.readAllBytes(keyFile), UTF_8), InsecureSecretKeyAccess.get());
// Generate enifd using tink library
Aead aead = handle.getPrimitive(Aead.class);
byte[] plaintext = idrp.toByteArray();
byte[] ciphertext = aead.encrypt(plaintext, thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get().getBytes(UTF_8));
String enifd = base64Url().omitPadding().encode(ciphertext);
// Build deeplink, escaping ampersands (TODO: verify this is necessary while testing e2e)
String deeplink =
"https://play.google.com/d?id="
+ packageName.get()
+ "\\&inline=true\\&enifd="
+ enifd
+ "\\&lft=1\\&3pAuthCallerId="
+ thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get();
System.out.println(deeplink);
}
}
ในที่สุด ให้สร้างโปรแกรม Java เป็นไบนารีและเรียกใช้โดยใช้โค้ดต่อไปนี้:
path/to/binary/ThirdPartyEnifdGuide --secret_filename=path/to/jsonfile/example3psecret.json --package_name=<package_name_of_target_app> --third_party_id=<3p_caller_auth_id>
- แฟล็ก
secret_filenameระบุเส้นทางไปยังไฟล์ JSON ที่มีเนื้อหาลับ package_nameคือรหัสเอกสารของแอปเป้าหมาย- แฟล็ก
third_party_idใช้เพื่อระบุ ID การตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ผู้เรียกของบุคคลที่สาม (นั่นคือ<sdk_id>)
เปิดตัวความตั้งใจในการติดตั้งแบบอินไลน์
หากต้องการทดสอบลิงก์ลึกที่สร้างขึ้นในขั้นตอนก่อนหน้านี้ ให้เชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ Android (ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าได้เปิดใช้งานการดีบัก USB แล้ว) เข้ากับเวิร์กสเตชันที่มีการติดตั้ง ADB และรันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
adb shell am start "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
ในโค้ดไคลเอนต์ ให้ส่งเจตนาโดยใช้หนึ่งในวิธีต่อไปนี้ (Kotlin หรือ Java)
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
val deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending")
intent.data = Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl)
val packageManager = context.getPackageManager()
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0)
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
String id = "exampleAppToBeInstalledId";
String deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>";
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending");
intent.setData(Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl));
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
ภาคผนวก
ส่วนต่อไปนี้จะให้คำแนะนำเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับกรณีการใช้งานบางอย่าง
เตรียมสภาพแวดล้อม Python
ในการเรียกใช้โค้ดตัวอย่าง Python ให้ตั้งค่าสภาพแวดล้อม Python บนเวิร์กสเตชันของคุณและติดตั้งส่วนที่ต้องมีที่จำเป็น
ตั้งค่าสภาพแวดล้อม Python
ติดตั้ง python3.11 (หากติดตั้งแล้ว ให้ข้ามขั้นตอนนี้):
sudo apt install python3.11ติดตั้ง pip:
sudo apt-get install pipติดตั้ง
virtualenv:sudo apt install python3-virtualenvสร้างสภาพแวดล้อมเสมือนจริง (จำเป็นสำหรับการอ้างอิง Tink):
virtualenv inlineinstall --python=/usr/bin/python3.11
เข้าสู่สภาพแวดล้อมเสมือนจริง:
source inlineinstall/bin/activateอัปเดต pip:
python -m pip install --upgrade pipติดตั้งสิ่งที่ต้องมี:
ติดตั้ง Tink:
pip install tinkติดตั้ง Google crc32c:
pip install google-crc32cติดตั้ง Secret Manager:
pip install google-cloud-secret-managerติดตั้งคอมไพเลอร์ protobuf:
sudo apt install protobuf-compiler
การสร้าง enifd ของ C++
ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่าง C++ ที่เราเขียนและตรวจสอบภายในเพื่อสร้าง enifd
การสร้าง enifd สามารถทำได้โดยใช้โค้ด C++ ดังต่อไปนี้:
// A command-line example for using Tink AEAD w/ key template aes128gcmsiv to
// encrypt an InlineInstallData proto.
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "<path_to_protoc_output>/inline_install_data.proto.h"
#include "absl/flags/flag.h"
#include "absl/flags/parse.h"
#include "absl/strings/escaping.h"
#include "absl/strings/string_view.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_config.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_key_templates.h"
#include "tink/cc/config/global_registry.h"
#include "tink/cc/examples/util/util.h"
#include "tink/cc/keyset_handle.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/status.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/statusor.h"
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, keyset_filename, "",
"Keyset file (downloaded from secretmanager) in JSON format");
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, associated_data, "",
"Associated data for AEAD (default: empty");
namespace {
using ::crypto::tink::Aead;
using ::crypto::tink::AeadConfig;
using ::crypto::tink::KeysetHandle;
using ::crypto::tink::util::Status;
using ::crypto::tink::util::StatusOr;
} // namespace
namespace tink_cc_examples {
// AEAD example CLI implementation.
void AeadCli(const std::string& keyset_filename,
absl::string_view associated_data) {
Status result = AeadConfig::Register();
if (!result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to register AeadConfig";
return;
}
// Read the keyset from file.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<KeysetHandle>> keyset_handle =
ReadJsonCleartextKeyset(keyset_filename);
if (!keyset_handle.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to read json keyset";
return;
}
// Get the primitive.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<Aead>> aead =
(*keyset_handle)
->GetPrimitive<crypto::tink::Aead>(
crypto::tink::ConfigGlobalRegistry());
if (!aead.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to get primitive";
return;
}
// Instantiate the enifd.
hsdpexperiments::InlineInstallData iid;
iid.set_timestamp_ms(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch())
.count());
iid.set_target_package_name("<TARGET_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_caller_package_name("<CALLER_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_ad_network_id("<SDK_ID>");
// Compute the output.
StatusOr<std::string> encrypt_result =
(*aead)->Encrypt(iid.SerializeAsString(), associated_data);
if (!encrypt_result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to encrypt Inline Install Data";
return;
}
const std::string& output = encrypt_result.value();
std::string enifd;
absl::WebSafeBase64Escape(output, &enifd);
std::clog << "enifd: " << enifd << '\n';
}
} // namespace tink_cc_examples
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
absl::ParseCommandLine(argc, argv);
std::string keyset_filename = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_keyset_filename);
std::string associated_data = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_associated_data);
std::clog << "Using keyset from file " << keyset_filename
<< " to AEAD-encrypt inline install data with associated data '"
<< associated_data << "'." << '\n';
tink_cc_examples::AeadCli(keyset_filename, associated_data);
return 0;
}
โค้ดนี้ได้รับการดัดแปลงจากตัวอย่างซึ่งสามารถพบได้ในเอกสาร Tink
