ב-Android 16 יש תכונות חדשות וממשקי API חדשים למפתחים. בקטעים הבאים מופיע סיכום של התכונות האלה שיעזור לכם להתחיל להשתמש בממשקי ה-API שקשורים אליהן.
רשימה מפורטת של ממשקי API חדשים, ממשקי API שעברו שינוי וממשקי API שהוסרו מופיעה בדוח השוואה בין גרסאות של API. פרטים על ממשקי API חדשים זמינים בהפניית Android API. ממשקי API חדשים מסומנים כדי להקל על האיתור שלהם.כדאי גם לבדוק תחומים שבהם שינויים בפלטפורמה עשויים להשפיע על האפליקציות שלכם. למידע נוסף, ראו את הדפים הבאים:
- שינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים על אפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16
- שינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים על כל האפליקציות בלי קשר ל-
targetSdkVersion.
פונקציונליות עיקרית
Android כוללת ממשקי API חדשים שמרחיבים את יכולות הליבה של מערכת Android.
שתי גרסאות של Android API בשנת 2025
- התצוגה המקדימה הזו מיועדת לגרסה הראשית הבאה של Android, שתושק ברבעון השני של שנת 2025. הגרסה הזו דומה לכל הגרסאות הקודמות של ה-API, שבהן יכולים להיות שינויים מתוכננים בהתנהגות, שקשורים לרוב ל-targetSdkVersion.
- אנחנו מתכננים את הגרסה הראשית רבעון מוקדם יותר (ברבעון השני במקום ברבעון השלישי בשנים קודמות), כדי להתאים את לוח הזמנים שלה ללוח הזמנים של השקות המכשירים בסביבה העסקית שלנו, וכך יותר מכשירים יוכלו לקבל את הגרסה הראשית של Android מוקדם יותר. הגרסה העיקרית תשוחרר ברבעון השני של השנה, ולכן תצטרכו לבצע את בדיקת התאימות השנתית כמה חודשים מוקדם יותר מאשר בשנים קודמות כדי לוודא שהאפליקציות שלכם מוכנות.
- אנחנו מתכננים להשיק גרסה נוספת ברבעון 4 של שנת 2025, שגם תכלול ממשקי API חדשים למפתחים. הגרסה הראשית של הרבעון השני תהיה הגרסה היחידה בשנת 2025 שתכלול שינויים מתוכננים בהתנהגות שעשויים להשפיע על אפליקציות.
בנוסף לממשקי API חדשים למפתחים, במהדורה המשנית של הרבעון הרביעי יהיו עדכוני תכונות, אופטימיזציות ותיקוני באגים. היא לא תכלול שינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים על האפליקציות.
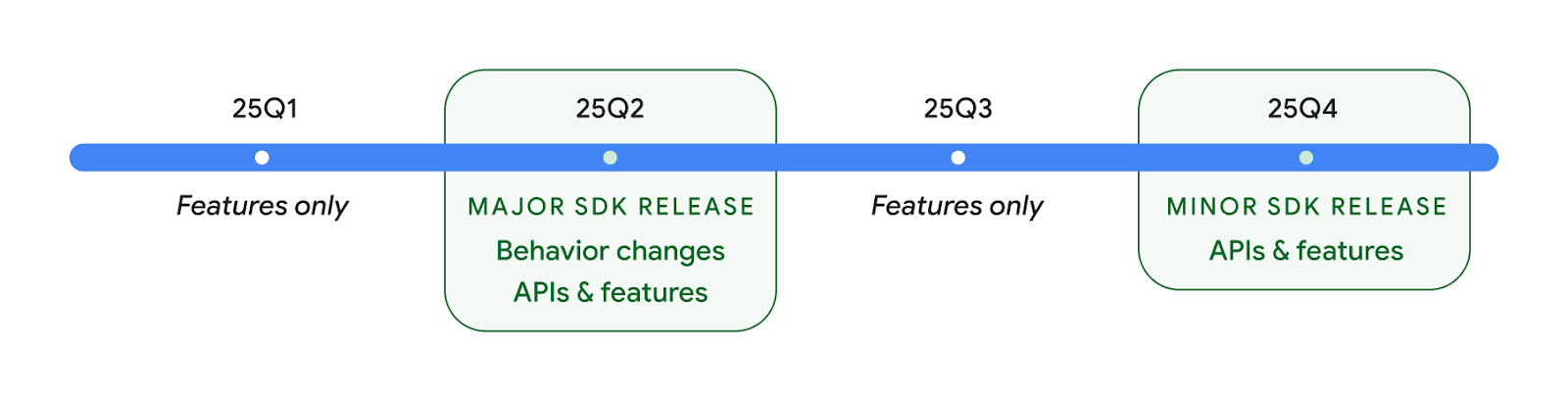
נמשיך להשיק גרסאות של Android מדי רבעון. העדכונים ברבעון הראשון וברבעון השלישי, בין הגרסאות של ה-API, יסופקו כעדכונים מצטברים כדי להבטיח איכות מתמשכת. אנחנו פועלים באופן פעיל עם שותפי המכשירים שלנו כדי להביא את הגרסה שתושק ברבעון השני לכמה שיותר מכשירים.
שימוש בממשקי API חדשים עם גרסאות ראשיות ומשנה
היום אפשר להגן על בלוק קוד באמצעות בדיקה של רמת ה-API באמצעות הקבוע SDK_INT עם VERSION_CODES. התמיכה באפשרות הזו תמשיך לפעול בגרסאות הראשיות של Android.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
אפשר להשתמש בערך הקבוע החדש SDK_INT_FULL לבדיקות API גם לגרסאות ראשיות וגם לגרסאות משניות באמצעות המניין החדש VERSION_CODES_FULL.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
אפשר גם להשתמש ב-method Build.getMinorSdkVersion() כדי לקבל רק את גרסת ה-SDK המשנית.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
ממשקי ה-API האלה עדיין לא הושלמו ועשויים להשתנות, לכן אם יש לכם חששות, תוכלו לשלוח לנו משוב.
חוויית המשתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
ב-Android 16, למפתחי אפליקציות ולמשתמשים יש יותר שליטה וגמישות בהגדרת המכשיר כך שיתאים לצרכים שלהם.
התראות שמתמקדות בהתקדמות
ב-Android 16 נוספו התראות שמתמקדות בהתקדמות, כדי לעזור למשתמשים לעקוב בצורה חלקה אחרי תהליכים שהם יזמו, מתחילתו ועד סופו.
Notification.ProgressStyle הוא סגנון התראות חדש שמאפשר ליצור התראות שמתמקדות בהתקדמות. תרחישי שימוש עיקריים כוללים שיתוף נסיעות, משלוחים וניווט. בתוך הכיתה Notification.ProgressStyle אפשר לציין מצבים ואבני דרך בתהליך השימוש של המשתמש באמצעות נקודות ופלחים.
למידע נוסף, אפשר לעיין בדף המסמכים בנושא התראות שמתמקדות בהתקדמות.
עדכונים של חיזוי החזרה
ב-Android 16 נוספו ממשקי API חדשים שיעזרו לכם להפעיל אנימציות מערכת חזרה חזויות בניווט באמצעות תנועות, כמו אנימציה של חזרה לדף הבית. רישום ה-onBackInvokedCallback באמצעות PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER החדש מאפשר לאפליקציה לקבל את הקריאה הרגילה onBackInvoked בכל פעם שהמערכת מטפלת בניווט לאחור, בלי להשפיע על תהליך הניווט לאחור הרגיל.
ב-Android 16 נוספו גם הסמלים finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() ו-moveTaskToBackCallback. כשרושמים את הפונקציות האלה באמצעות OnBackInvokedDispatcher, המערכת יכולה להפעיל התנהגויות ספציפיות ולהפעיל אנימציות מתאימות מראש כשמפעילים את תנועת החזרה.
משוב פיזי עשיר יותר
מערכת Android חשפה שליטה על המפעיל הרטט כבר מההתחלה.
ב-Android 11 נוספה תמיכה באפקטים הקטנים והחושתיים (haptic) מורכבים יותר, שיכולים לתמוך במפעילים מתקדמים יותר באמצעות VibrationEffect.Compositions של פרימיטיבים סמנטיים מוגדרים-מכשיר.
ב-Android 16 נוספו ממשקי API לחישה שמאפשרים לאפליקציות להגדיר את עקומות האמפליטודה והתדר של אפקטים לחושיים, תוך התעלמות מהבדלים בין יכולות המכשירים.
פרודוקטיביות וכלים למפתחים
רוב העבודה שלנו לשיפור הפרודוקטיביות מתמקדת בכלים כמו Android Studio, Jetpack Compose וספריות Android Jetpack, אבל אנחנו תמיד מחפשים דרכים לעזור לכם להגשים את החזון שלכם בפלטפורמה.
טיפול בתוכן של טפטים דינמיים
ב-Android 16, מסגרת הטפטים המונפשים מקבלת ממשק API חדש לתוכן כדי להתמודד עם האתגרים של טפטים דינמיים שמבוססים על המשתמשים. בשלב הזה, כדי להשתמש בתמונות רקע חיים שכוללות תוכן שהמשתמשים סיפקו, צריך להטמיע אותן בצורה מורכבת וספציפית לשירות. ב-Android 16 נוספו התכונות WallpaperDescription ו-WallpaperInstance. בעזרת השדה WallpaperDescription אפשר לזהות מופעים נפרדים של טפט דינמי מאותו שירות. לדוגמה, בטפט שיש לו מופעים גם במסך הבית וגם במסך הנעילה יכול להיות תוכן ייחודי בשני המקומות. הכלי לבחירת טפטים ו-WallpaperManager משתמשים במטא-נתונים האלה כדי להציג את הטפטים בצורה טובה יותר למשתמשים, וכך לייעל את התהליך שלכם ליצירת חוויות מגוונות ומותאמות אישית של טפטים חיים.
ביצועים וסוללה
Android 16 כולל ממשקי API שעוזרים לאסוף תובנות לגבי האפליקציות.
יצירת פרופילים שמופעלת על ידי המערכת
ProfilingManager נוסף ב-Android 15, ומאפשר לאפליקציות לבקש איסוף נתונים ליצירת פרופילים באמצעות Perfetto במכשירים ציבוריים בשטח.
עם זאת, מאחר שצריך להתחיל את הפרופיל הזה מהאפליקציה, לאפליקציות יהיה קשה או בלתי אפשרי לתעד תהליכים קריטיים כמו הפעלות או אירועי ANR.
כדי לעזור בכך, ב-Android 16 הוספנו ל-ProfilingManager פרופיל שמופעל על ידי המערכת. אפליקציות יכולות להירשם לקבלת מעקבים של טריגרים מסוימים, כמו הפעלה מחדש (cold start) reportFullyDrawn או אירועי ANR, ואז המערכת מתחילה ומפסיקה מעקב בשם האפליקציה. בסיום המעקב, התוצאות מועברות לספריית הנתונים של האפליקציה.
הפעלת רכיב ב-ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo נוסף ב-Android 15, ומאפשר לאפליקציה לראות את הסיבות להתחלת התהליך, סוג ההתחלה, זמני ההתחלה, הגבלת הקצב ונתוני אבחון שימושיים אחרים. ב-Android 16 נוספה הערך getStartComponent() כדי להבדיל בין סוגי הרכיבים שהפעילו את ההפעלה. הערך הזה יכול לעזור לכם לבצע אופטימיזציה לתהליך ההפעלה של האפליקציה.
בדיקה טובה יותר של המשרה
ה-API של JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() מחזיר את הסיבה לכך שמשימת
עשויה להמתין. עם זאת, יכולות להיות כמה סיבות לכך שמשימה נמצאת בהמתנה.
ב-Android 16 אנחנו משיקים ממשק API חדש, JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId), שמציג כמה סיבות לכך שמשימה נמצאת בהמתנה, גם בגלל אילוצים מפורשים שהמפתח הגדיר וגם בגלל אילוצים משתמעים שהמערכת הגדירה.
אנחנו גם משיקים את הפונקציה JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId), שמחזירה רשימה של השינויים האחרונים באילוצים.
מומלץ להשתמש ב-API כדי לנפות באגים ולגלות למה המשימות לא מתבצעות, במיוחד אם נתוני ההצלחה של משימות מסוימות נמוכים או אם יש באגים בזמן האחזור של משימות מסוימות. לדוגמה, העדכון של הווידג'טים ברקע נכשל או שהקריאה למשימה של אחסון נתונים לפני האצת האפליקציה נכשלה לפני הפעלת האפליקציה.
כך תוכלו גם להבין טוב יותר אם משימות מסוימות לא מסתיימות בגלל אילוצים שהוגדרו על ידי המערכת, לעומת אילוצים שהוגדרו באופן מפורש.
קצב רענון דינמי
שיעור הרענון המותאם (ARR), שהוצג ב-Android 15, מאפשר לשיעור הרענון של המסך בחומרה נתמכת להתאים את עצמו לשיעור הפריימים של התוכן באמצעות שלבים נפרדים של VSync. כך אפשר לצמצם את צריכת החשמל ולחסוך את הצורך במעבר בין המצבים, שעלול לגרום לתנודות בפריימים.
ב-Android 16 נוספו hasArrSupport() ו-getSuggestedFrameRate(int), תוך שחזור של getSupportedRefreshRates(), כדי שיהיה קל יותר לאפליקציות שלכם לנצל את ARR. RecyclerView 1.4 תומך באופן פנימי ב-ARR כשהוא מתייצב אחרי תנועה מהירה או גלילה חלקה, ואנחנו ממשיכים לעבוד כדי להוסיף תמיכה ב-ARR לספריות נוספות של Jetpack. במאמר הזה מוסבר על הרבה ממשקי API שאפשר להשתמש בהם כדי להגדיר את קצב הפריימים, כך שהאפליקציה תוכל להשתמש ישירות ב-ARR.
Headroom APIs in ADPF
ב-SystemHealthManager מופיעים ממשקי ה-API getCpuHeadroom ו-getGpuHeadroom, שנועדו לספק לאפליקציות ולמשחקים שמשתמשים במשאבים רבים אומדנים של משאבי המעבד (CPU) והמעבד הגרפי (GPU) שזמינים. השיטות האלה מאפשרות לכם להעריך איך אפשר לשפר את בריאות המערכת באמצעות האפליקציה או המשחק, במיוחד כשמשתמשים בהן בשילוב עם ממשקי API אחרים של Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF) שמזוהים את הבקרה על הביצועים כתוצאה מהתחממות.
באמצעות CpuHeadroomParams ו-GpuHeadroomParams במכשירים נתמכים, אפשר להתאים אישית את חלון הזמן שמשמש לחישוב מרווח הנשימה ולבחור בין זמינות משאבים ממוצעת לזמינות משאבים מינימלית. כך תוכלו לצמצם את השימוש במשאבי המעבד או ה-GPU בהתאם, וכתוצאה מכך לשפר את חוויית המשתמש ואת חיי הסוללה.
נגישות
ב-Android 16 נוספו ממשקי API ותכונות חדשים לנגישות, שיכולים לעזור לכם להנגיש את האפליקציה לכל המשתמשים.
ממשקי API משופרים לנגישות
ב-Android 16 נוספו ממשקי API נוספים לשיפור הסמנטיקה של ממשק המשתמש, כדי לשפר את העקביות למשתמשים שמסתמכים על שירותי נגישות, כמו TalkBack.
קו מתאר של הטקסט כדי לשפר את הניגודיות של הטקסט
לרוב, למשתמשים עם ליקויי ראייה יש רגישות נמוכה יותר לניגודיות, ולכן קשה להם להבחין בין אובייקטים לבין הרקעים שלהם. כדי לעזור למשתמשים האלה, ב-Android 16 הוספנו טקסט עם קו מתאר, שמחליף את הטקסט בניגודיות גבוהה. הטקסט עם קו מתאר כולל אזור ניגודיות גדול יותר סביב הטקסט כדי לשפר את הקריאוּת שלו.
מערכת Android 16 כוללת ממשקי API חדשים של AccessibilityManager שמאפשרים לאפליקציות לבדוק או לרשום מאזין כדי לבדוק אם המצב הזה מופעל. האפשרות הזו מיועדת בעיקר לערכות כלים של ממשק משתמש, כמו Compose, כדי לספק חוויה חזותית דומה. אם אתם מנהלים ספרייה של UI Toolkit או שהאפליקציה שלכם מבצעת עיבוד טקסט מותאם אישית שעובר על פני הכיתה android.text.Layout, תוכלו להשתמש בזה כדי לדעת מתי הטקסט בקו מתאר מופעל.

משך הזמן נוסף ל-TtsSpan
ב-Android 16, TtsSpan מורחב באמצעות TYPE_DURATION, שמכיל את ARG_HOURS, את ARG_MINUTES ואת ARG_SECONDS. כך תוכלו להוסיף הערות ישירות למשך הזמן, וכך להבטיח שהטקסט שהמערכת תקריא יהיה מדויק ועקבי באמצעות שירותים כמו TalkBack.
תמיכה ברכיבים עם כמה תוויות
כרגע, ב-Android אפשר להסיק את תווית הנגישות של רכיבי ממשק המשתמש מרכיב אחר, ועכשיו יש אפשרות לשייך כמה תוויות, תרחיש נפוץ בתוכן אינטרנט. בעזרת ממשק API שמבוסס על רשימה ב-AccessibilityNodeInfo, מערכת Android יכולה לתמוך ישירות ביחסים האלה של תוויות מרובות. כחלק מהשינוי, הוצאנו משימוש את AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy ואת #getLabeledBy והחלפנו אותם ב-#addLabeledBy, ב-#removeLabeledBy וב-#getLabeledByList.
תמיכה משופרת ברכיבים שניתן להרחיב
ב-Android 16 נוספו ממשקי API לנגישות שמאפשרים להעביר את המצב המורחב או המכווץ של רכיבים אינטראקטיביים, כמו תפריטים ורשימות שניתן להרחיב. כדי לוודא שקוראי מסך כמו TalkBack יקריאו את השינויים במצב, אפשר להגדיר את המצב המורחב באמצעות setExpandedState ולשלוח אירועי נגישות מסוג TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED עם סוג שינוי תוכן CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED. כך תוכלו לספק חוויית משתמש אינטואיטיבית ומכילה יותר.
סרגי התקדמות לא מוגדרים
ב-Android 16 נוספה התכונה RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, שמאפשרת לחשוף את RangeInfo גם לווידג'טים ProgressBar מוגדרים וגם לווידג'טים לא מוגדרים, וכך לאפשר לשירותים כמו TalkBack לספק משוב עקבי יותר לגבי אינדיקטורים של התקדמות.
תיבת סימון תלת-מצבית
השיטות החדשות AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked ו-setChecked(int)
ב-Android 16 תומכות עכשיו במצב 'מסומן חלקית' בנוסף למצבים 'מסומן' ו'לא מסומן'. הפונקציה הזו מחליפה את הפונקציות הבוליאניות isChecked ו-setChecked(boolean) שהוצאו משימוש.
תיאורים משלימים
כששירות נגישות מתאר ViewGroup, הוא משלב תוויות לתיאור התוכן מהתצוגות הצאצאיות שלו. אם תספקו את הערך contentDescription ל-ViewGroup, שירותי הנגישות יקבלו את ההנחה שאתם משנים גם את התיאור של תצוגות הצאצאים שלא ניתנות למיקוד. זה יכול להוות בעיה אם רוצים לתייג פריטים כמו תפריט נפתח (לדוגמה, 'משפחת גופנים') תוך שמירה על הבחירה הנוכחית לצורכי נגישות (לדוגמה, 'Roboto'). ב-Android 16 נוספה התגית setSupplementalDescription, שמאפשרת לספק טקסט שמספק מידע על ViewGroup בלי לשנות את המידע מהצאצאים שלו.
שדות חובה בטופס
ב-Android 16 נוספה התג setFieldRequired ל-AccessibilityNodeInfo כדי שאפליקציות יוכלו להודיע לשירותי נגישות שצריך להזין נתונים בשדה טופס. זהו תרחיש חשוב למשתמשים שממלאים סוגים רבים של טפסים, גם דברים פשוטים כמו תיבת סימון חובה לתנאים ולהגבלות. התכונה הזו עוזרת למשתמשים לזהות באופן עקבי את השדות הנדרשים ולנווט במהירות ביניהם.
הטלפון כקלט מיקרופון לשיחות קוליות עם מכשירי שמיעה בטכנולוגיית LEA
ב-Android 16 נוספה למשתמשים במכשירי שמיעה עם LE Audio היכולת לעבור בין המיקרופונים המובנים במכשירי השמיעה לבין המיקרופון בטלפון לשיחות קוליות. התכונה הזו יכולה להיות שימושית בסביבות רועשות או במצבים אחרים שבהם יכול להיות שהמיקרופונים של מכשיר השמיעה לא יפעלו טוב.
שליטה בעוצמת הקולות מהסביבה במכשירי שמיעה עם LEA
ב-Android 16 נוספה למשתמשים במכשירי שמיעה עם LE Audio היכולת לשנות את עוצמת הצליל של הסביבה שנקלט במיקרופונים של מכשיר השמיעה. האפשרות הזו יכולה להיות שימושית במצבים שבהם רעשי הרקע רועשים מדי או שקטים מדי.
מצלמה
Android 16 משפר את התמיכה במשתמשים מקצועיים במצלמה, ומאפשר חשיפה אוטומטית היברידית יחד עם התאמות מדויקות של טמפרטורת הצבע והגוון. מחוון חדש של מצב לילה עוזר לאפליקציה לדעת מתי לעבור למצב לילה ומתי לצאת ממנו במהלך צילום במצלמה. Intentפעולות חדשות מקלות על צילום תמונות עם תנועה, ואנחנו ממשיכים לשפר את תמונות ה-UltraHDR עם תמיכה בקידוד HEIC ופרמטרים חדשים מטיוטת התקן ISO 21496-1.
חשיפה אוטומטית היברידית
ב-Android 16 נוספו ל-Camera2 מצבי חשיפה אוטומטית היברידיים חדשים, שמאפשרים לשלוט באופן ידני בהיבטים ספציפיים של החשיפה, בזמן שהאלגוריתם של החשיפה האוטומטית (AE) מטפל בשאר הדברים. תוכלו לשלוט ב-ISO + AE וב-זמן חשיפה + AE, וכך ליהנות מגמישות רבה יותר בהשוואה לגישה הנוכחית שבה יש לכם שליטה ידנית מלאה או שאתם מסתמכים לחלוטין על חשיפה אוטומטית.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
התאמות מדויקות של טמפרטורת הצבע והגוון
ב-Android 16 נוספה תמיכה במצלמה לכוונון עדין של טמפרטורת הצבע והגוון, כדי לתמוך טוב יותר באפליקציות מקצועיות להקלטת וידאו. בגרסאות קודמות של Android, אפשר היה לשלוט בהגדרות של איזון הלבן דרך CONTROL_AWB_MODE, שמכילה אפשרויות מוגבלות לרשימת הגדרות מוגדרות מראש, כמו נורות ליבון, ענן ושקיעה. הלחצן COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT מאפשר להשתמש בלחצנים COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE ו-COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT כדי לבצע התאמות מדויקות של איזון הלבן על סמך טמפרטורת הצבע המתאימה.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
בדוגמאות הבאות אפשר לראות איך נראית תמונה אחרי שמחילים עליה התאמות שונות של טמפרטורת הצבע והגוון:





זיהוי סצנות במצב לילה במצלמה
כדי לעזור לאפליקציה לדעת מתי לעבור לסשן צילום במצב לילה ומתי לצאת ממנו, נוסף ל-Android 16 EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. אם התכונה נתמכת, היא תהיה זמינה בCaptureResult בתוך Camera2.
זהו ממשק ה-API שציינו בקצרה כשיגיע בקרוב בפוסט בבלוג איך Instagram אפשרה למשתמשים לצלם תמונות מדהימות בתאורה נמוכה. הפוסט הזה כולל מדריך מעשי להטמעת מצב לילה, יחד עם מחקר מקרה שמקשר בין תמונות באיכות גבוהה יותר שצולמו במצב לילה באפליקציה לבין עלייה במספר התמונות ששותפו מהמצלמה שבאפליקציה.
פעולות Intent של צילום תמונות עם תנועה
ב-Android 16 נוספו פעולות סטנדרטיות של Intent – ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE ו-ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE – שמבקשות מאפליקציית המצלמה לצלם תמונה בתנועה ולהחזיר אותה.
צריך להעביר EXTRA_OUTPUT נוסף כדי לקבוע לאן התמונה תירשם, או Uri דרך Intent.setClipData(ClipData). אם לא תגדירו ClipData, הוא יועתק לשם כשתבצעו את השיחה Context.startActivity(Intent).
שיפורים בתמונות UltraHDR

ב-Android 16 אנחנו ממשיכים את המאמצים שלנו לספק איכות תמונה מרהיבה באמצעות תמונות UltraHDR. נוספה תמיכה בתמונות UltraHDR בפורמט הקובץ HEIC. התמונות האלה יקבלו את הסוג ImageFormat HEIC_ULTRAHDR ויכללו מפת רווח מוטמעת (gainmap) שדומה לפורמט הקיים של UltraHDR JPEG. אנחנו עובדים גם על תמיכה ב-AVIF ב-UltraHDR, אז כדאי להמשיך להתעדכן.
בנוסף, ב-Android 16 מוטמעים פרמטרים נוספים ב-UltraHDR מטיוטת התקן ISO 21496-1, כולל היכולת לקבל ולהגדיר את מרחב הצבעים שבו צריך להחיל את החישובים של מפת הרווח, וגם תמיכה בתמונות בסיסיות בקידוד HDR עם מפות רווח של SDR.
גרפיקה
Android 16 כולל את השיפורים האחרונים בגרפיקה, כמו אפקטים גרפיים מותאמים אישית עם AGSL.
אפקטים גרפיים בהתאמה אישית באמצעות AGSL
ב-Android 16 נוספו RuntimeColorFilter ו-RuntimeXfermode, שמאפשרים ליצור אפקטים מורכבים כמו Threshold, Sepia ו-Hue Saturation ולהחיל אותם על קריאות לציור. החל מגרסה Android 13, אפשר להשתמש ב-AGSL כדי ליצור RuntimeShaders בהתאמה אישית שמרחיבים את Shader. ה-API החדש משקף את זה, ומוסיף את RuntimeColorFilter שמבוסס על AGSL ומרחיב את ColorFilter, ואת האפקט Xfermode שמאפשר להטמיע שילוב והתאמה אישית מבוססי AGSL בין פיקסלים של מקור ליעד.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
קישוריות
ב-Android 16, הפלטפורמה מתעדכנת כדי לתת לאפליקציה שלכם גישה לחידושים האחרונים בטכנולוגיות תקשורת וטכנולוגיות אלחוטיות.
טווח עם אבטחה משופרת
ב-Android 16 נוספה תמיכה בתכונות אבטחה חזקות במיקום Wi-Fi במכשירים נתמכים עם 802.11az של Wi-Fi 6. התכונות האלה מאפשרות לאפליקציות לשלב בין הדיוק הגבוה יותר, יכולת ההתאמה לעומס הגדולה יותר והתזמון הדינמי של הפרוטוקול עם שיפורים באבטחה, כולל הצפנה מבוססת AES-256 והגנה מפני התקפות MITM. כך אפשר להשתמש בה בבטחה רבה יותר בתרחישי שימוש בסביבה הקרובה, כמו ביטול הנעילה של מחשב נייד או של דלת רכב. 802.11az משתלב בתקן Wi-Fi 6, ומשתמש בתשתית וביכולות שלו כדי לאפשר הטמעה רחבה יותר ופריסה קלה יותר.
ממשקי API כלליים של טווחים
Android 16 כולל את RangingManager החדש, שמספק דרכים לקבוע את המרחק והזווית בחומרה נתמכת בין המכשיר המקומי למכשיר מרוחק. RangingManager תומך במגוון טכנולוגיות למדידת מרחק, כמו בדיקת ערוץ BLE, מדידת מרחק מבוססת RSSI ב-BLE, Ultra Wideband וזמן נסיעה הלוך ושוב ב-Wi-Fi.
נוכחות של מכשיר נלווה
ב-Android 16 נוספו ממשקי API חדשים לקישור של שירות האפליקציה הנלווית. השירות יקושר כש-BLE נמצא בטווח וחיבור ה-Bluetooth פועל, והוא ינותק כש-BLE יהיה מחוץ לטווח או כשחיבור ה-Bluetooth ינותק. האפליקציה תקבל קריאה חוזרת חדשה מסוג 'onDevicePresenceEvent()' על סמך ערכים שונים של DevicePresenceEvent.
פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר 'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
מדיה
Android 16 כולל מגוון תכונות שמשפרות את חוויית המדיה.
שיפורים בכלי לבחירת תמונות
הכלי לבחירת תמונות מספק למשתמשים דרך מובנית ובטוחה להעניק לאפליקציה גישה לתמונות ולסרטונים שנבחרו, גם מהאחסון המקומי וגם מהענן, במקום לגישה לכל ספריית המדיה שלהם. באמצעות שילוב של רכיבי מערכת מודולריים דרך Google System Updates ו-Google Play Services, התכונה נתמכת כבר מ-Android 4.4 (רמת API 19). לשילוב נדרשות רק כמה שורות קוד עם ספריית Android Jetpack המשויכת.
ב-Android 16 נוספו לשולחן הבחירה של התמונות השיפורים הבאים:
- בורר תמונות מוטמע: ממשקי API חדשים שמאפשרים לאפליקציות להטמיע את הבורר בתוך היררכיית התצוגה שלהן. כך הוא מרגיש כמו חלק משולב יותר באפליקציה, ועדיין מנצל את בידוד התהליכים שמאפשר למשתמשים לבחור מדיה בלי שהאפליקציה תצטרך הרשאות רחבות מדי. כדי למקסם את התאימות לגרסאות השונות של הפלטפורמה ולפשט את השילוב, אם אתם רוצים לשלב את הכלי המוטמע לבחירת תמונות, כדאי להשתמש בספרייה העתידית של Android Jetpack.
- חיפוש בענן בבורר התמונות: ממשקי API חדשים שמאפשרים חיפוש מספק המדיה בענן בבורר התמונות של Android. בקרוב נוסיף פונקציית חיפוש לבורר התמונות.
Advanced Professional Video
ב-Android 16 נוספה תמיכה בקודק Advanced Professional Video (APV), שנועד לשימוש ברמה מקצועית להקלטת וידאו באיכות גבוהה ולפוסט-פרודקשן.
תקן הקודק APV כולל את התכונות הבאות:
- איכות וידאו ללא אובדן מידע נתפס (קרוב לאיכות וידאו גולמי)
- קידוד בתוך פריים בלבד (ללא חיזוי של תחום הפיקסלים) עם מורכבות נמוכה ונתונים רבים, כדי לתמוך טוב יותר בתהליכי עבודה של עריכה
- תמיכה בטווח של קצב ביט גבוה עד כמה Gbps לתוכן ברזולוציות 2K, 4K ו-8K, באמצעות סכימה קלה של קידוד אנטרופי
- יצירת משבצות של פריימים לתוכן immersive ולאפשרות קידוד ופענוח במקביל
- תמיכה בפורמטים שונים של דגימת צבע ובעומק ביט שונים
- תמיכה במספר פענוחים וקידוד מחדש ללא פגיעה משמעותית באיכות החזותית
- תמיכה בסרטונים של צפייה בכמה משחקים בו-זמנית ובסרטונים משניים כמו סרטוני עומק, סרטוני אלפא וסרטוני תצוגה מקדימה
- תמיכה ב-HDR10/10+ ובמטא-נתונים מוגדרים על ידי משתמשים
יישום עזר של APV זמין דרך פרויקט OpenAPV. ב-Android 16 תהיה תמיכה בפרופיל APV 422-10, שמספק דגימת צבע YUV 422 עם קידוד 10 ביט, וקצב נתונים יעד של עד 2Gbps.
פרטיות
Android 16 כולל מגוון תכונות שעוזרות למפתחי אפליקציות להגן על פרטיות המשתמשים.
עדכונים של Health Connect
Health Connect מוסיף את הערך ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, סוג נתונים שמוגדר בהתאם להנחיות של ארגון הבריאות העולמי לגבי פעילות מתונה ופעילות מאומצת. בכל רשומה צריך לציין את שעת ההתחלה, שעת הסיום ואת מידת העצימות של הפעילות (מתונה או נמרצת).
Health Connect מכיל גם ממשקי API מעודכנים שתומכים בתיקים רפואיים. כך אפליקציות יכולות לקרוא ולכתוב תיעוד רפואי בפורמט FHIR עם הסכמה מפורשת של המשתמשים.
ארגז החול לפרטיות ב-Android
גרסת Android 16 כוללת את הגרסה העדכנית ביותר של ארגז החול לפרטיות ב-Android, כחלק מהעבודה המתמשכת שלנו לפיתוח טכנולוגיות שמאפשרות למשתמשים לדעת שהפרטיות שלהם מוגנת. באתר שלנו יש מידע נוסף על 'ארגז החול לפרטיות' בתוכנית הבטא למפתחי Android, שיעזור לכם להתחיל. כדאי לבדוק את זמן הריצה ל-SDK, שמאפשר לערכות SDK לפעול בסביבת זמן ריצה ייעודית בנפרד מהאפליקציה שבה הן פועלות, ומספק אמצעי הגנה חזקים יותר בנושא איסוף ושיתוף של נתוני משתמשים.
אבטחה
Android 16 כולל תכונות שעוזרות לשפר את האבטחה של האפליקציה ולהגן על הנתונים שלה.
Key sharing API
ב-Android 16 נוספו ממשקי API שתומכים בשיתוף הגישה למפתחות של Android Keystore עם אפליקציות אחרות. הכיתה החדשה KeyStoreManager תומכת בהענקת וביטול גישה למפתחות לפי uid של האפליקציה, וכוללת API לאפליקציות כדי לגשת למפתחות משותפים.
גורמי צורה של מכשירים
Android 16 מספק לאפליקציות שלכם תמיכה שתאפשר לכם להפיק את המרב מגורמי הצורה של Android.
מסגרת תקנים לאיכות התמונה והאודיו בטלוויזיות
חבילת MediaQuality החדשה ב-Android 16 חושפת קבוצה של ממשקי API סטנדרטיים לגישה לפרופילים של אודיו ותמונות ולהגדרות שקשורות לחומרה. כך אפליקציות סטרימינג יכולות לבצע שאילתות על פרופילים ולהחיל אותם על מדיה באופן דינמי:
- בסרטים שעברו עיבוד עם טווח דינמי רחב יותר, נדרשת רמת דיוק גבוהה יותר של צבעים כדי לראות פרטים עדינים בצללים ולהתאים את התמונה לאור הסביבה. לכן, יכול להיות שתתאים הגדרת פרופיל שמעדיפה דיוק צבעים על פני בהירות.
- לעיתים קרובות, אירועי ספורט בשידור חי עוברים עיבוד עם טווח דינמי צר, אבל לרוב צופים בהם באור יום, ולכן פרופיל שמעדיף בהירות על פני דיוק צבעים יכול להניב תוצאות טובות יותר.
- כדי להציג תוכן אינטראקטיבי מלא, צריך עיבוד מינימלי כדי לצמצם את זמן האחזור, ושיעור פריימים גבוה יותר. לכן, טלוויזיות רבות מגיעות עם פרופיל משחק.
ה-API מאפשר לאפליקציות לעבור בין פרופילים, ולמשתמשים ליהנות מהתאמה של טלוויזיות נתמכות לתוכן שלהם.
אינטרנציונליזציה
ב-Android 16 נוספו תכונות ויכולות שמשלימות את חוויית המשתמש כשמשתמשים במכשיר בשפות שונות.
טקסט אנכי
ב-Android 16 נוספה תמיכה ברמה נמוכה ברינדור ובמדידה של טקסט אנכית, כדי לספק לתכנת הספריות תמיכה בסיסית בכתיבה אנכית. האפשרות הזו שימושית במיוחד בשפות כמו יפנית, שבהן נעשה שימוש נפוץ בכתב אנכי. הוספנו דגל חדש, VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG, לכיתה Paint. כשהדגל הזה מוגדר באמצעות Paint.setFlags, ממשקי ה-API למדידת טקסט של Paint ידווחו על התקדמות אנכית במקום על התקדמות אופקית, ו-Canvas ידפיס טקסט באופן אנכי.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
התאמה אישית של יחידות המידה
עכשיו המשתמשים יכולים להתאים אישית את מערכת המדידה שלהם בהעדפות האזוריות שבקטע 'הגדרות'. העדפת המשתמש כלולה בקוד הלוקאל, כך שאפשר לרשום אירוע BroadcastReceiver ב-ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED כדי לטפל בשינויים בהגדרות הלוקאל כשהעדפות האזור משתנות.
שימוש בפורמטרים יכול לעזור להתאים את החוויה המקומית. לדוגמה, הערך '0.5 in' באנגלית (ארה"ב) הוא '12.7 mm' אצל משתמש שהגדיר את הטלפון לאנגלית (דנמרק) או משתמש שמשתמש בטלפון באנגלית (ארה"ב) עם המערכת המטרית כמערכת המדידה המועדפת.
כדי למצוא את ההגדרות האלה, פותחים את אפליקציית ההגדרות ועוברים אל מערכת > שפות ואזור.
