Android 16 memperkenalkan fitur dan API baru yang hebat untuk para developer. Bagian berikut merangkum fitur ini untuk membantu Anda mulai menggunakan API terkait.
Untuk melihat daftar mendetail tentang API yang baru, diubah, dan dihapus, baca laporan perbedaan API. Untuk mengetahui detail tentang API baru, buka referensi API Android — API baru ditandai agar lebih mudah dilihat.Anda juga harus meninjau area tempat perubahan platform dapat memengaruhi aplikasi Anda. Untuk informasi selengkapnya, lihat halaman berikut:
- Perubahan perilaku yang memengaruhi aplikasi saat menargetkan Android 16
- Perubahan perilaku yang memengaruhi semua aplikasi terlepas dari
targetSdkVersion.
Fungsi inti
Android menyertakan API baru yang memperluas kemampuan inti sistem Android.
Dua rilis Android API pada tahun 2025
- Pratinjau ini ditujukan untuk rilis utama Android berikutnya dengan peluncuran yang direncanakan pada Kuartal 2 2025. Rilis ini mirip dengan semua rilis API kami sebelumnya, yang memungkinkan kita memiliki perubahan perilaku terencana yang sering kali terkait dengan targetSdkVersion.
- Kami merencanakan rilis utama satu kuartal lebih awal (K2, bukan K3 pada tahun sebelumnya) agar lebih selaras dengan jadwal peluncuran perangkat di seluruh ekosistem kami, sehingga lebih banyak perangkat dapat mendapatkan rilis utama Android lebih cepat. Dengan rilis utama yang akan datang pada Kuartal 2, Anda harus melakukan pengujian kompatibilitas tahunan beberapa bulan lebih awal dari tahun-tahun sebelumnya untuk memastikan aplikasi Anda siap.
- Kami berencana untuk merilis versi lain pada Kuartal 4 tahun 2025 yang juga akan menyertakan API developer baru. Rilis utama K2 akan menjadi satu-satunya rilis pada tahun 2025 yang menyertakan perubahan perilaku terencana yang dapat memengaruhi aplikasi.
Selain API developer baru, rilis minor K4 akan mengambil update fitur, pengoptimalan, dan perbaikan bug; rilis ini tidak akan menyertakan perubahan perilaku yang memengaruhi aplikasi.
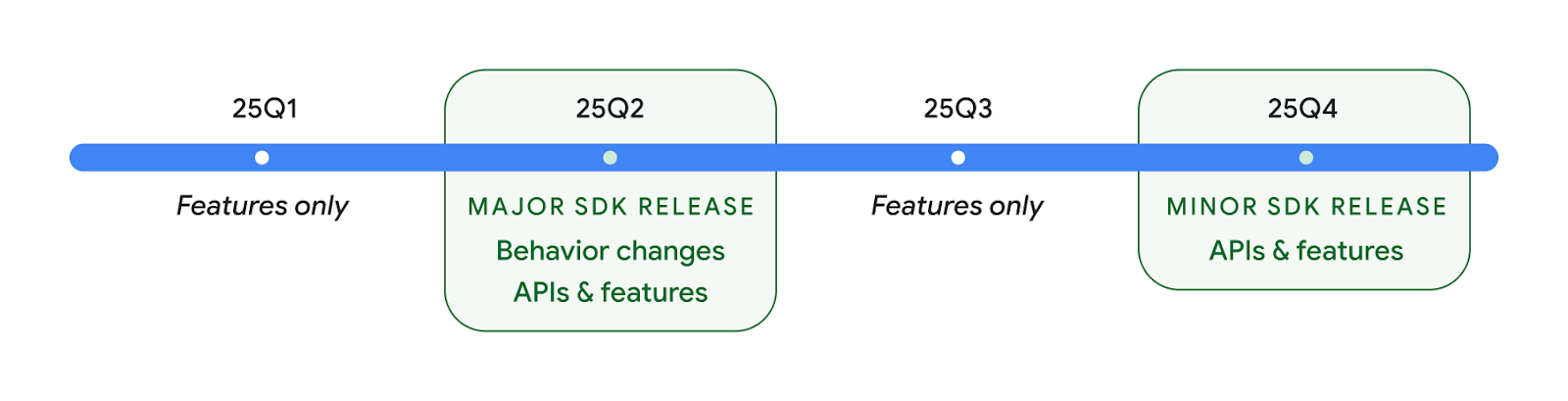
Kami akan terus merilis Android setiap tiga bulan sekali. Update Kuartal 1 dan Kuartal 3 di antara rilis API akan memberikan update inkremental untuk membantu memastikan kualitas yang berkelanjutan. Kami secara aktif bekerja sama dengan partner perangkat untuk menghadirkan rilis Q2 ke sebanyak mungkin perangkat.
Menggunakan API baru dengan rilis utama dan minor
Melindungi blok kode dengan pemeriksaan API level dilakukan saat ini menggunakan
konstanta SDK_INT dengan
VERSION_CODES. Fitur ini akan terus
didukung untuk rilis Android utama.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
Konstanta SDK_INT_FULL
baru dapat digunakan untuk pemeriksaan API terhadap versi utama dan minor dengan
enumerasi VERSION_CODES_FULL
baru.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
Anda juga dapat menggunakan metode
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
untuk mendapatkan versi SDK minor saja.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
API ini belum selesai dan dapat berubah sewaktu-waktu. Jadi, kirimkan masukan kepada kami jika Anda memiliki masalah.
Pengalaman pengguna dan UI sistem
Android 16 memberi developer dan pengguna aplikasi kontrol dan fleksibilitas yang lebih besar untuk mengonfigurasi perangkat agar sesuai dengan kebutuhan mereka.
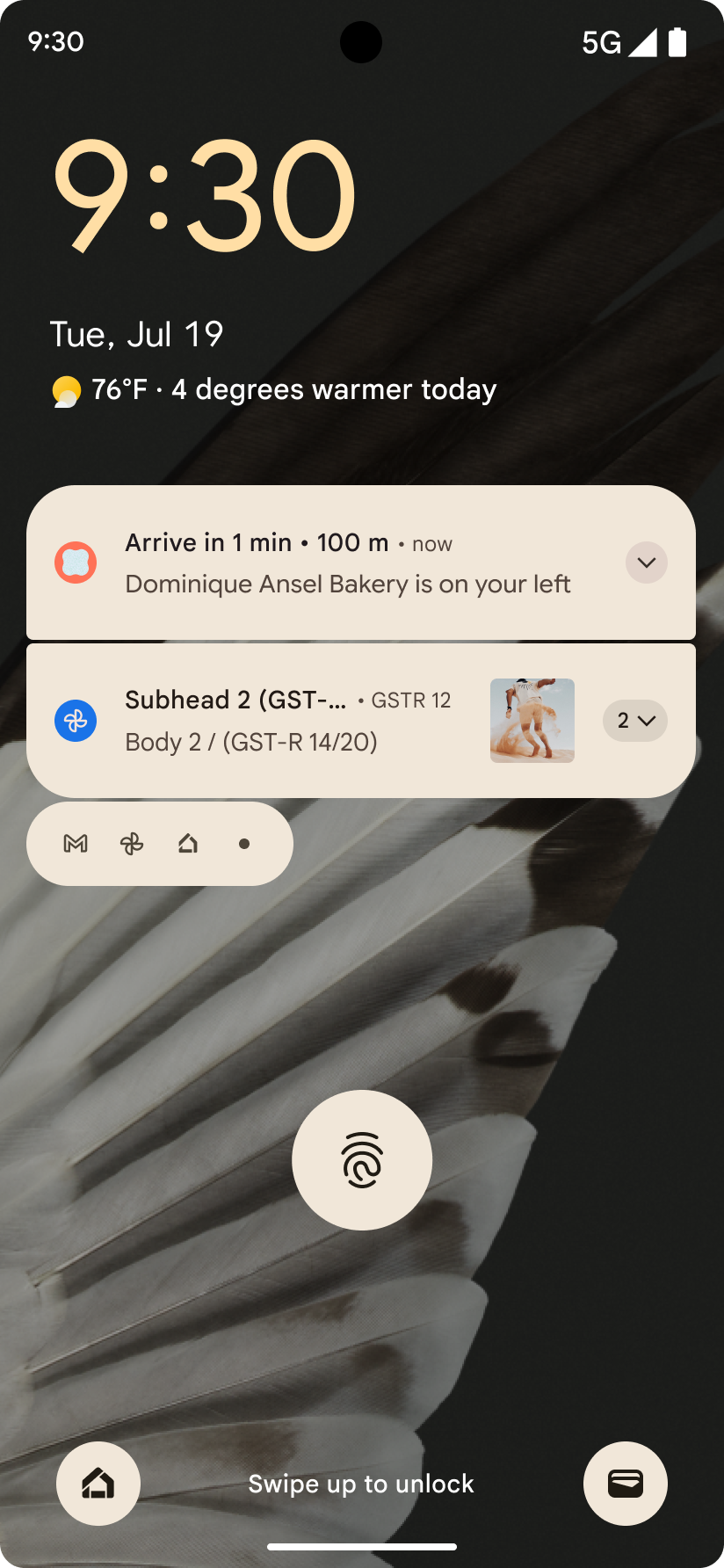
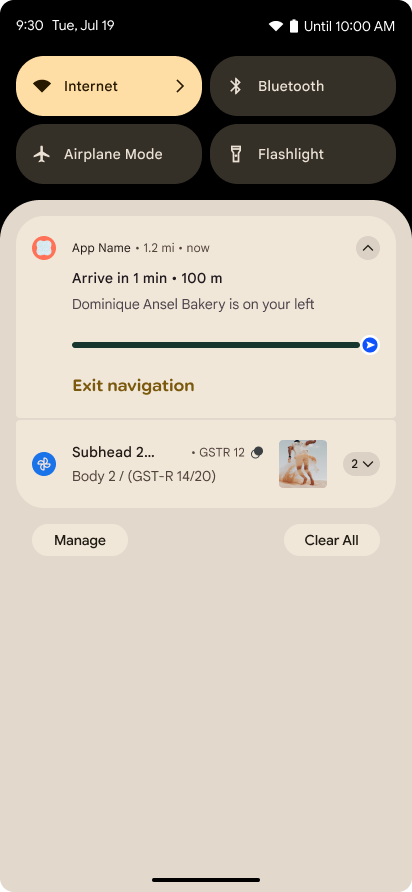
Notifikasi yang berfokus pada progres
Android 16 introduces progress-centric notifications to help users seamlessly track user-initiated, start-to-end journeys.
Notification.ProgressStyle is a new notification
style that lets you create progress-centric notifications. Key use cases include
rideshare, delivery, and navigation. Within the Notification.ProgressStyle
class, you can denote states and milestones in a user journey using
points and segments.
Untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut, lihat halaman dokumentasi Notifikasi yang berfokus pada progres.
Pembaruan kembali prediktif
Android 16 adds new APIs to help you enable predictive back system animations in
gesture navigation such as the back-to-home animation. Registering the
onBackInvokedCallback with the new
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER allows your app to
receive the regular onBackInvoked call whenever the
system handles a back navigation without impacting the normal back navigation
flow.
Android 16 additionally adds the
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() and
moveTaskToBackCallback. By registering these callbacks
with the OnBackInvokedDispatcher, the system can trigger
specific behaviors and play corresponding ahead-of-time animations when the back
gesture is invoked.
Haptik yang lebih kaya
Android has exposed control over the haptic actuator ever since its inception.
Android 11 added support for more complex haptic effects that more advanced
actuators could support through
VibrationEffect.Compositions of device-defined semantic
primitives.
Android 16 adds haptic APIs that let apps define the amplitude and frequency curves of a haptic effect while abstracting away differences between device capabilities.
Alat dan produktivitas developer
Meskipun sebagian besar upaya kami untuk meningkatkan produktivitas Anda berpusat pada alat seperti Android Studio, Jetpack Compose, dan library Android Jetpack, kami selalu mencari cara di platform untuk membantu Anda mewujudkan visi Anda.
Penanganan konten untuk wallpaper animasi
Di Android 16, framework wallpaper animasi mendapatkan API konten baru untuk
mengatasi tantangan wallpaper dinamis yang didorong pengguna. Saat ini, wallpaper
live yang menggabungkan konten yang disediakan pengguna memerlukan penerapan
khusus layanan yang kompleks. Android 16 memperkenalkan
WallpaperDescription dan
WallpaperInstance. WallpaperDescription memungkinkan Anda
mengidentifikasi instance wallpaper animasi yang berbeda dari layanan yang sama. Misalnya, wallpaper yang memiliki instance di layar utama dan layar
kunci mungkin memiliki konten unik di kedua tempat tersebut. Pemilih wallpaper dan
WallpaperManager menggunakan metadata ini untuk menampilkan
wallpaper dengan lebih baik kepada pengguna, sehingga menyederhanakan proses bagi Anda untuk membuat pengalaman wallpaper hidup yang beragam dan
dipersonalisasi.
Performa dan baterai
Android 16 memperkenalkan API yang membantu mengumpulkan insight tentang aplikasi Anda.
Pembuatan profil yang dipicu sistem
ProfilingManager was
added in Android 15, giving apps the ability to
request profiling data collection using Perfetto on public devices in the field.
However, since this profiling must be started from the app, critical flows such
as startups or ANRs would be difficult or impossible for apps to capture.
To help with this, Android 16 introduces system-triggered profiling to
ProfilingManager. Apps can register interest in receiving traces for certain
triggers such as cold start reportFullyDrawn
or ANRs, and then the system starts and stops a trace on the app's behalf. After
the trace completes, the results are delivered to the app's data directory.
Komponen awal di ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo ditambahkan di Android
15, yang memungkinkan aplikasi melihat alasan
awal proses, jenis awal, waktu mulai, throttling, dan data diagnostik
berguna lainnya. Android 16 menambahkan
getStartComponent()
untuk membedakan jenis komponen yang memicu awal, yang dapat membantu
mengoptimalkan alur startup aplikasi Anda.
Introspeksi tugas yang lebih baik
The JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API returns a reason why a job
might be pending. However, a job might be pending for multiple reasons.
In Android 16, we are introducing a new API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId), which returns multiple
reasons why a job is pending, due to both explicit constraints set by the
developer and implicit constraints set by the system.
We're also introducing
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId), which returns a list
of the most recent constraint changes.
We recommend using the API to help you debug why your jobs may not be executing, especially if you're seeing reduced success rates of certain tasks or have bugs around latency of certain job completion. For example, updating widgets in the background failed to occur or prefetch job failed to be called prior to app start.
This can also better help you understand if certain jobs are not completing due to system defined constraints versus explicitly set constraints.
Kecepatan refresh adaptif
Adaptive refresh rate (ARR), introduced in Android 15, enables the display refresh rate on supported hardware to adapt to the content frame rate using discrete VSync steps. This reduces power consumption while eliminating the need for potentially jank-inducing mode-switching.
Android 16 introduces hasArrSupport() and
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) while restoring
getSupportedRefreshRates() to make it easier for your apps to take
advantage of ARR. RecyclerView
1.4 internally supports ARR when it is settling from a fling or
smooth scroll, and we're continuing our work to add ARR
support into more Jetpack libraries. This frame rate article covers
many of the APIs you can use to set the frame rate so that your app can directly
use ARR.
API ruang kosong di ADPF
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
Aksesibilitas
Android 16 menambahkan API dan fitur aksesibilitas baru yang dapat membantu Anda menghadirkan aplikasi kepada setiap pengguna.
API aksesibilitas yang ditingkatkan
Android 16 adds additional APIs to enhance UI semantics that help improve consistency for users that rely on accessibility services, such as TalkBack.
Outline text for maximum text contrast
Users with low vision often have reduced contrast sensitivity, making it challenging to distinguish objects from their backgrounds. To help these users, Android 16 introduces outline text, replacing high contrast text, which draws a larger contrasting area around text to greatly improve legibility.
Android 16 contains new AccessibilityManager APIs to let
your apps check or register a listener to
see if this mode is enabled. This is primarily for UI Toolkits like Compose to
offer a similar visual experience. If you maintain a UI Toolkit library or your
app performs custom text rendering that bypasses the
android.text.Layout class then you can use this to know
when outline text is enabled.
Duration added to TtsSpan
Android 16 extends TtsSpan with a TYPE_DURATION,
consisting of ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES,
and ARG_SECONDS. This lets you directly annotate time
duration, ensuring accurate and consistent text-to-speech output with services
like TalkBack.
Support elements with multiple labels
Android currently allows UI elements to derive their accessibility label from
another, and now offers the ability for multiple labels to be associated, a
common scenario in web content. By introducing a list-based API within
AccessibilityNodeInfo, Android can directly support these
multi-label relationships. As part of this change, we've deprecated
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy and
#getLabeledBy in favor of
#addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy, and
#getLabeledByList.
Improved support for expandable elements
Android 16 adds accessibility APIs that allow you to convey the expanded or
collapsed state of interactive elements, such as menus and expandable lists. By
setting the expanded state using setExpandedState and
dispatching TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
with a CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED content change type,
you can ensure that screen readers like TalkBack announce
state changes, providing a more intuitive and inclusive user experience.
Indeterminate ProgressBars
Android 16 adds RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, giving a way for
you to expose RangeInfo for both determinate and
indeterminate ProgressBar widgets, allowing services like
TalkBack to more consistently provide feedback for progress
indicators.
Tri-state CheckBox
The new AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked and setChecked(int)
methods in Android 16 now support a "partially checked" state in addition to
"checked" and "unchecked." This replaces the deprecated boolean
isChecked and setChecked(boolean).
Supplemental descriptions
When an accessibility service describes a ViewGroup, it
combines content labels from its child views. If you provide a
contentDescription for the ViewGroup, accessibility services assume you are
also overriding the description of non-focusable child views. This can be
problematic if you want to label things like a drop-down (for example, "Font
Family") while preserving the current selection for accessibility (for example,
"Roboto"). Android 16 adds setSupplementalDescription so
you can provide text that provides information about a ViewGroup without
overriding information from its children.
Required form fields
Android 16 adds setFieldRequired to
AccessibilityNodeInfo so apps can tell an accessibility
service that input to a form field is required. This is an important scenario
for users filling out many types of forms, even things as simple as a required
terms and conditions checkbox, helping users to consistently identify and
quickly navigate between required fields.
Ponsel sebagai input mikrofon untuk panggilan suara dengan alat bantu dengar LEA
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to switch between the built-in microphones on the hearing aids and the microphone on their phone for voice calls. This can be helpful in noisy environments or other situations where the hearing aid's microphones might not perform well.
Kontrol volume sekitar untuk alat bantu dengar LEA
Android 16 menambahkan kemampuan bagi pengguna alat bantu dengar LE Audio untuk menyesuaikan volume suara sekitar yang ditangkap oleh mikrofon alat bantu dengar. Hal ini dapat membantu dalam situasi saat suara bising di latar belakang terlalu keras atau terlalu pelan.
Kamera
Android 16 meningkatkan dukungan untuk pengguna kamera profesional, sehingga memungkinkan eksposur otomatis hybrid bersama dengan penyesuaian suhu warna dan tint yang akurat. Indikator mode malam baru membantu aplikasi Anda mengetahui kapan harus beralih ke dan dari sesi kamera mode malam. Tindakan Intent baru mempermudah pengambilan foto bergerak, dan kami terus meningkatkan kualitas gambar UltraHDR dengan dukungan untuk encoding HEIC dan parameter baru dari draf standar ISO 21496-1.
Eksposur otomatis hybrid
Android 16 adds new hybrid auto-exposure modes to Camera2, allowing you to manually control specific aspects of exposure while letting the auto-exposure (AE) algorithm handle the rest. You can control ISO + AE, and exposure time + AE, providing greater flexibility compared to the current approach where you either have full manual control or rely entirely on auto-exposure.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
Penyesuaian tint dan color temperature yang presisi
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





Deteksi adegan mode malam kamera
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
Tindakan intent pengambilan foto motion
Android 16 adds standard Intent actions —
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE, and
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE — which request that
the camera application capture a motion photo and return
it.
You must either pass an extra EXTRA_OUTPUT to control
where the image will be written, or a Uri through
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). If you don't set a
ClipData, it will be copied there for you when calling
Context.startActivity(Intent).
Peningkatan gambar UltraHDR

Android 16 continues our work to deliver dazzling image quality with UltraHDR
images. It adds support for UltraHDR images in the HEIC file
format. These images will get ImageFormat type
HEIC_ULTRAHDR and will contain an embedded gainmap similar
to the existing UltraHDR JPEG format. We're working on AVIF support for UltraHDR
as well, so stay tuned.
In addition, Android 16 implements additional parameters in UltraHDR from the ISO 21496-1 draft standard, including the ability to get and set the colorspace that gainmap math should be applied in, as well as support for HDR encoded base images with SDR gainmaps.
Grafik
Android 16 menyertakan peningkatan grafis terbaru, seperti efek grafis kustom dengan AGSL.
Efek grafis kustom dengan AGSL
Android 16 adds RuntimeColorFilter and
RuntimeXfermode, allowing you to author complex effects like
Threshold, Sepia, and Hue Saturation and apply them to draw calls. Since Android
13, you've been able to use AGSL to create custom
RuntimeShaders that extend Shader. The new API
mirrors this, adding an AGSL-powered RuntimeColorFilter that
extends ColorFilter, and a Xfermode effect that
lets you implement AGSL-based custom compositing and blending between source and
destination pixels.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
Konektivitas
Android 16 mengupdate platform untuk memberi aplikasi Anda akses ke kemajuan terbaru dalam teknologi nirkabel dan komunikasi.
Pengukuran jarak dengan keamanan yang ditingkatkan
Android 16 adds support for robust security features in Wi-Fi location on supported devices with Wi-Fi 6's 802.11az, allowing apps to combine the higher accuracy, greater scalability, and dynamic scheduling of the protocol with security enhancements including AES-256-based encryption and protection against MITM attacks. This allows it to be used more safely in proximity use cases, such as unlocking a laptop or a vehicle door. 802.11az is integrated with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, leveraging its infrastructure and capabilities for wider adoption and easier deployment.
API pengukuran jarak generik
Android 16 includes the new RangingManager, which provides
ways to determine the distance and angle on supported hardware between the local
device and a remote device. RangingManager supports the usage of a variety of
ranging technologies such as BLE channel sounding, BLE RSSI-based ranging, Ultra
Wideband, and Wi-Fi round trip time.
Kehadiran perangkat pengelola perangkat pendamping
In Android 16, new APIs are being introduced for binding your companion app
service. Service will be bound when BLE is in range and Bluetooth is connected
and service will be unbound when BLE is out of range or Bluetooth is
disconnected. App will receives a new
'onDevicePresenceEvent()' callback based on various
of DevicePresenceEvent.
More details can be found in
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
Media
Android 16 menyertakan berbagai fitur yang meningkatkan pengalaman media.
Peningkatan pemilih foto
The photo picker provides a safe, built-in way for users to grant your app access to selected images and videos from both local and cloud storage, instead of their entire media library. Using a combination of Modular System Components through Google System Updates and Google Play services, it's supported back to Android 4.4 (API level 19). Integration requires just a few lines of code with the associated Android Jetpack library.
Android 16 includes the following improvements to the photo picker:
- Embedded photo picker: New APIs that enable apps to embed the photo picker into their view hierarchy. This allows it to feel like a more integrated part of the app while still leveraging the process isolation that allows users to select media without the app needing overly broad permissions. To maximize compatibility across platform versions and simplify your integration, you'll want to use the forthcoming Android Jetpack library if you want to integrate the embedded photo picker.
- Cloud search in photo picker: New APIs that enable searching from the cloud media provider for the Android photo picker. Search functionality in the photo picker is coming soon.
Video Profesional Lanjutan
Android 16 introduces support for the Advanced Professional Video (APV) codec which is designed to be used for professional level high quality video recording and post production.
The APV codec standard has the following features:
- Perceptually lossless video quality (close to raw video quality)
- Low complexity and high throughput intra-frame-only coding (without pixel domain prediction) to better support editing workflows
- Support for high bit-rate range up to a few Gbps for 2K, 4K and 8K resolution content, enabled by a lightweight entropy coding scheme
- Frame tiling for immersive content and for enabling parallel encoding and decoding
- Support for various chroma sampling formats and bit-depths
- Support for multiple decoding and re-encoding without severe visual quality degradation
- Support multi-view video and auxiliary video like depth, alpha, and preview
- Support for HDR10/10+ and user-defined metadata
A reference implementation of APV is provided through the OpenAPV project. Android 16 will implement support for the APV 422-10 Profile that provides YUV 422 color sampling along with 10-bit encoding and for target bitrates of up to 2Gbps.
Privasi
Android 16 menyertakan berbagai fitur yang membantu developer aplikasi melindungi privasi pengguna.
Update Health Connect
Health Connect adds ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, a data type defined according to World
Health Organization guidelines around moderate and vigorous activity. Each
record requires the start time, the end time, and whether the activity intensity
is moderate or vigorous.
Health Connect also contains updated APIs supporting medical records. This allows apps to read and write medical records in FHIR format with explicit user consent.
Privacy Sandbox di Android
Android 16 menggabungkan versi terbaru Privacy Sandbox di Android, yang merupakan bagian dari upaya berkelanjutan kami untuk mengembangkan teknologi yang memungkinkan pengguna mengetahui bahwa privasi mereka dilindungi. Situs kami memiliki informasi selengkapnya tentang program beta developer Privacy Sandbox di Android untuk membantu Anda memulai. Lihat Runtime SDK yang memungkinkan SDK berjalan di lingkungan runtime khusus yang terpisah dari aplikasi yang ditayangkan, sehingga memberikan pengamanan yang lebih kuat seputar pengumpulan dan pembagian data pengguna.
Keamanan
Android 16 menyertakan fitur yang membantu Anda meningkatkan keamanan aplikasi dan melindungi data aplikasi Anda.
API berbagi kunci
Android 16 adds APIs that support sharing access to
Android Keystore keys with other apps. The new
KeyStoreManager class supports
granting and revoking access to keys
by app uid, and includes an API for apps to access shared
keys.
Faktor bentuk perangkat
Android 16 memberikan dukungan bagi aplikasi Anda untuk mendapatkan manfaat maksimal dari faktor bentuk Android.
Framework kualitas gambar dan audio standar untuk TV
The new MediaQuality
package in Android 16 exposes
a set of standardized APIs for access to audio and picture profiles and
hardware-related settings. This allows streaming apps to query profiles and
apply them to media dynamically:
- Movies mastered with a wider dynamic range require greater color accuracy to see subtle details in shadows and adjust to ambient light, so a profile that prefers color accuracy over brightness may be appropriate.
- Live sporting events are often mastered with a narrow dynamic range, but are often watched in daylight, so a profile that preferences brightness over color accuracy can give better results.
- Fully interactive content wants minimal processing to reduce latency, and wants higher frame rates, which is why many TV's ship with a game profile.
The API allows apps to switch between profiles and users to enjoy tuning supported TVs to best suit their content.
Internasionalisasi
Android 16 menambahkan fitur dan kemampuan yang melengkapi pengalaman pengguna saat perangkat digunakan dalam bahasa yang berbeda.
Teks vertikal
Android 16 adds low-level support for rendering and measuring text vertically to
provide foundational vertical writing support for library developers. This is
particularly useful for languages like Japanese that commonly use vertical
writing systems. A new flag,
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG,
has been added to the Paint class. When
this flag is set using
Paint.setFlags, Paint's
text measurement APIs will report vertical advances instead of horizontal
advances, and Canvas will draw text
vertically.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
Penyesuaian sistem pengukuran
Users can now customize their measurement system in regional preferences within
Settings. The user preference is included as part of the locale code, so you can
register a BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED to handle locale configuration changes when
regional preferences change.
Using formatters can help match the local experience. For example, "0.5 in" in English (United States), is "12,7 mm" for a user who has set their phone to English (Denmark) or who uses their phone in English (United States) with the metric system as the measurement system preference.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & region.
