Android 16 mang đến cho nhà phát triển các tính năng và API mới tuyệt vời. Các phần sau đây tóm tắt những tính năng này để giúp bạn làm quen với các API liên quan.
Để biết danh sách chi tiết về các API mới, đã được sửa đổi, cũng như đã bị xoá, hãy đọc báo cáo điểm khác biệt về API. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về các API mới, hãy truy cập vào tài liệu tham khảo về API cho Android (các API mới được trình bày nổi bật).Bạn cũng nên xem xét những khía cạnh mà các thay đổi của nền tảng có thể ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng của bạn. Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem các trang sau:
- Các thay đổi về hành vi ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng khi ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16
- Các thay đổi về hành vi ảnh hưởng đến tất cả ứng dụng bất kể
targetSdkVersion.
Chức năng cốt lõi
Android có các API mới giúp mở rộng các chức năng cốt lõi của hệ thống Android.
Hai bản phát hành API Android vào năm 2025
- Bản xem trước này dành cho bản phát hành chính tiếp theo của Android, dự kiến sẽ ra mắt vào quý 2 năm 2025. Bản phát hành này tương tự như tất cả các bản phát hành API trước đây của chúng tôi, trong đó chúng tôi có thể có các thay đổi về hành vi theo kế hoạch thường liên kết với targetSdkVersion.
- Chúng tôi dự định phát hành bản phát hành lớn sớm hơn một quý (quý 2 thay vì quý 3 như các năm trước) để phù hợp hơn với lịch phát hành thiết bị trên hệ sinh thái của chúng tôi, nhờ đó, nhiều thiết bị có thể nhận được bản phát hành lớn của Android sớm hơn. Với bản phát hành chính sắp ra mắt vào quý 2, bạn cần tiến hành kiểm thử khả năng tương thích hằng năm sớm hơn vài tháng so với những năm trước để đảm bảo ứng dụng của bạn đã sẵn sàng.
- Chúng tôi dự định phát hành một bản phát hành khác vào Quý 4 năm 2025, trong đó cũng sẽ có các API mới dành cho nhà phát triển. Bản phát hành lớn quý 2 sẽ là bản phát hành duy nhất trong năm 2025 có chứa các thay đổi về hành vi theo kế hoạch có thể ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng.
Ngoài các API mới dành cho nhà phát triển, bản phát hành nhỏ quý 4 sẽ bao gồm các bản cập nhật tính năng, bản tối ưu hoá và bản sửa lỗi; bản phát hành này sẽ không bao gồm bất kỳ thay đổi nào về hành vi ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng.
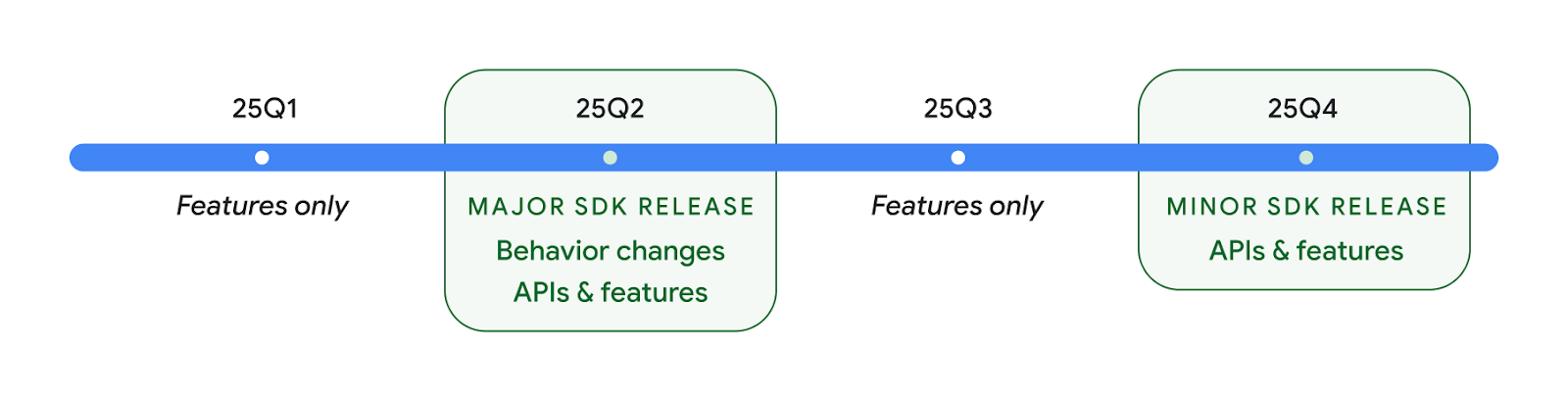
Chúng tôi sẽ tiếp tục phát hành Android theo quý. Các bản cập nhật vào Quý 1 và Quý 3 giữa các bản phát hành API sẽ cung cấp các bản cập nhật gia tăng để giúp đảm bảo chất lượng liên tục. Chúng tôi đang tích cực làm việc với các đối tác thiết bị để đưa bản phát hành quý 2 đến với nhiều thiết bị nhất có thể.
Sử dụng API mới với các bản phát hành chính và phụ
Ngày nay, bạn có thể bảo vệ một khối mã bằng cách kiểm tra cấp độ API bằng hằng số SDK_INT với VERSION_CODES. Chúng tôi sẽ tiếp tục hỗ trợ tính năng này cho các bản phát hành Android chính.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
Bạn có thể sử dụng hằng số SDK_INT_FULL mới để kiểm tra API dựa trên cả phiên bản chính và phiên bản phụ bằng cách liệt kê VERSION_CODES_FULL mới.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
Bạn cũng có thể sử dụng phương thức Build.getMinorSdkVersion() để chỉ nhận phiên bản SDK nhỏ.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
Các API này chưa được hoàn thiện và có thể thay đổi. Vì vậy, vui lòng gửi ý kiến phản hồi cho chúng tôi nếu bạn có bất kỳ mối lo ngại nào.
Trải nghiệm người dùng và giao diện người dùng hệ thống
Android 16 mang đến cho nhà phát triển ứng dụng và người dùng nhiều quyền kiểm soát và tính linh hoạt hơn khi định cấu hình thiết bị cho phù hợp với nhu cầu của họ.
Thông báo tập trung vào tiến trình
Android 16 ra mắt thông báo tập trung vào tiến trình để giúp người dùng theo dõi liền mạch hành trình từ đầu đến cuối do người dùng khởi tạo.
Notification.ProgressStyle là một kiểu thông báo mới cho phép bạn tạo thông báo tập trung vào tiến trình. Các trường hợp sử dụng chính bao gồm đi chung xe, giao hàng và chỉ đường. Trong lớp Notification.ProgressStyle, bạn có thể biểu thị các trạng thái và mốc quan trọng trong hành trình của người dùng bằng cách sử dụng điểm và phân đoạn.
Để tìm hiểu thêm, hãy xem trang tài liệu về Thông báo tập trung vào tiến trình.
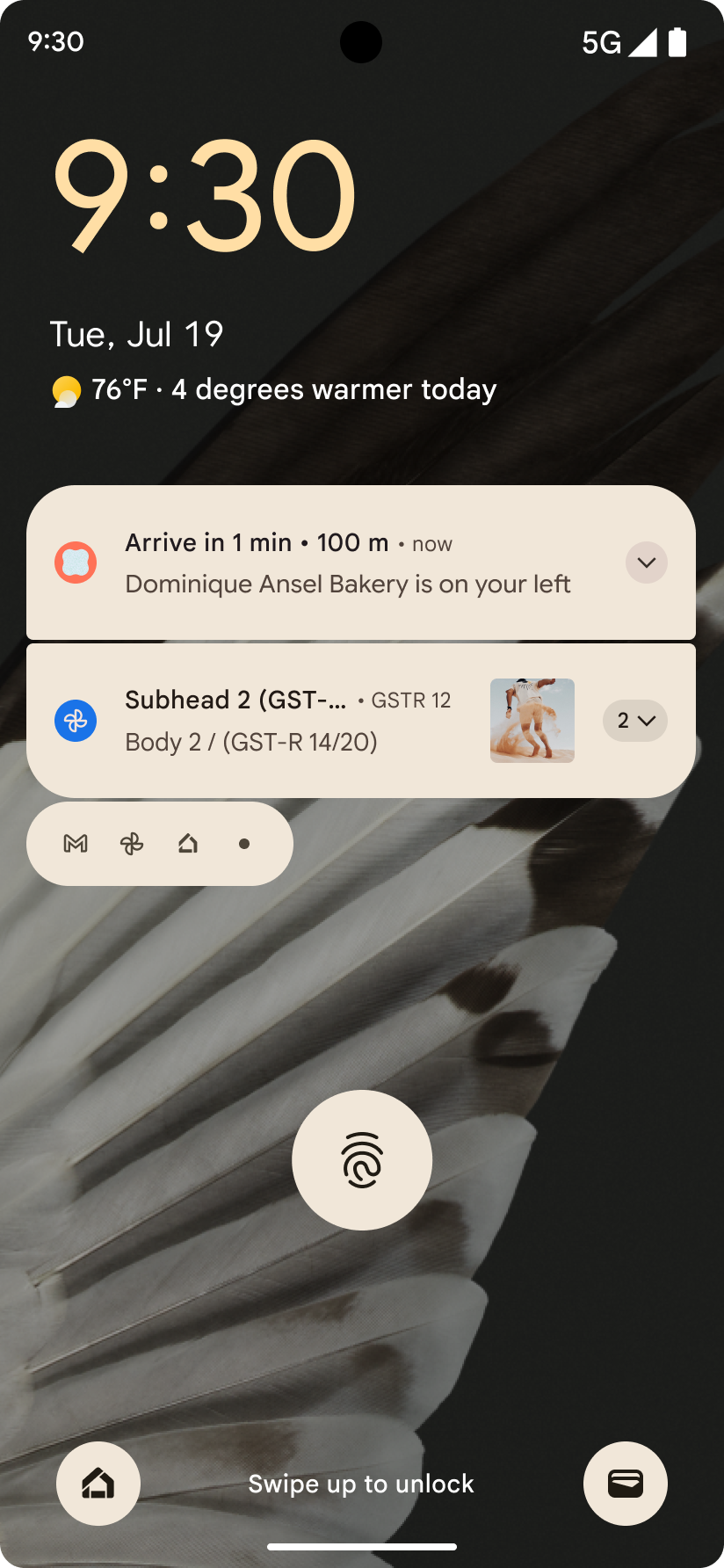
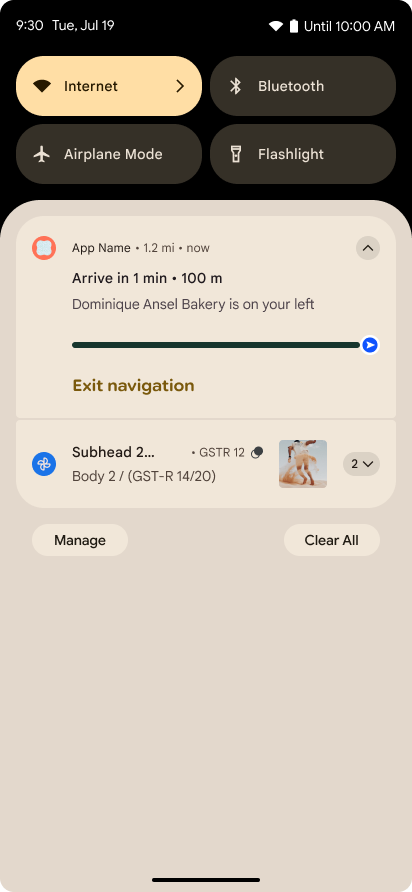
Thông tin cập nhật về tính năng xem trước thao tác quay lại
Android 16 bổ sung các API mới để giúp bạn bật ảnh động xem trước thao tác quay lại của hệ thống trong tính năng điều hướng bằng cử chỉ, chẳng hạn như ảnh động quay lại màn hình chính. Việc đăng ký onBackInvokedCallback bằng PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER mới cho phép ứng dụng của bạn nhận lệnh gọi onBackInvoked thông thường bất cứ khi nào hệ thống xử lý thao tác quay lại mà không ảnh hưởng đến luồng thao tác quay lại thông thường.
Android 16 cũng thêm finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() và moveTaskToBackCallback. Bằng cách đăng ký các lệnh gọi lại này với OnBackInvokedDispatcher, hệ thống có thể kích hoạt các hành vi cụ thể và phát ảnh động tương ứng trước khi thao tác vuốt ngược được gọi.
Phản hồi xúc giác phong phú hơn
Android đã hiển thị quyền kiểm soát đối với bộ truyền động xúc giác kể từ khi ra mắt.
Android 11 đã hỗ trợ thêm các hiệu ứng xúc giác phức tạp hơn mà các bộ truyền động nâng cao hơn có thể hỗ trợ thông qua VibrationEffect.Compositions của các nguyên hàm ngữ nghĩa do thiết bị xác định.
Android 16 thêm API xúc giác cho phép các ứng dụng xác định độ lớn và đường cong tần số của hiệu ứng xúc giác trong khi loại bỏ sự khác biệt giữa các chức năng của thiết bị.
Năng suất và công cụ dành cho nhà phát triển
Mặc dù hầu hết công việc của chúng tôi nhằm cải thiện hiệu suất của bạn đều tập trung vào các công cụ như Android Studio, Jetpack Compose và các thư viện Android Jetpack, nhưng chúng tôi luôn tìm cách giúp bạn hiện thực hoá ý tưởng của mình trên nền tảng này.
Xử lý nội dung cho hình nền động
Trong Android 16, khung hình nền động sẽ có một API nội dung mới để giải quyết các thách thức của hình nền động, do người dùng điều khiển. Hiện tại, các hình nền động kết hợp nội dung do người dùng cung cấp yêu cầu triển khai phức tạp, dành riêng cho dịch vụ. Android 16 giới thiệu WallpaperDescription và WallpaperInstance. WallpaperDescription cho phép bạn xác định các thực thể riêng biệt của hình nền động từ cùng một dịch vụ. Ví dụ: hình nền có các thực thể trên cả màn hình chính và màn hình khoá có thể có nội dung riêng biệt ở cả hai vị trí. Công cụ chọn hình nền và WallpaperManager sử dụng siêu dữ liệu này để trình bày hình nền tốt hơn cho người dùng, giúp đơn giản hoá quy trình để bạn tạo ra trải nghiệm hình nền động đa dạng và được cá nhân hoá.
Hiệu suất và pin
Android 16 giới thiệu các API giúp thu thập thông tin chi tiết về ứng dụng của bạn.
Lập hồ sơ do hệ thống kích hoạt
ProfilingManager được thêm vào Android 15, cho phép các ứng dụng yêu cầu thu thập dữ liệu phân tích tài nguyên bằng Perfetto trên các thiết bị công khai trong trường hợp thực tế.
Tuy nhiên, vì quá trình phân tích tài nguyên này phải bắt đầu từ ứng dụng, nên các luồng quan trọng như khởi động hoặc lỗi ANR sẽ khó hoặc không thể được ứng dụng ghi lại.
Để giúp giải quyết vấn đề này, Android 16 giới thiệu tính năng phân tích tài nguyên do hệ thống kích hoạt cho ProfilingManager. Các ứng dụng có thể đăng ký quan tâm đến việc nhận dấu vết cho một số trình kích hoạt nhất định, chẳng hạn như khởi động nguội reportFullyDrawn hoặc ANR, sau đó hệ thống sẽ bắt đầu và dừng dấu vết thay mặt cho ứng dụng. Sau khi quá trình theo dõi hoàn tất, kết quả sẽ được phân phối đến thư mục dữ liệu của ứng dụng.
Thành phần khởi động trong ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo được thêm vào Android 15, cho phép ứng dụng xem lý do khởi động quy trình, loại khởi động, thời gian khởi động, điều tiết và các dữ liệu chẩn đoán hữu ích khác. Android 16 thêm getStartComponent() để phân biệt loại thành phần nào đã kích hoạt quá trình khởi động. Điều này có thể hữu ích cho việc tối ưu hoá luồng khởi động của ứng dụng.
Khả năng tự xem xét công việc hiệu quả hơn
API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() trả về lý do khiến một công việc có thể đang chờ xử lý. Tuy nhiên, một công việc có thể đang chờ xử lý vì nhiều lý do.
Trong Android 16, chúng tôi sẽ ra mắt một API mới JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId). API này sẽ trả về nhiều lý do khiến một công việc đang chờ xử lý, do cả các quy tắc ràng buộc rõ ràng do nhà phát triển đặt ra và các quy tắc ràng buộc ngầm do hệ thống đặt ra.
Chúng tôi cũng sẽ ra mắt JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId). Phương thức này trả về danh sách các thay đổi gần đây nhất về quy tắc ràng buộc.
Bạn nên sử dụng API này để gỡ lỗi lý do các công việc của bạn có thể không thực thi, đặc biệt là nếu bạn thấy tỷ lệ thành công của một số tác vụ giảm hoặc gặp lỗi về độ trễ của một số công việc hoàn thành. Ví dụ: không cập nhật được tiện ích ở chế độ nền hoặc không gọi được công việc tìm nạp trước trước khi khởi động ứng dụng.
Điều này cũng có thể giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn liệu một số công việc nhất định có đang không hoàn tất do các quy tắc ràng buộc do hệ thống xác định hay do các quy tắc ràng buộc được đặt rõ ràng.
Tốc độ làm mới thích ứng
Tốc độ làm mới thích ứng (ARR), được giới thiệu trong Android 15, cho phép tốc độ làm mới màn hình trên phần cứng được hỗ trợ để thích ứng với tốc độ khung hình nội dung bằng cách sử dụng các bước VSync riêng biệt. Điều này giúp giảm mức tiêu thụ điện năng trong khi không cần phải chuyển đổi chế độ có thể gây ra hiện tượng giật.
Android 16 giới thiệu hasArrSupport() và getSuggestedFrameRate(int) trong khi khôi phục getSupportedRefreshRates() để giúp ứng dụng của bạn dễ dàng tận dụng ARR hơn. RecyclerView
1.4 hỗ trợ ARR nội bộ khi định vị từ một thao tác hất hoặc
cuộn mượt mà. Chúng tôi đang tiếp tục nỗ lực để thêm tính năng hỗ trợ
ARR vào nhiều thư viện Jetpack hơn. Bài viết về tốc độ khung hình này đề cập đến nhiều API mà bạn có thể sử dụng để đặt tốc độ khung hình để ứng dụng của bạn có thể trực tiếp sử dụng ARR.
Headroom API trong ADPF
SystemHealthManager giới thiệu các API getCpuHeadroom và getGpuHeadroom, được thiết kế để cung cấp cho các trò chơi và ứng dụng nặng về tài nguyên thông tin ước tính về tài nguyên CPU và GPU có sẵn. Các phương thức này giúp bạn đánh giá cách ứng dụng hoặc trò chơi của mình có thể cải thiện hiệu quả nhất trạng thái của hệ thống, đặc biệt là khi được sử dụng kết hợp với các API Khung hiệu suất động Android (ADPF) khác phát hiện tình trạng điều tiết nhiệt.
Bằng cách sử dụng CpuHeadroomParams và GpuHeadroomParams trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ, bạn có thể tuỳ chỉnh khoảng thời gian dùng để tính toán khoảng đầu vào và chọn giữa mức sử dụng tài nguyên trung bình hoặc tối thiểu. Điều này có thể giúp bạn giảm mức sử dụng tài nguyên CPU hoặc GPU cho phù hợp, mang lại trải nghiệm người dùng tốt hơn và cải thiện thời lượng pin.
Hỗ trợ tiếp cận
Android 16 bổ sung các API và tính năng hỗ trợ tiếp cận mới có thể giúp bạn đưa ứng dụng của mình đến với mọi người dùng.
API hỗ trợ tiếp cận được cải thiện
Android 16 bổ sung các API khác để nâng cao ngữ nghĩa giao diện người dùng, giúp cải thiện tính nhất quán cho những người dùng dựa vào các dịch vụ hỗ trợ tiếp cận, chẳng hạn như TalkBack.
Viền văn bản để tăng tối đa độ tương phản của văn bản
Người dùng có thị lực kém thường giảm độ nhạy cảm với độ tương phản, khiến họ khó phân biệt các đối tượng với nền. Để giúp những người dùng này, Android 16 ra mắt văn bản đường viền, thay thế văn bản có độ tương phản cao. Văn bản đường viền vẽ một vùng tương phản lớn hơn xung quanh văn bản để cải thiện đáng kể khả năng đọc.
Android 16 chứa các API AccessibilityManager mới để cho phép ứng dụng kiểm tra hoặc đăng ký trình nghe để xem chế độ này có được bật hay không. Điều này chủ yếu dành cho Bộ công cụ giao diện người dùng như Compose để mang lại trải nghiệm hình ảnh tương tự. Nếu duy trì thư viện Bộ công cụ giao diện người dùng hoặc ứng dụng của bạn thực hiện kết xuất văn bản tuỳ chỉnh bỏ qua lớp android.text.Layout, thì bạn có thể sử dụng lớp này để biết thời điểm bật văn bản đường viền.
Thêm thời lượng vào TtsSpan
Android 16 mở rộng TtsSpan bằng TYPE_DURATION, bao gồm ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES và ARG_SECONDS. Điều này cho phép bạn trực tiếp chú thích thời lượng, đảm bảo đầu ra chuyển văn bản sang lời nói chính xác và nhất quán với các dịch vụ như TalkBack.
Hỗ trợ các phần tử có nhiều nhãn
Android hiện cho phép các thành phần trên giao diện người dùng lấy nhãn hỗ trợ tiếp cận từ một thành phần khác và hiện cho phép liên kết nhiều nhãn, một tình huống phổ biến trong nội dung web. Bằng cách giới thiệu một API dựa trên danh sách trong AccessibilityNodeInfo, Android có thể hỗ trợ trực tiếp các mối quan hệ nhiều nhãn này. Trong quá trình thay đổi này, chúng tôi đã ngừng sử dụng AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy và #getLabeledBy thay vào đó là #addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy và #getLabeledByList.
Cải thiện khả năng hỗ trợ cho các phần tử có thể mở rộng
Android 16 thêm các API hỗ trợ tiếp cận cho phép bạn truyền tải trạng thái mở rộng hoặc thu gọn của các thành phần tương tác, chẳng hạn như trình đơn và danh sách có thể mở rộng. Bằng cách đặt trạng thái mở rộng bằng setExpandedState và gửi TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents với loại thay đổi nội dung CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED, bạn có thể đảm bảo rằng các trình đọc màn hình như TalkBack sẽ thông báo về các thay đổi trạng thái, mang lại trải nghiệm người dùng trực quan và toàn diện hơn.
Thanh tiến trình không xác định
Android 16 thêm RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, giúp bạn hiển thị RangeInfo cho cả tiện ích ProgressBar xác định và không xác định, cho phép các dịch vụ như TalkBack cung cấp phản hồi nhất quán hơn cho các chỉ báo tiến trình.
Hộp đánh dấu ba trạng thái
Các phương thức AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked và setChecked(int)
mới trong Android 16 hiện hỗ trợ trạng thái "đã đánh dấu một phần" ngoài trạng thái
"đã đánh dấu" và "chưa đánh dấu". Thao tác này sẽ thay thế boolean isChecked và setChecked(boolean) không dùng nữa.
Nội dung mô tả bổ sung
Khi mô tả ViewGroup, dịch vụ hỗ trợ tiếp cận sẽ kết hợp nhãn nội dung của các thành phần hiển thị con. Nếu bạn cung cấp contentDescription cho ViewGroup, các dịch vụ hỗ trợ tiếp cận sẽ giả định rằng bạn cũng đang ghi đè nội dung mô tả của các thành phần hiển thị con không thể làm tâm điểm. Điều này có thể gây ra vấn đề nếu bạn muốn gắn nhãn cho các mục như trình đơn thả xuống (ví dụ: "Font Family" (Gia đình phông chữ)) trong khi vẫn giữ nguyên lựa chọn hiện tại cho tính năng hỗ trợ tiếp cận (ví dụ: "Roboto"). Android 16 thêm setSupplementalDescription để bạn có thể cung cấp văn bản cung cấp thông tin về ViewGroup mà không ghi đè thông tin từ các thành phần con.
Các trường bắt buộc trên biểu mẫu
Android 16 thêm setFieldRequired vào AccessibilityNodeInfo để các ứng dụng có thể cho dịch vụ hỗ trợ tiếp cận biết rằng cần phải nhập vào trường biểu mẫu. Đây là một trường hợp quan trọng đối với người dùng khi điền vào nhiều loại biểu mẫu, ngay cả những trường hợp đơn giản như hộp đánh dấu điều khoản và điều kiện bắt buộc, giúp người dùng liên tục xác định và nhanh chóng di chuyển giữa các trường bắt buộc.
Điện thoại làm nguồn đầu vào micrô cho cuộc gọi thoại bằng thiết bị trợ thính LEA
Android 16 bổ sung tính năng cho phép người dùng thiết bị trợ thính LE Audio chuyển đổi giữa micrô tích hợp trên thiết bị trợ thính và micrô trên điện thoại để thực hiện cuộc gọi thoại. Điều này có thể hữu ích trong môi trường ồn ào hoặc các trường hợp khác mà micrô của thiết bị trợ thính có thể hoạt động kém.
Các nút điều chỉnh âm lượng môi trường xung quanh cho thiết bị trợ thính LEA
Android 16 bổ sung khả năng cho phép người dùng thiết bị trợ thính LE Audio điều chỉnh âm lượng của âm thanh môi trường xung quanh do micrô của thiết bị trợ thính thu được. Điều này có thể hữu ích trong trường hợp tạp âm quá lớn hoặc quá nhỏ.
Camera
Android 16 tăng cường hỗ trợ cho người dùng camera chuyên nghiệp, cho phép tự động phơi sáng kết hợp cùng với chế độ điều chỉnh nhiệt độ màu và sắc thái chính xác. Chỉ báo chế độ ban đêm mới giúp ứng dụng của bạn biết thời điểm chuyển đổi sang và từ phiên máy ảnh ở chế độ ban đêm. Các thao tác Intent mới giúp bạn dễ dàng chụp ảnh động hơn, đồng thời chúng tôi sẽ tiếp tục cải thiện hình ảnh UltraHDR bằng cách hỗ trợ mã hoá HEIC và các thông số mới theo tiêu chuẩn dự thảo ISO 21496-1.
Chế độ tự động phơi sáng kết hợp
Android 16 thêm các chế độ tự động phơi sáng kết hợp mới vào Camera2, cho phép bạn kiểm soát các khía cạnh cụ thể của chế độ phơi sáng theo cách thủ công, đồng thời để thuật toán tự động phơi sáng (AE) xử lý phần còn lại. Bạn có thể kiểm soát ISO + AE và thời gian phơi sáng + AE, mang lại tính linh hoạt cao hơn so với phương pháp hiện tại, trong đó bạn có toàn quyền kiểm soát thủ công hoặc hoàn toàn dựa vào chế độ tự động phơi sáng.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
Điều chỉnh chính xác nhiệt độ màu và sắc độ
Android 16 bổ sung tính năng hỗ trợ máy ảnh để điều chỉnh nhiệt độ màu và sắc độ một cách tinh tế nhằm hỗ trợ tốt hơn các ứng dụng quay video chuyên nghiệp. Trong các phiên bản Android trước, bạn có thể kiểm soát các chế độ cài đặt cân bằng trắng thông qua CONTROL_AWB_MODE. Phương thức này chứa các tuỳ chọn giới hạn ở danh sách đặt trước, chẳng hạn như Đèn sợi đốt, Mây và Hoàng hôn. COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT cho phép sử dụng COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE và COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT để điều chỉnh chính xác độ cân bằng trắng dựa trên nhiệt độ màu tương quan.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
Các ví dụ sau đây cho thấy hình ảnh sẽ trông như thế nào sau khi áp dụng các mức điều chỉnh nhiệt độ màu và sắc độ khác nhau:





Tính năng phát hiện cảnh ở chế độ ban đêm của camera
Để giúp ứng dụng của bạn biết thời điểm chuyển sang và thoát khỏi phiên máy ảnh ở chế độ ban đêm, Android 16 sẽ thêm EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. Nếu được hỗ trợ, bạn có thể sử dụng tính năng này trong CaptureResult trong Camera2.
Đây là API mà chúng tôi đã đề cập ngắn gọn trong bài đăng trên blog Cách Instagram giúp người dùng chụp những bức ảnh tuyệt đẹp trong điều kiện thiếu sáng. Bài đăng đó là một hướng dẫn thực tế về cách triển khai chế độ ban đêm cùng với một nghiên cứu điển hình liên kết ảnh chất lượng cao hơn ở chế độ ban đêm trong ứng dụng với việc tăng số lượng ảnh được chia sẻ từ máy ảnh trong ứng dụng.
Thao tác theo ý định chụp ảnh chuyển động
Android 16 thêm các thao tác theo Ý định chuẩn – ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE và ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE – yêu cầu ứng dụng máy ảnh chụp một ảnh động và trả về ảnh đó.
Bạn phải truyền thêm một EXTRA_OUTPUT để kiểm soát vị trí ghi hình ảnh hoặc một Uri thông qua Intent.setClipData(ClipData). Nếu bạn không đặt ClipData, thì ClipData sẽ được sao chép vào đó khi bạn gọi Context.startActivity(Intent).
Các tính năng nâng cao hình ảnh Ultra HDR

Android 16 tiếp tục nỗ lực của chúng tôi nhằm mang đến chất lượng hình ảnh rực rỡ với hình ảnh UltraHDR. Thêm tính năng hỗ trợ cho hình ảnh UltraHDR ở định dạng tệp HEIC. Những hình ảnh này sẽ có loại ImageFormat
HEIC_ULTRAHDR và sẽ chứa một bản đồ độ lợi được nhúng tương tự
như định dạng JPEG UltraHDR hiện có. Chúng tôi cũng đang nỗ lực để hỗ trợ AVIF cho UltraHDR, vì vậy, hãy chú ý theo dõi.
Ngoài ra, Android 16 triển khai các thông số bổ sung trong UltraHDR từ tiêu chuẩn dự thảo ISO 21496-1, bao gồm cả khả năng lấy và đặt không gian màu mà toán học bản đồ độ lợi sẽ được áp dụng, cũng như hỗ trợ hình ảnh cơ sở được mã hoá HDR bằng bản đồ độ lợi SDR.
Đồ hoạ
Android 16 có các điểm cải tiến mới nhất về đồ hoạ, chẳng hạn như hiệu ứng đồ hoạ tuỳ chỉnh bằng AGSL.
Hiệu ứng đồ hoạ tuỳ chỉnh bằng AGSL
Android 16 thêm RuntimeColorFilter và RuntimeXfermode, cho phép bạn tạo các hiệu ứng phức tạp như Ngưỡng, Nâu đỏ và Độ bão hoà màu sắc và áp dụng các hiệu ứng đó cho các lệnh gọi vẽ. Kể từ Android 13, bạn có thể sử dụng AGSL để tạo RuntimeShaders tuỳ chỉnh mở rộng Shader. API mới phản ánh điều này, thêm một RuntimeColorFilter dựa trên AGSL mở rộng ColorFilter và hiệu ứng Xfermode cho phép bạn triển khai tính năng kết hợp và pha trộn tuỳ chỉnh dựa trên AGSL giữa các pixel nguồn và đích.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
Khả năng kết nối
Android 16 cập nhật nền tảng để cho phép ứng dụng của bạn sử dụng những tiến bộ mới nhất về công nghệ truyền thông và không dây.
Đo khoảng cách với tính năng bảo mật nâng cao
Android 16 hỗ trợ thêm các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ trong vị trí Wi-Fi trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ bằng 802.11az của Wi-Fi 6, cho phép các ứng dụng kết hợp độ chính xác cao hơn, khả năng mở rộng lớn hơn và lập lịch biểu động của giao thức với các tính năng bảo mật nâng cao, bao gồm cả tính năng mã hoá dựa trên AES-256 và bảo vệ chống lại các cuộc tấn công MITM. Điều này cho phép sử dụng chip một cách an toàn hơn trong các trường hợp sử dụng ở cự ly gần, chẳng hạn như mở khoá máy tính xách tay hoặc cửa xe. 802.11az được tích hợp với tiêu chuẩn Wi-Fi 6, tận dụng cơ sở hạ tầng và các tính năng của tiêu chuẩn này để được áp dụng rộng rãi hơn và triển khai dễ dàng hơn.
API đo khoảng cách chung
Android 16 bao gồm RangingManager mới, cung cấp các cách xác định khoảng cách và góc trên phần cứng được hỗ trợ giữa thiết bị cục bộ và thiết bị từ xa. RangingManager hỗ trợ việc sử dụng nhiều công nghệ đo khoảng cách như đo khoảng cách dựa trên RSSI BLE, đo khoảng cách dựa trên kênh BLE, băng tần siêu rộng và thời gian truyền Wi-Fi.
Sự hiện diện của thiết bị trong trình quản lý thiết bị đồng hành
Trong Android 16, các API mới sẽ được giới thiệu để liên kết dịch vụ ứng dụng đồng hành. Dịch vụ sẽ được liên kết khi BLE ở trong phạm vi và Bluetooth được kết nối, đồng thời dịch vụ sẽ bị huỷ liên kết khi BLE ở ngoài phạm vi hoặc Bluetooth bị ngắt kết nối. Ứng dụng sẽ nhận được lệnh gọi lại "onDevicePresenceEvent()" mới dựa trên nhiều DevicePresenceEvent.
Bạn có thể xem thêm thông tin chi tiết trong "startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)".
Nội dung nghe nhìn
Android 16 có nhiều tính năng giúp cải thiện trải nghiệm nghe nhìn.
Cải tiến công cụ chọn ảnh
Công cụ chọn ảnh cung cấp cho người dùng một cách tích hợp an toàn để cấp cho ứng dụng của bạn quyền truy cập vào những hình ảnh và video đã chọn từ cả bộ nhớ cục bộ và bộ nhớ trên đám mây, thay vì toàn bộ thư viện nội dung nghe nhìn của họ. Bằng cách kết hợp Các thành phần hệ thống mô-đun thông qua Bản cập nhật hệ thống của Google và Dịch vụ Google Play, tính năng này được hỗ trợ trở lại cho Android 4.4 (API cấp 19). Bạn chỉ cần vài dòng mã để tích hợp với thư viện Android Jetpack được liên kết.
Android 16 có các điểm cải tiến sau đây cho công cụ chọn ảnh:
- Trình chọn ảnh được nhúng: Các API mới cho phép ứng dụng nhúng trình chọn ảnh vào hệ phân cấp chế độ xem của ứng dụng. Điều này giúp người dùng cảm thấy như một phần tích hợp hơn của ứng dụng, trong khi vẫn tận dụng tính năng tách biệt quy trình cho phép người dùng chọn nội dung nghe nhìn mà không cần ứng dụng có quyền quá rộng. Để tối đa hoá khả năng tương thích trên các phiên bản nền tảng và đơn giản hoá quá trình tích hợp, bạn nên sử dụng thư viện Android Jetpack sắp ra mắt nếu muốn tích hợp công cụ chọn ảnh được nhúng.
- Tìm kiếm trên đám mây trong công cụ chọn ảnh: Các API mới cho phép tìm kiếm từ nhà cung cấp nội dung đa phương tiện trên đám mây cho công cụ chọn ảnh trên Android. Chức năng tìm kiếm trong bộ chọn ảnh sẽ sớm ra mắt.
Video chuyên nghiệp nâng cao
Android 16 ra mắt tính năng hỗ trợ bộ mã hoá và giải mã Video chuyên nghiệp nâng cao (APV). Bộ mã hoá và giải mã này được thiết kế để dùng cho việc quay video chất lượng cao và xử lý hậu kỳ ở cấp chuyên nghiệp.
Tiêu chuẩn bộ mã hoá và giải mã APV có các tính năng sau:
- Chất lượng video không bị mất dữ liệu (gần với chất lượng video thô)
- Mã hoá chỉ trong khung hình có độ phức tạp thấp và thông lượng cao (không có tính năng dự đoán miền pixel) để hỗ trợ tốt hơn quy trình chỉnh sửa
- Hỗ trợ phạm vi tốc độ bit cao lên đến vài Gbps cho nội dung có độ phân giải 2K, 4K và 8K, được bật bằng lược đồ mã hoá entropy nhẹ
- Sắp xếp khung hình cho nội dung sống động và để bật tính năng mã hoá và giải mã song song
- Hỗ trợ nhiều định dạng lấy mẫu màu sắc và độ sâu bit
- Hỗ trợ nhiều lần giải mã và mã hoá lại mà không làm giảm chất lượng hình ảnh nghiêm trọng
- Hỗ trợ video nhiều khung hình và video phụ như độ sâu, alpha và bản xem trước
- Hỗ trợ HDR10/10+ và siêu dữ liệu do người dùng xác định
Phương thức triển khai tham chiếu của APV được cung cấp thông qua dự án OpenAPV. Android 16 sẽ triển khai tính năng hỗ trợ cho Hồ sơ APV 422-10, cung cấp tính năng lấy mẫu màu YUV 422 cùng với tính năng mã hoá 10 bit và tốc độ bit mục tiêu lên đến 2 Gbps.
Quyền riêng tư
Android 16 có nhiều tính năng giúp nhà phát triển ứng dụng bảo vệ quyền riêng tư của người dùng.
Thông tin cập nhật về Health Connect
Health Connect thêm ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, một loại dữ liệu được xác định theo hướng dẫn của Tổ chức Y tế Thế giới về hoạt động vừa phải và mạnh mẽ. Mỗi bản ghi yêu cầu thời gian bắt đầu, thời gian kết thúc và cường độ hoạt động là vừa phải hay mạnh.
Health Connect cũng chứa các API đã cập nhật hỗ trợ bản ghi y tế. Điều này cho phép các ứng dụng đọc và ghi hồ sơ y tế ở định dạng FHIR khi có sự đồng ý rõ ràng của người dùng.
Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android
Android 16 tích hợp phiên bản mới nhất của Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android, một phần trong nỗ lực liên tục của chúng tôi nhằm phát triển các công nghệ giúp người dùng biết rằng quyền riêng tư của họ được bảo vệ. Trang web của chúng tôi có thêm thông tin về chương trình beta dành cho nhà phát triển của Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android để giúp bạn bắt đầu. Hãy xem Thời gian chạy SDK cho phép SDK chạy trong một môi trường thời gian chạy chuyên dụng tách biệt với ứng dụng mà chúng đang phân phát, cung cấp các biện pháp bảo vệ mạnh mẽ hơn cho việc thu thập và chia sẻ dữ liệu người dùng.
Bảo mật
Android 16 có các tính năng giúp bạn tăng cường tính bảo mật của ứng dụng và bảo vệ dữ liệu của ứng dụng.
Key sharing API
Android 16 bổ sung các API hỗ trợ chia sẻ quyền truy cập vào khoá Kho khoá Android với các ứng dụng khác. Lớp KeyStoreManager mới hỗ trợ cấp và thu hồi quyền truy cập vào khoá theo uid của ứng dụng, đồng thời bao gồm một API để các ứng dụng truy cập vào khoá dùng chung.
Kiểu dáng thiết bị
Android 16 hỗ trợ các ứng dụng của bạn để khai thác tối đa các kiểu dáng của Android.
Khung hình ảnh và âm thanh tiêu chuẩn cho TV
Gói MediaQuality mới trong Android 16 hiển thị một tập hợp các API được chuẩn hoá để truy cập vào hồ sơ âm thanh và hình ảnh cũng như các chế độ cài đặt liên quan đến phần cứng. Điều này cho phép các ứng dụng phát trực tuyến truy vấn hồ sơ và áp dụng hồ sơ đó cho nội dung nghe nhìn một cách linh động:
- Những bộ phim được xử lý với dải động rộng hơn đòi hỏi độ chính xác màu cao hơn để thấy được các chi tiết tinh tế trong bóng tối và điều chỉnh theo ánh sáng xung quanh. Vì vậy, bạn nên sử dụng hồ sơ ưu tiên độ chính xác màu hơn độ sáng.
- Các sự kiện thể thao trực tiếp thường được xử lý với dải động hẹp, nhưng thường được xem dưới ánh sáng ban ngày, vì vậy, một hồ sơ ưu tiên độ sáng hơn độ chính xác màu có thể mang lại kết quả tốt hơn.
- Nội dung tương tác hoàn toàn cần có mức xử lý tối thiểu để giảm độ trễ và cần tốc độ khung hình cao hơn. Đó là lý do nhiều TV được trang bị hồ sơ trò chơi.
API này cho phép các ứng dụng chuyển đổi giữa các hồ sơ và người dùng có thể điều chỉnh TV được hỗ trợ sao cho phù hợp nhất với nội dung của họ.
Quốc tế hoá
Android 16 bổ sung các tính năng và chức năng bổ trợ cho trải nghiệm người dùng khi thiết bị được dùng bằng nhiều ngôn ngữ.
Văn bản dọc
Android 16 bổ sung tính năng hỗ trợ cấp thấp để hiển thị và đo lường văn bản theo chiều dọc nhằm cung cấp tính năng hỗ trợ viết theo chiều dọc cơ bản cho nhà phát triển thư viện. Điều này đặc biệt hữu ích đối với các ngôn ngữ như tiếng Nhật thường sử dụng hệ thống viết theo chiều dọc. Thêm cờ mới, VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG vào lớp Paint. Khi bạn đặt cờ này bằng Paint.setFlags, API đo lường văn bản của Paint sẽ báo cáo các tiến trình dọc thay vì tiến trình ngang và Canvas sẽ vẽ văn bản theo chiều dọc.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
Tuỳ chỉnh hệ thống đo lường
Giờ đây, người dùng có thể tuỳ chỉnh hệ thống đo lường theo lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực trong phần Cài đặt. Lựa chọn ưu tiên của người dùng được đưa vào mã ngôn ngữ, vì vậy, bạn có thể đăng ký BroadcastReceiver trên ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED để xử lý các thay đổi về cấu hình ngôn ngữ khi lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực thay đổi.
Việc sử dụng trình định dạng có thể giúp phù hợp với trải nghiệm cục bộ. Ví dụ: "0,5 in" (inch) bằng tiếng Anh (Hoa Kỳ) là "12,7 mm" đối với người dùng đã đặt điện thoại thành tiếng Anh (Đan Mạch) hoặc người dùng sử dụng điện thoại bằng tiếng Anh (Hoa Kỳ) với hệ mét là hệ thống đo lường ưu tiên.
Để tìm các chế độ cài đặt này, hãy mở ứng dụng Cài đặt rồi chuyển đến Hệ thống > Ngôn ngữ và khu vực.
