Nền tảng Android 16 có các thay đổi về hành vi có thể ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng của bạn. Những thay đổi về hành vi sau đây áp dụng cho tất cả ứng dụng khi chạy trên Android 16, bất kể targetSdkVersion. Bạn nên kiểm thử ứng dụng rồi sửa đổi để hỗ trợ những thay đổi này cho phù hợp (nếu cần).
Ngoài ra, hãy nhớ tham khảo danh sách các thay đổi về hành vi chỉ ảnh hưởng đến những ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16.
Chức năng cốt lõi
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây nhằm sửa đổi hoặc mở rộng nhiều chức năng cốt lõi của hệ thống Android.
Tối ưu hoá hạn mức JobScheduler
Kể từ Android 16, chúng tôi sẽ điều chỉnh hạn mức thời gian chạy thực thi công việc thông thường và công việc khẩn cấp dựa trên các yếu tố sau:
- Ứng dụng nằm trong nhóm chờ của ứng dụng nào: trong Android 16, các nhóm chờ đang hoạt động sẽ bắt đầu được thực thi theo hạn mức thời gian chạy lớn.
- Nếu lệnh bắt đầu thực thi trong khi ứng dụng ở trạng thái trên cùng: trong Android 16, các lệnh bắt đầu trong khi ứng dụng hiển thị với người dùng và tiếp tục sau khi ứng dụng trở nên không hiển thị sẽ tuân thủ hạn mức thời gian chạy của lệnh.
- Nếu lệnh đang thực thi trong khi chạy Dịch vụ trên nền trước: trong Android 16, những lệnh đang thực thi đồng thời với một dịch vụ trên nền trước sẽ tuân thủ hạn mức thời gian chạy lệnh. Nếu bạn đang tận dụng các công việc để chuyển dữ liệu do người dùng yêu cầu, hãy cân nhắc sử dụng công việc chuyển dữ liệu do người dùng yêu cầu.
Thay đổi này ảnh hưởng đến các tác vụ được lên lịch bằng WorkManager, JobScheduler và DownloadManager. Để gỡ lỗi lý do một công việc bị dừng, bạn nên ghi nhật ký lý do công việc của bạn bị dừng bằng cách gọi WorkInfo.getStopReason() (đối với các công việc JobScheduler, hãy gọi JobParameters.getStopReason()).
Để biết thông tin về cách trạng thái của ứng dụng ảnh hưởng đến những tài nguyên mà ứng dụng có thể sử dụng, hãy xem phần Hạn mức tài nguyên quản lý nguồn. Để biết thêm thông tin về các phương pháp hay nhất giúp tối ưu hoá pin, hãy tham khảo hướng dẫn về cách tối ưu hoá mức sử dụng pin cho các API lập lịch tác vụ.
Bạn cũng nên tận dụng API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory mới được ra mắt trong Android 16 để biết lý do một công việc chưa được thực thi.
Thử nghiệm
Để kiểm thử hành vi của ứng dụng, bạn có thể bật chế độ ghi đè một số hoạt động tối ưu hoá hạn ngạch công việc nhất định miễn là ứng dụng đang chạy trên thiết bị Android 16.
Để tắt chế độ thực thi "trạng thái hàng đầu sẽ tuân thủ hạn mức thời gian chạy của công việc", hãy chạy lệnh adb sau:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Để tắt việc thực thi "các công việc đang thực thi đồng thời với một dịch vụ trên nền trước sẽ tuân thủ hạn ngạch thời gian chạy công việc", hãy chạy lệnh adb sau:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Để kiểm thử một số hành vi của nhóm chế độ chờ của ứng dụng, bạn có thể đặt nhóm chế độ chờ của ứng dụng bằng lệnh adb sau:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
Để biết ứng dụng của bạn nằm trong nhóm chế độ chờ ứng dụng nào, bạn có thể lấy nhóm chế độ chờ ứng dụng của ứng dụng bằng lệnh adb sau:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Lý do dừng các công việc bị bỏ dở khi không có dữ liệu
Công việc bị bỏ dở xảy ra khi đối tượng JobParameters liên kết với công việc đã được thu thập rác, nhưng JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) chưa được gọi để báo hiệu công việc đã hoàn tất. Điều này cho biết rằng công việc có thể đang chạy và được lên lịch lại mà ứng dụng không biết.
Các ứng dụng dựa vào JobScheduler không duy trì tham chiếu mạnh đến đối tượng JobParameters và giờ đây, thời gian chờ sẽ được cấp lý do dừng công việc mới STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED thay vì STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
Nếu lý do dừng mới bị bỏ dở thường xuyên xuất hiện, hệ thống sẽ thực hiện các bước giảm thiểu để giảm tần suất công việc.
Ứng dụng nên sử dụng lý do dừng mới để phát hiện và giảm số lượng công việc bị bỏ ngang.
Nếu đang sử dụng WorkManager, AsyncTask hoặc DownloadManager, bạn sẽ không bị ảnh hưởng vì các API này thay mặt ứng dụng quản lý vòng đời công việc.
Hoàn toàn không dùng JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground nữa
Phương thức JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) cho biết tầm quan trọng của một công việc trong khi ứng dụng lên lịch chạy ở nền trước hoặc khi tạm thời được miễn các quy định hạn chế về chế độ nền.
Phương thức này không được dùng nữa kể từ Android 12 (API cấp 31). Kể từ Android 16, phương thức này không còn hoạt động hiệu quả và việc gọi phương thức này sẽ bị bỏ qua.
Việc xoá chức năng này cũng áp dụng cho
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). Kể từ Android 16, nếu được gọi, phương thức này sẽ trả về false.
Phạm vi ưu tiên của thông báo truyền tin theo thứ tự không còn là phạm vi toàn cầu nữa
Ứng dụng Android được phép xác định mức độ ưu tiên trên broadcast receiver để kiểm soát thứ tự mà các broadcast receiver nhận và xử lý thông báo truyền tin. Đối với trình nhận được khai báo trong tệp kê khai, ứng dụng có thể sử dụng thuộc tính android:priority để xác định mức độ ưu tiên và đối với trình nhận được đăng ký theo ngữ cảnh, ứng dụng có thể sử dụng API IntentFilter#setPriority() để xác định mức độ ưu tiên. Khi gửi thông báo truyền tin, hệ thống sẽ phân phối thông báo đó đến các trình thu nhận theo thứ tự ưu tiên, từ cao nhất đến thấp nhất.
Trong Android 16, thứ tự phân phối thông báo truyền tin bằng thuộc tính android:priority hoặc IntentFilter#setPriority() trên các quy trình khác nhau sẽ không được đảm bảo. Mức độ ưu tiên của thông báo truyền tin sẽ chỉ được tuân thủ trong cùng một quy trình ứng dụng thay vì trên tất cả các quy trình.
Ngoài ra, mức độ ưu tiên của thông báo truyền tin sẽ tự động được giới hạn trong phạm vi (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY – 1). Chỉ các thành phần hệ thống mới được phép đặt SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY làm mức độ ưu tiên truyền tin.
Ứng dụng của bạn có thể bị ảnh hưởng nếu thực hiện một trong những hành động sau:
- Ứng dụng của bạn đã khai báo nhiều quy trình có cùng một ý định truyền tin và có kỳ vọng về việc nhận các ý định đó theo một thứ tự nhất định dựa trên mức độ ưu tiên.
- Quy trình ứng dụng của bạn tương tác với các quy trình khác và có những kỳ vọng về việc nhận ý định truyền tin theo một thứ tự nhất định.
Nếu các quy trình cần phối hợp với nhau, thì các quy trình đó phải giao tiếp bằng các kênh phối hợp khác.
Thay đổi nội bộ về ART
Android 16 bao gồm các bản cập nhật mới nhất cho Android Runtime (ART) giúp cải thiện hiệu suất của Android Runtime (ART) và hỗ trợ thêm các tính năng Java. Thông qua Bản cập nhật hệ thống Google Play, hơn một tỷ thiết bị chạy Android 12 (API cấp 31) trở lên cũng có thể sử dụng các điểm cải tiến này.
Khi những thay đổi này được phát hành, các thư viện và mã ứng dụng dựa vào cấu trúc nội bộ của ART có thể không hoạt động chính xác trên các thiết bị chạy Android 16, cùng với các phiên bản Android cũ cập nhật mô-đun ART thông qua bản cập nhật hệ thống Google Play.
Việc dựa vào các cấu trúc nội bộ (chẳng hạn như giao diện không phải SDK) luôn có thể dẫn đến các vấn đề về khả năng tương thích, nhưng điều đặc biệt quan trọng là tránh dựa vào mã (hoặc thư viện chứa mã) tận dụng các cấu trúc ART nội bộ, vì các thay đổi về ART không liên quan đến phiên bản nền tảng mà thiết bị đang chạy và các thay đổi này sẽ được áp dụng cho hơn một tỷ thiết bị thông qua các bản cập nhật hệ thống của Google Play.
Tất cả nhà phát triển đều nên kiểm tra xem ứng dụng của họ có bị ảnh hưởng hay không bằng cách kiểm thử kỹ lưỡng ứng dụng trên Android 16. Ngoài ra, hãy kiểm tra các vấn đề đã biết để xem ứng dụng của bạn có phụ thuộc vào bất kỳ thư viện nào mà chúng tôi đã xác định là dựa vào cấu trúc ART nội bộ hay không. Nếu mã ứng dụng hoặc các phần phụ thuộc thư viện của bạn bị ảnh hưởng, hãy tìm các API công khai thay thế bất cứ khi nào có thể và yêu cầu API công khai cho các trường hợp sử dụng mới bằng cách tạo yêu cầu về tính năng trong công cụ theo dõi lỗi của chúng tôi.
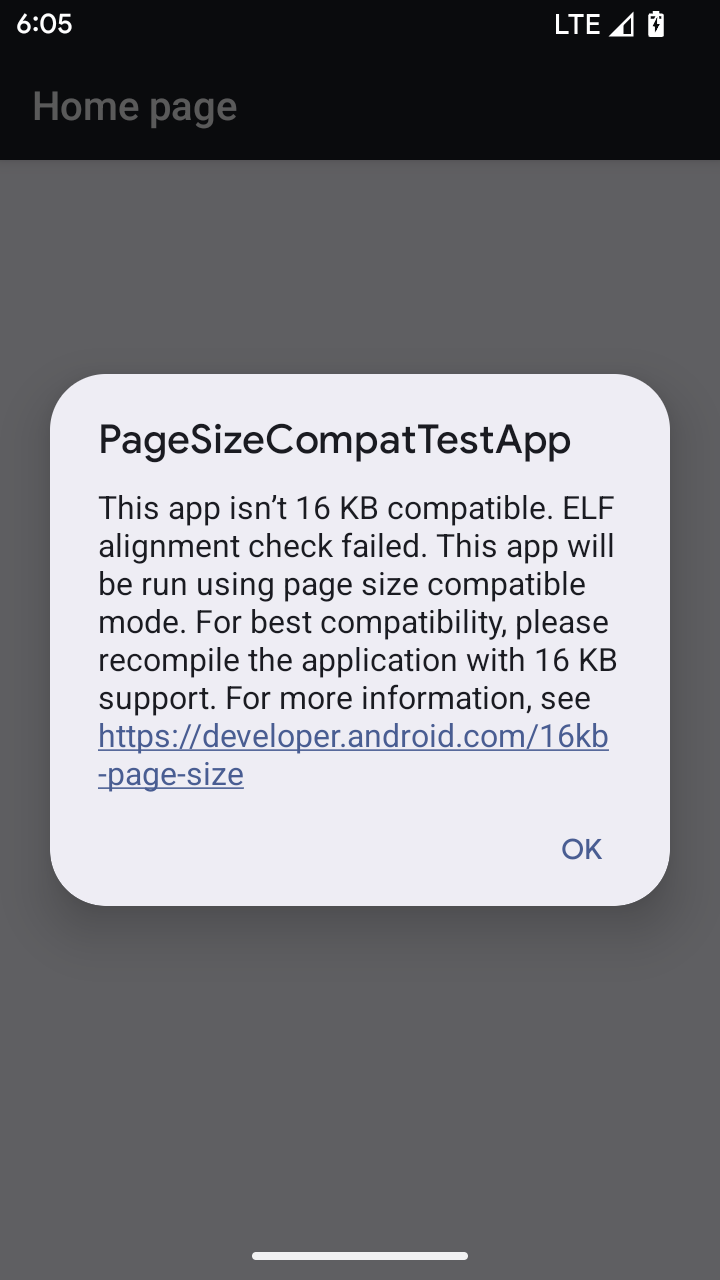
Chế độ tương thích với kích thước trang 16 KB
Android 15 đã ra mắt tính năng hỗ trợ trang bộ nhớ 16 KB để tối ưu hoá hiệu suất của nền tảng. Android 16 bổ sung một chế độ tương thích, cho phép một số ứng dụng được tạo cho các trang bộ nhớ 4 KB chạy trên một thiết bị được định cấu hình cho các trang bộ nhớ 16 KB.
Khi ứng dụng của bạn đang chạy trên một thiết bị chạy Android 16 trở lên, nếu Android phát hiện thấy ứng dụng của bạn có các trang bộ nhớ được căn chỉnh 4 KB, thì Android sẽ tự động sử dụng chế độ tương thích và hiển thị hộp thoại thông báo cho người dùng. Việc đặt thuộc tính android:pageSizeCompat trong AndroidManifest.xml để bật chế độ tương thích ngược sẽ ngăn hộp thoại hiển thị khi ứng dụng khởi chạy. Để sử dụng thuộc tính android:pageSizeCompat, hãy biên dịch ứng dụng bằng SDK Android 16.
Để có hiệu suất, độ tin cậy và độ ổn định tốt nhất, ứng dụng của bạn vẫn phải được căn chỉnh 16 KB. Hãy xem bài đăng gần đây trên blog của chúng tôi về cách cập nhật ứng dụng để hỗ trợ trang bộ nhớ 16 KB để biết thêm thông tin chi tiết.
Trải nghiệm người dùng và giao diện người dùng hệ thống
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây nhằm tạo ra trải nghiệm người dùng nhất quán và trực quan hơn.
Ngừng sử dụng các thông báo hỗ trợ tiếp cận gây phiền toái
Android 16 không dùng thông báo hỗ trợ tiếp cận nữa, được xác định bằng việc sử dụng announceForAccessibility hoặc gửi sự kiện hỗ trợ tiếp cận TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT. Những điều này có thể tạo ra trải nghiệm người dùng không nhất quán cho người dùng TalkBack và trình đọc màn hình của Android, đồng thời các giải pháp thay thế sẽ phục vụ tốt hơn nhiều nhu cầu của người dùng trên nhiều công nghệ hỗ trợ của Android.
Ví dụ về các lựa chọn thay thế:
- Đối với các thay đổi đáng kể về giao diện người dùng như thay đổi cửa sổ, hãy sử dụng
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)vàsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). Trong Compose, hãy sử dụngModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - Để thông báo cho người dùng về những thay đổi đối với giao diện người dùng quan trọng, hãy sử dụng
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). Trong Compose, hãy sử dụngModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. Bạn nên sử dụng các thông báo này một cách tiết kiệm vì chúng có thể tạo thông báo mỗi khi Chế độ xem được cập nhật. - Để thông báo cho người dùng về lỗi, hãy gửi
AccessibilityEventthuộc loạiAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORvà đặtAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)hoặc sử dụngTextView#setError(CharSequence).
Tài liệu tham khảo cho API announceForAccessibility không dùng nữa bao gồm thêm thông tin chi tiết về các giải pháp thay thế được đề xuất.
Hỗ trợ chế độ thao tác bằng 3 nút
Android 16 hỗ trợ tính năng xem trước thao tác quay lại cho chế độ điều hướng bằng 3 nút cho các ứng dụng đã di chuyển đúng cách sang tính năng xem trước thao tác quay lại. Thao tác nhấn và giữ nút quay lại sẽ bắt đầu ảnh động xem trước thao tác quay lại, cho bạn xem trước vị trí mà thao tác vuốt ngược sẽ đưa bạn đến.
Hành vi này áp dụng cho tất cả các khu vực của hệ thống hỗ trợ ảnh động xem trước thao tác quay lại, bao gồm cả ảnh động hệ thống (quay lại màn hình chính, giữa các tác vụ và giữa các hoạt động).
Biểu tượng ứng dụng theo chủ đề tự động
Kể từ Android 16 QPR 2, Android sẽ tự động áp dụng các giao diện cho biểu tượng ứng dụng để tạo trải nghiệm nhất quán trên màn hình chính. Tình trạng này xảy ra nếu một ứng dụng không cung cấp biểu tượng ứng dụng theo chủ đề riêng. Các ứng dụng có thể kiểm soát thiết kế của biểu tượng ứng dụng theo chủ đề bằng cách thêm một lớp đơn sắc vào biểu tượng thích ứng và xem trước giao diện của biểu tượng ứng dụng trong Android Studio.
Kiểu dáng thiết bị
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây đối với các ứng dụng khi được chủ sở hữu thiết bị ảo chiếu lên màn hình.
Chủ sở hữu thiết bị ảo ghi đè
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that creates and manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners run apps on a virtual device and then project the apps to the display of a remote device, such as a personal computer, virtual reality device, or car infotainment system. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a mobile phone.
Per-app overrides
On devices running Android 16 (API level 36), virtual device owners can override app settings on select virtual devices that the virtual device owners manage. For example, to improve app layout, a virtual device owner can ignore orientation, aspect ratio, and resizability restrictions when projecting apps onto an external display.
Common breaking changes
The Android 16 behavior might impact your app's UI on large screen form factors such as car displays or Chromebooks, especially layouts that were designed for small displays in portrait orientation. To learn how to make your app adaptive for all device form factors, see About adaptive layouts.
References
Bảo mật
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi giúp tăng cường tính bảo mật của hệ thống để bảo vệ ứng dụng và người dùng khỏi các ứng dụng độc hại.
Cải thiện khả năng bảo mật để chống lại các cuộc tấn công chuyển hướng Ý định
Android 16 cung cấp chế độ bảo mật mặc định để chống lại các cuộc tấn công chuyển hướng Intent nói chung, với khả năng tương thích tối thiểu và các thay đổi cần thiết cho nhà phát triển.
Chúng tôi đang giới thiệu các giải pháp tăng cường bảo mật theo mặc định để khai thác việc chuyển hướng Intent. Trong hầu hết trường hợp, các ứng dụng sử dụng ý định thường sẽ không gặp phải bất kỳ vấn đề nào về khả năng tương thích; chúng tôi đã thu thập các chỉ số trong suốt quá trình phát triển để theo dõi những ứng dụng có thể gặp phải sự cố.
Chuyển hướng ý định trong Android xảy ra khi kẻ tấn công có thể kiểm soát một phần hoặc toàn bộ nội dung của một ý định dùng để chạy một thành phần mới trong bối cảnh một ứng dụng dễ bị tấn công, trong khi ứng dụng mục tiêu chạy một ý định cấp dưới không đáng tin cậy trong một trường bổ sung của một ý định ("cấp cao nhất"). Điều này có thể dẫn đến việc ứng dụng của kẻ tấn công khởi chạy các thành phần riêng tư trong bối cảnh của ứng dụng mục tiêu, kích hoạt các hành động đặc quyền hoặc giành được quyền truy cập URI vào dữ liệu nhạy cảm, có khả năng dẫn đến hành vi đánh cắp dữ liệu và thực thi mã tuỳ ý.
Chọn không xử lý việc chuyển hướng theo ý định
Android 16 giới thiệu một API mới cho phép các ứng dụng chọn không sử dụng các biện pháp bảo vệ khi khởi chạy. Điều này có thể cần thiết trong một số trường hợp cụ thể khi hành vi bảo mật mặc định gây trở ngại cho các trường hợp sử dụng ứng dụng hợp pháp.
Đối với các ứng dụng biên dịch dựa trên SDK Android 16 (API cấp 36) trở lên
Bạn có thể trực tiếp sử dụng phương thức removeLaunchSecurityProtection() trên đối tượng Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Đối với các ứng dụng biên dịch dựa trên Android 15 (API cấp 35) trở xuống
Mặc dù không nên, nhưng bạn có thể dùng tính năng phản chiếu để truy cập vào phương thức removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Ứng dụng đồng hành sẽ không còn nhận được thông báo về thời gian chờ phát hiện nữa
Android 16 giới thiệu một hành vi mới trong quy trình ghép nối thiết bị đồng hành để bảo vệ quyền riêng tư về vị trí của người dùng khỏi các ứng dụng độc hại. Tất cả ứng dụng đồng hành chạy trên Android 16 không còn được thông báo trực tiếp về thời gian chờ khám phá bằng RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Thay vào đó, người dùng sẽ được thông báo về các sự kiện hết thời gian chờ bằng một hộp thoại trực quan. Khi người dùng đóng hộp thoại, ứng dụng sẽ được cảnh báo về lỗi liên kết với RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
Thời lượng tìm kiếm cũng được kéo dài từ 20 giây ban đầu, và người dùng có thể dừng quá trình khám phá thiết bị bất cứ lúc nào trong quá trình tìm kiếm. Nếu phát hiện được ít nhất một thiết bị trong 20 giây đầu tiên kể từ khi bắt đầu tìm kiếm, thì CDM sẽ ngừng tìm kiếm các thiết bị khác.
Khả năng kết nối
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây trong ngăn xếp Bluetooth để cải thiện khả năng kết nối với các thiết bị ngoại vi.
Cải thiện khả năng xử lý tình trạng mất liên kết
Kể từ Android 16, ngăn xếp Bluetooth đã được cập nhật để cải thiện tính bảo mật và trải nghiệm người dùng khi phát hiện thấy mất liên kết từ xa. Trước đây, hệ thống sẽ tự động xoá mối liên kết và bắt đầu một quy trình ghép nối mới, điều này có thể dẫn đến việc ghép nối lại ngoài ý muốn. Chúng tôi nhận thấy trong nhiều trường hợp, các ứng dụng không xử lý sự kiện mất liên kết một cách nhất quán.
Để hợp nhất trải nghiệm, Android 16 đã cải thiện khả năng xử lý mất liên kết với hệ thống. Nếu không xác thực được thiết bị Bluetooth đã liên kết trước đó khi kết nối lại, hệ thống sẽ ngắt kết nối đường liên kết, giữ lại thông tin liên kết cục bộ và hiển thị hộp thoại hệ thống thông báo cho người dùng về việc mất liên kết và hướng dẫn họ ghép nối lại.
