Android 16 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた新しい機能と API が導入されました。以降のセクションでは、関連する API の使用を開始する際に役立つように、これらの機能の概要を説明します。
新しい API、変更された API、削除された API の一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。新しい API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。新しい API は、見つけやすいようにハイライト表示されています。また、プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する可能性がある領域も確認する必要があります。詳しくは、次のページをご覧ください。
コア機能
Android には、Android システムのコア機能を拡張する新しい API が含まれています。
2025 年に 2 つの Android API がリリース
- This preview is for the next major release of Android with a planned launch in Q2 of 2025. This release is similar to all of our API releases in the past, where we can have planned behavior changes that are often tied to a targetSdkVersion.
- We're planning the major release a quarter earlier (Q2 rather than Q3 in prior years) to better align with the schedule of device launches across our ecosystem, so more devices can get the major release of Android sooner. With the major release coming in Q2, you'll need to do your annual compatibility testing a few months earlier than in previous years to make sure your apps are ready.
- We plan to have another release in Q4 of 2025 which also will include new developer APIs. The Q2 major release will be the only release in 2025 to include planned behavior changes that could affect apps.
In addition to new developer APIs, the Q4 minor release will pick up feature updates, optimizations, and bug fixes; it will not include any app-impacting behavior changes.
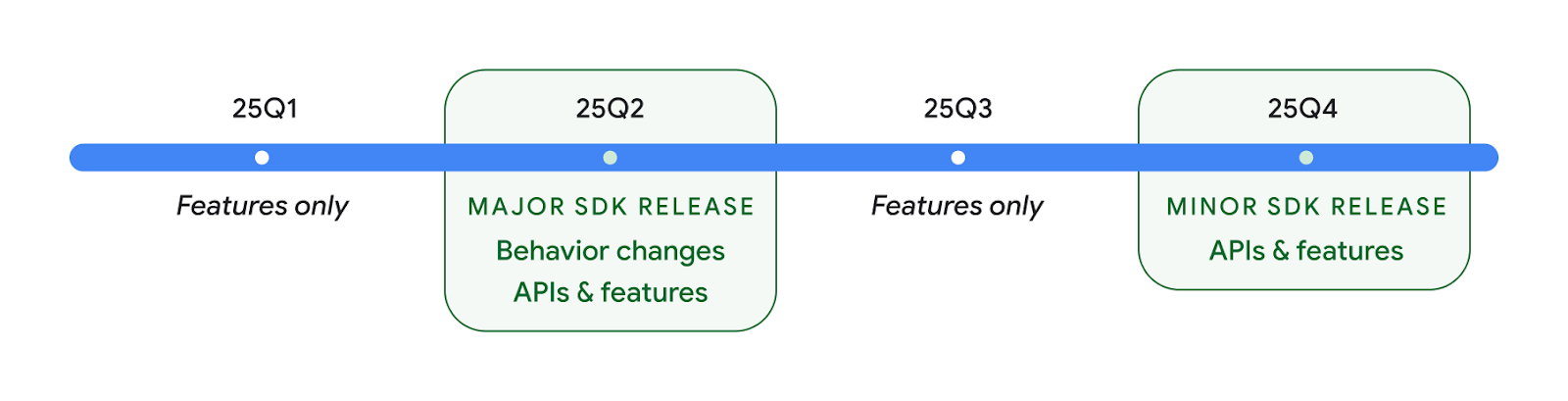
We'll continue to have quarterly Android releases. The Q1 and Q3 updates in-between the API releases will provide incremental updates to help ensure continuous quality. We're actively working with our device partners to bring the Q2 release to as many devices as possible.
Using new APIs with major and minor releases
Guarding a code block with a check for API level is done today using
the SDK_INT constant with
VERSION_CODES. This will continue
to be supported for major Android releases.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
The new SDK_INT_FULL
constant can be used for API checks against both major and minor versions with
the new VERSION_CODES_FULL
enumeration.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
You can also use the
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
method to get just the minor SDK version.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
These APIs have not yet been finalized and are subject to change, so please send us feedback if you have any concerns.
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16 では、アプリ デベロッパーとユーザーが、ニーズに合わせてデバイスをより細かく柔軟に構成できるようになりました。
進行状況重視の通知
Android 16 では、ユーザーが開始した、最初から最後までのジャーニーをシームレスに追跡できるように、進行状況重視の通知が導入されています。
Notification.ProgressStyle は、進行状況重視の通知を作成できる新しい通知スタイルです。主なユースケースには、乗車シェアリング、配達、ナビゲーションなどがあります。Notification.ProgressStyle クラス内で、ポイントとセグメントを使用して、ユーザー ジャーニー内の状態とマイルストーンを指定できます。
To learn more, see the Progress-centric notifications documentation page.
予測型「戻る」の更新
Android 16 adds new APIs to help you enable predictive back system animations in
gesture navigation such as the back-to-home animation. Registering the
onBackInvokedCallback with the new
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER allows your app to
receive the regular onBackInvoked call whenever the
system handles a back navigation without impacting the normal back navigation
flow.
Android 16 additionally adds the
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() and
moveTaskToBackCallback. By registering these callbacks
with the OnBackInvokedDispatcher, the system can trigger
specific behaviors and play corresponding ahead-of-time animations when the back
gesture is invoked.
リッチ ハプティクス
Android has exposed control over the haptic actuator ever since its inception.
Android 11 added support for more complex haptic effects that more advanced
actuators could support through
VibrationEffect.Compositions of device-defined semantic
primitives.
Android 16 adds haptic APIs that let apps define the amplitude and frequency curves of a haptic effect while abstracting away differences between device capabilities.
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
生産性を向上させるための Google の取り組みのほとんどは、Android Studio、Jetpack Compose、Android Jetpack ライブラリなどのツールに重点を置いていますが、Google は常に、デベロッパーのビジョンの実現を支援する方法についてプラットフォーム内で検討しています。
ライブ壁紙のコンテンツの処理
In Android 16, the live wallpaper framework is gaining a new content API to
address the challenges of dynamic, user-driven wallpapers. Currently, live
wallpapers incorporating user-provided content require complex, service-specific
implementations. Android 16 introduces
WallpaperDescription and
WallpaperInstance. WallpaperDescription lets you
identify distinct instances of a live wallpaper from the same service. For
example, a wallpaper that has instances on both the home screen and on the lock
screen may have unique content in both places. The wallpaper picker and
WallpaperManager use this metadata to better present
wallpapers to users, streamlining the process for you to create diverse and
personalized live wallpaper experiences.
パフォーマンスとバッテリー
Android 16 では、アプリに関する分析情報を収集するのに役立つ API が導入されています。
システムによってトリガーされるプロファイリング
ProfilingManager was
added in Android 15, giving apps the ability to
request profiling data collection using Perfetto on public devices in the field.
However, since this profiling must be started from the app, critical flows such
as startups or ANRs would be difficult or impossible for apps to capture.
To help with this, Android 16 introduces system-triggered profiling to
ProfilingManager. Apps can register interest in receiving traces for certain
triggers such as cold start reportFullyDrawn
or ANRs, and then the system starts and stops a trace on the app's behalf. After
the trace completes, the results are delivered to the app's data directory.
ApplicationStartInfo でコンポーネントを開始する
ApplicationStartInfo was added in Android
15, allowing an app to see reasons
for process start, start type, start times, throttling, and other useful
diagnostic data. Android 16 adds
getStartComponent()
to distinguish what component type triggered the start, which can be helpful for
optimizing the startup flow of your app.
ジョブ内省の改善
The JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API returns a reason why a job
might be pending. However, a job might be pending for multiple reasons.
In Android 16, we are introducing a new API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId), which returns multiple
reasons why a job is pending, due to both explicit constraints set by the
developer and implicit constraints set by the system.
We're also introducing
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId), which returns a list
of the most recent constraint changes.
We recommend using the API to help you debug why your jobs may not be executing, especially if you're seeing reduced success rates of certain tasks or have bugs around latency of certain job completion. For example, updating widgets in the background failed to occur or prefetch job failed to be called prior to app start.
This can also better help you understand if certain jobs are not completing due to system defined constraints versus explicitly set constraints.
リフレッシュ レートの自動調整
Adaptive refresh rate (ARR), introduced in Android 15, enables the display refresh rate on supported hardware to adapt to the content frame rate using discrete VSync steps. This reduces power consumption while eliminating the need for potentially jank-inducing mode-switching.
Android 16 introduces hasArrSupport() and
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) while restoring
getSupportedRefreshRates() to make it easier for your apps to take
advantage of ARR. RecyclerView
1.4 internally supports ARR when it is settling from a fling or
smooth scroll, and we're continuing our work to add ARR
support into more Jetpack libraries. This frame rate article covers
many of the APIs you can use to set the frame rate so that your app can directly
use ARR.
ADPF の Headroom API
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
ユーザー補助
Android 16 では、すべてのユーザーにアプリを提供する際に役立つ新しいユーザー補助 API と機能が追加されています。
ユーザー補助 API の改善
Android 16 では、UI セマンティクスを強化する API が追加され、TalkBack などのユーザー補助サービスに依存するユーザーの整合性が向上します。
テキストのコントラストを最大化するためにテキストの輪郭を表示する
視力の弱いユーザーはコントラスト感度が低下していることが多いため、オブジェクトを背景と区別するのが困難です。このようなユーザーをサポートするため、Android 16 では高コントラスト テキストに代わるアウトライン テキストが導入されました。アウトライン テキストは、テキストの周囲に大きなコントラスト領域を描画して、読みやすさを大幅に改善します。
Android 16 には、アプリがこのモードが有効になっているかどうかを確認またはリスナーを登録できる新しい AccessibilityManager API が含まれています。これは主に、Compose などの UI ツールキットが同様のビジュアル エクスペリエンスを提供するために使用されます。UI ツールキット ライブラリを維持している場合や、アプリが android.text.Layout クラスをバイパスするカスタム テキスト レンダリングを実行している場合は、このクラスを使用して、アウトライン テキストが有効になっているかどうかを確認できます。
TtsSpan に時間の長さを追加
Android 16 では、TtsSpan を TYPE_DURATION で拡張しています。これは、ARG_HOURS、ARG_MINUTES、ARG_SECONDS で構成されています。これにより、時間の長さを直接アノテーションして、TalkBack などのサービスで正確で一貫したテキスト読み上げ出力を実現できます。
複数のラベルを持つ要素をサポートする
現在、Android では UI 要素が別の要素からユーザー補助ラベルを派生させることができますが、ウェブ コンテンツでよくあるシナリオとして、複数のラベルを関連付ける機能が追加されました。AccessibilityNodeInfo 内にリストベースの API を導入することで、Android はこれらのマルチラベル関係を直接サポートできるようになります。この変更の一環として、AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy と #getLabeledBy のサポートが終了し、代わりに #addLabeledBy、#removeLabeledBy、#getLabeledByList が使用されるようになりました。
展開可能な要素のサポートを改善しました
Android 16 では、メニューや展開可能なリストなどのインタラクティブな要素の展開状態や閉じ状態を伝達できるユーザー補助 API が追加されています。setExpandedState を使用して展開状態を設定し、CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED コンテンツ変更タイプで TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents をディスパッチすると、TalkBack などのスクリーン リーダーが状態の変化を通知し、より直感的で包括的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを提供できます。
不確定形式の ProgressBar
Android 16 では RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE が追加され、確定型と不確定型の両方の ProgressBar ウィジェットに RangeInfo を公開できるようになりました。これにより、TalkBack などのサービスが進行状況インジケータのフィードバックをより一貫して提供できるようになります。
3 つの状態のチェックボックス
Android 16 の新しい AccessibilityNodeInfo メソッド getChecked と setChecked(int) は、「チェック済み」と「未チェック」に加えて、「部分的にチェック済み」の状態をサポートするようになりました。これは、非推奨のブール値 isChecked と setChecked(boolean) に代わるものです。
補足説明
ユーザー補助サービスが ViewGroup を記述する場合は、その子ビューのコンテンツ ラベルと組み合わせます。ViewGroup に contentDescription を指定すると、ユーザー補助サービスは、フォーカス不可能な子ビューの説明もオーバーライドしていると想定します。たとえば、ドロップダウン(「フォント ファミリー」など)にラベルを付けながら、ユーザー補助用に現在の選択内容(「Roboto」など)を保持したい場合、この点が問題になることがあります。Android 16 では setSupplementalDescription が追加され、子からの情報を上書きせずに ViewGroup に関する情報を提供するテキストを指定できるようになりました。
必須のフォーム フィールド
Android 16 では、AccessibilityNodeInfo に setFieldRequired が追加され、アプリがフォーム フィールドへの入力が必須であることをユーザー補助サービスに通知できるようになりました。これは、必須の利用規約チェックボックスなど、さまざまな種類のフォームに記入するユーザーにとって重要なシナリオです。ユーザーは、必須フィールドを一貫して識別し、すばやく移動できます。
LEA 補聴器での音声通話のマイク入力としてスマートフォンを使用する
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to switch between the built-in microphones on the hearing aids and the microphone on their phone for voice calls. This can be helpful in noisy environments or other situations where the hearing aid's microphones might not perform well.
LEA 補聴器のアンビエント音量調節
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to adjust the volume of ambient sound that is picked up by the hearing aid's microphones. This can be helpful in situations where background noise is too loud or too quiet.
カメラ
Android 16 では、プロのカメラユーザー向けのサポートが強化され、ハイブリッド自動露出と、正確な色温度と色合いの調整が可能になりました。新しい夜景モードのインジケーターは、アプリが夜景モードのカメラ セッションとの切り替えを行うタイミングを把握するのに役立ちます。新しい Intent アクションにより、モーション フォトの撮影が容易になりました。また、HEIC エンコードと ISO 21496-1 ドラフト標準の新しいパラメータのサポートにより、UltraHDR 画像の改善が継続されています。
ハイブリッド自動露出
Android 16 adds new hybrid auto-exposure modes to Camera2, allowing you to manually control specific aspects of exposure while letting the auto-exposure (AE) algorithm handle the rest. You can control ISO + AE, and exposure time + AE, providing greater flexibility compared to the current approach where you either have full manual control or rely entirely on auto-exposure.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
色温度と色合いを正確に調整
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





カメラの夜間モードでのシーン検出
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
モーション フォトのキャプチャ インテントのアクション
Android 16 adds standard Intent actions —
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE, and
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE — which request that
the camera application capture a motion photo and return
it.
You must either pass an extra EXTRA_OUTPUT to control
where the image will be written, or a Uri through
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). If you don't set a
ClipData, it will be copied there for you when calling
Context.startActivity(Intent).
ウルトラ HDR 画像の補正

Android 16 continues our work to deliver dazzling image quality with UltraHDR
images. It adds support for UltraHDR images in the HEIC file
format. These images will get ImageFormat type
HEIC_ULTRAHDR and will contain an embedded gainmap similar
to the existing UltraHDR JPEG format. We're working on AVIF support for UltraHDR
as well, so stay tuned.
In addition, Android 16 implements additional parameters in UltraHDR from the ISO 21496-1 draft standard, including the ability to get and set the colorspace that gainmap math should be applied in, as well as support for HDR encoded base images with SDR gainmaps.
グラフィック
Android 16 には、AGSL を使用したカスタム グラフィック効果など、最新のグラフィック改善が含まれています。
AGSL によるカスタム グラフィック エフェクト
Android 16 adds RuntimeColorFilter and
RuntimeXfermode, allowing you to author complex effects like
Threshold, Sepia, and Hue Saturation and apply them to draw calls. Since Android
13, you've been able to use AGSL to create custom
RuntimeShaders that extend Shader. The new API
mirrors this, adding an AGSL-powered RuntimeColorFilter that
extends ColorFilter, and a Xfermode effect that
lets you implement AGSL-based custom compositing and blending between source and
destination pixels.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
接続
Android 16 では、通信とワイヤレス技術の最新の進歩をアプリで利用できるようにプラットフォームが更新されています。
高度なセキュリティによる測距
Android 16 では、Wi-Fi 6 の 802.11az を搭載したサポート対象デバイスの Wi-Fi 位置情報で堅牢なセキュリティ機能がサポートされるようになりました。これにより、アプリは、プロトコルの精度、スケーラビリティ、動的スケジューリングの向上と、AES-256 ベースの暗号化や MITM 攻撃からの保護などのセキュリティ強化を組み合わせることができます。これにより、ノートパソコンや車のドアのロック解除など、近接型のユースケースでより安全に使用できます。802.11az は Wi-Fi 6 規格と統合されており、そのインフラストラクチャと機能を活用することで、より広範な導入とより簡単なデプロイを実現します。
汎用測距 API
Android 16 includes the new RangingManager, which provides
ways to determine the distance and angle on supported hardware between the local
device and a remote device. RangingManager supports the usage of a variety of
ranging technologies such as BLE channel sounding, BLE RSSI-based ranging, Ultra
Wideband, and Wi-Fi round trip time.
メディア
Android 16 には、メディア エクスペリエンスを向上させるさまざまな機能が含まれています。
写真選択ツールの改善
The photo picker provides a safe, built-in way for users to grant your app access to selected images and videos from both local and cloud storage, instead of their entire media library. Using a combination of Modular System Components through Google System Updates and Google Play services, it's supported back to Android 4.4 (API level 19). Integration requires just a few lines of code with the associated Android Jetpack library.
Android 16 includes the following improvements to the photo picker:
- Embedded photo picker: New APIs that enable apps to embed the photo picker into their view hierarchy. This allows it to feel like a more integrated part of the app while still leveraging the process isolation that allows users to select media without the app needing overly broad permissions. To maximize compatibility across platform versions and simplify your integration, you'll want to use the forthcoming Android Jetpack library if you want to integrate the embedded photo picker.
- Cloud search in photo picker: New APIs that enable searching from the cloud media provider for the Android photo picker. Search functionality in the photo picker is coming soon.
高度なプロ向け動画
Android 16 introduces support for the Advanced Professional Video (APV) codec which is designed to be used for professional level high quality video recording and post production.
The APV codec standard has the following features:
- Perceptually lossless video quality (close to raw video quality)
- Low complexity and high throughput intra-frame-only coding (without pixel domain prediction) to better support editing workflows
- Support for high bit-rate range up to a few Gbps for 2K, 4K and 8K resolution content, enabled by a lightweight entropy coding scheme
- Frame tiling for immersive content and for enabling parallel encoding and decoding
- Support for various chroma sampling formats and bit-depths
- Support for multiple decoding and re-encoding without severe visual quality degradation
- Support multi-view video and auxiliary video like depth, alpha, and preview
- Support for HDR10/10+ and user-defined metadata
A reference implementation of APV is provided through the OpenAPV project. Android 16 will implement support for the APV 422-10 Profile that provides YUV 422 color sampling along with 10-bit encoding and for target bitrates of up to 2Gbps.
プライバシー
Android 16 には、アプリ デベロッパーがユーザーのプライバシーを保護するのに役立つさまざまな機能が含まれています。
ヘルスコネクトの更新
デベロッパー プレビュー版のヘルスコネクトでは、中程度および激しいアクティビティに関する世界保健機関のガイドラインに従って定義された新しいデータ型 ACTIVITY_INTENSITY が追加されています。各レコードには、開始時間、終了時間、アクティビティの強度(中程度または激しい)が必要です。
ヘルスコネクトには、健康記録をサポートする更新された API も含まれています。これにより、アプリはユーザーの明示的な同意を得て、FHIR 形式の医療記録の読み取りと書き込みを行うことができます。この API は早期アクセス プログラムです。ご参加を希望される場合は、早期アクセス プログラムにご登録ください。
Android 版プライバシー サンドボックス
Android 16 incorporates the latest version of the Privacy Sandbox on Android, part of our ongoing work to develop technologies where users know their privacy is protected. Our website has more about the Privacy Sandbox on Android developer beta program to help you get started. Check out the SDK Runtime which allows SDKs to run in a dedicated runtime environment separate from the app they are serving, providing stronger safeguards around user data collection and sharing.
セキュリティ
Android 16 には、アプリのセキュリティを強化し、アプリのデータを保護する機能が含まれています。
Key sharing API
Android 16 では、Android Keystore キーへのアクセスを他のアプリと共有する API が追加されています。新しい KeyStoreManager クラスは、アプリの uid による鍵へのアクセスの付与と取り消しをサポートし、アプリが共有鍵にアクセスするための API が含まれています。
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16 では、Android のフォーム ファクタを最大限に活用できるアプリのサポートが提供されます。
テレビの画質と音質の標準化フレームワーク
Android 16 の新しい MediaQuality パッケージは、オーディオ プロファイルと画像プロファイル、ハードウェア関連の設定にアクセスするための標準化された API のセットを公開します。これにより、ストリーミング アプリはプロファイルをクエリし、メディアに動的に適用できます。
- ダイナミック レンジが広い映画では、シャドウの微細なディテールを認識し、周囲光に合わせて調整するために、より高い色の精度が必要になります。そのため、明るさよりも色の精度を重視したプロファイルが適している場合があります。
- スポーツのライブ配信は、ダイナミック レンジが狭い状態でマスタリングされることが多く、日光の下で視聴されることも多いので、色の精度よりも明るさを優先するプロファイルの方が良い結果が得られます。
- 完全にインタラクティブなコンテンツでは、レイテンシを低減するために最小限の処理と高いフレームレートが必要です。そのため、多くのテレビにはゲーム プロファイルが付属しています。
この API を使用すると、アプリでプロファイルを切り替えたり、ユーザーがサポートされているテレビをコンテンツに合わせて調整したりできます。
多言語対応
Android 16 では、デバイスが異なる言語で使用されている場合のユーザー エクスペリエンスを補完する機能が追加されています。
縦向きのテキスト
Android 16 adds low-level support for rendering and measuring text vertically to
provide foundational vertical writing support for library developers. This is
particularly useful for languages like Japanese that commonly use vertical
writing systems. A new flag,
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG,
has been added to the Paint class. When
this flag is set using
Paint.setFlags, Paint's
text measurement APIs will report vertical advances instead of horizontal
advances, and Canvas will draw text
vertically.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
測定システムのカスタマイズ
ユーザーは、[設定] の地域別の設定で測定単位をカスタマイズできるようになりました。ユーザー設定はロケール コードの一部として含まれるため、ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED に BroadcastReceiver を登録して、地域の設定が変更されたときに言語 / 地域の構成の変更を処理できます。
フォーマッタを使用すると、ローカル エクスペリエンスに合わせることができます。たとえば、英語(米国)の「0.5 in」は、スマートフォンを英語(デンマーク)に設定しているユーザー、または英語(米国)でスマートフォンを使用しているユーザーで、測定単位としてメートル法を設定している場合は「12,7 mm」になります。
これらの設定を確認するには、設定アプリを開いて [システム] > [言語と地域] に移動します。

