Android 16 平台包含可能對應用程式造成影響的行為變更。無論 targetSdkVersion 為何,當應用程式在 Android 16 上執行時,下列行為變更將會套用至所有應用程式。您應測試應用程式,並視需要修改,以便在適當情況下支援這些變更。
另請務必查看僅對指定 Android 16 為目標版本的應用程式造成影響的行為變更。
核心功能
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列變更,可修改或擴充 Android 系統的各種核心功能。
JobScheduler 配額最佳化
Starting in Android 16, we're adjusting regular and expedited job execution runtime quota based on the following factors:
- Which app standby bucket the application is in: in Android 16, active standby buckets will start being enforced by a generous runtime quota.
- If the job starts execution while the app is in a top state: in Android 16, Jobs started while the app is visible to the user and continues after the app becomes invisible, will adhere to the job runtime quota.
- If the job is executing while running a Foreground Service: in Android 16, jobs that are executing concurrently with a foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota. If you're leveraging jobs for user initiated data transfer, consider using user initiated data transfer jobs instead.
This change impacts tasks scheduled using WorkManager, JobScheduler, and
DownloadManager. To debug why a job was stopped, we recommend logging why your
job was stopped by calling WorkInfo.getStopReason() (for
JobScheduler jobs, call JobParameters.getStopReason()).
For information about how your app's state affects the resources it can use, see Power management resource limits. For more information on battery-optimal best practices, refer to guidance on optimize battery use for task scheduling APIs.
We also recommend leveraging the new
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API introduced in
Android 16 to understand why a job has not executed.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable override of certain job quota optimizations as long as the app is running on an Android 16 device.
To disable enforcement of "top state will adhere to job runtime quota", run the
following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To disable enforcement of "jobs that are executing while concurrently with a
foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota", run the following
adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To test certain app standby bucket behavior, you can set the app standby bucket
of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
To understand the app standby bucket your app is in, you can get the app standby
bucket of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Abandoned empty jobs stop reason
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
完全淘汰 JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
The JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
method indicates the importance of a job while the scheduling app is in the
foreground or when temporarily exempted from background restrictions.
This method has been deprecated since Android 12 (API level 31). Starting in Android 16, it no longer functions effectively and calling this method will be ignored.
This removal of functionality also applies to
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). Starting in Android
16, if the method is called, the method returns false.
已排序的廣播優先順序範圍不再是全域
Android 應用程式可定義廣播接收器的優先順序,藉此控制接收器接收及處理廣播的順序。對於資訊清單宣告的接收器,應用程式可以使用 android:priority 屬性來定義優先順序,而對於內容註冊的接收器,應用程式可以使用 IntentFilter#setPriority() API 來定義優先順序。傳送廣播訊息時,系統會依優先順序 (由高至低) 將訊息傳送給接收器。
在 Android 16 中,系統無法保證使用 android:priority 屬性或在不同程序中使用 IntentFilter#setPriority() 的廣播傳送順序。廣播優先順序只會在相同的應用程式程序中受到尊重,而不會跨所有程序。
此外,廣播優先順序會自動限制在 (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) 的範圍內。只有系統元件可將 SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY、SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY 設為廣播優先順序。
如果您的應用程式執行下列任一操作,可能會受到影響:
- 您的應用程式已宣告多個使用相同廣播意圖的程序,並且預期會按照優先順序接收這些意圖。
- 您的應用程式程序會與其他程序互動,並預期以特定順序接收廣播意圖。
如果程序需要相互協調,則應使用其他協調管道進行通訊。
ART 內部變更
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
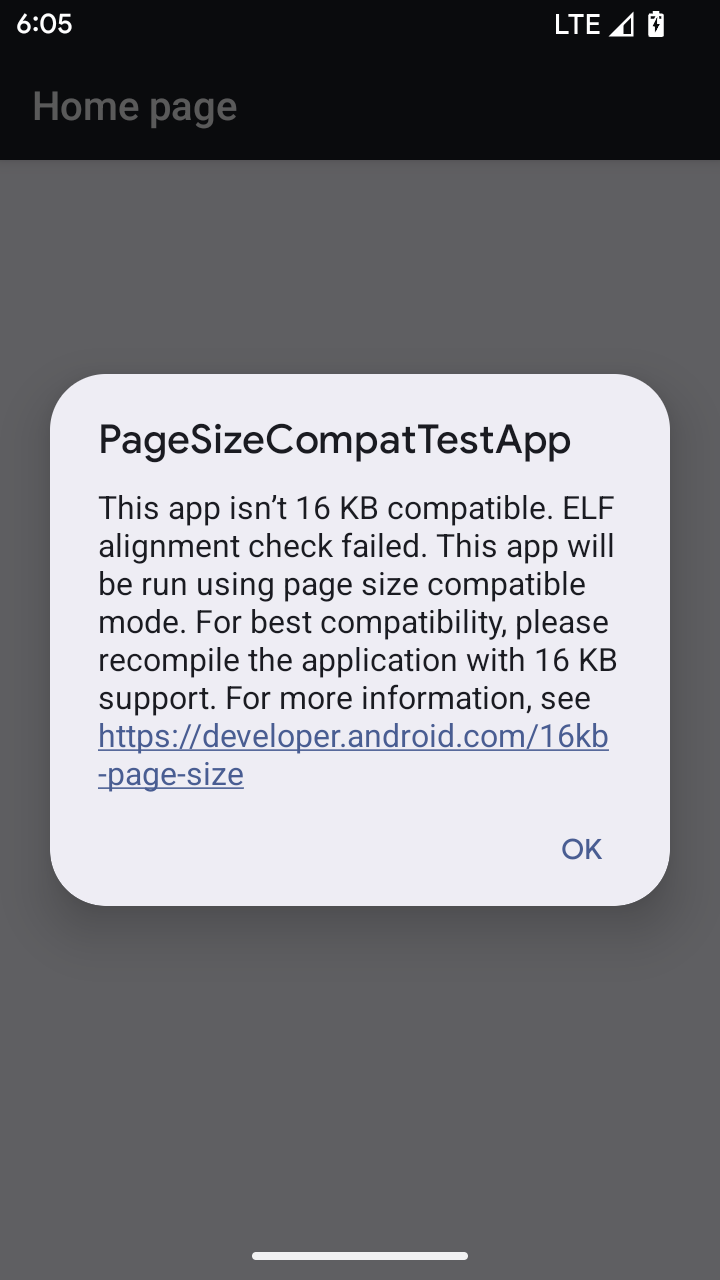
16 KB 頁面大小相容模式
Android 15 introduced support for 16 KB memory pages to optimize performance of the platform. Android 16 adds a compatibility mode, allowing some apps built for 4 KB memory pages to run on a device configured for 16 KB memory pages.
When your app is running on a device with Android 16 or higher, if Android
detects that your app has 4 KB aligned memory pages, it automatically uses
compatibility mode and display a notification dialog to the user. Setting the
android:pageSizeCompat property in the AndroidManifest.xml to enable the
backwards compatibility mode will prevent the display of the dialog when your
app launches. To use the android:pageSizeCompat property, compile your app
using the Android 16 SDK.
For best performance, reliability, and stability, your app should still be 16 KB aligned. Check out our recent blog post on updating your apps to support 16 KB memory pages for more details.
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列異動,旨在打造更一致、直觀的使用者體驗。
淘汰干擾性無障礙公告
Android 16 已淘汰無障礙公告,這類公告的特色是使用 announceForAccessibility 或調度 TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT 無障礙事件。這可能會為 TalkBack 和 Android 螢幕閱讀器的使用者帶來不一致的使用者體驗,而替代方案可在各種 Android 輔助技術中,滿足更廣泛的使用者需求。
替代方案範例:
- 如要進行重大的 UI 變更 (例如變更視窗),請使用
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)和setAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)。在 Compose 中使用Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - 如要通知使用者關鍵 UI 的變更,請使用
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)。在 Compose 中使用Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}。這些事件應謹慎使用,因為每次 View 更新時,這些事件都可能產生通知。 - 如要通知使用者錯誤,請傳送
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERROR類型的AccessibilityEvent,並設定AccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence),或使用TextView#setError(CharSequence)。
如要進一步瞭解建議的替代方案,請參閱已淘汰的 announceForAccessibility API 參考說明文件。
支援三按鈕操作模式
Android 16 brings predictive back support to the 3-button navigation for apps that have properly migrated to predictive back. Long-pressing the back button initiates a predictive back animation, giving you a preview of where the back swipe takes you.
This behavior applies across all areas of the system that support predictive back animations, including the system animations (back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity).
自動套用主題色應用程式圖示
從 Android 16 QPR 2 開始,Android 會自動將主題套用至應用程式圖示,打造一致的主畫面體驗。如果應用程式未提供自己的主題式應用程式圖示,就會發生這種情況。應用程式可以在自動調整式圖示中加入單色圖層,並在 Android Studio 中預覽應用程式圖示的外觀,藉此控制主題式應用程式圖示的設計。
裝置板型規格
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含以下變更,適用於虛擬裝置擁有者將應用程式投放到螢幕時。
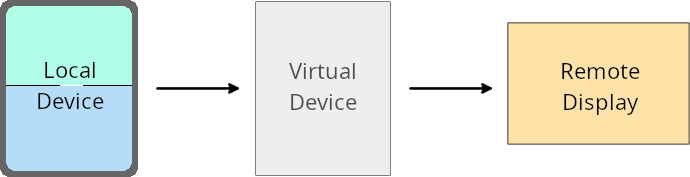
虛擬裝置擁有者覆寫
虛擬裝置擁有者是可信任或具備特殊權限的應用程式,可建立及管理虛擬裝置。虛擬裝置擁有者可以在虛擬裝置上執行應用程式,然後將應用程式投影到遠端裝置的螢幕,例如個人電腦、虛擬實境裝置或車輛資訊娛樂系統。虛擬裝置擁有者使用本機裝置,例如手機。
個別應用程式覆寫值
在搭載 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 的裝置上,虛擬裝置擁有者可以覆寫所管理特定虛擬裝置的應用程式設定。舉例來說,為了改善應用程式版面配置,虛擬裝置擁有者在將應用程式投影到外部螢幕時,可以忽略方向、長寬比和可調整大小的限制。
常見的破壞性變更
Android 16 的行為可能會影響應用程式在大型螢幕 (例如車用螢幕或 Chromebook) 上的 UI,尤其是專為直向小螢幕設計的版面配置。如要瞭解如何讓應用程式自動調整版面,以配合所有裝置板型規格,請參閱「關於自動調整版面」。
參考資料
安全性
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含多項異動,可提升系統安全性,協助保護應用程式和使用者免受惡意應用程式侵害。
安全性提高,避免意圖重新導向攻擊
Android 16 provides default security against general Intent redirection
attacks, with minimum compatibility and developer changes required.
We are introducing by-default security hardening solutions to Intent
redirection exploits. In most cases, apps that use intents normally won't
experience any compatibility issues; we've gathered metrics throughout our
development process to monitor which apps might experience breakages.
Intent redirection in Android occurs when an attacker can partly or fully control the contents of an intent used to launch a new component in the context of a vulnerable app, while the victim app launches an untrusted sub-level intent in an extras field of an ("top-level") Intent. This can lead to the attacker app launching private components in the context of the victim app, triggering privileged actions, or gaining URI access to sensitive data, potentially leading to data theft and arbitrary code execution.
Opt out of Intent redirection handling
Android 16 introduces a new API that allows apps to opt out of launch security protections. This might be necessary in specific cases where the default security behavior interferes with legitimate app use cases.
For applications compiling against Android 16 (API level 36) SDK or higher
You can directly use the removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method on the Intent
object.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
For applications compiling against Android 15 (API level 35) or lower
While not recommended, you can use reflection to access the
removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
隨附應用程式不再收到探索逾時通知
Android 16 introduces a new behavior during
companion device pairing flow to protect the user's location
privacy from malicious apps. All companion apps running on Android 16 are no
longer directly notified of discovery timeout using
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Instead, the user is
notified of timeout events with a visual dialog. When the user dismisses
the dialog, the app is alerted of the association failure with
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
The search duration has also been extended from the original 20 seconds, and the device discovery can be stopped by the user at any point during the search. If at least one device was discovered within the first 20 seconds of starting the search, the CDM stops searching for additional devices.
連線能力
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 的藍牙堆疊包含下列變更,可提升與周邊裝置的連線能力。
改善債券損失處理方式
自 Android 16 起,我們已更新藍牙堆疊,以便在偵測到遠端連結遺失時,提升安全性和使用者體驗。先前系統會自動移除配對連結,並啟動新的配對程序,這可能會導致不小心重新配對。我們發現許多應用程式並未以一致的方式處理連結失效事件。
為統一使用體驗,Android 16 改善了系統的連結遺失處理方式。如果先前已配對的藍牙裝置無法在重新連線時驗證,系統會中斷連結、保留本機配對資訊,並顯示系統對話方塊,告知使用者配對失敗,並引導他們重新配對。

