पिछली रिलीज़ की तरह, Android 16 में भी कुछ ऐसे बदलाव किए गए हैं जिनसे आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर पड़ सकता है. यहां दिए गए बदलाव, सिर्फ़ उन ऐप्लिकेशन पर लागू होते हैं जो Android 16 या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट कर रहे हैं. अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, Android 16 या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट कर रहा है, तो आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में बदलाव करना चाहिए, ताकि वह इन बदलावों के साथ काम कर सके.
Android 16 पर चलने वाले सभी ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर डालने वाले बदलावों की सूची भी ज़रूर देखें. इससे कोई फ़र्क़ नहीं पड़ता कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन का targetSdkVersion क्या है.
उपयोगकर्ता अनुभव और सिस्टम यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई)
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में ये बदलाव शामिल हैं. इनका मकसद, उपयोगकर्ताओं को बेहतर अनुभव देना है.
एज-टू-एज डिसप्ले से ऑप्ट-आउट करने की सुविधा बंद की जा रही है
Android 15 में, Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, एज-टू-एज डिसप्ले फ़ॉर्मैट को लागू किया गया था. हालांकि, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement को true पर सेट करके, इस सुविधा से ऑप्ट-आउट कर सकता था. Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement काम नहीं करेगा और इसे बंद कर दिया जाएगा. साथ ही, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन एज-टू-एज डिसप्ले की सुविधा से ऑप्ट-आउट नहीं कर पाएगा.
- अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) को टारगेट करता है और Android 15 वाले डिवाइस पर चल रहा है, तो
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementकाम करता रहेगा. - अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) को टारगेट करता है और Android 16 डिवाइस पर चल रहा है, तो
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementबंद हो जाता है.
Android 16 में टेस्टिंग के लिए, पक्का करें कि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन एज-टू-एज डिसप्ले को सपोर्ट करता हो. साथ ही, R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement का इस्तेमाल हटा दें, ताकि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 15 डिवाइस पर भी एज-टू-एज डिसप्ले को सपोर्ट कर सके. एंड-टू-एंड लेआउट के लिए, Compose और Views के बारे में दिशा-निर्देश देखें.
अनुमान लगाने वाली 'वापस जाएं' सुविधा के लिए, माइग्रेशन या ऑप्ट-आउट करना ज़रूरी है
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन और Android 16 या इसके बाद के वर्शन वाले डिवाइस पर चलने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, पीछे जाने पर झलक दिखाने वाले सिस्टम ऐनिमेशन (होम पेज पर वापस जाना, अलग-अलग ऐप्लिकेशन पर काम करना, और ऐप्लिकेशन में मौजूद अलग-अलग गतिविधि) डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से चालू होते हैं.
इसके अलावा, onBackPressed को कॉल नहीं किया जाता है और KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK को अब डिसपैच नहीं किया जाता है.
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, 'वापस जाएं' इवेंट को इंटरसेप्ट करता है और आपने अब तक अनुमानित बैक जेस्चर पर माइग्रेट नहीं किया है, तो बैक नेविगेशन के लिए उपलब्ध एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को अपडेट करें. इसके अलावा, AndroidManifest.xml फ़ाइल के <application> या <activity> टैग में android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback एट्रिब्यूट को false पर सेट करके, कुछ समय के लिए ऑप्ट आउट करें.
Elegant फ़ॉन्ट एपीआई बंद कर दिए गए हैं और अब काम नहीं करते
Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, elegantTextHeight
TextView एट्रिब्यूट की वैल्यू डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से true पर सेट होती है. इससे कॉम्पैक्ट फ़ॉन्ट को ऐसे फ़ॉन्ट से बदल दिया जाता है जिसे पढ़ना आसान होता है. elegantTextHeight एट्रिब्यूट को false पर सेट करके, इसे बदला जा सकता है.
Android 16 में, elegantTextHeight एट्रिब्यूट का इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जा सकता. साथ ही, आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 16 को टारगेट करने के बाद, इस एट्रिब्यूट को अनदेखा कर दिया जाएगा. इन एपीआई से कंट्रोल किए जाने वाले "यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) फ़ॉन्ट" बंद किए जा रहे हैं. इसलिए, आपको किसी भी लेआउट को अडैप्ट करना चाहिए, ताकि यह पक्का किया जा सके कि आने वाले समय में भी ऐरेबिक, लाओ, म्यांमार, तमिल, गुजराती, कन्नड़, मलयालम, ओडिया, तेलुगु या थाई भाषा में टेक्स्ट को एक जैसा और सही तरीके से रेंडर किया जा सके.
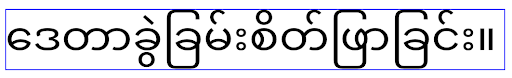
elegantTextHeight एट्रिब्यूट के लिए, Android 14 (एपीआई लेवल 34) और उससे पहले के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन या Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐसे ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए व्यवहार, जिन्होंने elegantTextHeight एट्रिब्यूट को false पर सेट करके डिफ़ॉल्ट सेटिंग को बदल दिया है.
elegantTextHeight एट्रिब्यूट के लिए, Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन या Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) को टारगेट करने वाले उन ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए व्यवहार, जिन्होंने elegantTextHeight एट्रिब्यूट को false पर सेट करके, डिफ़ॉल्ट सेटिंग को बदला नहीं है.मुख्य फ़ंक्शन
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में ये बदलाव शामिल हैं. इनसे Android सिस्टम की कई मुख्य क्षमताओं में बदलाव होता है या उन्हें बढ़ाया जाता है.
तय की गई दर के हिसाब से काम के शेड्यूल को ऑप्टिमाइज़ करना
Android 16 को टारगेट करने से पहले, जब scheduleAtFixedRate किसी टास्क को पूरा करने के लिए, प्रोसेस लाइफ़साइकल के मान्य समयसीमा के बाहर होने की वजह से, टास्क पूरा नहीं हो पाता था, तो ऐप्लिकेशन के मान्य लाइफ़साइकल में वापस आने पर, सभी टास्क तुरंत पूरे हो जाते थे.
Android 16 को टारगेट करते समय, scheduleAtFixedRate को एक बार भी पूरा न करने पर, ऐप्लिकेशन के मान्य लाइफ़साइकल पर वापस आने के बाद, उसे तुरंत पूरा कर दिया जाता है. इस बदलाव से, ऐप्लिकेशन की परफ़ॉर्मेंस बेहतर हो सकती है. अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में इस व्यवहार की जांच करें और देखें कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर इसका असर पड़ा है या नहीं.
ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ काम करने की सुविधा वाले फ़्रेमवर्क का इस्तेमाल करके और STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS के साथ काम करने की सुविधा वाले फ़्लैग को चालू करके भी जांच की जा सकती है.
डिवाइस के नाप या आकार
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में, बड़ी स्क्रीन वाले डिवाइसों पर ऐप्लिकेशन दिखाने के लिए ये बदलाव किए गए हैं.
अडैप्टिव लेआउट
Android ऐप्लिकेशन अब कई तरह के डिवाइसों (जैसे कि फ़ोन, टैबलेट, फ़ोल्ड किए जा सकने वाले डिवाइस, डेस्कटॉप, कार, और टीवी) पर काम करते हैं. साथ ही, बड़ी स्क्रीन पर विंडो मोड (जैसे कि स्प्लिट स्क्रीन और डेस्कटॉप विंडो) में भी काम करते हैं. इसलिए, डेवलपर को ऐसे Android ऐप्लिकेशन बनाने चाहिए जो डिवाइस के ओरिएंटेशन के हिसाब से, किसी भी स्क्रीन और विंडो के साइज़ के मुताबिक अपने-आप अडजस्ट हो जाएं. आज के समय में, अलग-अलग डिवाइसों का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है. इसलिए, ओरिएंटेशन और साइज़ बदलने जैसी पाबंदियां बहुत ज़्यादा हैं.
ओरिएंटेशन, साइज़ बदलने, और आसपेक्ट रेशियो (लंबाई-चौड़ाई का अनुपात) से जुड़ी पाबंदियों को अनदेखा करें
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, ओरिएंटेशन, साइज़ बदलने, और आसपेक्ट रेशियो (लंबाई-चौड़ाई का अनुपात) से जुड़ी पाबंदियां अब उन डिसप्ले पर लागू नहीं होती जिनकी चौड़ाई >= 600dp है. ऐप्लिकेशन, पूरी डिसप्ले विंडो को भरते हैं. भले ही, आसपेक्ट रेशियो कुछ भी हो या उपयोगकर्ता का पसंदीदा ओरिएंटेशन कुछ भी हो. साथ ही, पिलरबॉक्सिंग का इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जाता है.
इस बदलाव से, प्लैटफ़ॉर्म के नए स्टैंडर्ड बिहेवियर के बारे में पता चलता है. Android एक ऐसे मॉडल की ओर बढ़ रहा है जहां ऐप्लिकेशन को अलग-अलग ओरिएंटेशन, डिसप्ले साइज़, और आसपेक्ट रेशियो के हिसाब से काम करना होगा. स्क्रीन के ओरिएंटेशन को लॉक करने या स्क्रीन का साइज़ बदलने की सुविधा को सीमित करने जैसी पाबंदियों की वजह से, ऐप्लिकेशन को अलग-अलग डिवाइसों के हिसाब से अडजस्ट करने में समस्याएं आती हैं. उपयोगकर्ताओं को बेहतर अनुभव देने के लिए, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को अडैप्टिव बनाएं.
ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ काम करने वाले फ़्रेमवर्क का इस्तेमाल करके और UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT कंपैट फ़्लैग चालू करके भी, इस व्यवहार की जांच की जा सकती है.
नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले सामान्य बदलाव
ओरिएंटेशन, साइज़ बदलने की सुविधा, और आसपेक्ट रेशियो से जुड़ी पाबंदियों को अनदेखा करने से, कुछ डिवाइसों पर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) पर असर पड़ सकता है. खास तौर पर, उन एलिमेंट पर जो पोर्ट्रेट ओरिएंटेशन में लॉक किए गए छोटे लेआउट के लिए डिज़ाइन किए गए थे. उदाहरण के लिए, स्ट्रेच किए गए लेआउट और स्क्रीन से बाहर की ओर ऐनिमेशन और कॉम्पोनेंट जैसी समस्याएं. आस्पेक्ट रेशियो या ओरिएंटेशन के बारे में कोई भी अनुमान लगाने से, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में विज़ुअल से जुड़ी समस्याएं हो सकती हैं. ज़्यादा जानें कि इन समस्याओं से कैसे बचा जा सकता है और अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के अडैप्टिव बिहेवियर को कैसे बेहतर बनाया जा सकता है.
डिवाइस को घुमाने की सुविधा चालू करने से, गतिविधि को फिर से बनाने की प्रोसेस ज़्यादा बार होती है. अगर उपयोगकर्ता की स्थिति को ठीक से सेव नहीं किया जाता है, तो इससे उपयोगकर्ता की स्थिति खो सकती है. यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस की स्थितियां सेव करें में, यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस की स्थिति को सही तरीके से सेव करने का तरीका जानें.
लागू करने से जुड़ी जानकारी
फ़ुल-स्क्रीन और मल्टी-विंडो मोड में, बड़ी स्क्रीन वाले डिवाइसों पर मेनिफ़ेस्ट के इन एट्रिब्यूट और रनटाइम एपीआई को अनदेखा किया जाता है:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), और getRequestedOrientation() के लिए इन वैल्यू को अनदेखा किया जाता है:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
डिसप्ले के साइज़ में बदलाव करने से जुड़ी समस्या के लिए, android:resizeableActivity="false", android:minAspectRatio, और android:maxAspectRatio का कोई असर नहीं पड़ता.
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, बड़ी स्क्रीन पर ऐप्लिकेशन के ओरिएंटेशन, साइज़ बदलने, और आसपेक्ट रेशियो से जुड़ी पाबंदियों को डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से अनदेखा किया जाता है. हालांकि, जो ऐप्लिकेशन पूरी तरह से तैयार नहीं हैं वे कुछ समय के लिए इस सेटिंग को बदल सकते हैं. इसके लिए, उन्हें ऑप्ट आउट करना होगा. इससे ऐप्लिकेशन, कंपैटिबिलिटी मोड में काम करने लगेगा.
अपवाद
Android 16 में ओरिएंटेशन, साइज़ बदलने, और आसपेक्ट रेशियो (लंबाई-चौड़ाई का अनुपात) से जुड़ी पाबंदियां इन स्थितियों में लागू नहीं होती हैं:
- गेम (
android:appCategoryफ़्लैग के आधार पर) - उपयोगकर्ताओं ने डिवाइस की आसपेक्ट रेशियो (लंबाई-चौड़ाई का अनुपात) सेटिंग में, ऐप्लिकेशन के डिफ़ॉल्ट व्यवहार के लिए साफ़ तौर पर ऑप्ट-इन किया हो
sw600dpसे छोटी स्क्रीन
कुछ समय के लिए ऑप्ट आउट करना
किसी गतिविधि के लिए ऑप्ट आउट करने के लिए, PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY मेनिफ़ेस्ट प्रॉपर्टी का एलान करें:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के कई हिस्से Android 16 के लिए तैयार नहीं हैं, तो ऐप्लिकेशन लेवल पर एक ही प्रॉपर्टी लागू करके, पूरी तरह से ऑप्ट आउट किया जा सकता है:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
सेहत और फ़िटनेस
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में, सेहत और फ़िटनेस से जुड़े डेटा के लिए ये बदलाव किए गए हैं.
सेहत और फ़िटनेस से जुड़ी अनुमतियां
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, BODY_SENSORS अनुमतियां, android.permissions.health में मौजूद ज़्यादा बारीकी से कंट्रोल की जा सकने वाली अनुमतियों का इस्तेमाल करती हैं. Health Connect भी इनका इस्तेमाल करता है. Android 16 से, BODY_SENSORS या BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND की ज़रूरत वाले किसी भी एपीआई के लिए, अब android.permissions.health अनुमति की ज़रूरत होगी. इससे इन डेटा टाइप, एपीआई, और फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा टाइप पर असर पड़ता है:
- Wear OS पर Health Services से
HEART_RATE_BPM - Android Sensor Manager से
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - Wear OS पर
ProtoLayoutसेheartRateAccuracyऔरheartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH, जहांBODY_SENSORSकी जगहandroid.permission.healthकी अनुमति ज़रूरी है
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन इन एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो उसे अनुमति के लिए अनुरोध करना चाहिए:
- डिवाइस के इस्तेमाल के दौरान, धड़कन की दर, SpO2 या त्वचा के तापमान की निगरानी करने के लिए:
BODY_SENSORSके बजाय,android.permissions.healthमें जाकरREAD_HEART_RATEजैसी खास अनुमति का अनुरोध करें. - बैकग्राउंड में सेंसर ऐक्सेस करने के लिए:
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDके बजायREAD_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDका अनुरोध करें.
ये अनुमतियां, Health Connect से डेटा पढ़ने के ऐक्सेस को सुरक्षित रखने वाली अनुमतियों के जैसी ही होती हैं. Health Connect, सेहत, फ़िटनेस, और तंदुरुस्ती से जुड़े डेटा के लिए Android का डेटास्टोर है.
मोबाइल ऐप्लिकेशन पर मौजूद हैं
READ_HEART_RATE और अन्य ज़्यादा जानकारी वाली अनुमतियों का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए माइग्रेट करने वाले मोबाइल ऐप्लिकेशन को, ऐप्लिकेशन की निजता नीति दिखाने के लिए गतिविधि का एलान करना होगा. यह Health Connect की ज़रूरी शर्त के जैसी ही है.
कनेक्टिविटी
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में, ब्लूटूथ स्टैक में ये बदलाव किए गए हैं, ताकि सहायक डिवाइसों से कनेक्टिविटी को बेहतर बनाया जा सके.
बॉन्ड के खत्म होने और एन्क्रिप्शन में बदलावों को मैनेज करने के लिए नए इंटेंट
बॉन्ड के खोने की बेहतर तरीके से निगरानी करने के लिए, Android 16 में दो नए इंटेंट भी जोड़े गए हैं. इनसे ऐप्लिकेशन को बॉन्ड के खोने और एन्क्रिप्शन में हुए बदलावों के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी मिलती है.
Android 16 को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन अब ये काम कर सकते हैं:
- रिमोट बॉन्ड के गायब होने का पता चलने पर,
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGइंटेंट पाएं. इससे, उपयोगकर्ता को ज़्यादा जानकारी देने और ज़रूरी कार्रवाई करने में मदद मिलती है. - लिंक के एन्क्रिप्शन की स्थिति में बदलाव होने पर,
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEइंटेंट पाना. इसमें एन्क्रिप्शन की स्थिति में बदलाव, एन्क्रिप्शन एल्गोरिदम में बदलाव, और एन्क्रिप्शन कुंजी के साइज़ में बदलाव शामिल है. अगर बाद मेंACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEइंटेंट मिलने पर लिंक को एन्क्रिप्ट कर दिया जाता है, तो ऐप्लिकेशन को यह मान लेना चाहिए कि बॉन्ड फिर से चालू हो गया है.
अलग-अलग ओईएम के लागू करने के तरीकों के हिसाब से बदलाव करना
Android 16 में ये नए इंटेंट जोड़े गए हैं. हालांकि, इन्हें लागू करने और ब्रॉडकास्ट करने का तरीका, डिवाइस बनाने वाली अलग-अलग कंपनियों (ओईएम) के हिसाब से अलग-अलग हो सकता है. यह पक्का करने के लिए कि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन सभी डिवाइसों पर एक जैसा और भरोसेमंद अनुभव दे, डेवलपर को बॉन्ड लॉस मैनेजमेंट को इस तरह डिज़ाइन करना चाहिए कि वह इन संभावित बदलावों के हिसाब से आसानी से काम कर सके.
हमारा सुझाव है कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में ये काम किए जाएं:
अगर
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGइंटेंट ब्रॉडकास्ट किया जाता है, तो:सिस्टम, एसीएल (असिंक्रोनस कनेक्शन-लेस) लिंक को डिसकनेक्ट कर देगा. हालांकि, डिवाइस के लिए बॉन्ड की जानकारी को बनाए रखा जाएगा, जैसा कि यहां बताया गया है.
आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, इस इंटेंट का इस्तेमाल, डिवाइस के कनेक्ट होने की सुविधा बंद होने का पता लगाने के लिए मुख्य सिग्नल के तौर पर करना चाहिए. साथ ही, डिवाइस को अनलिंक करने या फिर से जोड़ने की प्रोसेस शुरू करने से पहले, उपयोगकर्ता को यह पुष्टि करने के लिए गाइड करना चाहिए कि रिमोट डिवाइस, कनेक्ट होने की सुविधा की रेंज में है या नहीं.
अगर
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGमिलने के बाद कोई डिवाइस डिसकनेक्ट हो जाता है, तो आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को उसे फिर से कनेक्ट करने में सावधानी बरतनी चाहिए. ऐसा इसलिए, क्योंकि हो सकता है कि डिवाइस अब सिस्टम से बंधा न हो.अगर
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGइंटेंट ब्रॉडकास्ट नहीं किया जाता है, तो:एसीएल लिंक कनेक्ट रहेगा. साथ ही, सिस्टम डिवाइस के लिए बॉन्ड की जानकारी हटा देगा. यह Android 15 में होने वाली प्रोसेस जैसी ही होगी.
इस स्थिति में, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को बॉन्ड के खत्म होने की जानकारी देने वाले मौजूदा तरीकों का इस्तेमाल करना जारी रखना चाहिए. ऐसा Android की पिछली रिलीज़ की तरह ही करना होगा, ताकि बॉन्ड के खत्म होने की जानकारी का पता लगाया जा सके और उसे मैनेज किया जा सके.
ब्लूटूथ कनेक्शन हटाने का नया तरीका
Android 16 को टारगेट करने वाले सभी ऐप्लिकेशन, अब CompanionDeviceManager में मौजूद सार्वजनिक एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करके, ब्लूटूथ डिवाइसों को अनपेयर कर सकते हैं. अगर किसी साथी डिवाइस को सीडीएम असोसिएशन के तौर पर मैनेज किया जा रहा है, तो ऐप्लिकेशन, उससे जुड़े डिवाइस पर नए removeBond(int) एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करके, ब्लूटूथ बॉन्ड हटाने की प्रोसेस को ट्रिगर कर सकता है. ऐप्लिकेशन, ब्लूटूथ डिवाइस के ब्रॉडकास्ट इवेंट ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED को सुनकर, बॉन्ड की स्थिति में हुए बदलावों को मॉनिटर कर सकता है.
सुरक्षा
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में, सुरक्षा से जुड़े ये बदलाव शामिल हैं.
MediaStore के वर्शन को लॉक करना
Android 16 या इसके बाद के वर्शन को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, MediaStore#getVersion() अब हर ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए यूनीक होगा. इससे वर्शन स्ट्रिंग से पहचान करने वाली प्रॉपर्टी हट जाती हैं, ताकि फ़िंगरप्रिंटिंग तकनीकों के गलत इस्तेमाल को रोका जा सके. ऐप्लिकेशन को इस वर्शन के फ़ॉर्मैट के बारे में कोई अनुमान नहीं लगाना चाहिए. इस एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करते समय, ऐप्लिकेशन को पहले से ही वर्शन में होने वाले बदलावों को मैनेज करना चाहिए. ज़्यादातर मामलों में, उन्हें अपने मौजूदा व्यवहार में बदलाव करने की ज़रूरत नहीं पड़ती. हालांकि, ऐसा तब तक नहीं होगा, जब तक डेवलपर ने इस एपीआई के दायरे से बाहर की अतिरिक्त जानकारी का अनुमान लगाने की कोशिश नहीं की है.
ज़्यादा सुरक्षित इंटेंट
Safer Intents सुविधा, सुरक्षा से जुड़ी एक पहल है. इसे कई चरणों में लागू किया जाता है. इसका मकसद, Android के इंटेंट रिज़ॉल्यूशन मैकेनिज़्म की सुरक्षा को बेहतर बनाना है. इसका मकसद, ऐप्लिकेशन को नुकसान पहुंचाने वाली गतिविधियों से बचाना है. इसके लिए, इंटेंट प्रोसेसिंग के दौरान जांचें जोड़ी जाती हैं. साथ ही, उन इंटेंट को फ़िल्टर किया जाता है जो कुछ खास शर्तों को पूरा नहीं करते.
Android 15 में, यह सुविधा मैसेज भेजने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन पर फ़ोकस करती थी. अब Android 16 में, इसका कंट्रोल मैसेज पाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन को मिल गया है. इससे डेवलपर, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन मेनिफ़ेस्ट का इस्तेमाल करके, इंटेंट रिज़ॉल्यूशन की सख्त सेटिंग के लिए ऑप्ट-इन कर सकते हैं.
दो मुख्य बदलाव लागू किए जा रहे हैं:
एक्सप्लिसिट इंटेंट, टारगेट कॉम्पोनेंट के इंटेंट फ़िल्टर से मेल खाने चाहिए: अगर कोई इंटेंट किसी कॉम्पोनेंट को साफ़ तौर पर टारगेट करता है, तो उसे उस कॉम्पोनेंट के इंटेंट फ़िल्टर से मेल खाना चाहिए.
कार्रवाई के बिना इंटेंट, किसी भी इंटेंट फ़िल्टर से मैच नहीं हो सकते: जिन इंटेंट में कोई कार्रवाई तय नहीं की गई है उन्हें किसी भी इंटेंट फ़िल्टर से हल नहीं किया जाना चाहिए.
ये बदलाव सिर्फ़ तब लागू होते हैं, जब एक से ज़्यादा ऐप्लिकेशन शामिल हों. इनका असर, किसी एक ऐप्लिकेशन में इंटेंट हैंडलिंग पर नहीं पड़ता.
असर
ऑप्ट-इन करने का मतलब है कि डेवलपर को इसे अपने ऐप्लिकेशन मेनिफ़ेस्ट में साफ़ तौर पर चालू करना होगा, ताकि यह सुविधा काम कर सके. इसलिए, इस सुविधा का असर सिर्फ़ उन ऐप्लिकेशन पर पड़ेगा जिनके डेवलपर:
- Safer Intents सुविधा और इसके फ़ायदों के बारे में जानते हों.
- अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में, उपयोगकर्ता के इरादे को समझने के लिए बेहतर तरीकों का इस्तेमाल करें.
ऑप्ट-इन करने के इस तरीके से, उन मौजूदा ऐप्लिकेशन के काम करने में आने वाली समस्याओं का जोखिम कम हो जाता है जो इंटेंट रिज़ॉल्यूशन के मौजूदा, कम सुरक्षित तरीके पर निर्भर हो सकते हैं.
Android 16 में इसका शुरुआती असर सीमित हो सकता है. हालांकि, Safer Intents पहल के तहत, Android के आने वाले वर्शन में इसका असर ज़्यादा होगा. हमारा प्लान, इंटेंट को सटीक तरीके से समझने की सुविधा को डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से चालू करने का है.
Safer Intents सुविधा, Android नेटवर्क की सुरक्षा को काफ़ी हद तक बेहतर बना सकती है. ऐसा इसलिए, क्योंकि इससे नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, इंटेंट रिज़ॉल्यूशन मैकेनिज़्म में मौजूद जोखिमों का फ़ायदा उठाना ज़्यादा मुश्किल हो जाता है.
हालांकि, ऑप्ट-आउट करने और नीति उल्लंघन ठीक करने के तरीके (एनफ़ोर्समेंट) को लागू करने के दौरान, मौजूदा ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ काम करने से जुड़ी संभावित समस्याओं को हल करने के लिए, सावधानी से काम करना होगा.
लागू करना
डेवलपर को अपने ऐप्लिकेशन मेनिफ़ेस्ट में intentMatchingFlags एट्रिब्यूट का इस्तेमाल करके, इंटेंट मैचिंग की सुविधा को साफ़ तौर पर चालू करना होगा.
यहां एक उदाहरण दिया गया है, जिसमें पूरी सुविधा के लिए ऑप्ट-इन किया गया है. हालांकि, इसे पाने वाले व्यक्ति के लिए यह सुविधा बंद है/ऑप्ट-आउट की गई है:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले फ़्लैग के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी:
| फ़्लैग का नाम | ब्यौरा |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | इससे आने वाले इंटेंट के लिए, ज़्यादा सटीक मैचिंग लागू की जाती है |
| कोई नहीं | यह विकल्प, आने वाले इंटेंट के लिए मैचिंग के सभी खास नियमों को बंद कर देता है. एक से ज़्यादा फ़्लैग तय करते समय, अलग-अलग वैल्यू को "none" फ़्लैग को प्राथमिकता देकर हल किया जाता है |
| allowNullAction | यह मैचिंग के नियमों को आसान बनाता है, ताकि बिना किसी कार्रवाई वाले इंटेंट को मैच किया जा सके. इस फ़्लैग का इस्तेमाल "enforceIntentFilter" के साथ किया जाता है, ताकि किसी खास व्यवहार को लागू किया जा सके |
जांच और डीबग करना
नीति उल्लंघन ठीक करने के लिए लागू की गई कार्रवाई के चालू होने पर, ऐप्लिकेशन ठीक से काम करने चाहिए. ऐसा तब होगा, जब इंटेंट कॉलर ने इंटेंट को सही तरीके से भरा हो.
हालांकि, ब्लॉक किए गए इंटेंट, चेतावनी वाले लॉग मैसेज ट्रिगर करेंगे. जैसे, "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" और "Access blocked:". इनमें "PackageManager." टैग होगा. इससे पता चलता है कि कोई ऐसी समस्या है जो ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर डाल सकती है और इस पर ध्यान देने की ज़रूरत है.
Logcat फ़िल्टर:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
जीपीयू सिस्टम कॉल फ़िल्टरिंग
Mali GPU की सुरक्षा को बेहतर बनाने के लिए, प्रोडक्शन बिल्ड में उन Mali GPU IOCTL को ब्लॉक कर दिया गया है जो अब काम नहीं करते या जिनका इस्तेमाल सिर्फ़ GPU डेवलपमेंट के लिए किया जाता है. इसके अलावा, GPU प्रोफ़ाइलिंग के लिए इस्तेमाल किए जाने वाले IOCTL को शेल प्रोसेस या डीबग किए जा सकने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन तक सीमित कर दिया गया है. प्लैटफ़ॉर्म लेवल की नीति के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, SAC से जुड़ा अपडेट देखें.
यह बदलाव, Mali GPU का इस्तेमाल करने वाले Pixel डिवाइसों (Pixel 6 से 9) पर होता है. Arm ने r54p2 रिलीज़ के Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst में, अपने IOCTL को आधिकारिक तौर पर कैटगरी में बांटा है. ड्राइवर के आने वाले वर्शन में, इस सूची को अपडेट किया जाता रहेगा.
इस बदलाव से, ग्राफ़िक्स एपीआई (इनमें Vulkan और OpenGL शामिल हैं) पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ेगा. साथ ही, इससे डेवलपर या मौजूदा ऐप्लिकेशन पर भी कोई असर नहीं पड़ेगा. GPU की परफ़ॉर्मेंस की जांच करने वाले टूल, जैसे कि Streamline Performance Analyzer और Android GPU Inspector पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ेगा.
टेस्ट करना
अगर आपको SELinux से जुड़ी इस तरह की कोई सूचना मिलती है, तो हो सकता है कि इस बदलाव का असर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर पड़ा हो:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन को ब्लॉक किए गए IOCTL का इस्तेमाल करना है, तो कृपया एक बग फ़ाइल करें और उसे android-partner-security@google.com को असाइन करें.
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले सवाल
क्या नीति में किया गया यह बदलाव सभी ओईएम पर लागू होता है? यह बदलाव ऑप्ट-इन होगा. हालांकि, यह उन सभी ओईएम के लिए उपलब्ध होगा जो इस सुरक्षा को बेहतर बनाने वाले तरीके का इस्तेमाल करना चाहते हैं. बदलाव को लागू करने के निर्देश, लागू करने से जुड़े दस्तावेज़ में दिए गए हैं.
क्या इसे लागू करने के लिए, ओईएम कोडबेस में बदलाव करना ज़रूरी है या यह डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से AOSP की नई रिलीज़ के साथ आता है? प्लैटफ़ॉर्म लेवल पर किए गए बदलाव, डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से AOSP की नई रिलीज़ के साथ उपलब्ध होंगे. अगर वेंडर इस बदलाव को लागू करना चाहते हैं, तो वे अपने कोडबेस में इस बदलाव के लिए ऑप्ट-इन कर सकते हैं.
क्या एसओसी, आईओसीएल की सूची को अप-टू-डेट रखने के लिए ज़िम्मेदार हैं? उदाहरण के लिए, अगर मेरे डिवाइस में ARM Mali GPU का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है, तो क्या मुझे किसी भी बदलाव के लिए ARM से संपर्क करना होगा? ड्राइवर रिलीज़ होने पर, हर डिवाइस के हिसाब से अलग-अलग एसओसी को अपनी IOCTL सूचियां अपडेट करनी होंगी. उदाहरण के लिए, ड्राइवर अपडेट होने पर, एआरएम पब्लिश की गई IOCTL सूची को अपडेट करेगा. हालांकि, ओईएम को यह पक्का करना चाहिए कि वे अपनी SEPolicy में अपडेट शामिल करें. साथ ही, ज़रूरत के मुताबिक चुनी गई कस्टम IOCTL को सूचियों में जोड़ें.
क्या यह बदलाव, बाज़ार में उपलब्ध सभी Pixel डिवाइसों पर अपने-आप लागू हो जाता है या इस बदलाव को लागू करने के लिए, उपयोगकर्ता को कोई कार्रवाई करनी पड़ती है? यह बदलाव, Mali GPU का इस्तेमाल करने वाले सभी Pixel डिवाइसों पर लागू होता है. जैसे, Pixel 6 से Pixel 9 तक के डिवाइस. इस बदलाव को लागू करने के लिए, उपयोगकर्ता को कुछ नहीं करना होगा.
क्या इस नीति का इस्तेमाल करने से, कर्नल ड्राइवर की परफ़ॉर्मेंस पर असर पड़ेगा? इस नीति को GFXBench का इस्तेमाल करके, Mali GPU पर टेस्ट किया गया था. इसमें GPU की परफ़ॉर्मेंस में कोई खास बदलाव नहीं देखा गया.
क्या IOCTL सूची का, मौजूदा यूज़रस्पेस और कर्नेल ड्राइवर वर्शन के साथ अलाइन होना ज़रूरी है? हां, अनुमति वाले IOCTL की सूची को, उपयोगकर्ताओं के स्पेस और कर्नल ड्राइवर, दोनों के साथ काम करने वाले IOCTL के साथ सिंक किया जाना चाहिए. अगर उपयोगकर्ता स्पेस या कर्नल ड्राइवर में IOCTL अपडेट किए जाते हैं, तो SEPolicy IOCTL सूची को अपडेट किया जाना चाहिए, ताकि वह मेल खा सके.
ARM ने IOCTL को 'प्रतिबंधित' / 'इंस्ट्रुमेंटेशन' के तौर पर कैटगरी में रखा है. हालांकि, हमें प्रोडक्शन के इस्तेमाल के मामलों में इनमें से कुछ का इस्तेमाल करना है और/या दूसरों को अस्वीकार करना है. उपयोगकर्ता स्पेस वाली Mali लाइब्रेरी के कॉन्फ़िगरेशन के आधार पर, इस्तेमाल किए गए IOCTL को कैटगरी में बांटने का फ़ैसला लेने की ज़िम्मेदारी, अलग-अलग ओईएम/SoC की होती है. इनके बारे में फ़ैसला लेने के लिए, एआरएम की सूची का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. हालांकि, हर ओईएम/एसओसी के इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण अलग-अलग हो सकते हैं.
निजता
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में, निजता से जुड़े ये बदलाव किए गए हैं.
लोकल नेटवर्क ऐक्सेस करने की अनुमति
LAN पर मौजूद डिवाइसों को, INTERNET की अनुमति वाले किसी भी ऐप्लिकेशन से ऐक्सेस किया जा सकता है.
इससे ऐप्लिकेशन को स्थानीय डिवाइसों से कनेक्ट करना आसान हो जाता है. हालांकि, इससे निजता पर भी असर पड़ता है. जैसे, उपयोगकर्ता का फ़िंगरप्रिंट बनाना और जगह की जानकारी के लिए प्रॉक्सी के तौर पर काम करना.
Local Network Protections प्रोजेक्ट का मकसद, उपयोगकर्ता की निजता को सुरक्षित रखना है. इसके लिए, लोकल नेटवर्क के ऐक्सेस को नई रनटाइम अनुमति के पीछे रखा जाता है.
रिलीज़ प्लान
यह बदलाव, दो रिलीज़ के बीच में लागू किया जाएगा. ये रिलीज़, 25Q2 और 26Q2 हैं. डेवलपर के लिए, 25Q2 के लिए इस गाइडलाइन का पालन करना ज़रूरी है. साथ ही, उन्हें अपना सुझाव/राय या शिकायत शेयर करनी चाहिए, क्योंकि Android के आने वाले वर्शन में इन सुरक्षा सुविधाओं को लागू किया जाएगा. इसके अलावा, उन्हें उन स्थितियों को अपडेट करना होगा जो स्थानीय नेटवर्क के इंप्लिसिट ऐक्सेस पर निर्भर करती हैं. इसके लिए, उन्हें यहां दिए गए दिशा-निर्देशों का पालन करना होगा. साथ ही, उन्हें उपयोगकर्ता के अनुमति अस्वीकार करने और नई अनुमति को रद्द करने के लिए तैयार रहना होगा.
असर
फ़िलहाल, एलएनपी एक ऑप्ट-इन सुविधा है. इसका मतलब है कि इसका असर सिर्फ़ उन ऐप्लिकेशन पर पड़ेगा जिन्होंने ऑप्ट-इन किया है. ऑप्ट-इन फ़ेज़ का मकसद, ऐप्लिकेशन डेवलपर को यह समझने में मदद करना है कि उनके ऐप्लिकेशन के कौनसे हिस्से, लोकल नेटवर्क के इंप्लिसिट ऐक्सेस पर निर्भर करते हैं. इससे वे अगली रिलीज़ के लिए, ऐक्सेस की अनुमति को सुरक्षित रखने की तैयारी कर सकते हैं.
अगर ऐप्लिकेशन, उपयोगकर्ता के लोकल नेटवर्क को इन तरीकों से ऐक्सेस करते हैं, तो उन पर असर पड़ेगा:
- लोकल नेटवर्क पतों पर रॉ सॉकेट का सीधे तौर पर या लाइब्रेरी के तौर पर इस्तेमाल करना. जैसे, mDNS या SSDP सर्विस डिस्कवरी प्रोटोकॉल
- फ़्रेमवर्क लेवल की उन क्लास का इस्तेमाल करना जो लोकल नेटवर्क को ऐक्सेस करती हैं. जैसे, NsdManager
लोकल नेटवर्क पते से और पर ट्रैफ़िक भेजने के लिए, लोकल नेटवर्क ऐक्सेस करने की अनुमति ज़रूरी है. यहां दी गई टेबल में, कुछ सामान्य मामलों के बारे में बताया गया है:
| ऐप्लिकेशन के लो लेवल नेटवर्क ऑपरेशन | लोकल नेटवर्क का ऐक्सेस पाने की अनुमति ज़रूरी है |
|---|---|
| आउटगोइंग टीसीपी कनेक्शन बनाना | हां |
| इनकमिंग टीसीपी कनेक्शन स्वीकार करना | हां |
| यूडीपी यूनिकास्ट, मल्टीकास्ट, ब्रॉडकास्ट भेजना | हां |
| यूडीपी यूनिकास्ट, मल्टीकास्ट, ब्रॉडकास्ट पाना | हां |
ये पाबंदियां, नेटवर्किंग स्टैक में गहराई से लागू की जाती हैं. इसलिए, ये सभी नेटवर्किंग एपीआई पर लागू होती हैं. इसमें नेटिव या मैनेज किए गए कोड में बनाए गए सॉकेट, Cronet और OkHttp जैसी नेटवर्किंग लाइब्रेरी, और उनके ऊपर लागू किए गए एपीआई शामिल हैं. लोकल नेटवर्क पर मौजूद सेवाओं (जैसे, .local सफ़िक्स वाली सेवाएं) को हल करने के लिए, लोकल नेटवर्क की अनुमति ज़रूरी होगी.
ऊपर दिए गए नियमों के अपवाद:
- अगर किसी डिवाइस का डीएनएस सर्वर लोकल नेटवर्क पर है, तो पोर्ट 53 पर उससे आने-जाने वाले ट्रैफ़िक के लिए, लोकल नेटवर्क के ऐक्सेस की अनुमति की ज़रूरत नहीं होती.
- ऐप्लिकेशन में आउटपुट स्विचर का इस्तेमाल करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन को, लोकल नेटवर्क की अनुमतियों की ज़रूरत नहीं होगी. इस बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी, 2025 की चौथी तिमाही में उपलब्ध कराई जाएगी.
डेवलपर के लिए दिशा-निर्देश (ऑप्ट-इन)
लोकल नेटवर्क ऐक्सेस से जुड़ी पाबंदियों के लिए ऑप्ट इन करने के लिए, यह तरीका अपनाएं:
- डिवाइस पर 25Q2 Beta 3 या उसके बाद का वर्शन फ़्लैश करें.
- टेस्ट किया जाने वाला ऐप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल करें.
adb में Appcompat फ़्लैग को टॉगल करें:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>डिवाइस को रीबूट करें
अब आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के पास लोकल नेटवर्क का ऐक्सेस नहीं है. साथ ही, लोकल नेटवर्क को ऐक्सेस करने की किसी भी कोशिश से सॉकेट से जुड़ी गड़बड़ियां होंगी. अगर ऐसे एपीआई का इस्तेमाल किया जा रहा है जो आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की प्रोसेस के बाहर लोकल नेटवर्क ऑपरेशन करते हैं (जैसे: NsdManager), तो ऑप्ट-इन फ़ेज़ के दौरान उन पर कोई असर नहीं पड़ेगा.
ऐक्सेस वापस पाने के लिए, आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES की अनुमति देनी होगी.
- पक्का करें कि ऐप्लिकेशन ने अपने मेनिफ़ेस्ट में
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESअनुमति का एलान किया हो. - सेटिंग > ऐप्लिकेशन > [ऐप्लिकेशन का नाम] > अनुमतियां > आस-पास के डिवाइस > अनुमति दें पर जाएं.
अब आपके ऐप्लिकेशन का ऐक्सेस, लोकल नेटवर्क पर वापस आ जाना चाहिए. साथ ही, सभी सुविधाएं पहले की तरह काम करनी चाहिए.
लोकल नेटवर्क को सुरक्षित रखने की सुविधा लागू होने के बाद, ऐप्लिकेशन के नेटवर्क ट्रैफ़िक पर इस तरह असर पड़ेगा.
| अनुमति | आउटबाउंड LAN अनुरोध | आउटबाउंड/इनबाउंड इंटरनेट अनुरोध | इनबाउंड लैन अनुरोध |
|---|---|---|---|
| प्रदान किया गया | Works | Works | Works |
| अनुमति नहीं दी गई | विफल | Works | विफल |
ऐप्लिकेशन के साथ काम करने की सुविधा वाले फ़्लैग को टॉगल-ऑफ़ करने के लिए, इस कमांड का इस्तेमाल करें
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
गड़बड़ियां
इन पाबंदियों की वजह से होने वाली गड़बड़ियों को कॉलिंग सॉकेट पर वापस भेज दिया जाएगा. ऐसा तब होगा, जब वह लोकल नेटवर्क पते पर send या send variant को लागू करेगा.
गड़बड़ियों के उदाहरण:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
लोकल नेटवर्क की परिभाषा
इस प्रोजेक्ट में लोकल नेटवर्क का मतलब ऐसे आईपी नेटवर्क से है जो ब्रॉडकास्ट करने की सुविधा वाले नेटवर्क इंटरफ़ेस का इस्तेमाल करता है. जैसे, वाई-फ़ाई या ईथरनेट. हालांकि, इसमें सेल्युलर (WWAN) या वीपीएन कनेक्शन शामिल नहीं होते हैं.
इन्हें लोकल नेटवर्क माना जाता है:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // लिंक लोकल
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- लिंक-लोकल
- सीधे तौर पर कनेक्ट किए गए रूट
- Thread जैसे स्टब नेटवर्क
- एक से ज़्यादा सबनेट (अभी तय नहीं है)
इसके अलावा, मल्टीकास्ट पते (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) और IPv4 ब्रॉडकास्ट पते (255.255.255.255) को लोकल नेटवर्क पते के तौर पर क्लासिफ़ाई किया जाता है.
ऐप्लिकेशन के मालिकाना हक वाली फ़ोटो
जब Android 16 या उसके बाद के वर्शन वाले डिवाइसों पर, SDK टूल 36 या उसके बाद के वर्शन का इस्तेमाल करने वाले किसी ऐप्लिकेशन से फ़ोटो और वीडियो की अनुमतियां मांगी जाती हैं, तो जिन उपयोगकर्ताओं ने चुने गए मीडिया का ऐक्सेस सीमित करने का विकल्प चुना है उन्हें फ़ोटो पिकर में, ऐप्लिकेशन के मालिकाना हक वाली फ़ोटो पहले से ही दिखेंगी. उपयोगकर्ता, पहले से चुने गए इनमें से किसी भी आइटम से चुने हुए का निशान हटा सकते हैं. ऐसा करने पर, ऐप्लिकेशन को उन फ़ोटो और वीडियो का ऐक्सेस नहीं मिलेगा.
