Android 14 มีฟีเจอร์และ API ที่ยอดเยี่ยมสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ความช่วยเหลือต่อไปนี้จะช่วย ให้คุณทราบเกี่ยวกับฟีเจอร์สำหรับแอปและเริ่มต้นใช้งาน API ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ดูรายการ API ที่เพิ่ม แก้ไข และนำออกโดยละเอียดได้ในรายงานความแตกต่างของ API ดูรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับ API ที่เพิ่มได้ที่เอกสารอ้างอิง Android API สำหรับ Android 14 ให้มองหา API ที่เพิ่มใน API ระดับ 34 หากต้องการดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับส่วนที่การเปลี่ยนแปลงของแพลตฟอร์มอาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ โปรดดูการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของ Android 14 สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 14 และสำหรับแอปทั้งหมด
การทำให้เป็นสากล
ค่ากำหนดภาษาที่ใช้ในแอป
Android 14 ขยายฟีเจอร์ภาษาต่อแอปที่เปิดตัวใน Android 13 (API ระดับ 33) ด้วยความสามารถเพิ่มเติมต่อไปนี้
สร้าง
localeConfigของแอปโดยอัตโนมัติ: ตั้งแต่ Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 และ AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 เป็นต้นไป คุณสามารถกําหนดค่าแอปให้รองรับค่ากําหนดภาษาของแต่ละแอปโดยอัตโนมัติ ปลั๊กอิน Android Gradle จะสร้างไฟล์LocaleConfigและเพิ่มการอ้างอิงไฟล์ดังกล่าวในไฟล์ Manifest สุดท้ายโดยอิงตามทรัพยากรของโปรเจ็กต์ คุณจึงไม่ต้องสร้างหรืออัปเดตไฟล์ด้วยตนเองอีกต่อไป AGP ใช้ทรัพยากรในโฟลเดอร์resของโมดูลแอปและทรัพยากร Dependency ของโมดูลไลบรารีเพื่อระบุภาษาที่จะรวมไว้ในไฟล์LocaleConfigการอัปเดตแบบไดนามิกสำหรับ
localeConfigของแอป: ใช้วิธีในsetOverrideLocaleConfig()และgetOverrideLocaleConfig()ในLocaleManagerเพื่ออัปเดตรายการภาษาที่รองรับของแอปแบบไดนามิกในการตั้งค่าระบบของอุปกรณ์ ใช้ความยืดหยุ่นนี้เพื่อปรับแต่งรายการภาษาที่รองรับตามภูมิภาค ทำการทดสอบ A/B หรือระบุรายการภาษาที่อัปเดตแล้วหากแอปใช้การพุชฝั่งเซิร์ฟเวอร์สำหรับการแปลระดับการเข้าถึงภาษาของแอปสําหรับตัวแก้ไขวิธีการป้อนข้อมูล (IME): IME สามารถใช้วิธี
getApplicationLocales()เพื่อตรวจสอบภาษาของแอปปัจจุบันและจับคู่ภาษา IME กับภาษานั้น
Grammatical Inflection API
ผู้คนกว่า 3 พันล้านคนพูดภาษาที่มีเพศ ซึ่งเป็นภาษาที่คำในหมวดหมู่ทางไวยากรณ์ เช่น คำนาม คำกริยา คำคุณศัพท์ และคำบุพบท จะผันตามเพศของบุคคลและวัตถุที่คุณพูดด้วยหรือพูดถึง โดยทั่วไปแล้ว ภาษาที่มีเพศหลายเพศหลายภาษาใช้เพศทางไวยากรณ์เพศชายเป็นเพศเริ่มต้นหรือเพศทั่วไป
การเรียกผู้ใช้ด้วยเพศทางไวยากรณ์ที่ไม่ถูกต้อง เช่น การเรียกผู้หญิงด้วยเพศทางไวยากรณ์ของผู้ชาย อาจส่งผลเสียต่อประสิทธิภาพและทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ ในทางตรงกันข้าม UI ที่มีภาษาที่แสดงเพศตามไวยากรณ์ของผู้ใช้อย่างถูกต้องจะช่วยเพิ่มการมีส่วนร่วมของผู้ใช้ และมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับผู้ใช้แต่ละคนและฟังดูเป็นธรรมชาติมากขึ้น
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
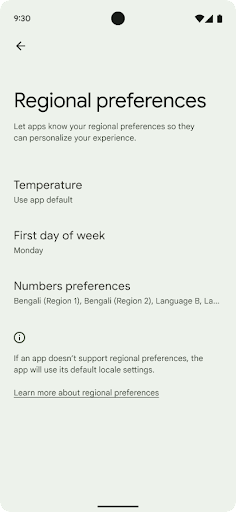
ค่ากำหนดตามพื้นที่
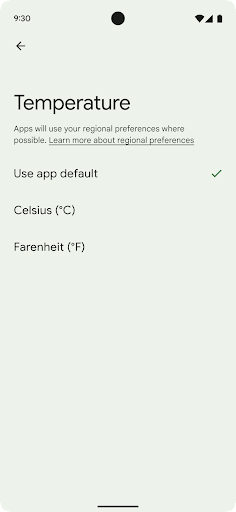
ค่ากำหนดระดับภูมิภาคช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ปรับเปลี่ยนหน่วยอุณหภูมิในแบบของคุณได้ วันของสัปดาห์ และระบบลำดับตัวเลข ชาวยุโรปที่อาศัยอยู่ในสหรัฐอเมริกา คุณอาจต้องการให้หน่วยอุณหภูมิเป็นเซลเซียสมากกว่าฟาเรนไฮต์ และสำหรับ แอปที่กำหนดให้วันจันทร์เป็นวันเริ่มต้นของสัปดาห์แทนที่จะเป็นค่าเริ่มต้นของสหรัฐอเมริกา วันอาทิตย์
เมนูใหม่ในการตั้งค่า Android สำหรับค่ากำหนดเหล่านี้ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้สามารถ
ตำแหน่งส่วนกลางที่ค้นพบได้เพื่อเปลี่ยนค่ากำหนดของแอป การตั้งค่าเหล่านี้จะยังคงอยู่ผ่านการสํารองและคืนค่าด้วย API และ Intent หลายรายการ เช่น getTemperatureUnit และ getFirstDayOfWeek จะให้สิทธิ์แอปของคุณอ่านค่ากําหนดของผู้ใช้ เพื่อให้แอปปรับวิธีแสดงข้อมูลได้ นอกจากนี้ คุณยังจดทะเบียน
BroadcastReceiver ใน
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
เพื่อจัดการการเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่าภาษาเมื่อค่ากำหนดระดับภูมิภาคมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงได้
หากต้องการค้นหาการตั้งค่าเหล่านี้ ให้เปิดแอปการตั้งค่าแล้วไปที่ระบบ >ภาษาและการป้อนข้อมูล > ค่ากําหนดระดับภูมิภาค
การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ
การปรับขนาดแบบอักษรที่ไม่ใช่แบบเชิงเส้นเป็น 200%
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing low-vision users with additional accessibility options that align with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
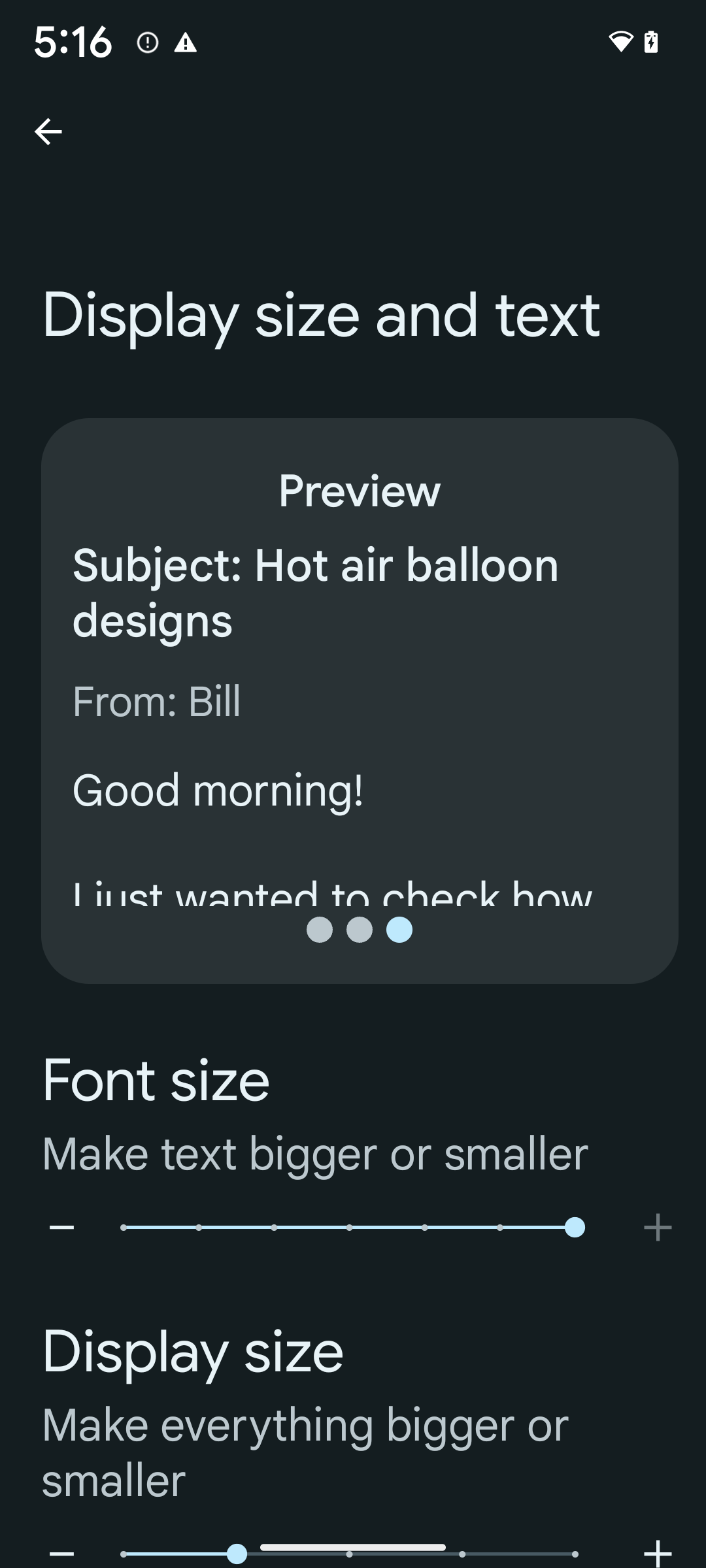
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
กล้องและสื่อ
Ultra HDR สำหรับรูปภาพ

Android 14 เพิ่มการรองรับรูปภาพ High Dynamic Range (HDR) ที่จะเก็บข้อมูลจากเซ็นเซอร์ได้มากขึ้นเมื่อถ่ายภาพ ซึ่งช่วยให้สีสันสดใสและคอนทราสต์มากขึ้น Android ใช้รูปแบบ Ultra HDR ซึ่งเข้ากันได้กับรูปภาพ JPEG อย่างสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปทำงานร่วมกับรูปภาพ HDR ได้อย่างราบรื่น โดยแสดงรูปภาพในรูปแบบมาตรฐานไดนามิกเรนจ์ (SDR) ตามต้องการ
เฟรมเวิร์กจะแสดงผลรูปภาพเหล่านี้ใน UI เป็น HDR โดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อแอปเลือกใช้ UI HDR สำหรับกรอบเวลากิจกรรม ไม่ว่าจะผ่านรายการไฟล์ Manifest หรือที่รันไทม์โดยการเรียกใช้ Window.setColorMode() นอกจากนี้ คุณยังจับภาพภาพนิ่ง HDR แบบ Ultra ที่บีบอัดในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับได้ด้วย การกู้คืนสีจากเซ็นเซอร์ได้มากขึ้นช่วยให้การแก้ไขในขั้นตอนหลังมีความยืดหยุ่นมากขึ้น คุณสามารถใช้ Gainmap ที่เชื่อมโยงกับภาพ Ultra HDR เพื่อแสดงผลภาพโดยใช้ OpenGL หรือ Vulkan
ซูม โฟกัส ดูตัวอย่างหลังถ่าย และอื่นๆ ในส่วนขยายกล้อง
Android 14 upgrades and improves camera extensions, allowing apps to handle longer processing times, which enables improved images using compute-intensive algorithms like low-light photography on supported devices. These features give users an even more robust experience when using camera extension capabilities. Examples of these improvements include:
- Dynamic still capture processing latency estimation provides much more
accurate still capture latency estimates based on the current scene and
environment conditions. Call
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()to get aStillCaptureLatencyobject that has two latency estimation methods. ThegetCaptureLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureStartedandonCaptureProcessStarted(), and thegetProcessingLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureProcessStarted()and the final processed frame being available. - Support for capture progress callbacks so that apps can display the current
progress of long-running, still-capture processing operations. You can check
if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, and if it is, you implement theonCaptureProcessProgressed()callback, which has the progress (from 0 to 100) passed in as a parameter. Extension specific metadata, such as
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHfor dialing in the amount of an extension effect, such as the amount of background blur withEXTENSION_BOKEH.Postview Feature for Still Capture in camera extensions, which provides a less-processed image more quickly than the final image. If an extension has increased processing latency, a postview image could be provided as a placeholder to improve UX and switched out later for the final image. You can check if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Then you can pass anOutputConfigurationtoExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Support for
SurfaceViewallowing for a more optimized and power-efficient preview render path.Support for tap to focus and zoom during extension usage.
การซูมในเซ็นเซอร์
เมื่อ REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE ใน
CameraCharacteristics มี
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW แอปของคุณจะใช้ความสามารถขั้นสูงของเซ็นเซอร์เพื่อให้สตรีม RAW ที่ครอบตัดมีจำนวนพิกเซลเท่ากับมุมมองแบบเต็มได้โดยใช้ CaptureRequest ที่มีเป้าหมาย RAW ซึ่งตั้งค่า Use Case ของสตรีมเป็น CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW
การใช้การควบคุมการลบล้างคําขอช่วยให้กล้องที่อัปเดตแล้วให้ผู้ใช้ควบคุมการซูมได้ก่อนที่ตัวควบคุมกล้องอื่นๆ จะพร้อมใช้งาน
เสียง USB แบบไม่สูญเสียข้อมูล
Android 14 รองรับรูปแบบเสียงแบบไม่สูญเสียคุณภาพเพื่อให้คุณได้รับประสบการณ์ระดับออดิโอไฟล์ผ่านชุดหูฟังแบบใช้สาย USB คุณสามารถค้นหาอุปกรณ์ USB เพื่อดูแอตทริบิวต์ของมิกเซอร์ที่ต้องการ ลงทะเบียนโปรแกรมรับฟังการเปลี่ยนแปลงแอตทริบิวต์ของมิกเซอร์ที่ต้องการ และกำหนดค่าแอตทริบิวต์ของมิกเซอร์โดยใช้คลาส AudioMixerAttributes คลาสนี้แสดงรูปแบบ เช่น มาสก์ช่อง อัตราตัวอย่าง และลักษณะการทำงานของมิกเซอร์เสียง คลาสนี้ช่วยให้ส่งเสียงได้โดยตรงโดยไม่ต้องผสม ปรับระดับเสียง หรือประมวลผลเอฟเฟกต์
ประสิทธิภาพการทำงานและเครื่องมือสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์
Credential Manager
Android 14 เพิ่ม Credential Manager เป็น API ของแพลตฟอร์ม โดยรองรับอุปกรณ์ Android 4.4 (API ระดับ 19) เพิ่มเติมผ่านคลัง Jetpack โดยใช้บริการ Google Play Credential Manager มีเป้าหมายเพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ได้ง่ายขึ้นด้วย API ที่ดึงข้อมูลและจัดเก็บข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบด้วยผู้ให้บริการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบที่ผู้ใช้กําหนดค่าไว้ Credential Manager รองรับวิธีการลงชื่อเข้าใช้หลายวิธี รวมถึงชื่อผู้ใช้และรหัสผ่าน พาสคีย์ และโซลูชันการลงชื่อเข้าใช้แบบรวมศูนย์ (เช่น ฟีเจอร์ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ด้วย Google) ใน API เดียว
พาสคีย์มีข้อดีหลายประการ เช่น พาสคีย์สร้างขึ้นตามมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรม ทำงานได้กับระบบปฏิบัติการและระบบนิเวศของเบราว์เซอร์ต่างๆ รวมถึงใช้ได้กับทั้งเว็บไซต์และแอป
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์และบล็อกโพสต์เกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์
Health Connect
Health Connect เป็นพื้นที่เก็บข้อมูลในอุปกรณ์สำหรับข้อมูลสุขภาพและการออกกำลังกายของผู้ใช้ ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้แชร์ข้อมูลระหว่างแอปโปรดได้โดยมีที่เดียวในการควบคุมข้อมูลที่ต้องการแชร์กับแอปเหล่านี้
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android เวอร์ชันก่อน Android 14 คุณจะดาวน์โหลด Health Connect ในรูปแบบแอปได้ใน Google Play Store ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป Health Connect จะเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแพลตฟอร์มและได้รับการอัปเดตผ่านการอัปเดตระบบ Google Play โดยไม่ต้องดาวน์โหลดแยกต่างหาก ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ Health Connect ได้รับการอัปเดตบ่อยครั้ง และแอปของคุณจะใช้ Health Connect ได้บนอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 14 ขึ้นไป ผู้ใช้สามารถเข้าถึง Health Connect ได้จากการตั้งค่าในอุปกรณ์ โดยจะมีการควบคุมความเป็นส่วนตัวที่ผสานรวมอยู่ในการตั้งค่าระบบ
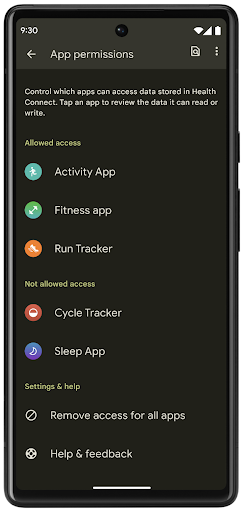
Health Connect มีฟีเจอร์ใหม่ๆ หลายอย่างใน Android 14 เช่น เส้นทางออกกำลังกาย ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้แชร์เส้นทางการออกกําลังกายที่แสดงเป็นภาพบนแผนที่ได้ เส้นทางหมายถึงรายการสถานที่ที่บันทึกไว้ภายในกรอบเวลาหนึ่งๆ และแอปของคุณสามารถแทรกเส้นทางลงในเซสชันการออกกำลังกายเพื่อเชื่อมโยงเข้าด้วยกัน ผู้ใช้ต้องอนุญาตให้แชร์เส้นทางแต่ละเส้นทางกับแอปอื่นๆ เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าผู้ใช้มีสิทธิ์ควบคุมข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อนนี้อย่างสมบูรณ์
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับการเชื่อมต่อ Health และบล็อกโพสต์เกี่ยวกับมีอะไรใหม่ใน Android Health
การอัปเดต OpenJDK 17
Android 14 ยังคงปรับปรุงไลบรารีหลักของ Android ให้สอดคล้องกับฟีเจอร์ใน OpenJDK LTS เวอร์ชันล่าสุด ซึ่งรวมถึงทั้งการอัปเดตไลบรารีและการรองรับภาษา Java 17 สําหรับนักพัฒนาแอปและแพลตฟอร์ม
ฟีเจอร์และการปรับปรุงต่อไปนี้จะรวมอยู่ด้วย
- อัปเดตคลาส
java.baseประมาณ 300 คลาสให้รองรับ Java 17 - บล็อกข้อความ ซึ่งจะนําสตริงตัวอักษรหลายบรรทัดมาสู่ภาษาโปรแกรม Java
- การจับคู่รูปแบบสำหรับ instanceof ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบถือว่าออบเจ็กต์มีประเภทที่เฉพาะเจาะจงใน
instanceofโดยไม่ต้องมีตัวแปรเพิ่มเติม - คลาสที่ปิด ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณจำกัดคลาสและอินเทอร์เฟซที่ขยายหรือนำไปใช้ได้
การอัปเดตระบบ Google Play (Project Mainline) ช่วยให้อุปกรณ์กว่า 600 ล้านเครื่องสามารถรับการอัปเดต Android Runtime (ART) ล่าสุดที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ ซึ่งเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของความมุ่งมั่นของเราที่จะมอบสภาพแวดล้อมที่ปลอดภัยและสอดคล้องกันมากขึ้นให้แก่แอปในอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ รวมถึงมอบฟีเจอร์และความสามารถใหม่ๆ ให้แก่ผู้ใช้โดยไม่ขึ้นอยู่กับรุ่นของแพลตฟอร์ม
Java และ OpenJDK เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าหรือเครื่องหมายการค้าจดทะเบียนของ Oracle และ/หรือบริษัทในเครือ
การปรับปรุงสำหรับ App Store
Android 14 เปิดตัว PackageInstaller API หลายรายการที่ช่วยปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้สำหรับ App Store
ขอการอนุมัติการติดตั้งก่อนดาวน์โหลด
การติดตั้งหรืออัปเดตแอปอาจต้องการอนุมัติของผู้ใช้
เช่น เมื่อผู้ติดตั้งที่ใช้สิทธิ์ REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES พยายามติดตั้งแอปใหม่ ใน Android เวอร์ชันก่อนๆ แอปสโตร์จะขอการอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้ได้หลังจากมีการเขียน APK ลงในเซสชันการติดตั้งและบันทึกเซสชันแล้วเท่านั้น
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป เมธอด requestUserPreapproval() จะอนุญาตให้ผู้ติดตั้งขอการอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้ก่อนยืนยันเซสชันการติดตั้ง การปรับปรุงนี้ช่วยให้ App Store เลื่อนการดาวน์โหลด APK ไว้ได้จนกว่าจะได้รับการอนุมัติการติดตั้งจากผู้ใช้ นอกจากนี้ เมื่อผู้ใช้อนุมัติการติดตั้งแล้ว แอปสโตร์จะดาวน์โหลดและติดตั้งแอปในเบื้องหลังได้โดยไม่รบกวนผู้ใช้
อ้างความรับผิดชอบสำหรับการอัปเดตในอนาคต
วิธีการ setRequestUpdateOwnership() ช่วยให้ผู้ติดตั้งระบุต่อระบบว่าตนตั้งใจที่จะรับผิดชอบต่อการอัปเดตแอปที่ติดตั้งในอนาคต ความสามารถนี้ช่วยให้สามารถบังคับใช้การเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตได้ ซึ่งหมายความว่ามีเพียงเจ้าของการอัปเดตเท่านั้นที่ได้รับอนุญาตให้ติดตั้งการอัปเดตอัตโนมัติในแอป การบังคับใช้การเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าผู้ใช้จะได้รับอัปเดตจาก App Store ที่คาดไว้เท่านั้น
โปรแกรมติดตั้งอื่นๆ รวมถึงโปรแกรมที่ใช้สิทธิ์ INSTALL_PACKAGES จะต้องได้รับอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้อย่างชัดเจนจึงจะติดตั้งการอัปเดตได้ หากผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจที่จะอัปเดตจากแหล่งที่มาอื่น ความเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตจะหายไป
อัปเดตแอปในเวลาที่รบกวนน้อยลง
โดยปกติแล้ว App Store ต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงการอัปเดตแอปที่ผู้ใช้กำลังใช้งานอยู่ เนื่องจากจะส่งผลให้กระบวนการที่ทำงานอยู่ของแอปหยุดลง ซึ่งอาจขัดจังหวะสิ่งที่ผู้ใช้กำลังทำอยู่
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป InstallConstraints API จะเปิดโอกาสให้ผู้ติดตั้งตรวจสอบว่าการอัปเดตแอปเกิดขึ้นในเวลาที่เหมาะสม ตัวอย่างเช่น แอปสโตร์สามารถเรียกใช้เมธอด commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าการอัปเดตจะดำเนินการต่อเมื่อผู้ใช้ไม่ได้โต้ตอบกับแอปที่เป็นปัญหาแล้ว
ติดตั้งส่วนแยกที่ไม่บังคับได้อย่างราบรื่น
เมื่อใช้ APK แบบแยก คุณจะส่งฟีเจอร์ของแอปเป็นไฟล์ APK แยกต่างหากได้ แทนที่จะส่งเป็น APK แบบรวม APK แบบแยกช่วยให้ App Store เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการนำส่งคอมโพเนนต์ต่างๆ ของแอปได้ เช่น แอปสโตร์อาจเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพตามพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ของอุปกรณ์เป้าหมาย PackageInstaller API รองรับการแยกตั้งแต่เปิดตัวใน API ระดับ 22
ใน Android 14 วิธีการ setDontKillApp() ช่วยให้ผู้ติดตั้งระบุได้ว่าไม่ควรหยุดกระบวนการที่ทำงานอยู่ของแอปเมื่อติดตั้งแยกใหม่ App Store สามารถใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้เพื่อติดตั้งฟีเจอร์ใหม่ของแอปได้อย่างราบรื่นขณะที่ผู้ใช้กำลังใช้แอปอยู่
App Bundle ข้อมูลเมตา
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป เครื่องมือติดตั้งแพ็กเกจ Android จะช่วยให้คุณระบุข้อมูลเมตาของแอป เช่น แนวทางปฏิบัติด้านความปลอดภัยของข้อมูล เพื่อรวมไว้ในหน้าร้านค้าแอป เช่น Google Play
ตรวจหาเวลาที่ผู้ใช้ถ่ายภาพหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้
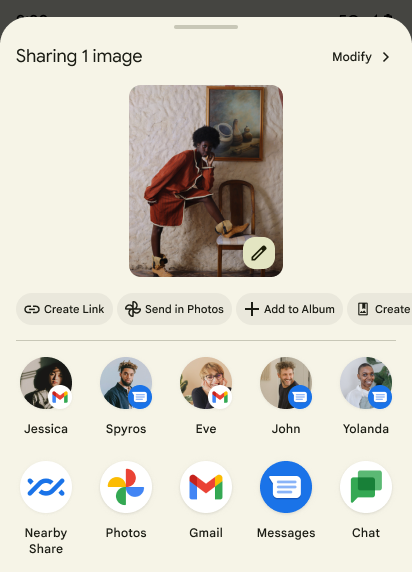
การทำงานที่กำหนดเองของชีตการแชร์และการจัดอันดับที่ดียิ่งขึ้น
Android 14 อัปเดตชีตการแชร์ของระบบเพื่อรองรับการดำเนินการของแอปที่กำหนดเองและแสดงตัวอย่างผลลัพธ์ที่เป็นประโยชน์มากขึ้นสำหรับผู้ใช้
เพิ่มการดําเนินการที่กำหนดเอง
เมื่อใช้ Android 14 แอปของคุณจะเพิ่มการดำเนินการที่กำหนดเองลงในชีตการแชร์ของระบบที่เรียกใช้
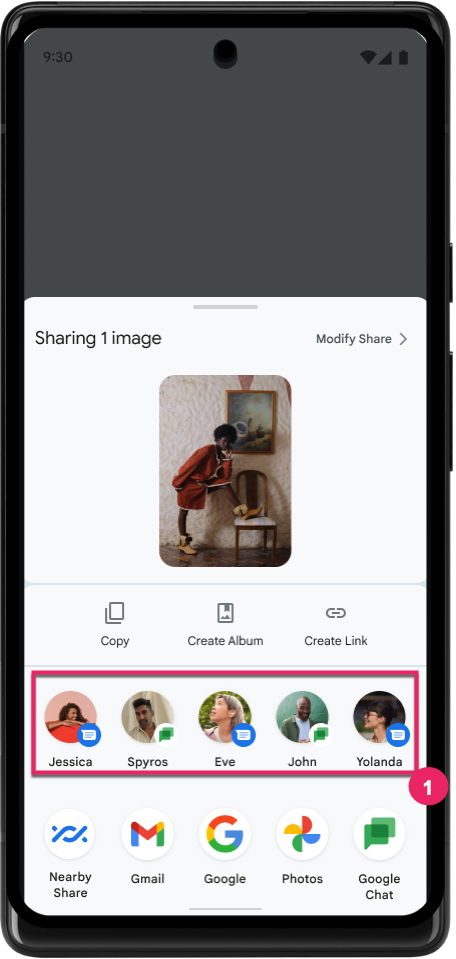
ปรับปรุงการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรง
Android 14 ใช้สัญญาณจากแอปมากขึ้นเพื่อกำหนดการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรงเพื่อให้ผลการค้นหาที่เป็นประโยชน์มากขึ้นแก่ผู้ใช้ โปรดปฏิบัติตามคำแนะนำสำหรับการปรับปรุงการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรงเพื่อให้สัญญาณที่มีประโยชน์มากที่สุดสำหรับการจัดอันดับ นอกจากนี้ แอปการสื่อสารยังรายงานการใช้งานแป้นพิมพ์ลัดสำหรับข้อความขาออกและขาเข้าได้ด้วย
รองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวในตัวและภาพเคลื่อนไหวที่กำหนดเองสำหรับท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
การลบล้างต่อแอปของผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การลบล้างค่าแอปต่อแอปช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์เปลี่ยนลักษณะการทำงานของแอปในอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น การลบล้าง FORCE_RESIZE_APP จะสั่งให้ระบบปรับขนาดแอปให้พอดีกับขนาดการแสดงผล (หลีกเลี่ยงโหมดความเข้ากันได้ของขนาด) แม้ว่าจะมีการตั้งค่า resizeableActivity="false" ในไฟล์ Manifest ของแอปก็ตาม
การลบล้างมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้บนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ไฟล์ Manifest ใหม่ช่วยให้คุณปิดใช้การลบล้างผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์บางรายสำหรับแอปของคุณได้
การลบล้างต่อแอปสำหรับผู้ใช้หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
Per-app overrides change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE device manufacturer override sets the app aspect ratio to 16:9 regardless of the app's configuration.
Android 14 QPR1 enables users to apply per‑app overrides by means of a new settings menu on large screen devices.
การแชร์หน้าจอแอป
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
ฟีเจอร์ช่วยตอบที่ทำงานด้วย LLM ใน Gboard บน Pixel 8 Pro
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
กราฟิก
เส้นทางจะค้นหาและประมาณค่าได้
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
Custom meshes with vertex and fragment shaders
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
เครื่องมือแสดงผลบัฟเฟอร์ฮาร์ดแวร์สำหรับ Canvas
To assist in using Android's Canvas API to draw with
hardware acceleration into a HardwareBuffer, Android 14
introduces HardwareBufferRenderer. This API is
particularly useful when your use case involves communication with the system
compositor through SurfaceControl for low-latency
drawing.

