يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 14 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات رائعة للمطوّرين. تساعدك المعلومات التالية في التعرّف على ميزات تطبيقاتك والبدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها وتعديلها وإزالتها، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المضافة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهات برمجة تطبيقات Android. بالنسبة إلى نظام التشغيل Android 14، ابحث عن واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها في المستوى 34 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات. للتعرّف على المجالات التي قد تؤثّر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك، احرص على الاطّلاع على تغييرات السلوك في الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android ولجميع التطبيقات.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
إعدادات اللغة المخصصة حسب التطبيقات
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 14 ميزات إضافية لكل تطبيق باللغة تم تقديمها في Android 13 (المستوى 33 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، وهي:
إنشاء
localeConfigللتطبيق تلقائيًا: بدءًا من الإصدار Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 والإصدار AGP 8.1.0-alpha07، يمكنك ضبط تطبيقك ليعمل تلقائيًا على إتاحة الإعدادات المفضّلة للغة لكل تطبيق. استنادًا إلى موارد مشروعك، ينشئ المكوّن الإضافي لنظام Gradle المتوافق مع Android ملفLocaleConfigويضيف إليه إشارة في ملف البيان النهائي، ما يغنيك عن إنشاء الملف أو تعديله يدويًا. يستخدم AGP الموارد في مجلداتresالخاصة بوحدات تطبيقك وأي ملحقات لوحدات المكتبة لتحديد اللغات المطلوب تضمينها فيملفLocaleConfig.التحديثات الديناميكية لقائمة
localeConfigللتطبيق: استخدِم الطريقتَينsetOverrideLocaleConfig()وgetOverrideLocaleConfig()فيLocaleManagerلتعديل قائمة اللغات المتاحة في تطبيقك ديناميكيًا في إعدادات نظام الجهاز. يمكنك الاستفادة من هذه المرونة لتخصيص قائمة اللغات المتاحة لكل منطقة، أو إجراء تجارب أ/ب، أو تقديم قائمة محدّثة للغات إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم عمليات الإرسال من جهة الخادم لعملية التعريب.إظهار لغة التطبيق لمحرّري أساليب الإدخال (IME): يمكن لمحرّري أساليب الإدخال استخدام الأسلوب
getApplicationLocales()للتحقّق من لغة التطبيق الحالي ومطابقة لغة محرّر أسلوب الإدخال مع هذه اللغة.
Grammatical Inflection API
يتحدّث 3 مليارات شخص لغات جنسانية: وهي لغات تتغيّر فيها فئاتها النحوية، مثل الأسماء والأفعال والصفات وحروف الجر، وفقًا للجنس الذي يحدّده الشخص أو الشيء الذي تتحدث عنه. في العادة، تستخدم العديد من اللغات التي تراعي الجنس النوع النحوي الذكوري كجنس تلقائي أو عام.
يمكن أن يؤدي استخدام الجنس النحوي غير الصحيح للمستخدمين، مثل مخاطبة النساء باستخدام الجنس النحوي للذكور، إلى التأثير سلبًا في أدائهم وسلوكهم. في المقابل، يمكن أن يؤدي استخدام واجهة مستخدم تتضمّن لغة تمثل بشكلٍ صحيح الجنس النحوي للمستخدم إلى تحسين تفاعله مع التطبيق وتوفير تجربة أكثر تخصيصًا وطبيعية.
لمساعدتك في إنشاء واجهة مستخدم تركّز على المستخدم للغات التي تراعي الجنس، يوفّر الإصدار 14 من Android واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Grammatical Inflection API، التي تتيح لك إضافة ميزة مراعاة الجنس النحوي بدون إعادة صياغة تطبيقك.
الإعدادات المفضّلة للمنطقة
تتيح الإعدادات المفضّلة الإقليمية للمستخدمين تخصيص وحدات درجة الحرارة، وهي أول ويوم من الأسبوع وأنظمة الترقيم. أوروبي يعيش في الولايات المتحدة قد يفضلون أن تكون وحدات درجة الحرارة بالدرجة المئوية بدلاً من الفهرنهايت التي تتعامل مع يوم الاثنين على أنه بداية الأسبوع بدلاً من الوضع الافتراضي في الولايات المتحدة الأحد
توفّر قوائم إعدادات Android الجديدة لهذه الإعدادات المفضّلة للمستخدمين مكانًا
يسهل العثور عليه ويكون مركزيًا لتغيير الإعدادات المفضّلة للتطبيقات. هذه
والتفضيلات أيضًا من خلال النسخ الاحتياطي والاستعادة. هناك العديد من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
الأهداف - مثل
getTemperatureUnit
أو
getFirstDayOfWeek—
منح تطبيقك إذن الوصول للقراءة إلى إعدادات المستخدم المفضّلة، حتى يتمكّن التطبيق من تعديل إعداداته
تعرض المعلومات. يمكنك أيضًا تسجيل
خيار "BroadcastReceiver" مفعَّل
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
لمعالجة تغييرات إعدادات اللغة عند تغيير الإعدادات المفضّلة للمنطقة.
للعثور على هذه الإعدادات، افتح تطبيق "الإعدادات" وانتقِل إلى النظام > اللغات والإدخال > الإعدادات المفضّلة على مستوى المنطقة.


تسهيل الاستخدام
الضبط غير الخطي لحجم الخط بما يصل إلى 200%
بدءًا من الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android، يتيح النظام تكبير الخط بنسبة تصل إلى %200، ما يوفّر للمستخدمين خيارات إضافية لتسهيل الاستخدام.
لمنع عناصر النص الكبيرة على الشاشة من التوسّع بشكل مفرط، يطبّق النظام منحنى توسيع غير خطي. تعني استراتيجية تغيير الحجم هذه أنّ النص الكبير لا يتم تغيير حجمه بنفس معدّل النص الأصغر. يساعد الضبط غير الخطي لحجم الخط في الحفاظ على التسلسل الهرمي النسبي بين العناصر ذات الأحجام المختلفة مع الحد من المشاكل المتعلقة بالضبط الخطي لحجم النص بدرجات عالية (مثل اقتطاع النص أو صعوبة قراءته بسبب أحجام العرض الكبيرة جدًا).
اختبار تطبيقك باستخدام الضبط غير الخطي لحجم الخط
إذا كنت تستخدم وحدات بكسل قابلة لتغيير الحجم (sp) لتحديد حجم النص، سيتم تطبيق هذه الخيارات الإضافية وتحسينات تغيير الحجم تلقائيًا على النص في تطبيقك. ومع ذلك، عليك إجراء اختبار واجهة المستخدم مع تفعيل الحد الأقصى لحجم الخط (200%) للتأكّد من أنّ تطبيقك يطبّق أحجام الخطوط بشكل صحيح ويمكنه استيعاب أحجام الخطوط الأكبر بدون التأثير في سهولة الاستخدام.
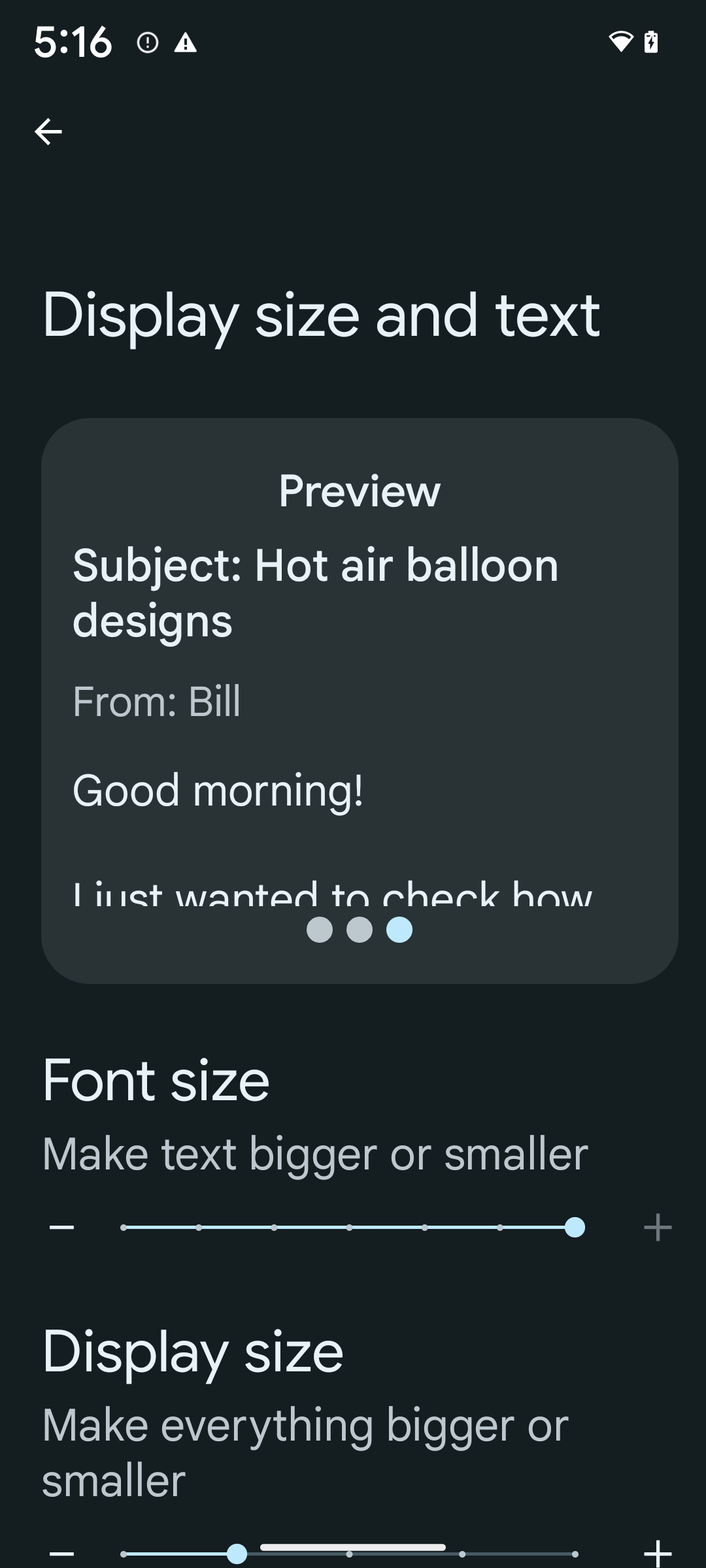
لتفعيل حجم الخط بنسبة% 200، اتّبِع الخطوات التالية:
- افتح تطبيق "الإعدادات" وانتقِل إلى تسهيل الاستخدام > حجم شاشة العرض والنص.
- بالنسبة إلى خيار حجم الخط، انقر على رمز علامة الجمع (+) إلى أن يتم تفعيل الحد الأقصى لحجم الخط، كما هو موضّح في الصورة المرفقة بهذا القسم.
استخدام وحدات البكسل المعدَّلة (sp) لأحجام النصوص
تذكَّر دائمًا تحديد أحجام النصوص بوحدات sp. عندما يستخدم تطبيقك وحدات sp، يمكن لنظام التشغيل Android تطبيق حجم النص المفضّل لدى المستخدم وتغيير حجمه بشكل مناسب.
لا تستخدِم وحدات sp للمساحة المتروكة أو تحدّد ارتفاعات العرض بافتراض مساحة متروكة ضمنية: مع تغيير حجم الخط غير الخطي، قد لا تكون أبعاد sp متناسبة، لذا قد لا يكون 4sp + 20sp يساوي 24sp.
تحويل وحدات البكسل القابلة للتوسّع
استخدِم TypedValue.applyDimension() للتحويل من وحدات sp إلى وحدات بكسل، واستخدِم TypedValue.deriveDimension() للتحويل من وحدات بكسل إلى وحدات sp. وتطبِّق هاتان الطريقتان منحنى التحجيم غير الخطي المناسب تلقائيًا.
تجنَّب الترميز الثابت للمعادلات باستخدام
Configuration.fontScale أو
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. بما أنّ تغيير حجم الخط غير خطي، لم يعُد الحقل scaledDensity دقيقًا. يجب استخدام الحقل fontScale لأغراض إعلامية فقط لأنّه لم يعُد يتم تغيير حجم الخطوط باستخدام قيمة عددية واحدة.
استخدام وحدات sp لـ lineHeight
يجب دائمًا تحديد android:lineHeight باستخدام وحدات sp بدلاً من وحدات dp، حتى يتم تغيير حجم ارتفاع السطر مع النص. في المقابل، إذا كان النص بوحدة sp ولكن lineHeight بوحدة dp أو px، لن يتم تغيير حجمه وسيبدو مضغوطًا.
يصحّح TextView تلقائيًا قيمة lineHeight للحفاظ على النسب التي تريدها، ولكن فقط إذا تم تحديد كل من textSize وlineHeight بوحدات sp.
الكاميرا والوسائط
دقة HDR فائقة للصور

يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 14 استخدام صور النطاق العالي الديناميكية (HDR) التي تحتفظ بمزيد من المعلومات الواردة من أداة الاستشعار عند التقاط صورة، ما يتيح الحصول على ألوان زاهية ودرجة تباين أكبر. يستخدم نظام Android تنسيق Ultra HDR، وهو متوافق تمامًا مع صور JPEG القديمة، ما يسمح للتطبيقات بالعمل بسلاسة مع صور HDR وعرضها بنطاق ديناميكي عادي (SDR) عند الحاجة.
ويتم عرض هذه الصور في واجهة المستخدم بتنسيق HDR تلقائيًا من خلال إطار العمل
عندما يختار تطبيقك استخدام واجهة مستخدم بتنسيق HDR لـ "نافذة النشاط"، إما من خلال أحد إدخالات ملف البيان أو أثناء التشغيل من خلال استدعاء Window.setColorMode(). يمكنك أيضًا التقاط صور ثابتة فائقة
التباين الديناميكي (HDR) المضغوطة على الأجهزة المتوافقة. من خلال استرداد المزيد من الألوان
من أداة الاستشعار، يمكن أن يكون التعديل في مرحلة ما بعد الإنتاج أكثر مرونة. يمكن استخدام رمز الترميز
Gainmap المرتبط بالصور ذات النطاق العالي الديناميكية الفائق لعرضها
باستخدام OpenGL أو Vulkan.
التكبير/التصغير والتركيز والمعاينة بعد الالتقاط والمزيد في إضافات الكاميرا
يُجري نظام Android 14 ترقيات وتحسينات على إضافات الكاميرا، ويسمح للتطبيقات بمعالجة الصور لفترات أطول، ما يؤدي إلى تحسين الصور باستخدام خوارزميات كثيفة الاستخدام للمعالجة، مثل التصوير في الإضاءة المنخفضة على الأجهزة المتوافقة. وتوفّر هذه الميزات للمستخدمين تجربة أكثر فعالية عند استخدام إمكانات توسيع نطاق الكاميرا. تشمل أمثلة هذه التحسينات ما يلي:
- يقدّم تقدير وقت الاستجابة لمعالجة الصور الثابتة الديناميكية مزيدًا من الدقة في تقدير وقت الاستجابة لالتقاط الصور الثابتة استنادًا إلى المشهد الحالي وظروف التصوير. استخدِم دالة
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()للحصول على عنصرStillCaptureLatencyيتضمّن طريقتَين لتقدير وقت الاستجابة. تُرجع الطريقةgetCaptureLatency()وقت الاستجابة المقدَّر بينonCaptureStartedوonCaptureProcessStarted()، وتُرجع الطريقةgetProcessingLatency()وقت الاستجابة المقدَّر بينonCaptureProcessStarted()ووقت توفُّر الإطار النهائي الذي تمت معالجته. - إتاحة عمليات استدعاء لعرض مستوى التقدّم في الالتقاط كي تتمكّن التطبيقات من عرض المستوى الحالي
للتقدّم في عمليات معالجة الصور الثابتة التي تستغرق وقتًا طويلاً يمكنك التحقّق مما إذا كانت هذه الميزة متاحة مع
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable، وإذا كانت متاحة، يمكنك تنفيذ دالة callback الخاصة بتسجيل التقدّمonCaptureProcessProgressed()، والتي تم تمرير التقدّم (من 0 إلى 100) إليها كمَعلمة. البيانات الوصفية الخاصة بالإضافة، مثل
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHللاتصال برقم هاتفي مقدار تأثير الإضافة، مثل مقدار التمويه في الخلفية باستخدامEXTENSION_BOKEHميزة "العرض اللاحق" لالتقاط الصور في إضافات الكاميرا، والتي تقدّم صورة تمّت معالجتها بشكل أقلّ بسرعة أكبر من الصورة النهائية إذا كانت إضافة الصور تزيد من وقت الاستجابة في المعالجة، يمكن تقديم صورة ما بعد المشاهدة كعنصر بدلٍ لتحسين تجربة المستخدم واستبدالها لاحقًا بالصورة النهائية. يمكنك معرفة ما إذا كانت هذه الميزة متاحة باستخدام
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. بعد ذلك، يمكنك تمريرOutputConfigurationإلىExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.إتاحة استخدام
SurfaceViewللاستفادة من مسار عرض معاينة أكثر فعالية من حيث الطاقةإتاحة ميزة "النقر للتركيز" والتكبير/التصغير أثناء استخدام الإضافة
التكبير داخل المستشعر
عندما يحتوي REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE في
CameraCharacteristics على
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW، يمكن لتطبيقك
استخدام إمكانات أداة الاستشعار المتقدّمة لتوفير بثّ RAW مقطّع يحتوي على كثافة بكسل مماثلة لكثافة بكسل مجال العرض الكامل باستخدام CaptureRequest
مع هدف RAW تم ضبط حالة استخدام البث عليه على
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
من خلال تنفيذ عناصر التحكّم في إلغاء الطلبات، تمنح الكاميرا المعدَّلة المستخدمين إمكانية التحكّم في التكبير/التصغير حتى قبل أن تصبح عناصر التحكّم الأخرى في الكاميرا جاهزة.
صوت عالي الدقة عبر USB
يتيح نظام Android 14 استخدام تنسيقات الصوت غير القابل للفقد لتوفير تجارب رائعة تتعلّق بالصوت عبر سماعات الرأس السلكية USB. يمكنك الاستعلام عن جهاز USB للحصول على
سمات أداة المزج المفضّلة، وتسجيل مستمع للتغييرات فيسمات أداة المزج المفضّلة، وضبط سمات أداة المزج باستخدام فئة
AudioMixerAttributes. تمثّل هذه الفئة
التنسيق، مثل قناع القناة ومعدّل أخذ العينات وسلوك أداة مزج الصوت. تسمح
الفئة بإرسال الصوت مباشرةً، بدون مزج أو
تعديل مستوى الصوت أو تطبيق تأثيرات المعالجة.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مدير بيانات الاعتماد
يضيف الإصدار 14 من Android واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Credential Manager كواجهة برمجة تطبيقات لمنصّة Android، مع إتاحة استخدامها على أجهزة Android 4.4 (المستوى 19 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأقدم من خلال مكتبة Jetpack باستخدام "خدمات Google Play". يهدف Credential Manager إلى تسهيل تسجيل الدخول للمستخدمين من خلال واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تسترجع بيانات الاعتماد وتخزّنها باستخدام موفّري بيانات الاعتماد الذين يضبطهم المستخدم. توفِّر واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Credential Manager طُرق تسجيل دخول متعدّدة، بما في ذلك اسم المستخدم وكلمة المرور ومفاتيح المرور، وحلول تسجيل الدخول الموحَّدة (مثل "تسجيل الدخول باستخدام حساب Google") في واجهة برمجة تطبيقات واحدة.
توفّر مفاتيح المرور العديد من المزايا. على سبيل المثال، تم إنشاء مفاتيح المرور استنادًا إلى المعايير المتّبعة في المجال، ويمكن استخدامها في مختلَف أنظمة التشغيل والمنظومات المتكاملة للمتصفِّحات، ويمكن استخدامها مع كلٍّ من المواقع الإلكترونية والتطبيقات.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على مستندات "مدير بيانات الاعتماد" ومفاتيح المرور ومقالة المدونة حول "مدير بيانات الاعتماد" ومفاتيح المرور.
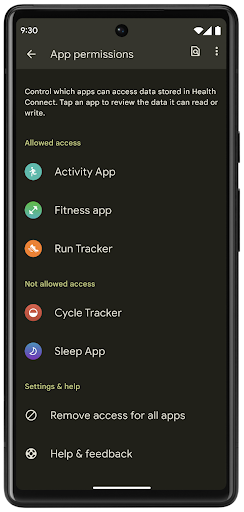
Health Connect
Health Connect هو مستودع على الجهاز لبيانات الصحة واللياقة البدنية للمستخدم. ويسمح الإعداد للمستخدمين بمشاركة البيانات بين تطبيقاتهم المفضّلة، مع توفير مكان واحد للتحكّم في البيانات التي يريدون مشاركتها مع هذه التطبيقات.
على الأجهزة التي تعمل بإصدارات Android أقدم من Android 14، يمكن تنزيل تطبيق Health Connect من متجر Google Play. بدءًا من الإصدار Android 14، أصبح تطبيق Health Connect جزءًا من المنصة ويتلقّى تحديثات من خلال تحديثات نظام Google Play بدون الحاجة إلى تنزيله بشكل منفصل. وبفضل ذلك، يمكن تحديث Health Connect بشكل متكرّر، ويمكن لتطبيقاتك الاعتماد على توفّر Health Connect على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 14 من نظام Android أو الإصدارات الأحدث. يمكن للمستخدمين الوصول إلى Health Connect من خلال "الإعدادات" في أجهزتهم، مع دمج عناصر التحكّم في الخصوصية في إعدادات النظام.
يتضمّن Health Connect العديد من الميزات الجديدة في Android 14، مثل مسار التمارين، ما يتيح للمستخدمين مشاركة مسار تمرينهم الذي يمكن عرضه visually على خريطة. يتم تعريف المسار على أنّه قائمة بالمواقع الجغرافية المحفوظة خلال فترة زمنية معيّنة، ويمكن لتطبيقك إدراج المسارات في جلسات التمارين، وربطها معًا. لضمان حصول المستخدمين على التحكّم الكامل في هذه البيانات الحسّاسة، يجب أن يسمح المستخدمون بمشاركة مسارات فردية مع تطبيقات أخرى.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على مستندات Health Connect والمقالة في المدونة حول الميزات الجديدة في تطبيق "صحة Android".
تعديلات على OpenJDK 17
يواصل نظام التشغيل Android 14 العمل على تحديث المكتبات الأساسية في Android لمواءمتها مع الميزات في أحدث إصدارات OpenJDK LTS، بما في ذلك تحديثات مكتبة ودعم لغة Java 17 لمطوّري التطبيقات والمنصات.
تشمل الميزات والتحسينات التالية:
- تم تعديل 300 فئة تقريبًا من فئات
java.baseلتتوافق مع Java 17. - كتل النصوص التي تُعرِض سلاسل نصية حرفية متعددة الأسطر في لغة البرمجة Java
- مطابقة الأنماط لـ instanceof، التي تسمح بالتعامل مع عنصر على أنّه يملك نوعًا معيّنًا في
instanceofبدون أي متغيّرات إضافية - الفئات المُغلقة، التي تتيح لك فرض قيود على الفئات والواجهات التي يمكنها توسيع نطاقها أو تنفيذها
بفضل تحديثات نظام Google Play (Project Mainline)، تم تفعيل أكثر من 600 مليون جهاز لتلقّي آخر تحديثات Android Runtime (ART) التي تتضمن هذه التغييرات. يأتي ذلك في إطار التزامنا بتوفير بيئة أكثر اتساقًا وأمانًا للتطبيقات على جميع الأجهزة، وتقديم ميزات و إمكانات جديدة للمستخدمين بغض النظر عن إصدارات المنصة.
Java وOpenJDK هما علامتان تجاريتان مسجَّلتان لشركة Oracle و/أو شركائها التابعين.
تحسينات على متاجر التطبيقات
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 14 العديد من واجهات برمجة تطبيقات PackageInstaller التي تسمح لمتاجر التطبيقات بتحسين تجربة المستخدمين.
طلب الموافقة على التثبيت قبل التنزيل
قد يتطلّب تثبيت تطبيق أو تحديثه موافقة المستخدم.
على سبيل المثال، عندما يحاول أحد تطبيقات التثبيت التي تستخدم إذن
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES تثبيت
تطبيق جديد، لا يمكن لمتاجر التطبيقات طلب موافقة المستخدم إلا بعد كتابة حِزم APK في جلسة التثبيت وإتمام الجلسة.
اعتبارًا من Android 14، تتيح طريقة requestUserPreapproval()
للمُثبّتين طلب موافقة المستخدم قبل إكمال جلسة التثبيت. يتيح هذا التحسين لمتجر التطبيقات تأجيل تنزيل أي حِزم APK إلى
بعد أن يوافق المستخدم على التثبيت. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، بعد أن يمنح أحد المستخدمين موافقته على التثبيت، يمكن لمتجر التطبيقات تنزيل التطبيق وتثبيته في
الخلفية بدون مقاطعة المستخدم.
تأكيد مسؤولية التعديلات المستقبلية
تسمح طريقة setRequestUpdateOwnership() للمثبّت
بإعلام النظام بأنّه سيتحمّل مسؤولية التحديثات المستقبلية
للتطبيق الذي يتم تثبيته. تتيح هذه الميزة فرض ملكية التحديث، ما يعني أنّه لا يُسمح إلا لمالك التحديث
بتثبيت التحديثات التلقائية للتطبيق. ويساعد فرض ملكية التحديث في
ضمان تلقّي المستخدمين للتحديثات من متجر التطبيقات المتوقّع فقط.
يجب أن يحصل أي مُثبِّت آخر، بما في ذلك مُثبِّتي التطبيقات الذين يستخدمون إذن
INSTALL_PACKAGES، على موافقة صريحة من المستخدمين لتثبيت التحديث. إذا قرّر أحد المستخدِمين مواصلة تعديل
من مصدر آخر، ستتم فقدان ملكية التعديل.
تحديث التطبيقات في أوقات أقل إزعاجًا
تحاول متاجر التطبيقات عادةً تجنُّب تحديث تطبيق قيد الاستخدام بشكل نشط، لأنّ ذلك يؤدي إلى إيقاف العمليات الجارية للتطبيق، ما قد يؤدي بدوره إلى إيقاف ما كان يفعله المستخدم.
بدءًا من Android 14، تقدّم واجهة برمجة التطبيقات InstallConstraints
للمُثبّتين طريقة لضمان إجراء تحديثات التطبيقات في الوقت المناسب. على سبيل المثال، يمكن لمتجر تطبيقات استدعاء الأسلوب
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() لمحاولة التأكد من عدم التزام المستخدم بالتغييرات إلا عندما يتوقف عن التفاعل مع التطبيق المعني.
تثبيت الفواصل الاختيارية بسلاسة
باستخدام حِزم APK المجزّأة، يمكن توفير ميزات التطبيق في حِزم APK منفصلة، بدلاً من حزمة APK واحدة. تسمح ملفات APK المجزّأة لمتاجر التطبيقات بتحسين
عرض مكوّنات التطبيق المختلفة. على سبيل المثال، قد تعمل متاجر التطبيقات على تحسين
التطبيقات استنادًا إلى خصائص الجهاز المستهدَف. كانت واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
PackageInstaller متوافقة مع عمليات التقسيم منذ
إدخالها في المستوى 22 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات.
في نظام التشغيل Android 14، تسمح طريقة setDontKillApp() لتطبيق
التثبيت بتحديد أنّه يجب عدم إنهاء عمليات التطبيق الجارية عند
تثبيت أقسام جديدة. يمكن لمتاجر التطبيقات استخدام هذه الميزة لتثبيت
ميزات جديدة للتطبيق بسلاسة أثناء استخدام المستخدم للتطبيق.
حِزم البيانات الوصفية للتطبيق
اعتبارًا من الإصدار Android 14، يتيح لك أداة تثبيت حِزم Android تحديد البيانات الوصفية للتطبيق، مثل ممارسات أمان البيانات، لتضمينها في صفحات متجر التطبيقات، مثل Google Play.
رصد وقت أخذ المستخدمين لقطات شاشة للجهاز
لإنشاء تجربة أكثر توحيدًا في ما يتعلّق برصد لقطات الشاشة، يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 14 واجهة برمجة تطبيقات لرصد لقطات الشاشة تحافظ على الخصوصية. تتيح واجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه للتطبيقات تسجيل عمليات ردّ على مستوى كل نشاط. يتم استدعاء عمليات الرجوع هذه وإرسال إشعار إلى المستخدم عندما يلتقط لقطة شاشة أثناء ظهور هذا النشاط.
تجربة المستخدم
الإجراءات المخصّصة في ورقة المشاركة والترتيب المحسّن
يُعدّل نظام التشغيل Android 14 جدول مشاركة النظام ليتيح إجراءات التطبيقات المخصّصة ونتائج معاينة أكثر فائدة للمستخدمين.
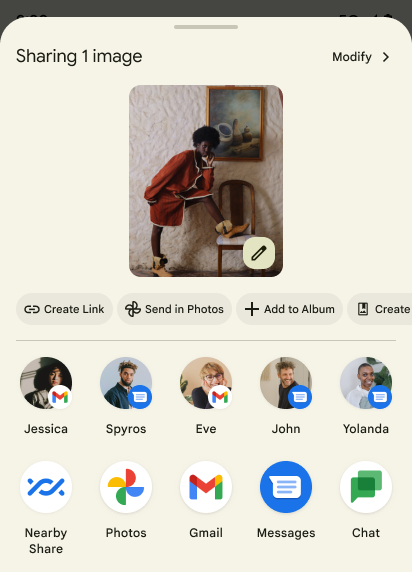
إضافة إجراءات مخصّصة
باستخدام الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android، يمكن لتطبيقك إضافة إجراءات مخصّصة إلى جدول مشاركة النظام الذي يستدعيه.
تحسين ترتيب استهدافات المشاركة المباشرة
يستخدم الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android المزيد من الإشارات من التطبيقات لتحديد ترتيب استهدافات مشاركة المحتوى المباشر من أجل تقديم نتائج أكثر فائدة للمستخدم. لتقديم الإشارة الأكثر فائدة للترتيب، اتّبِع الإرشادات المتعلقة ب تحسين ترتيب استهدافات "المشاركة المباشرة". يمكن أيضًا لتطبيقات التواصل الإبلاغ عن استخدام الاختصارات للرسائل المغادرة والواردة.
إتاحة صور متحركة مضمّنة ومخصّصة لإيماءة "الرجوع التنبؤي"
قدّم نظام التشغيل Android 13 إيماءة الرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية التنبؤية من خلال خيار مخصّص للمطوّرين. عند استخدامها في تطبيق متوافق مع تفعيل خيار المطوّر، يؤدي التمرير سريعًا للخلف إلى عرض صورة متحركة تشير إلى أنّ إيماءة الرجوع تؤدي إلى الخروج من التطبيق والرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية.
يتضمّن Android 14 تحسينات متعدّدة وإرشادات جديدة بشأن ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي":
- يمكنك ضبط
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueلتفعيل الصور المتحركة في النظام لإيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية لكل نشاط بدلاً من تفعيلها للتطبيق بأكمله. - أضفنا صورًا متحركة جديدة للنظام لترافق الصورة المتحركة للرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية من Android 13. إنّ الصور المتحركة الجديدة في النظام تعمل على جميع الأنشطة والمهام، ويتم عرضها تلقائيًا بعد نقل البيانات إلى ميزة "الرجوع التلقائي".
- أضفنا رسومًا متحركة جديدة لعناصر Material Design في الجدولَين المعروضَين في أسفل الشاشة والجدولَين الجانبيَين والبحث.
- لقد أنشأنا إرشادات تصميم لإنشاء مؤثرات مخصّصة للصور المتحركة والانتقالات داخل التطبيق.
- لقد أضفنا واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة تتيح استخدام صور متحركة مخصّصة للانتقالات داخل التطبيق:
handleOnBackStartedوhandleOnBackProgressedوhandleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStartedوonBackProgressedوonBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- استخدِم
overrideActivityTransitionبدلاً منoverridePendingTransitionللانتقالات التي تستجيب عندما يقلب المستخدم الشاشة للخلف.
في إصدار معاينة Android 14 هذا، تظل جميع ميزات "الترجيع التوقّعي" متاحة فقط من خلال خيار المطوّر. اطّلِع على دليل المطوّر لنقل بيانات تطبيقك إلى ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي"، بالإضافة إلى دليل المطوّر لإنشاء التحولات المخصّصة داخل التطبيق.
عمليات الإلغاء على مستوى التطبيق من قِبل مصنّع الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة
تتيح عمليات إلغاء الإعدادات على مستوى التطبيق لصنّاع الأجهزة تغيير سلوك التطبيقات على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة. على سبيل المثال، عند إلغاء FORCE_RESIZE_APP، يتم توجيه النظام لتغيير حجم التطبيق ليلائم أبعاد العرض (وتجنُّب وضع توافق الحجم) حتى في حال ضبط resizeableActivity="false" في بيان التطبيق.
تهدف عمليات الإلغاء إلى تحسين تجربة المستخدم على الشاشات الكبيرة.
تتيح لك سمات البيان الجديدة إيقاف بعض عمليات إلغاء الشركة المصنّعة للجهاز لتطبيقك.
عمليات إلغاء على مستوى التطبيق لمستخدمي الشاشات الكبيرة
تؤدي عمليات التجاوز لكل تطبيق إلى تغيير سلوك التطبيقات على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة. على سبيل المثال، يمكن للشركة المصنّعة للجهاز OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE إلغاء الإعدادات وضبط نسبة عرض إلى ارتفاع التطبيق على 16:9 بغض النظر عن إعدادات التطبيق.
يتيح الإصدار 1 من الربع الثاني من العام 2021 من نظام التشغيل Android 14 للمستخدمين تطبيق عمليات إلغاء على مستوى كل تطبيق من خلال قائمة إعدادات جديدة على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة.
مشاركة شاشة التطبيق
تتيح ميزة "مشاركة شاشة التطبيق" للمستخدمين مشاركة نافذة تطبيق بدلاً من شاشة الجهاز بالكامل أثناء تسجيل محتوى الشاشة.
عند مشاركة شاشة التطبيق، يتم استبعاد شريط الحالة وشريط التنقّل والإشعارات وعناصر واجهة مستخدم النظام الأخرى من الشاشة المشترَكة. تتم مشاركة محتوى التطبيق المحدّد فقط.
تعمل ميزة "مشاركة شاشة التطبيق" على تحسين الإنتاجية والخصوصية من خلال السماح للمستخدمين بتشغيل تطبيقات متعددة مع حصر مشاركة المحتوى بتطبيق واحد.
ميزة "الرد السريع" المستندة إلى نماذج اللغات الكبيرة في Gboard على هاتف Pixel 8 Pro
على أجهزة Pixel 8 Pro التي تم تثبيت حزمة ميزات شهر كانون الأول (ديسمبر) عليها، يمكن للمطوّرين تجربة ردود سريعة بجودة أعلى في Gboard، وذلك باستخدام نماذج لغوية كبيرة (LLM) على الجهاز تعمل على معالج Google Tensor.
تتوفّر هذه الميزة في إصدار تجريبي محدود باللغة الإنجليزية (الولايات المتحدة) في WhatsApp وLine وKakaoTalk. تتطلّب الميزة استخدام جهاز Pixel 8 Pro مع Gboard ك keyboard.
لتجربة هذه الميزة، عليك أولاً تفعيلها من خلال الانتقال إلى الإعدادات > خيارات المطوّرين > إعدادات AICore > تفعيل ميزة Aicore Persistent.
بعد ذلك، افتح محادثة في تطبيق متوافق للاطّلاع على ميزة "الرد السريع" المستندة إلى نموذج اللغة الكبيرة في شريط اقتراحات Gboard استجابةً للرسائل الواردة.
الرسومات
يمكن البحث عن المسارات وتعديلها.
Path API هي آلية فعّالة ومرنة ل
إنشاء الرسومات المتجهّة وعرضها، مع إمكانية رسم خطوط أو ملء
مسار أو إنشاء مسار من أجزاء خطية أو منحنيات ثنائية أو ثلاثية الحدود، أو تنفيذ
عمليات منطقية للحصول على أشكال أكثر تعقيدًا، أو كل ذلك
في الوقت نفسه. ويتمثل أحد القيود في القدرة على معرفة ما هو موجود بالفعل في كائن "مسار"، وتكون العناصر الداخلية للكائن معتمة للمتصلين بعد إنشائه.
لإنشاء Path، يمكنك استدعاء طرق مثل
moveTo() وlineTo() و
cubicTo() لإضافة شرائح مسار. ولكن لم تكن هناك طريقة للسؤال عن
الأجزاء في هذا المسار، لذلك يجب عليك الاحتفاظ بهذه المعلومات في وقت الإنشاء.
بدءًا من Android 14، يمكنك طلب البحث عن المسارات لمعرفة ما بداخلها.
عليك أولاً الحصول على كائن PathIterator باستخدام واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Path.getPathIterator:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
بعد ذلك، يمكنك استدعاء الدالة PathIterator لتكرار الشرائح الواحد تلو الآخر، واسترداد جميع البيانات اللازمة لكل شريحة. يستخدم هذا المثال
كائنات PathIterator.Segment التي تحزم البيانات
نيابةً عنك:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
لدى PathIterator أيضًا إصدار غير مخصّص من next() يمكنك تمريره
في مخزن مؤقت للاحتفاظ ببيانات النقاط.
من حالات الاستخدام المهمة لطلب بيانات Path هي الاستقراء. على سبيل المثال، قد ترغب في إضافة تأثير متحرك (أو تحويل) بين مسارين مختلفين. لتبسيط حالة الاستخدام هذه بشكل أكبر، يتضمّن Android 14 أيضًا طريقة
interpolate() في Path. بافتراض أنّ المسارَين لهما البنية الداخلية نفسها، تنشئ الطريقة interpolate() Path جديدة مع تلك النتيجة المضمَّنة. يعرض هذا المثال مسارًا يكون شكله
في منتصف الطريق (تداخل خطي بنسبة 0.5) بين path وotherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
تتيح مكتبة graphics-path في Jetpack واجهات برمجة تطبيقات مشابهة لإصدارات Android الأقدم أيضًا.
شبكات مخصّصة مع مظلّلات الرؤوس والأجزاء
منذ فترة طويلة، يتيح Android رسم شبكات مثلثية باستخدام تظليل مخصّص، ولكن كان تنسيق شبكة الإدخال يقتصر على بعض مجموعات السمات المحدّدة مسبقًا. يتيح نظام Android 14 استخدام الشبكات المخصّصة التي يمكن تحديدها على أنّها مثلثات أو شرائح مثلثية، ويمكن فهرستها اختياريًا. يتم تحديد هذه الشبكات باستخدام سمات مخصّصة وخطوات رؤوس العناصر المتغيّرة وبرامج تشويش رؤوس العناصر والعناصر الصغيرة المكتوبة بلغة AGSL.
يحدّد برنامج تظليل رؤوس المضلّعات المتغيّرات، مثل الموضع واللون، في حين يمكن لبرنامج تظليل العناصر تحديد لون البكسل اختياريًا، عادةً باستخدام المتغيّرات التي أنشأها برنامج تظليل رؤوس المضلّعات. إذا كان اللون مقدَّمًا منshader
القطعة، يتم دمجه بعد ذلك مع Paint
اللون الحالي باستخدام وضع الدمج الذي تم اختياره عند
رسم الشبكة. يمكن تمرير المتجانسات
إلى برامج تظليل الشرائح والرؤوس للحصول على مرونة إضافية.
أداة عرض المخزن المؤقت للأجهزة في Canvas
للمساعدة في استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Canvas في Android للرسم باستخدام
التسارع في الأجهزة في HardwareBuffer، يوفّر الإصدار 14 من Android HardwareBufferRenderer. واجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه
عندما تشتمل حالة الاستخدام على التواصل مع النظام
المكون من خلال SurfaceControl لوقت الاستجابة المنخفض
رسم.

