Espresso आपको एक ऐसा तरीका ऑफ़र करता है जिसके ज़रिए दो सूचियों के टाइप: अडैप्टर व्यू और रीसाइकलर व्यू.
सूचियों के साथ काम करते समय, खास तौर पर वे सूचियां जो RecyclerView या
AdapterView ऑब्जेक्ट, हो सकता है कि आपकी दिलचस्पी का व्यू, यहां भी न हो
क्योंकि कुछ ही बच्चे दिखाए गए हैं और
रीसाइकल किया जा सकता है. इस मामले में scrollTo() तरीका इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जा सकता
क्योंकि इसके लिए एक मौजूदा व्यू की ज़रूरत है.
अडैप्टर के व्यू की सूची में मौजूद आइटम के साथ इंटरैक्ट करें
onView() तरीके का इस्तेमाल करने के बजाय, onData() से अपनी खोज शुरू करें और
मैचर को उस डेटा के लिए मैच करें जो उस व्यू का बैक अप ले रहा है जिसे आपको मैच करना है.
Adapter ऑब्जेक्ट में लाइन को ढूंढने का सारा काम एस्प्रेसो करेगा और
आइटम को व्यूपोर्ट में दिखाने के लिए.
कस्टम व्यू मैचर का इस्तेमाल करके डेटा मैच करें
नीचे दी गई गतिविधि में एक ListView शामिल है, जो SimpleAdapter के साथ सुरक्षित है
जो Map<String, Object> ऑब्जेक्ट की हर लाइन का डेटा होल्ड करता है.
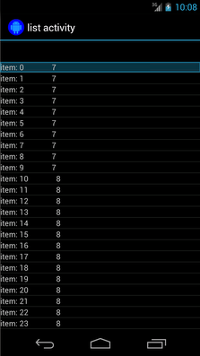
हर मैप में दो एंट्री होती हैं: एक कुंजी "STR" जिसमें एक स्ट्रिंग होती है, जैसे
"item: x" और एक कुंजी "LEN" होती है, जिसमें Integer मौजूद होता है, जो
कॉन्टेंट की लंबाई. उदाहरण के लिए:
{"STR" : "item: 0", "LEN": 7}
"आइटम: 50" वाली पंक्ति पर क्लिक के लिए कोड ऐसा दिखता है:
Kotlin
onData(allOf(`is`(instanceOf(Map::class.java)), hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), `is`("item: 50")))).perform(click())
Java
onData(allOf(is(instanceOf(Map.class)), hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), is("item: 50")))) .perform(click());
ध्यान दें कि ज़रूरत पड़ने पर Espresso अपने-आप सूची में स्क्रोल करता है.
onData() के अंदर मौजूद Matcher<Object> को एक अलग पहचान दें. कॉन्टेंट बनाने
is(instanceOf(Map.class)) तरीका, खोज के नतीजों को
AdapterView, जो Map ऑब्जेक्ट का इस्तेमाल करता है.
हमारे मामले में, क्वेरी का यह पहलू सूची व्यू की हर लाइन से मेल खाता है, लेकिन हम किसी आइटम पर विशेष रूप से क्लिक करना चाहते हैं, इसलिए हम खोज को और सटीक बनाते हैं:
Kotlin
hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), `is`("item: 50"))
Java
hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), is("item: 50"))
यह Matcher<String, Object> उन सभी मैप से मेल खाएगा जिनमें
कुंजी "STR" और मान "item: 50". क्योंकि इसे देखने के लिए कोड
लंबा और हम इसे अन्य स्थानों में फिर से उपयोग करना चाहते हैं, तो आइए एक कस्टम
उसके लिए withItemContent मैचर:
Kotlin
return object : BoundedMatcher<Object, Map>(Map::class.java) { override fun matchesSafely(map: Map): Boolean { return hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), itemTextMatcher).matches(map) } override fun describeTo(description: Description) { description.appendText("with item content: ") itemTextMatcher.describeTo(description) } }
Java
return new BoundedMatcher<Object, Map>(Map.class) { @Override public boolean matchesSafely(Map map) { return hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), itemTextMatcher).matches(map); } @Override public void describeTo(Description description) { description.appendText("with item content: "); itemTextMatcher.describeTo(description); } };
BoundedMatcher का इस्तेमाल बेस के तौर पर किया जाता है, क्योंकि इसका इस्तेमाल सिर्फ़ टाइप के ऑब्जेक्ट से मैच करने के लिए किया जाता है
Map. 'मिल गया' कॉलम में, matchesSafely() तरीके को बदलें
साथ ही, Matcher<String> से मैच करना होगा, जिसे
तर्क है. इसकी मदद से, withItemContent(equalTo("foo")) को कॉल किया जा सकेगा. कोड के लिए
तो आपके पास ऐसा दूसरा मैचर बनाने का विकल्प है जो पहले से ही equalTo() और
String ऑब्जेक्ट स्वीकार करता है:
Kotlin
fun withItemContent(expectedText: String): Matcher<Object> { checkNotNull(expectedText) return withItemContent(equalTo(expectedText)) }
Java
public static Matcher<Object> withItemContent(String expectedText) { checkNotNull(expectedText); return withItemContent(equalTo(expectedText)); }
अब किसी आइटम पर क्लिक करने के लिए कोड बनाना आसान है:
Kotlin
onData(withItemContent("item: 50")).perform(click())
Java
onData(withItemContent("item: 50")).perform(click());
इस टेस्ट के पूरे कोड के लिए, testClickOnItem50() तरीके पर एक नज़र डालें
के अंदर
AdapterViewTest
क्लास और
यह कस्टम LongListMatchers
GitHub पर मैचर है.
किसी चाइल्ड व्यू को मैच करना
ऊपर दिया गया सैंपल, ListView की पूरी लाइन के बीच में एक क्लिक दिखाता है.
लेकिन अगर हमें लाइन के किसी खास चाइल्ड पर काम करना हो, तो क्या होगा? उदाहरण के लिए, हम
LongListActivity की पंक्ति के दूसरे कॉलम पर क्लिक करना चाहेगा,
जो पहले कॉलम में, कॉन्टेंट की String.length दिखाता है:

बस इसे लागू करने के लिए onChildView() का स्पेसिफ़िकेशन जोड़ें
DataInteraction:
Kotlin
onData(withItemContent("item: 60")) .onChildView(withId(R.id.item_size)) .perform(click())
Java
onData(withItemContent("item: 60")) .onChildView(withId(R.id.item_size)) .perform(click());
रीसाइकलर के व्यू की सूची में शामिल आइटम के साथ इंटरैक्ट करें
RecyclerView ऑब्जेक्ट, AdapterView ऑब्जेक्ट से अलग तरीके से काम करते हैं, इसलिए
इन संपर्कों से इंटरैक्ट करने के लिए, onData() का इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जा सकता.
Espresso का इस्तेमाल करके, RecyclerViews के साथ इंटरैक्ट करने के लिए,
espresso-contrib पैकेज, जिसमें इसका संग्रह है
RecyclerViewActions
जिनका इस्तेमाल स्थितियों तक स्क्रोल करने या आइटम पर कार्रवाइयां करने के लिए किया जा सकता है:
scrollTo()- मेल खाने वाले व्यू के मौजूद होने पर, उस पर स्क्रोल करता है.scrollToHolder()- मेल खाने वाले व्यू होल्डर तक स्क्रोल करता है, अगर वह मौजूद है.scrollToPosition()- किसी खास जगह तक स्क्रोल करता है.actionOnHolderItem()- मिलते-जुलते व्यू होल्डर पर व्यू कार्रवाई करता है.actionOnItem()- मेल खाने वाले व्यू पर व्यू कार्रवाई करता है.actionOnItemAtPosition()- किसी खास पोज़िशन पर व्यू के लिए ViewAction करता है.
नीचे दिए गए स्निपेट में RecyclerViewSample नमूना:
Kotlin
@Test(expected = PerformException::class) fun itemWithText_doesNotExist() { // Attempt to scroll to an item that contains the special text. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform( // scrollTo will fail the test if no item matches. RecyclerViewActions.scrollTo( hasDescendant(withText("not in the list")) ) ) }
Java
@Test(expected = PerformException.class) public void itemWithText_doesNotExist() { // Attempt to scroll to an item that contains the special text. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) // scrollTo will fail the test if no item matches. .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollTo( hasDescendant(withText("not in the list")) )); }
Kotlin
@Test fun scrollToItemBelowFold_checkItsText() { // First, scroll to the position that needs to be matched and click on it. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform( RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItemAtPosition( ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD, click() ) ) // Match the text in an item below the fold and check that it's displayed. val itemElementText = "${activityRule.activity.resources .getString(R.string.item_element_text)} ${ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD.toString()}" onView(withText(itemElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())) }
Java
@Test public void scrollToItemBelowFold_checkItsText() { // First, scroll to the position that needs to be matched and click on it. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItemAtPosition(ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD, click())); // Match the text in an item below the fold and check that it's displayed. String itemElementText = activityRule.getActivity().getResources() .getString(R.string.item_element_text) + String.valueOf(ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD); onView(withText(itemElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())); }
Kotlin
@Test fun itemInMiddleOfList_hasSpecialText() { // First, scroll to the view holder using the isInTheMiddle() matcher. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollToHolder(isInTheMiddle())) // Check that the item has the special text. val middleElementText = activityRule.activity.resources .getString(R.string.middle) onView(withText(middleElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())) }
Java
@Test public void itemInMiddleOfList_hasSpecialText() { // First, scroll to the view holder using the isInTheMiddle() matcher. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollToHolder(isInTheMiddle())); // Check that the item has the special text. String middleElementText = activityRule.getActivity().getResources() .getString(R.string.middle); onView(withText(middleElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())); }
अन्य संसाधन
Android परीक्षणों में Espresso सूचियों का उपयोग करने के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, इन संसाधनों को देखें.
सैंपल
- DataAdapterSample:
यह दिखाता है कि सूचियों और
AdapterViewके लिए, Espresso काonData()एंट्री पॉइंट है ऑब्जेक्ट हैं.
