內建意圖 (BII) 可讓應用程式表達其執行要求功能。 Google。在 shortcuts.xml 檔案中宣告功能,並 只要將意圖參數對應至執行要求,就能 讓 Google 助理在特定畫面上啟動您的應用程式以回應 以便使用者完成工作
系統會根據應用程式類別將內建意圖分組。每個類別 代表使用者經常執行的工作之一 應用程式。可用 BII 的完整清單、參數與範例 如需可供測試的查詢,請參閱內建意圖參考資料。
許多 BII 都有特定的部署需求和 最佳化建議。這些規定和建議有助應用程式達成目標 就能為使用者提供最佳體驗。
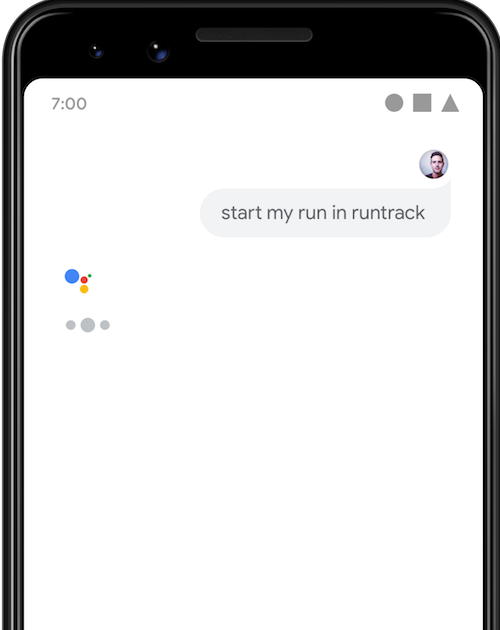
START_EXERCISE BII
向 Google 助理下達的指令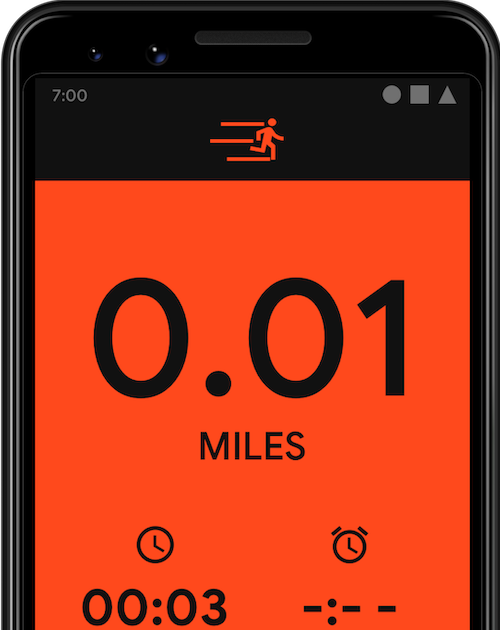
START_EXERCISE 工作。
實作 BII 及處理意圖參數
對於應用程式動作,您需要宣告功能及處理 BII 參數 shortcuts.xml 檔案。如要實作 BII,並處理 參數,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 使用所選的 BII 宣告
capability。 - 為您要新增的每個 BII 欄位加入巢狀
parameter元素。- 如果您使用
targetClass或targetPackage,請將其對應至 Androidextras。 - 如果您使用深層連結網址,請在查詢中使用具名參數 字串字串。
- 如果您使用
如要處理 BII 參數,請將 BII 參數對應至
capability 中明確 Android 意圖的對應參數。
接著,您就可以在應用程式中使用這個值。應用程式無須處理
BII 參數。然而,請務必嘗試處理標記為「推薦」的資料欄位
內建意圖參考資料中所列。
您可以定義多個意圖執行要求,每個意圖都有各自的一組 建議使用的參數Google 會根據 功能參數會從使用者查詢加以識別,以及宣告的 或擷取在意圖中寫入的資料
例如:actions.intent.START_EXERCISE
意圖建議應用程式處理 exercise.name BII 參數,但
但不需參數,就能在應用程式中實作 BII。
如想在不使用特定鍵的情況下處理使用者查詢
運動的名稱,例如「要求範例應用程式開始追蹤運動」。
下列程式碼片段具有不含必要參數的執行要求做為備用執行方式 表示使用者的查詢不包含參數:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shortcuts xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<capability android:name="actions.intent.START_EXERCISE">
<intent
android:action="android.intent.action.VIEW"
android:targetClass="com.example.myapplication.Activity1"
android:targetPackage="com.example.myapplication">
<parameter
android:name="exercise.name"
android:key="exerciseType"
android:required="true"
/>
</intent>
<intent
android:action="android.intent.action.VIEW"
android:targetClass="com.example.myapplication.Activity2">
</intent>
</capability>
</shortcuts>
Google 助理會盡力為 將參數值傳回給應用程式的使用者。例如,使用者查詢 透過範例餐廳的行動應用程式訂購披薩時,不一定會包含 或 HTTP/HTTPS 位置為了提供使用者更優質的服務,Google 助理可能會提供緯度 距離該應用程式最近的範例餐廳 (Example Restaurant) 和經度值。
額外規定,您不希望應用程式直接 會修改使用者實際狀態的動作 (例如: 付款、下單或傳送訊息) 時, 執行動作
消歧
透過 <url-parameter> 或意圖額外項目傳遞至應用程式的引數可能無法
明確識別您要向使用者顯示的項目。在本例中
使用引數值做為搜尋引數,並將使用者導向搜尋
頁面。以便區分和選擇正確的商品。
舉例來說,如果使用者查詢是「前往範例餐廳訂購」
BII ORDER_MENU_ITEM,您可以向使用者顯示
與「"Example Restaurant"」字詞相符的餐廳。
語言和語言代碼支援
每個應用程式動作 BII 支援的開發和測試語言代碼 內建意圖參考資料列出。某些 BII 有差異 支援開發人員測試和透過 Google 助理觸發的使用者語言。
