इस पेज पर बताया गया है कि तीसरे पक्ष के एसडीके, वेबपेज से इंस्टॉल करने की सुविधा को कैसे इंटिग्रेट कर सकते हैं. यह Google Play के लिए नई टेस्ट सुविधा है. इसमें Google Play ऐप्लिकेशन के प्रॉडक्ट की जानकारी, हाफ़ शीट इंटरफ़ेस में दिखाई जाती है. इनलाइन इंस्टॉल की सुविधा की मदद से, उपयोगकर्ता ऐप्लिकेशन के कॉन्टेक्स्ट से बाहर जाए बिना, ऐप्लिकेशन इंस्टॉल करने की प्रोसेस को आसानी से पूरा कर सकते हैं.
तीसरे पक्ष के एसडीके डेवलपर, इनलाइन इंस्टॉल करने की सुविधा को अपने एसडीके में इंटिग्रेट कर सकते हैं. इससे, उन एसडीके का इस्तेमाल करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन डेवलपर को अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, इनलाइन इंस्टॉल करने की सुविधा को ऐक्सेस करने में मदद मिलती है.
ज़रूरी शर्तें
किसी ऐप्लिकेशन में वेबपेज से इंस्टॉल करने की सुविधा वाला हाफ़ शीट इंटरफ़ेस दिखाने के लिए:
- Google Play का कम से कम वर्शन 40.4 होना चाहिए.
- Android का एपीआई लेवल 23 या इसके बाद का वर्शन होना चाहिए.
प्रोसेस आर्किटेक्चर
वेबपेज से इंस्टॉल करने की प्रोसेस का आर्किटेक्चर इस इमेज में दिखाया गया है:
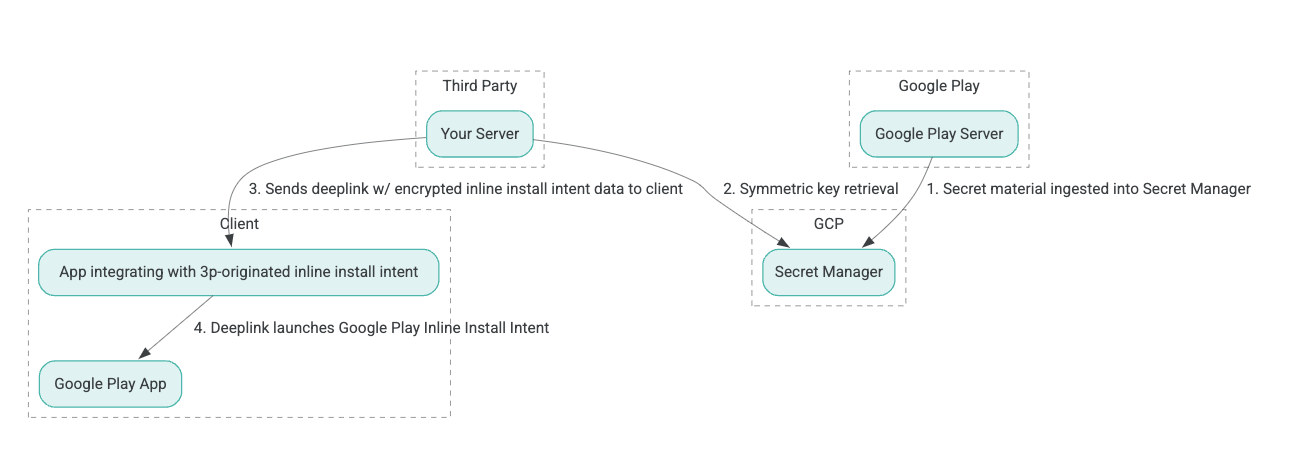
- Google Play सर्वर, 'असोसिएटेड डेटा के साथ पुष्टि किया गया एन्क्रिप्शन' (एईएडी) एन्क्रिप्शन कुंजियां जनरेट करते हैं. साथ ही, इन कुंजियों को Google Cloud Platform (GCP) के Secret Manager इंस्टेंस में डालते हैं.
- तीसरे पक्ष का इंटिग्रेटर, GCP Secret Manager से AEAD कुंजी को वापस पाता है.
- तृतीय-पक्ष इंटीग्रेटर इनलाइन इंस्टॉल
Intentडेटा को एन्क्रिप्ट करता है, इनलाइन इंस्टॉल इंटेंट को लागू करने के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले डीप लिंक में पास किए गए सिफरटेक्स्ट को जनरेट करता है, और क्लाइंट को प्रतिक्रियाओं में डीप लिंक भेजता है. - जब डीप लिंक का अनुसरण किया जाता है, तो Google Play ऐप्लिकेशन इंटेंट को संभालता है.
इनलाइन इंस्टॉल प्रक्रिया का उपयोग करने के लिए किसी तृतीय-पक्ष SDK को कॉन्फ़िगर करने के लिए, निम्न चरणों को पूरा करें.
Google Cloud प्रोजेक्ट में सेवा खाते बनाना
इस चरण में, Google Cloud Console का इस्तेमाल करके, सेवा खाता सेट अप किया जाता है.
- Google Cloud प्रोजेक्ट सेट अप करें:
- Google क्लाउड संगठन बनाएं. जब आप Google Workspace या Cloud Identity खाता बनाते हैं और उसे अपने डोमेन नाम से जोड़ते हैं, तो संगठन संसाधन अपने आप बन जाता है. विवरण के लिए, संगठन संसाधन बनाना और प्रबंधित करना देखें.
- पिछले चरण में बनाए गए Google Cloud खाते का इस्तेमाल करके, GCP Console में लॉग इन करें. इसके बाद, Google Cloud प्रोजेक्ट बनाएं. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, Google Cloud प्रोजेक्ट बनाना लेख पढ़ें.
- बनाए गए Google Cloud प्रोजेक्ट में एक सेवा खाता बनाएं. सेवा खाते का इस्तेमाल, Google Cloud Identity के तौर पर किया जाता है. इससे आपके सर्वर की ओर से सिमेट्रिक कुंजी को ऐक्सेस किया जा सकता है. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, सेवा खाता बनाना लेख पढ़ें.
- वही Google Workspace ग्राहक आईडी (GWCID) / Dasher आईडी इस्तेमाल करें जो दिलचस्पी दिखाने वाले फ़ॉर्म में डाला गया था.
- उस सेवा खाते का निजी पासकोड बनाएं और उसे डाउनलोड करें.
- उस सेवा खाते के लिए एक कुंजी बनाएं. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, सेवा खाते की कुंजी बनाना लेख पढ़ें.
- सेवा खाते की कुंजी डाउनलोड करें और इसे अपने सर्वर पर ऐक्सेस किया जा सकने वाला बनाएं. ऐसा इसलिए, क्योंकि इसका इस्तेमाल सिमेट्रिक कुंजियों के लिए, Google Cloud के संसाधनों को ऐक्सेस करने के लिए पुष्टि करने के लिए किया जाता है. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, सेवा खाता कुंजी पाना लेख पढ़ें.
क्रेडेंशियल वापस पाना
इस चरण में, Secret Manager से सिमेट्रिक कुंजी वापस पाई जाती है. इसके बाद, इसे अपने सर्वर स्टोरेज में सुरक्षित रूप से सेव किया जाता है. उदाहरण के लिए, JSON फ़ाइल में. इस कुंजी का उपयोग इनलाइन इंस्टॉल डेटा सिफरटेक्स्ट उत्पन्न करने के लिए किया जाता है.
secret_id/secretId वैल्यू, SecretManager में मौजूद सीक्रेट के नाम को दिखाती हैं. यह नाम, Play की ओर से दी गई वैल्यू sdk_id में hsdp-3p-key- को पहले जोड़कर जनरेट किया जाता है. उदाहरण के लिए, अगर sdk_id abc है, तो सीक्रेट का नाम hsdp-3p-key-abc होगा.
सीक्रेट वर्शन, हर हफ़्ते मंगलवार को दोपहर 2 बजे यूटीसी पर अपडेट किए जाते हैं. दूसरी सबसे नई कुंजियां, अगले रोटेशन तक काम करती रहेंगी. साथ ही, कुंजी मटीरियल को हर हफ़्ते फ़ेच और सेव किया जाना चाहिए.
Python का उदाहरण
यहां दिए गए कोड के उदाहरण में, JSON फ़ाइल में सेव किए गए ऐक्सेस टोकन का इस्तेमाल करके, GCP Secret Manager में मौजूद मुख्य मटीरियल को ऐक्सेस किया जाता है. साथ ही, इसे कंसोल में प्रिंट किया जाता है.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
from google.cloud import secretmanager
from google.oauth2 import service_account
import google_crc32c
# Create a service account key file.
service_account_key_file = "<json key file of the service account>"
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(service_account_key_file)
# Create the Secret Manager client.
client = secretmanager.SecretManagerServiceClient(
credentials=credentials
)
# Build the resource name of the secret version.
name = f"projects/prod-play-hsdp-3p-caller-auth/secrets/<secret_id>/versions/latest"
# Access the secret version.
response = client.access_secret_version(request={"name": name})
# Verify payload checksum.
crc32c = google_crc32c.Checksum()
crc32c.update(response.payload.data)
if response.payload.data_crc32c != int(crc32c.hexdigest(), 16):
print("Data corruption detected.")
# A keyset created with "tinkey create-keyset --key-template=AES256_GCM". Note
# that this keyset has the secret key information in cleartext.
keyset = response.payload.data.decode("UTF-8")
# WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment. Please store it
# in a secure storage.
with open('<key file name>', 'w') as f:
f.write(keyset)
Java का उदाहरण
यहां दिए गए कोड के उदाहरण में, JSON फ़ाइल में सेव किए गए ऐक्सेस टोकन का इस्तेमाल करके, GCP Secret Manager में मौजूद मुख्य मटीरियल को ऐक्सेस किया जाता है. साथ ही, इसे JSON फ़ाइल में लिखा जाता है.
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.api.gax.core.CredentialsProvider;
import com.google.api.gax.core.FixedCredentialsProvider;
import com.google.auth.oauth2.ServiceAccountCredentials;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.AccessSecretVersionResponse;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceClient;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceSettings;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretVersionName;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.zip.CRC32C;
import java.util.zip.Checksum;
/** */
final class ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide {
private ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
accessSecretVersion();
}
public static void accessSecretVersion() throws IOException {
// TODO(developer): Replace these variables before running the sample.
String projectId = "projectId";
String secretId = "secretId";
String versionId = "versionId";
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath = "path/to/credentials.json";
String secretMaterialOutputPath = "path/to/secret.json";
accessSecretVersion(
projectId, secretId, versionId, accessTokenPrivateKeyPath, secretMaterialOutputPath);
}
// Access the payload for the given secret version if one exists. The version
// can be a version number as a string (e.g. "5") or an alias (e.g. "latest").
public static void accessSecretVersion(
String projectId,
String secretId,
String versionId,
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath,
String secretMaterialOutputPath)
throws IOException {
// We can explicitly instantiate the SecretManagerServiceClient (below) from a json file if we:
// 1. Create a CredentialsProvider from a FileInputStream of the JSON file,
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider =
FixedCredentialsProvider.create(
ServiceAccountCredentials.fromStream(new FileInputStream(accessTokenPrivateKeyPath)));
// 2. Build a SecretManagerService Settings object from that credentials provider, and
SecretManagerServiceSettings secretManagerServiceSettings =
SecretManagerServiceSettings.newBuilder()
.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.build();
// 3. Initialize client that will be used to send requests by passing the settings object to
// create(). This client only needs to be created once, and can be reused for multiple requests.
// After completing all of your requests, call the "close" method on the client to safely clean
// up any remaining background resources.
try (SecretManagerServiceClient client =
SecretManagerServiceClient.create(secretManagerServiceSettings)) {
SecretVersionName secretVersionName = SecretVersionName.of(projectId, secretId, versionId);
// Access the secret version.
AccessSecretVersionResponse response = client.accessSecretVersion(secretVersionName);
// Verify checksum. The used library is available in Java 9+.
// If using Java 8, you may use the following:
// https://github.com/google/guava/blob/e62d6a0456420d295089a9c319b7593a3eae4a83/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/Hashing.java#L395
byte[] data = response.getPayload().getData().toByteArray();
Checksum checksum = new CRC32C();
checksum.update(data, 0, data.length);
if (response.getPayload().getDataCrc32C() != checksum.getValue()) {
System.out.printf("Data corruption detected.");
return;
}
String payload = response.getPayload().getData().toStringUtf8();
// Print the secret payload.
//
// WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment - this
// snippet is showing how to access the secret material.
System.out.printf("Plaintext: %s\n", payload);
// Write the JSON secret material payload to a json file
try (PrintWriter out =
new PrintWriter(Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get(secretMaterialOutputPath), UTF_8))) {
out.write(payload);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ऐप्लिकेशन के डिफ़ॉल्ट क्रेडेंशियल सेट करना
अगर आपको Java में लागू करने के दौरान, JSON फ़ाइल में निजी कुंजी भेजने के लिए CredentialsProvider का इस्तेमाल नहीं करना है, तो ऐप्लिकेशन के डिफ़ॉल्ट क्रेडेंशियल (एडीसी) सेट करके, लागू करने के तरीके में बदलाव किया जा सकता है:
- क्लाइंट लाइब्रेरी को बताएं कि सेवा खाता कुंजी कहां मिलेगी.
- Java प्रोजेक्ट में Maven निर्भरताएँ जोड़ें.
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()पर कॉल करें, जो स्वचालित रूप से प्रमाणीकरण कर लेता है (चरण 1 के कारण).
ये चरण जावा कार्यान्वयन को इस प्रकार संशोधित करते हैं:
- इससे
CredentialsProviderऔरSecretManagerServiceSettingsऑब्जेक्ट बनाने की ज़रूरत नहीं पड़ती. SecretManagerServiceClient.create()कॉल को बदलकर कोई तर्क शामिल नहीं किया जा रहा है.
साइफ़रटेक्स्ट बनाना और डीप लिंक जनरेट करना
इस चरण में, आप InlineInstallData प्रोटोबफ ऑब्जेक्ट से enifd (InlineInstallData सिफरटेक्स्ट) बनाने के लिए टिंक क्रिप्टोग्राफी लाइब्रेरी का उपयोग करते हैं.
InlineInstallData प्रोटो को इस प्रकार परिभाषित किया गया है:
syntax = "proto2";
package hsdpexperiments;
option java_package = "com.google.hsdpexperiments";
option java_multiple_files = true;
// InlineInstallData is used by 3p auth callers to generate "encrypted inline
// flow data" (enifd) which is decrypted in PGS to verify authenticity and
// freshness.
message InlineInstallData {
// The timestamp which indicates the time encrypted data is generated.
// Used to validate freshness (i.e. generation time in past 4 hours).
// Required.
optional int64 timestamp_ms = 1;
// The docid of the app that we want to open inline install page for.
// This is the package name.
// Required.
optional string target_package_name = 2;
// This is the name of the app requesting the ad from Google Ad Serving
// system.
// Required.
optional string caller_package_name = 3;
// This is the advertising id that will be collected by 3P Ad SDKs.
// Optional.
optional string advertising_id = 4;
// This is used to indicate the network from where the inline install was
// requested.
// Required.
optional string ad_network_id = 5;
}
इस चरण में, इन पैरामीटर का इस्तेमाल करके डीप लिंक यूआरएल भी बनाया जाता है:
| फ़ील्ड्स की फ़िल्में | ब्यौरा | ज़रूरी है |
|---|---|---|
| id | इंस्टॉल किए जाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन का पैकेज नाम. | हां |
| इनलाइन | अगर इनलाइन इंस्टॉल हाफ शीट का अनुरोध किया जाता है, तो इसे true पर सेट करें; अगर false, तो इंटेंट Google Play के लिए डीप लिंक करता है. |
हां |
| एनिफ्ड | तीसरे पक्ष के एसडीके के लिए एन्क्रिप्ट किया गया आइडेंटिफ़ायर. | हां |
| lft | यह एक इंटरनल आइडेंटिफ़ायर है. | हां |
| 3pAuthCallerId | SDK पहचानकर्ता. | हां |
| स्टोर पेज | कस्टम स्टोर सूची के लिए लक्ष्य निर्दिष्ट करने हेतु एक वैकल्पिक पैरामीटर. | नहीं |
| रेफरर | रेफ़रर ट्रैकिंग स्ट्रिंग, जो ज़रूरी नहीं है. | नहीं |
Python का उदाहरण
निम्न आदेश InlineInstallData.proto से पायथन कोड जनरेट करता है:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --python_out=.
निम्नलिखित पायथन नमूना कोड InlineInstallData का निर्माण करता है और सिफरटेक्स्ट बनाने के लिए इसे सममित कुंजी के साथ एन्क्रिप्ट करता है:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
import base64
import time
import inline_install_data_pb2 as InlineInstallData
import tink
from tink import aead
from tink import cleartext_keyset_handle
# Read the stored symmetric key.
with open("example3psecret.json", "r") as f:
keyset = f.read()
"""Encrypt and decrypt using AEAD."""
# Register the AEAD key managers. This is needed to create an Aead primitive later.
aead.register()
# Create a keyset handle from the cleartext keyset in the previous
# step. The keyset handle provides abstract access to the underlying keyset to
# limit access of the raw key material. WARNING: In practice, it is unlikely
# you will want to use a cleartext_keyset_handle, as it implies that your key
# material is passed in cleartext, which is a security risk.
keyset_handle = cleartext_keyset_handle.read(tink.JsonKeysetReader(keyset))
# Retrieve the Aead primitive we want to use from the keyset handle.
primitive = keyset_handle.primitive(aead.Aead)
inlineInstallData = InlineInstallData.InlineInstallData()
inlineInstallData.timestamp_ms = int(time.time() * 1000)
inlineInstallData.target_package_name = "x.y.z"
inlineInstallData.caller_package_name = "a.b.c"
inlineInstallData.ad_network_id = "<sdk_id>"
# Use the primitive to encrypt a message. In this case the primary key of the
# keyset will be used (which is also the only key in this example).
ciphertext = primitive.encrypt(inlineInstallData.SerializeToString(), b'<sdk_id>')
print(f"InlineInstallData Ciphertext: {ciphertext}")
# Base64 Encoded InlineInstallData Ciphertext
enifd = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(ciphertext).decode('utf-8')
print(enifd)
# Deeplink
print(f"https://play.google.com/d?id={inlineInstallData.target_package_name}\&inline=true\&enifd={enifd}\&lft=1\&3pAuthCallerId={inlineInstallData.ad_network_id}")
निम्नलिखित कमांड चलाकर पायथन स्क्रिप्ट निष्पादित करें:
python <file_name>.py
जावा उदाहरण
निम्न आदेश InlineInstallData.proto से जावा कोड जनरेट करता है:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --java_out=.
यहां दिया गया Java का सैंपल कोड, InlineInstallData बनाता है और सिमेट्रिक कुंजी की मदद से इसे एन्क्रिप्ट (सुरक्षित) करता है, ताकि साइफ़रटेक्स्ट बनाया जा सके:
package com.google.hsdpexperiments;
import static com.google.common.io.BaseEncoding.base64Url;
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.common.flags.Flag;
import com.google.common.flags.FlagSpec;
import com.google.common.flags.Flags;
import com.google.crypto.tink.Aead;
import com.google.crypto.tink.InsecureSecretKeyAccess;
import com.google.crypto.tink.KeysetHandle;
import com.google.crypto.tink.TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat;
import com.google.crypto.tink.aead.AeadConfig;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.Security;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.conscrypt.Conscrypt;
/** info on encryption in https://github.com/google/tink#learn-more */
final class ThirdPartyEnifdGuide {
@FlagSpec(
name = "third_party_id",
help = "the identifier associated with the 3p for which to generate the enifd")
private static final Flag<String> thirdPartyAuthCallerId = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "package_name", help = "the package name of the target app")
private static final Flag<String> packageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "caller_package_name", help = "the package name of the caller app")
private static final Flag<String> callerPackageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "secret_filename", help = "the path to the json file with the secret material")
private static final Flag<String> secretFilename = Flag.value("");
private ThirdPartyEnifdGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// parse flags
Flags.parse(args);
// File keyFile = new File(args[0]);
Path keyFile = Paths.get(secretFilename.get());
// Create structured inline flow data
InlineInstallData idrp =
InlineInstallData.newBuilder()
.setTargetPackageName(packageName.get())
.setCallerPackageName(callerPackageName.get())
.setTimestampMs(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setAdNetworkId(thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get())
.build();
// we can print this out here to make sure it's well formatted, this will help debug
System.out.println(idrp.toString());
// Register all AEAD key types with the Tink runtime.
Conscrypt.checkAvailability();
Security.addProvider(Conscrypt.newProvider());
AeadConfig.register();
// Read AEAD key downloaded from secretmanager into keysethandle
KeysetHandle handle =
TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat.parseKeyset(
new String(Files.readAllBytes(keyFile), UTF_8), InsecureSecretKeyAccess.get());
// Generate enifd using tink library
Aead aead = handle.getPrimitive(Aead.class);
byte[] plaintext = idrp.toByteArray();
byte[] ciphertext = aead.encrypt(plaintext, thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get().getBytes(UTF_8));
String enifd = base64Url().omitPadding().encode(ciphertext);
// Build deeplink, escaping ampersands (TODO: verify this is necessary while testing e2e)
String deeplink =
"https://play.google.com/d?id="
+ packageName.get()
+ "\\&inline=true\\&enifd="
+ enifd
+ "\\&lft=1\\&3pAuthCallerId="
+ thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get();
System.out.println(deeplink);
}
}
अंत में, जावा प्रोग्राम को बाइनरी में बनाएँ और निम्नलिखित कोड का उपयोग करके इसे लागू करें:
path/to/binary/ThirdPartyEnifdGuide --secret_filename=path/to/jsonfile/example3psecret.json --package_name=<package_name_of_target_app> --third_party_id=<3p_caller_auth_id>
secret_filenameफ़्लैग, गुप्त सामग्री वाली JSON फ़ाइल का पथ निर्दिष्ट करता है.package_nameफ़्लैग, टारगेट ऐप्लिकेशन का दस्तावेज़ आईडी है.third_party_idफ़्लैग का इस्तेमाल तीसरे पक्ष के कॉलर की प्राधिकरण आईडी (यानी<sdk_id>) तय करने के लिए किया जाता है.
इनलाइन इंस्टॉल इंटेंट लॉन्च करें
पिछले चरण में जनरेट किए गए डीप लिंक की जांच करने के लिए, किसी Android डिवाइस को ऐसे वर्कस्टेशन से कनेक्ट करें जिस पर ADB इंस्टॉल हो. साथ ही, पक्का करें कि यूएसबी डीबगिंग चालू हो. इसके बाद, यह कमांड चलाएं:
adb shell am start "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
क्लाइंट कोड में, निम्नलिखित विधियों (कोटलिन या जावा) में से किसी एक का उपयोग करके आशय भेजें.
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
val deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending")
intent.data = Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl)
val packageManager = context.getPackageManager()
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0)
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
String id = "exampleAppToBeInstalledId";
String deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>";
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending");
intent.setData(Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl));
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
अपेंडिक्स
यहां दिए गए सेक्शन में, इस्तेमाल के कुछ उदाहरणों के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी दी गई है.
Python एनवायरमेंट तैयार करना
पायथन नमूना कोड चलाने के लिए, अपने वर्कस्टेशन पर पायथन वातावरण सेट करें और आवश्यक निर्भरताएं स्थापित करें.
पायथन वातावरण सेट करें:
python3.11 इंस्टॉल करें (अगर यह पहले से इंस्टॉल है, तो इस चरण को छोड़ दें):
sudo apt install python3.11पाइप स्थापित करें:
sudo apt-get install pipvirtualenvइंस्टॉल करें:sudo apt install python3-virtualenvएक आभासी वातावरण बनाएँ (टिंक निर्भरता के लिए आवश्यक):
virtualenv inlineinstall --python=/usr/bin/python3.11
आभासी वातावरण में प्रवेश करें:
source inlineinstall/bin/activateपाइप अद्यतन करें:
python -m pip install --upgrade pipआवश्यक निर्भरताएँ स्थापित करें:
टिंक स्थापित करें:
pip install tinkGoogle crc32c स्थापित करें:
pip install google-crc32cगुप्त प्रबंधक स्थापित करें:
pip install google-cloud-secret-managerप्रोटोबफ कंपाइलर स्थापित करें:
sudo apt install protobuf-compiler
C++ enifd जनरेशन
निम्नलिखित एक C++ उदाहरण है जिसे हमने enifd जनरेट करने के लिए आंतरिक रूप से लिखा और सत्यापित किया है.
enifd का निर्माण C++ कोड का उपयोग करके इस प्रकार किया जा सकता है:
// A command-line example for using Tink AEAD w/ key template aes128gcmsiv to
// encrypt an InlineInstallData proto.
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "<path_to_protoc_output>/inline_install_data.proto.h"
#include "absl/flags/flag.h"
#include "absl/flags/parse.h"
#include "absl/strings/escaping.h"
#include "absl/strings/string_view.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_config.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_key_templates.h"
#include "tink/cc/config/global_registry.h"
#include "tink/cc/examples/util/util.h"
#include "tink/cc/keyset_handle.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/status.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/statusor.h"
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, keyset_filename, "",
"Keyset file (downloaded from secretmanager) in JSON format");
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, associated_data, "",
"Associated data for AEAD (default: empty");
namespace {
using ::crypto::tink::Aead;
using ::crypto::tink::AeadConfig;
using ::crypto::tink::KeysetHandle;
using ::crypto::tink::util::Status;
using ::crypto::tink::util::StatusOr;
} // namespace
namespace tink_cc_examples {
// AEAD example CLI implementation.
void AeadCli(const std::string& keyset_filename,
absl::string_view associated_data) {
Status result = AeadConfig::Register();
if (!result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to register AeadConfig";
return;
}
// Read the keyset from file.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<KeysetHandle>> keyset_handle =
ReadJsonCleartextKeyset(keyset_filename);
if (!keyset_handle.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to read json keyset";
return;
}
// Get the primitive.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<Aead>> aead =
(*keyset_handle)
->GetPrimitive<crypto::tink::Aead>(
crypto::tink::ConfigGlobalRegistry());
if (!aead.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to get primitive";
return;
}
// Instantiate the enifd.
hsdpexperiments::InlineInstallData iid;
iid.set_timestamp_ms(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch())
.count());
iid.set_target_package_name("<TARGET_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_caller_package_name("<CALLER_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_ad_network_id("<SDK_ID>");
// Compute the output.
StatusOr<std::string> encrypt_result =
(*aead)->Encrypt(iid.SerializeAsString(), associated_data);
if (!encrypt_result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to encrypt Inline Install Data";
return;
}
const std::string& output = encrypt_result.value();
std::string enifd;
absl::WebSafeBase64Escape(output, &enifd);
std::clog << "enifd: " << enifd << '\n';
}
} // namespace tink_cc_examples
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
absl::ParseCommandLine(argc, argv);
std::string keyset_filename = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_keyset_filename);
std::string associated_data = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_associated_data);
std::clog << "Using keyset from file " << keyset_filename
<< " to AEAD-encrypt inline install data with associated data '"
<< associated_data << "'." << '\n';
tink_cc_examples::AeadCli(keyset_filename, associated_data);
return 0;
}
यह कोड एक नमूने से अनुकूलित किया गया है जो टिंक दस्तावेज़ों में पाया जा सकता है.
