توضّح هذه الصفحة كيف يمكن لحِزم تطوير البرامج (SDK) التابعة لجهات خارجية دمج ميزة التثبيت المضمَّن، وهي ميزة اختبارية جديدة على Google Play تعرض تفاصيل منتجات التطبيقات على Google Play في واجهة نصفية. تتيح ميزة "التثبيت المضمّن" للمستخدمين الاستفادة من عملية سلسة لتثبيت التطبيق بدون مغادرة سياق التطبيق.
يمكن لمطوّري حِزم SDK التابعة لجهات خارجية دمج ميزة "التثبيت بدون مغادرة التطبيق" في حِزم SDK الخاصة بهم، ما يتيح لمطوّري التطبيقات الذين يستخدمون هذه الحِزم إمكانية الاستفادة من ميزة "التثبيت بدون مغادرة التطبيق" في تطبيقاتهم.
المتطلبات
لكي تظهر واجهة ورقة نصفية للتثبيت المضمّن في أحد التطبيقات، يجب استيفاء الشروط التالية:
- يجب أن يكون الحد الأدنى لإصدار Google Play هو 40.4.
- يجب أن يكون مستوى واجهة برمجة التطبيقات في Android 23 أو أعلى.
بنية العملية
يوضّح الشكل التالي بنية عملية التثبيت بدون مغادرة التطبيق:
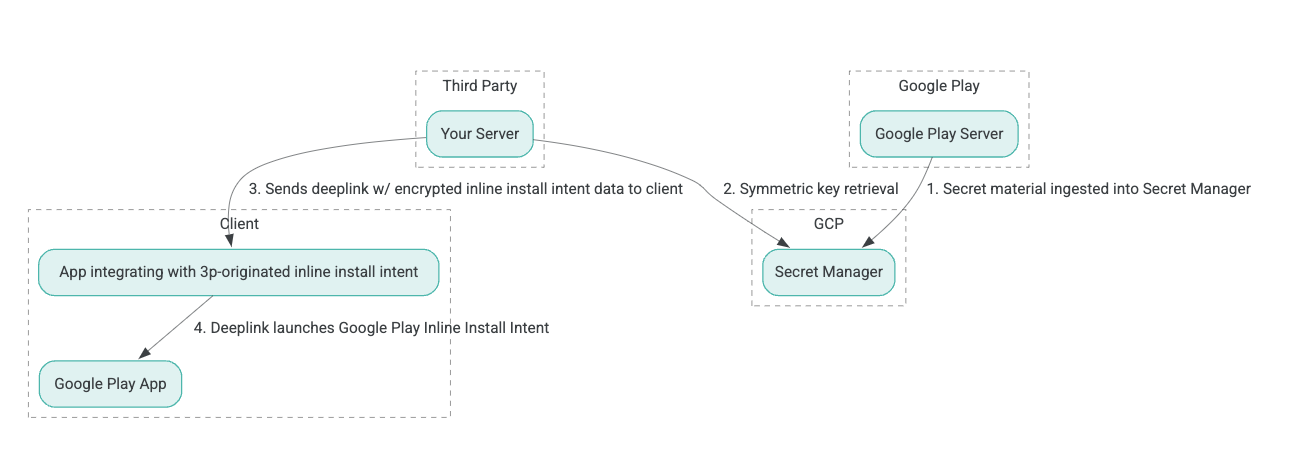
- تنشئ خوادم Google Play مفاتيح تشفير باستخدام خوارزمية Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD) وتستورد المفاتيح إلى مثيل Secret Manager في Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- يستردّ برنامج التكامل التابع لجهة خارجية مفتاح AEAD من GCP Secret Manager.
- يعمل برنامج الدمج التابع لجهة خارجية على تشفير بيانات
Intentالتثبيت المضمّن، وإنشاء النص المشفّر الذي يتم تمريره في الرابط لصفحة في التطبيق المستخدَم لتفعيل نية التثبيت المضمّن، وإرسال روابط لصفحات في التطبيق إلى العميل في الردود. - عند اتباع الرابط العميق، يتولى تطبيق Google Play التعامل مع القصد.
لتكوين SDK لجهة خارجية لاستخدام عملية التثبيت المضمنة، أكمل الخطوات التالية.
إنشاء حسابات خدمة في مشروع Google Cloud
في هذه الخطوة، عليك إعداد حساب خدمة باستخدام وحدة تحكّم Google Cloud.
- إعداد مشروع Google Cloud:
- أنشئ مؤسسة على Google Cloud. عند إنشاء حساب على Google Workspace أو Cloud Identity وربطه باسم نطاقك، يتم إنشاء مورد المؤسسة تلقائيًا. لمعرفة التفاصيل، يُرجى الاطّلاع على إنشاء موارد المؤسسة وإدارتها.
- سجِّل الدخول إلى وحدة تحكّم Google Cloud Platform باستخدام حساب Google Cloud الذي تم إنشاؤه في الخطوة السابقة، ثم أنشئ مشروعًا على Google Cloud. للاطّلاع على التفاصيل، يُرجى الرجوع إلى مقالة إنشاء مشروع على Google Cloud.
- أنشئ حساب خدمة في مشروع Google Cloud الذي تم إنشاؤه. يتم استخدام حساب الخدمة كمعرّف Google Cloud Identity للوصول إلى المفتاح المتماثل نيابةً عن خوادمك. لمعرفة التفاصيل، يُرجى الاطّلاع على إنشاء حساب خدمة.
- استخدِم رقم تعريف عميل Google Workspace (GWCID) / رقم تعريف Dasher نفسه الذي تم إدخاله في نموذج الاهتمام.
- أنشئ المفتاح الخاص لحساب الخدمة هذا ونزِّله.
- أنشئ مفتاحًا لحساب الخدمة هذا. لمعرفة التفاصيل، يُرجى الاطّلاع على إنشاء مفتاح حساب خدمة.
- نزِّل مفتاح حساب الخدمة واحتفِظ به في مكان يسهل الوصول إليه على الخادم، لأنّه يُستخدم للمصادقة من أجل الوصول إلى موارد Google Cloud الخاصة بالمفاتيح المتماثلة. لمعرفة التفاصيل، يُرجى الاطّلاع على الحصول على مفتاح حساب خدمة.
استرداد بيانات الاعتماد
في هذه الخطوة، يمكنك استرداد المفتاح المتماثل من Secret Manager وتخزينه بأمان (على سبيل المثال، في ملف JSON) في مساحة تخزين الخادم الخاص بك. يُستخدَم هذا المفتاح لإنشاء نص مشفّر لبيانات التثبيت بدون اتصال بالإنترنت.
تشير قيم secret_id/secretId إلى اسم المفتاح السرّي داخل Secret Manager، ويتم إنشاء هذا الاسم من خلال إضافة البادئة hsdp-3p-key- إلى القيمة sdk_id التي توفّرها Play. على سبيل المثال، إذا كان sdk_id هو abc، فسيكون الاسم السري هو hsdp-3p-key-abc.
يتم تحديث الإصدارات السرية أسبوعيًا يوم الثلاثاء الساعة 2 مساءً بتوقيت UTC. تستمر المفاتيح الثانية الأحدث في العمل حتى عملية التدوير التالية، ويجب جلب مواد المفاتيح وتخزينها بشكل جديد أسبوعيًا.
مثال بايثون
يستخدم مثال التعليمات البرمجية التالي رمز وصول مخزن في ملف JSON للوصول إلى المواد الأساسية في GCP Secret Manager وطباعتها في وحدة التحكم.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
from google.cloud import secretmanager
from google.oauth2 import service_account
import google_crc32c
# Create a service account key file.
service_account_key_file = "<json key file of the service account>"
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(service_account_key_file)
# Create the Secret Manager client.
client = secretmanager.SecretManagerServiceClient(
credentials=credentials
)
# Build the resource name of the secret version.
name = f"projects/prod-play-hsdp-3p-caller-auth/secrets/<secret_id>/versions/latest"
# Access the secret version.
response = client.access_secret_version(request={"name": name})
# Verify payload checksum.
crc32c = google_crc32c.Checksum()
crc32c.update(response.payload.data)
if response.payload.data_crc32c != int(crc32c.hexdigest(), 16):
print("Data corruption detected.")
# A keyset created with "tinkey create-keyset --key-template=AES256_GCM". Note
# that this keyset has the secret key information in cleartext.
keyset = response.payload.data.decode("UTF-8")
# WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment. Please store it
# in a secure storage.
with open('<key file name>', 'w') as f:
f.write(keyset)
مثال جافا
يستخدم مثال الرمز البرمجي التالي رمز دخول مخزَّنًا في ملف JSON للوصول إلى مواد المفاتيح في خدمة Secret Manager على Google Cloud Platform وكتابتها في ملف JSON.
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.api.gax.core.CredentialsProvider;
import com.google.api.gax.core.FixedCredentialsProvider;
import com.google.auth.oauth2.ServiceAccountCredentials;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.AccessSecretVersionResponse;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceClient;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretManagerServiceSettings;
import com.google.cloud.secretmanager.v1.SecretVersionName;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.zip.CRC32C;
import java.util.zip.Checksum;
/** */
final class ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide {
private ThirdPartySecretAccessGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
accessSecretVersion();
}
public static void accessSecretVersion() throws IOException {
// TODO(developer): Replace these variables before running the sample.
String projectId = "projectId";
String secretId = "secretId";
String versionId = "versionId";
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath = "path/to/credentials.json";
String secretMaterialOutputPath = "path/to/secret.json";
accessSecretVersion(
projectId, secretId, versionId, accessTokenPrivateKeyPath, secretMaterialOutputPath);
}
// Access the payload for the given secret version if one exists. The version
// can be a version number as a string (e.g. "5") or an alias (e.g. "latest").
public static void accessSecretVersion(
String projectId,
String secretId,
String versionId,
String accessTokenPrivateKeyPath,
String secretMaterialOutputPath)
throws IOException {
// We can explicitly instantiate the SecretManagerServiceClient (below) from a json file if we:
// 1. Create a CredentialsProvider from a FileInputStream of the JSON file,
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider =
FixedCredentialsProvider.create(
ServiceAccountCredentials.fromStream(new FileInputStream(accessTokenPrivateKeyPath)));
// 2. Build a SecretManagerService Settings object from that credentials provider, and
SecretManagerServiceSettings secretManagerServiceSettings =
SecretManagerServiceSettings.newBuilder()
.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.build();
// 3. Initialize client that will be used to send requests by passing the settings object to
// create(). This client only needs to be created once, and can be reused for multiple requests.
// After completing all of your requests, call the "close" method on the client to safely clean
// up any remaining background resources.
try (SecretManagerServiceClient client =
SecretManagerServiceClient.create(secretManagerServiceSettings)) {
SecretVersionName secretVersionName = SecretVersionName.of(projectId, secretId, versionId);
// Access the secret version.
AccessSecretVersionResponse response = client.accessSecretVersion(secretVersionName);
// Verify checksum. The used library is available in Java 9+.
// If using Java 8, you may use the following:
// https://github.com/google/guava/blob/e62d6a0456420d295089a9c319b7593a3eae4a83/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/Hashing.java#L395
byte[] data = response.getPayload().getData().toByteArray();
Checksum checksum = new CRC32C();
checksum.update(data, 0, data.length);
if (response.getPayload().getDataCrc32C() != checksum.getValue()) {
System.out.printf("Data corruption detected.");
return;
}
String payload = response.getPayload().getData().toStringUtf8();
// Print the secret payload.
//
// WARNING: Do not print the secret in a production environment - this
// snippet is showing how to access the secret material.
System.out.printf("Plaintext: %s\n", payload);
// Write the JSON secret material payload to a json file
try (PrintWriter out =
new PrintWriter(Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get(secretMaterialOutputPath), UTF_8))) {
out.write(payload);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ضبط بيانات الاعتماد التلقائية للتطبيق
إذا كنت لا تريد استخدام CredentialsProvider لتمرير المفتاح الخاص إلى ملف JSON في تنفيذ Java، فيمكنك تعديل التنفيذ عن طريق تعيين بيانات اعتماد التطبيق الافتراضية (ADC):
- أخبِر مكتبات البرامج بمكان العثور على مفتاح حساب الخدمة.
- أضِف تبعيات Maven إلى مشروع Java.
- اتّصِل بالرقم
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()، وسيتم الرد على المكالمة وإجراء عملية المصادقة تلقائيًا (بسبب الخطوة 1).
تعدّل هذه الخطوات تنفيذ Java من خلال:
- إلغاء الحاجة إلى إنشاء العنصرَين
CredentialsProviderوSecretManagerServiceSettings - تغيير المكالمة إلى
SecretManagerServiceClient.create()لتضمين أي وسيطات
إنشاء نص مشفّر وإنشاء رابط لصفحة معيّنة
في هذه الخطوة، يمكنك استخدام مكتبة تشفير Tink لإنشاء enifd (نص مشفر InlineInstallData) من كائن protobuf InlineInstallData.
يتم تعريف بروتوكول InlineInstallData على النحو التالي:
syntax = "proto2";
package hsdpexperiments;
option java_package = "com.google.hsdpexperiments";
option java_multiple_files = true;
// InlineInstallData is used by 3p auth callers to generate "encrypted inline
// flow data" (enifd) which is decrypted in PGS to verify authenticity and
// freshness.
message InlineInstallData {
// The timestamp which indicates the time encrypted data is generated.
// Used to validate freshness (i.e. generation time in past 4 hours).
// Required.
optional int64 timestamp_ms = 1;
// The docid of the app that we want to open inline install page for.
// This is the package name.
// Required.
optional string target_package_name = 2;
// This is the name of the app requesting the ad from Google Ad Serving
// system.
// Required.
optional string caller_package_name = 3;
// This is the advertising id that will be collected by 3P Ad SDKs.
// Optional.
optional string advertising_id = 4;
// This is used to indicate the network from where the inline install was
// requested.
// Required.
optional string ad_network_id = 5;
}
في هذه الخطوة، يمكنك أيضًا إنشاء عنوان URL لصفحة معيّنة في التطبيق باستخدام المَعلمات التالية:
| الحقول | الوصف | مطلوب |
|---|---|---|
| id | تمثّل هذه السمة اسم الحزمة للتطبيق الذي سيتم تثبيته. | نعم |
| تضمين | اضبط القيمة على true إذا كان مطلوبًا عرض ورقة نصفية لعملية التثبيت المضمَّنة، أو على false إذا كان الرابط لصفحة معيّنة في التطبيق يؤدي إلى Google Play. |
نعم |
| enifd | المعرّف المشفّر لحِزم تطوير البرامج (SDK) التابعة لجهات خارجية | نعم |
| lft | معرّف داخلي | نعم |
| 3pAuthCallerId | معرّف حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) | نعم |
| بطاقة بيانات المتجر | مَعلمة اختيارية لتحديد الهدف من بطاقة بيانات المتجر المخصّصة. | لا |
| المُحيل | سلسلة تتبُّع المُحيل اختيارية. | لا |
مثال على Python
ينشئ الأمر التالي رمز Python من InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --python_out=.
يقوم كود عينة Python التالي بإنشاء InlineInstallData وتشفيره باستخدام المفتاح المتماثل لإنشاء النص المشفر:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Import the Secret Manager client library.
import base64
import time
import inline_install_data_pb2 as InlineInstallData
import tink
from tink import aead
from tink import cleartext_keyset_handle
# Read the stored symmetric key.
with open("example3psecret.json", "r") as f:
keyset = f.read()
"""Encrypt and decrypt using AEAD."""
# Register the AEAD key managers. This is needed to create an Aead primitive later.
aead.register()
# Create a keyset handle from the cleartext keyset in the previous
# step. The keyset handle provides abstract access to the underlying keyset to
# limit access of the raw key material. WARNING: In practice, it is unlikely
# you will want to use a cleartext_keyset_handle, as it implies that your key
# material is passed in cleartext, which is a security risk.
keyset_handle = cleartext_keyset_handle.read(tink.JsonKeysetReader(keyset))
# Retrieve the Aead primitive we want to use from the keyset handle.
primitive = keyset_handle.primitive(aead.Aead)
inlineInstallData = InlineInstallData.InlineInstallData()
inlineInstallData.timestamp_ms = int(time.time() * 1000)
inlineInstallData.target_package_name = "x.y.z"
inlineInstallData.caller_package_name = "a.b.c"
inlineInstallData.ad_network_id = "<sdk_id>"
# Use the primitive to encrypt a message. In this case the primary key of the
# keyset will be used (which is also the only key in this example).
ciphertext = primitive.encrypt(inlineInstallData.SerializeToString(), b'<sdk_id>')
print(f"InlineInstallData Ciphertext: {ciphertext}")
# Base64 Encoded InlineInstallData Ciphertext
enifd = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(ciphertext).decode('utf-8')
print(enifd)
# Deeplink
print(f"https://play.google.com/d?id={inlineInstallData.target_package_name}\&inline=true\&enifd={enifd}\&lft=1\&3pAuthCallerId={inlineInstallData.ad_network_id}")
نفِّذ نص Python البرمجي عن طريق تشغيل الأمر التالي:
python <file_name>.py
مثال على Java
ينشئ الأمر التالي رمز Java من InlineInstallData.proto:
protoc InlineInstallData.proto --java_out=.
ينشئ نموذج رمز Java التالي InlineInstallData ويشفّره
باستخدام المفتاح المتماثل لإنشاء النص المشفّر:
package com.google.hsdpexperiments;
import static com.google.common.io.BaseEncoding.base64Url;
import static java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
import com.google.common.flags.Flag;
import com.google.common.flags.FlagSpec;
import com.google.common.flags.Flags;
import com.google.crypto.tink.Aead;
import com.google.crypto.tink.InsecureSecretKeyAccess;
import com.google.crypto.tink.KeysetHandle;
import com.google.crypto.tink.TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat;
import com.google.crypto.tink.aead.AeadConfig;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.Security;
import java.time.Duration;
import org.conscrypt.Conscrypt;
/** info on encryption in https://github.com/google/tink#learn-more */
final class ThirdPartyEnifdGuide {
@FlagSpec(
name = "third_party_id",
help = "the identifier associated with the 3p for which to generate the enifd")
private static final Flag<String> thirdPartyAuthCallerId = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "package_name", help = "the package name of the target app")
private static final Flag<String> packageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "caller_package_name", help = "the package name of the caller app")
private static final Flag<String> callerPackageName = Flag.value("");
@FlagSpec(name = "secret_filename", help = "the path to the json file with the secret material")
private static final Flag<String> secretFilename = Flag.value("");
private ThirdPartyEnifdGuide() {}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// parse flags
Flags.parse(args);
// File keyFile = new File(args[0]);
Path keyFile = Paths.get(secretFilename.get());
// Create structured inline flow data
InlineInstallData idrp =
InlineInstallData.newBuilder()
.setTargetPackageName(packageName.get())
.setCallerPackageName(callerPackageName.get())
.setTimestampMs(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setAdNetworkId(thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get())
.build();
// we can print this out here to make sure it's well formatted, this will help debug
System.out.println(idrp.toString());
// Register all AEAD key types with the Tink runtime.
Conscrypt.checkAvailability();
Security.addProvider(Conscrypt.newProvider());
AeadConfig.register();
// Read AEAD key downloaded from secretmanager into keysethandle
KeysetHandle handle =
TinkJsonProtoKeysetFormat.parseKeyset(
new String(Files.readAllBytes(keyFile), UTF_8), InsecureSecretKeyAccess.get());
// Generate enifd using tink library
Aead aead = handle.getPrimitive(Aead.class);
byte[] plaintext = idrp.toByteArray();
byte[] ciphertext = aead.encrypt(plaintext, thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get().getBytes(UTF_8));
String enifd = base64Url().omitPadding().encode(ciphertext);
// Build deeplink, escaping ampersands (TODO: verify this is necessary while testing e2e)
String deeplink =
"https://play.google.com/d?id="
+ packageName.get()
+ "\\&inline=true\\&enifd="
+ enifd
+ "\\&lft=1\\&3pAuthCallerId="
+ thirdPartyAuthCallerId.get();
System.out.println(deeplink);
}
}
أخيرًا، أنشئ برنامج Java كملف ثنائي وشغِّله باستخدام الرمز التالي:
path/to/binary/ThirdPartyEnifdGuide --secret_filename=path/to/jsonfile/example3psecret.json --package_name=<package_name_of_target_app> --third_party_id=<3p_caller_auth_id>
- يحدد العلم
secret_filenameالمسار إلى ملف JSON الذي يحتوي على المادة السرية. - العلامة
package_nameهي معرّف المستند الخاص بالتطبيق المستهدف. - يُستخدَم العلامة
third_party_idلتحديد معرّف مصادقة المتصل الخارجي (أي<sdk_id>).
تشغيل نية التثبيت المضمَّن
لاختبار الرابط العميق الذي تم إنشاؤه أثناء الخطوة السابقة، قم بتوصيل جهاز Android (تأكد من تمكين تصحيح أخطاء USB) بمحطة عمل مثبت عليها ADB وقم بتشغيل الأمر التالي:
adb shell am start "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
في كود العميل، أرسل النية باستخدام إحدى الطرق التالية (Kotlin أو Java).
Kotlin
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
val deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>"
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending")
intent.data = Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl)
val packageManager = context.getPackageManager()
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0)
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
Java
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
String id = "exampleAppToBeInstalledId";
String deepLinkUrl = "<output_from_the_previous_python_or_java_code>";
intent.setPackage("com.android.vending");
intent.setData(Uri.parse(deepLinkUrl));
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
if (intent.resolveActivity(packageManager) != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
} else {
// Fallback to deep linking to full Play Store.
}
الملحق
تقدّم الأقسام التالية إرشادات إضافية بشأن حالات استخدام معيّنة.
إعداد بيئة Python
لتشغيل كود عينة Python، قم بإعداد بيئة Python على محطة العمل لديك وقم بتثبيت التبعيات المطلوبة.
إعداد بيئة Python:
ثبِّت الإصدار 3.11 من Python (إذا كان مثبّتًا، يمكنك تخطّي هذه الخطوة):
sudo apt install python3.11تثبيت pip:
sudo apt-get install pipتثبيت
virtualenv:sudo apt install python3-virtualenvإنشاء بيئة افتراضية (مطلوبة لتبعية Tink):
virtualenv inlineinstall --python=/usr/bin/python3.11
أدخِل البيئة الافتراضية:
source inlineinstall/bin/activateتحديث pip:
python -m pip install --upgrade pipثبِّت التبعيات المطلوبة:
تثبيت Tink:
pip install tinkثبِّت Google crc32c:
pip install google-crc32cثبِّت Secret Manager باتّباع الخطوات التالية:
pip install google-cloud-secret-managerتثبيت مُجمِّع protobuf:
sudo apt install protobuf-compiler
الجيل الأول من C++
في ما يلي مثال على رمز C++ كتبناه وتحقّقنا منه داخليًا لإنشاء enifd.
يمكن تنفيذ إنشاء enifd باستخدام رمز C++ على النحو التالي:
// A command-line example for using Tink AEAD w/ key template aes128gcmsiv to
// encrypt an InlineInstallData proto.
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "<path_to_protoc_output>/inline_install_data.proto.h"
#include "absl/flags/flag.h"
#include "absl/flags/parse.h"
#include "absl/strings/escaping.h"
#include "absl/strings/string_view.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_config.h"
#include "tink/cc/aead_key_templates.h"
#include "tink/cc/config/global_registry.h"
#include "tink/cc/examples/util/util.h"
#include "tink/cc/keyset_handle.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/status.h"
#include "tink/cc/util/statusor.h"
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, keyset_filename, "",
"Keyset file (downloaded from secretmanager) in JSON format");
ABSL_FLAG(std::string, associated_data, "",
"Associated data for AEAD (default: empty");
namespace {
using ::crypto::tink::Aead;
using ::crypto::tink::AeadConfig;
using ::crypto::tink::KeysetHandle;
using ::crypto::tink::util::Status;
using ::crypto::tink::util::StatusOr;
} // namespace
namespace tink_cc_examples {
// AEAD example CLI implementation.
void AeadCli(const std::string& keyset_filename,
absl::string_view associated_data) {
Status result = AeadConfig::Register();
if (!result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to register AeadConfig";
return;
}
// Read the keyset from file.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<KeysetHandle>> keyset_handle =
ReadJsonCleartextKeyset(keyset_filename);
if (!keyset_handle.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to read json keyset";
return;
}
// Get the primitive.
StatusOr<std::unique_ptr<Aead>> aead =
(*keyset_handle)
->GetPrimitive<crypto::tink::Aead>(
crypto::tink::ConfigGlobalRegistry());
if (!aead.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to get primitive";
return;
}
// Instantiate the enifd.
hsdpexperiments::InlineInstallData iid;
iid.set_timestamp_ms(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch())
.count());
iid.set_target_package_name("<TARGET_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_caller_package_name("<CALLER_PACKAGE_NAME>");
iid.set_ad_network_id("<SDK_ID>");
// Compute the output.
StatusOr<std::string> encrypt_result =
(*aead)->Encrypt(iid.SerializeAsString(), associated_data);
if (!encrypt_result.ok()) {
std::clog << "Failed to encrypt Inline Install Data";
return;
}
const std::string& output = encrypt_result.value();
std::string enifd;
absl::WebSafeBase64Escape(output, &enifd);
std::clog << "enifd: " << enifd << '\n';
}
} // namespace tink_cc_examples
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
absl::ParseCommandLine(argc, argv);
std::string keyset_filename = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_keyset_filename);
std::string associated_data = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_associated_data);
std::clog << "Using keyset from file " << keyset_filename
<< " to AEAD-encrypt inline install data with associated data '"
<< associated_data << "'." << '\n';
tink_cc_examples::AeadCli(keyset_filename, associated_data);
return 0;
}
تم تعديل هذا الرمز من نموذج يمكن العثور عليه في مستندات Tink.
