ב-Material Design, תומך הוא מבנה בסיסי שמספק פלטפורמה סטנדרטית לממשקי משתמש מורכבים. הוא מחבר בין חלקים שונים בממשק המשתמש, כמו שורת האפליקציות ולחצני הפעולה הצפים, ומעניק לאפליקציות מראה וסגנון עקביים.
תאימות גרסאות
כדי להטמיע את האפשרות הזו, צריך להגדיר את minSDK של הפרויקט לרמת API 21 ואילך.
יחסי תלות
יצירת אב טיפוס
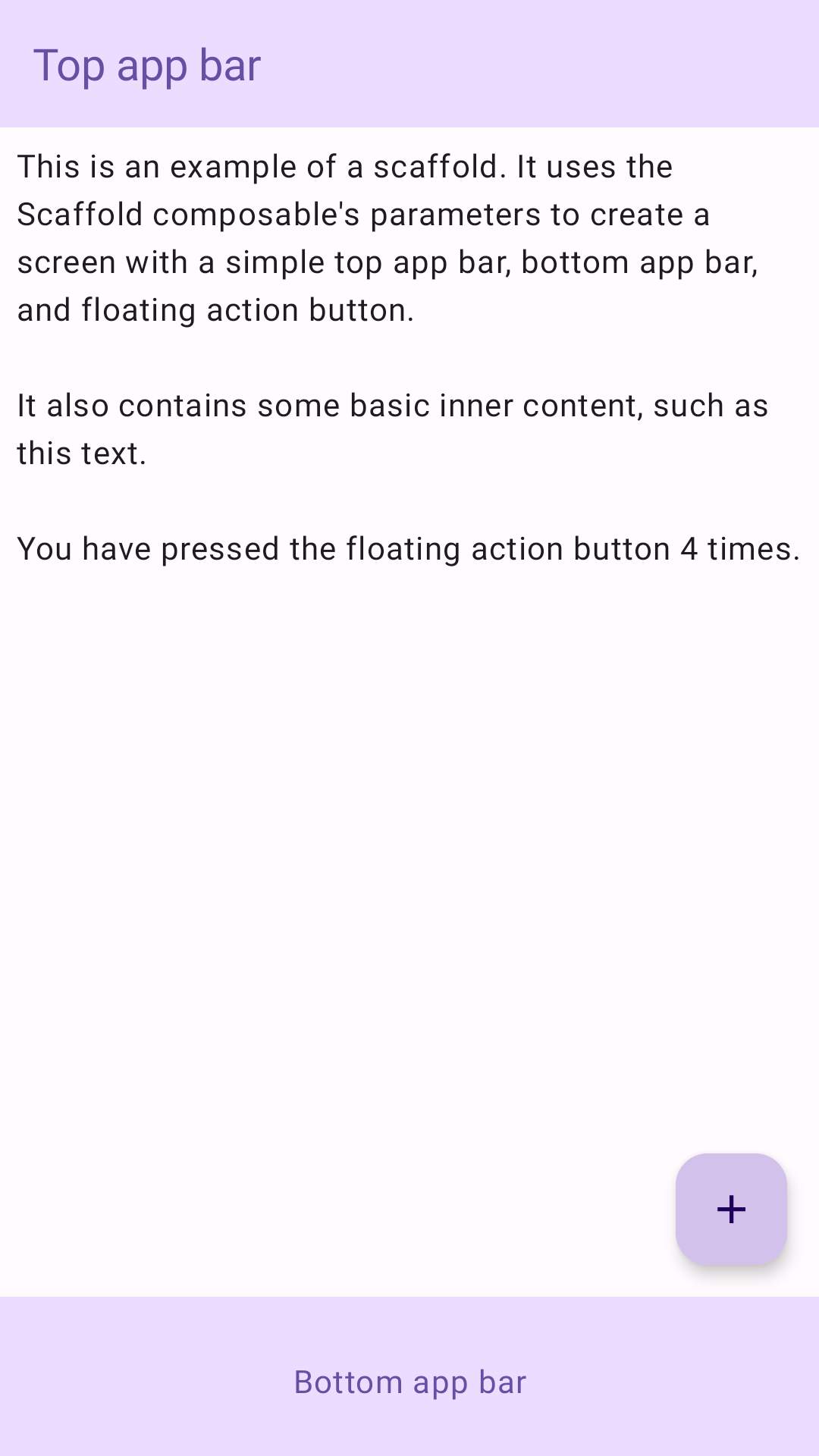
בדוגמה הבאה מופיעה דוגמה מלאה להטמעה של Scaffold. הוא מכיל סרגל אפליקציות עליון, סרגל אפליקציות תחתון ולחצן פעולה צף שמקיים אינטראקציה עם המצב הפנימי של Scaffold.
תוצאות
נקודות עיקריות
הרכיב הניתן לקישור Scaffold מספק ממשק API פשוט שבעזרתו אפשר להרכיב במהירות את המבנה של האפליקציה בהתאם להנחיות של Material Design.
Scaffold מקבלת כמה רכיבים קומפוזביליים כפרמטרים. בין היתר:
topBar: שורת האפליקציות בחלק העליון של המסך.bottomBar: סרגל האפליקציות בחלק התחתון של המסך.floatingActionButton: לחצן שמרחף מעל הפינה השמאלית התחתונה של המסך, שבעזרתו אפשר לחשוף פעולות של מפתחות.
בדף 'סרגל האפליקציה' מפורטות דוגמאות מפורטות יותר להטמעה של סרגל האפליקציה בחלק העליון ובחלק התחתון של המסך.
אפשר גם להעביר תוכן של Scaffold כמו שמעבירים תוכן לקונטיינרים אחרים. הוא מעביר ערך innerPadding ל-lambda של content, שבו אפשר להשתמש לאחר מכן ברכיבים נגזרים.
אוספים שמכילים את המדריך הזה
המדריך הזה הוא חלק מהאוספים הבאים של מדריכים מהירים, שמכסים יעדים רחבים יותר לפיתוח Android:
יצירת אב טיפוס של מסך הבית



