В Android 16 представлены новые замечательные функции и API для разработчиков. В следующих разделах кратко описаны эти функции, чтобы помочь вам начать работу с соответствующими API.
Подробный список новых, изменённых и удалённых API можно найти в отчёте о различиях в API . Подробнее о новых API см. в справочнике по API Android — новые API выделены для наглядности.Вам также следует изучить области, в которых изменения платформы могут повлиять на ваши приложения. Подробнее см. на следующих страницах:
- Изменения в поведении приложений, ориентированных на Android 16
- Изменения поведения, которые влияют на все приложения независимо от
targetSdkVersion.
Основная функциональность
Android включает в себя новые API, расширяющие основные возможности системы Android.
Два релиза Android API в 2025 году
- Эта предварительная версия предназначена для следующего основного выпуска Android, запуск которого запланирован на второй квартал 2025 года. Этот выпуск похож на все наши предыдущие выпуски API, в которых мы можем планировать изменения поведения, которые часто привязаны к targetSdkVersion.
- Мы планируем выпуск основного выпуска на квартал раньше (второй квартал, а не третий квартал в предыдущие годы), чтобы лучше согласовываться с графиком запуска устройств в нашей экосистеме, чтобы больше устройств могли получить основной выпуск Android раньше. Поскольку основной выпуск выйдет во втором квартале, вам нужно будет проводить ежегодное тестирование совместимости на несколько месяцев раньше, чем в предыдущие годы, чтобы убедиться, что ваши приложения готовы.
- Мы планируем выпустить еще один выпуск в четвертом квартале 2025 года, который также будет включать новые API для разработчиков. Основной выпуск второго квартала станет единственным выпуском в 2025 году, включающим запланированные изменения в поведении, которые могут повлиять на приложения.
Помимо новых API-интерфейсов для разработчиков, второстепенный выпуск четвертого квартала будет содержать обновления функций, оптимизации и исправления ошибок; он не будет включать никаких изменений в поведении, влияющих на приложение.
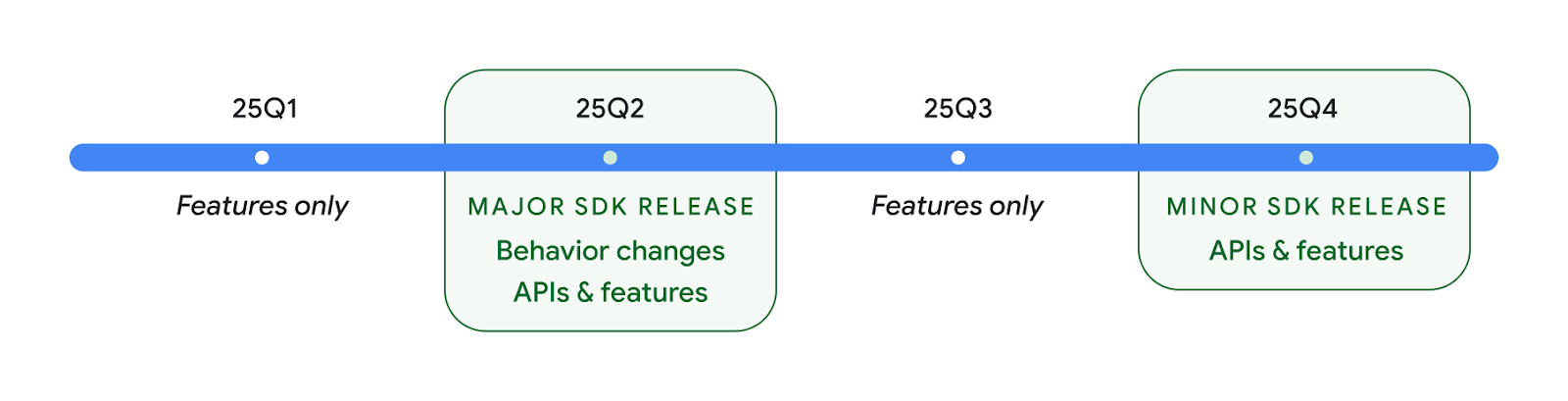
Мы продолжим выпускать ежеквартальные выпуски Android. Обновления Q1 и Q3 между выпусками API будут предоставлять дополнительные обновления, которые помогут обеспечить постоянное качество. Мы активно работаем с нашими партнерами по устройствам, чтобы сделать выпуск Q2 доступным как можно большему количеству устройств.
Использование новых API с основными и второстепенными выпусками
Защита блока кода с помощью проверки уровня API сегодня осуществляется с использованием константы SDK_INT с помощью VERSION_CODES . Это будет по-прежнему поддерживаться в основных выпусках Android.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
Новую константу SDK_INT_FULL можно использовать для проверки API как на основные, так и на второстепенные версии с помощью нового перечисления VERSION_CODES_FULL .
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
Вы также можете использовать метод Build.getMinorSdkVersion() чтобы получить только второстепенную версию SDK.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
Эти API еще не доработаны и могут быть изменены, поэтому, если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы, отправьте нам свой отзыв .
Пользовательский опыт и системный пользовательский интерфейс
Android 16 предоставляет разработчикам приложений и пользователям больше возможностей и гибкости для настройки устройств в соответствии со своими потребностями.
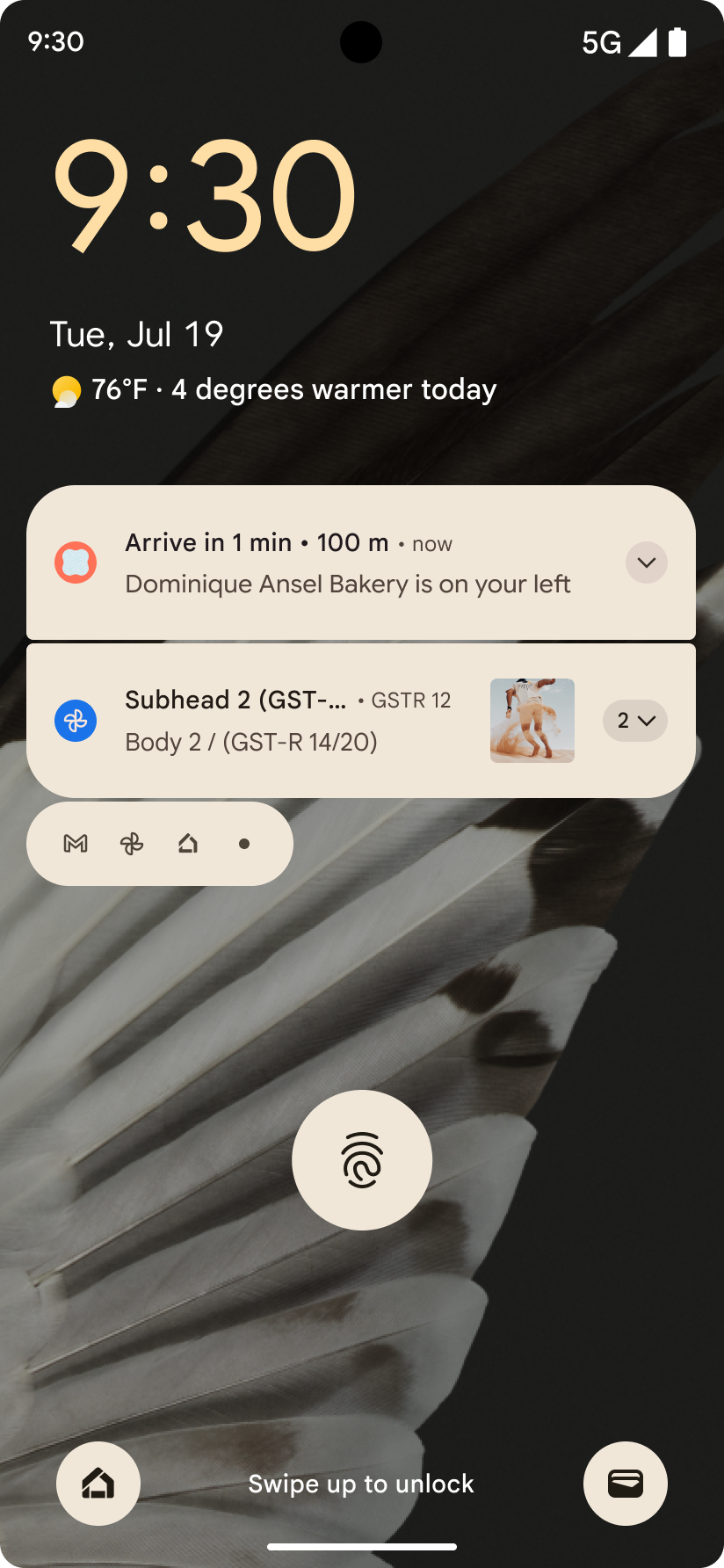
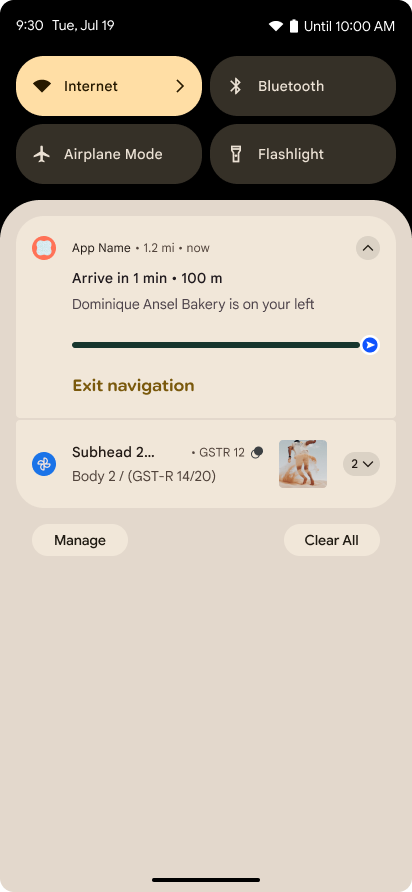
Уведомления, ориентированные на прогресс
Android 16 introduces progress-centric notifications to help users seamlessly track user-initiated, start-to-end journeys.
Notification.ProgressStyle is a new notification
style that lets you create progress-centric notifications. Key use cases include
rideshare, delivery, and navigation. Within the Notification.ProgressStyle
class, you can denote states and milestones in a user journey using
points and segments.
To learn more, see the Progress-centric notifications documentation page.
Прогнозируемые обратные обновления
Android 16 adds new APIs to help you enable predictive back system animations in
gesture navigation such as the back-to-home animation. Registering the
onBackInvokedCallback with the new
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER allows your app to
receive the regular onBackInvoked call whenever the
system handles a back navigation without impacting the normal back navigation
flow.
Android 16 additionally adds the
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() and
moveTaskToBackCallback. By registering these callbacks
with the OnBackInvokedDispatcher, the system can trigger
specific behaviors and play corresponding ahead-of-time animations when the back
gesture is invoked.
Более богатые тактильные ощущения
Android has exposed control over the haptic actuator ever since its inception.
Android 11 added support for more complex haptic effects that more advanced
actuators could support through
VibrationEffect.Compositions of device-defined semantic
primitives.
Android 16 adds haptic APIs that let apps define the amplitude and frequency curves of a haptic effect while abstracting away differences between device capabilities.
Производительность и инструменты разработчика
Хотя большая часть нашей работы по повышению вашей производительности сосредоточена вокруг таких инструментов, как Android Studio , Jetpack Compose и библиотеки Android Jetpack , мы всегда ищем способы на платформе помочь вам реализовать ваше видение.
Обработка контента для живых обоев
In Android 16, the live wallpaper framework is gaining a new content API to
address the challenges of dynamic, user-driven wallpapers. Currently, live
wallpapers incorporating user-provided content require complex, service-specific
implementations. Android 16 introduces
WallpaperDescription and
WallpaperInstance. WallpaperDescription lets you
identify distinct instances of a live wallpaper from the same service. For
example, a wallpaper that has instances on both the home screen and on the lock
screen may have unique content in both places. The wallpaper picker and
WallpaperManager use this metadata to better present
wallpapers to users, streamlining the process for you to create diverse and
personalized live wallpaper experiences.
Производительность и аккумулятор
В Android 16 представлены API, которые помогают собирать информацию о ваших приложениях.
Системное профилирование
ProfilingManager was
added in Android 15, giving apps the ability to
request profiling data collection using Perfetto on public devices in the field.
However, since this profiling must be started from the app, critical flows such
as startups or ANRs would be difficult or impossible for apps to capture.
To help with this, Android 16 introduces system-triggered profiling to
ProfilingManager. Apps can register interest in receiving traces for certain
triggers such as cold start reportFullyDrawn
or ANRs, and then the system starts and stops a trace on the app's behalf. After
the trace completes, the results are delivered to the app's data directory.
Запустить компонент в ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo was added in Android
15, allowing an app to see reasons
for process start, start type, start times, throttling, and other useful
diagnostic data. Android 16 adds
getStartComponent()
to distinguish what component type triggered the start, which can be helpful for
optimizing the startup flow of your app.
Лучшая работа по самоанализу
The JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API returns a reason why a job
might be pending. However, a job might be pending for multiple reasons.
In Android 16, we are introducing a new API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId), which returns multiple
reasons why a job is pending, due to both explicit constraints set by the
developer and implicit constraints set by the system.
We're also introducing
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId), which returns a list
of the most recent constraint changes.
We recommend using the API to help you debug why your jobs may not be executing, especially if you're seeing reduced success rates of certain tasks or have bugs around latency of certain job completion. For example, updating widgets in the background failed to occur or prefetch job failed to be called prior to app start.
This can also better help you understand if certain jobs are not completing due to system defined constraints versus explicitly set constraints.
Адаптивная частота обновления
Адаптивная частота обновления (ARR), представленная в Android 15, позволяет частоте обновления дисплея на поддерживаемом оборудовании адаптироваться к частоте кадров контента с помощью дискретных шагов VSync. Это снижает энергопотребление, устраняя при этом необходимость в переключении режимов, которое может привести к рывкам.
В Android 16 представлены hasArrSupport() и getSuggestedFrameRate(int) при восстановлении getSupportedRefreshRates() , чтобы вашим приложениям было проще использовать преимущества ARR. RecyclerView 1.4 внутренне поддерживает ARR, когда он устанавливается при прокрутке или плавной прокрутке , и мы продолжаем работу по добавлению поддержки ARR в другие библиотеки Jetpack. В этой статье о частоте кадров рассматриваются многие API-интерфейсы, которые вы можете использовать для установки частоты кадров, чтобы ваше приложение могло напрямую использовать ARR.
API-интерфейсы Headroom в ADPF
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
Доступность
В Android 16 добавлены новые API и функции специальных возможностей, которые помогут вам сделать ваше приложение доступным для каждого пользователя.
Улучшенные API-интерфейсы доступности
Android 16 adds additional APIs to enhance UI semantics that help improve consistency for users that rely on accessibility services, such as TalkBack.
Outline text for maximum text contrast
Users with low vision often have reduced contrast sensitivity, making it challenging to distinguish objects from their backgrounds. To help these users, Android 16 introduces outline text, replacing high contrast text, which draws a larger contrasting area around text to greatly improve legibility.
Android 16 contains new AccessibilityManager APIs to let
your apps check or register a listener to
see if this mode is enabled. This is primarily for UI Toolkits like Compose to
offer a similar visual experience. If you maintain a UI Toolkit library or your
app performs custom text rendering that bypasses the
android.text.Layout class then you can use this to know
when outline text is enabled.
Duration added to TtsSpan
Android 16 extends TtsSpan with a TYPE_DURATION,
consisting of ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES,
and ARG_SECONDS. This lets you directly annotate time
duration, ensuring accurate and consistent text-to-speech output with services
like TalkBack.
Support elements with multiple labels
Android currently allows UI elements to derive their accessibility label from
another, and now offers the ability for multiple labels to be associated, a
common scenario in web content. By introducing a list-based API within
AccessibilityNodeInfo, Android can directly support these
multi-label relationships. As part of this change, we've deprecated
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy and
#getLabeledBy in favor of
#addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy, and
#getLabeledByList.
Improved support for expandable elements
Android 16 adds accessibility APIs that allow you to convey the expanded or
collapsed state of interactive elements, such as menus and expandable lists. By
setting the expanded state using setExpandedState and
dispatching TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
with a CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED content change type,
you can ensure that screen readers like TalkBack announce
state changes, providing a more intuitive and inclusive user experience.
Indeterminate ProgressBars
Android 16 adds RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, giving a way for
you to expose RangeInfo for both determinate and
indeterminate ProgressBar widgets, allowing services like
TalkBack to more consistently provide feedback for progress
indicators.
Tri-state CheckBox
The new AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked and setChecked(int)
methods in Android 16 now support a "partially checked" state in addition to
"checked" and "unchecked." This replaces the deprecated boolean
isChecked and setChecked(boolean).
Supplemental descriptions
When an accessibility service describes a ViewGroup, it
combines content labels from its child views. If you provide a
contentDescription for the ViewGroup, accessibility services assume you are
also overriding the description of non-focusable child views. This can be
problematic if you want to label things like a drop-down (for example, "Font
Family") while preserving the current selection for accessibility (for example,
"Roboto"). Android 16 adds setSupplementalDescription so
you can provide text that provides information about a ViewGroup without
overriding information from its children.
Required form fields
Android 16 adds setFieldRequired to
AccessibilityNodeInfo so apps can tell an accessibility
service that input to a form field is required. This is an important scenario
for users filling out many types of forms, even things as simple as a required
terms and conditions checkbox, helping users to consistently identify and
quickly navigate between required fields.
Телефон как микрофонный вход для голосовых вызовов со слуховыми аппаратами LEA
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to switch between the built-in microphones on the hearing aids and the microphone on their phone for voice calls. This can be helpful in noisy environments or other situations where the hearing aid's microphones might not perform well.
Регуляторы громкости звука для слуховых аппаратов LEA
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to adjust the volume of ambient sound that is picked up by the hearing aid's microphones. This can be helpful in situations where background noise is too loud or too quiet.
Камера
В Android 16 улучшена поддержка профессиональных пользователей камер, включая гибридную автоматическую экспозицию, а также точную настройку цветовой температуры и оттенков. Новый индикатор ночного режима помогает вашему приложению определить, когда следует переключаться на ночной режим съёмки и выходить из него. Новые действия Intent упрощают съёмку движущихся объектов, и мы продолжаем улучшать качество изображений UltraHDR, добавляя поддержку кодирования HEIC и новых параметров из проекта стандарта ISO 21496-1.
Гибридная автоэкспозиция
В Android 16 в Camera2 добавлены новые гибридные режимы автоэкспозиции, позволяющие вручную контролировать определенные аспекты экспозиции, а алгоритм автоэкспозиции (AE) позаботится обо всем остальном. Вы можете управлять ISO + AE и временем экспозиции + AE , что обеспечивает большую гибкость по сравнению с текущим подходом, при котором вы либо имеете полное ручное управление, либо полностью полагаетесь на автоматическую экспозицию.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
Точная регулировка цветовой температуры и оттенка
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





Распознавание сцен в ночном режиме камеры
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
Действия при захвате фото движения
Android 16 adds standard Intent actions —
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE, and
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE — which request that
the camera application capture a motion photo and return
it.
You must either pass an extra EXTRA_OUTPUT to control
where the image will be written, or a Uri through
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). If you don't set a
ClipData, it will be copied there for you when calling
Context.startActivity(Intent).
Улучшения изображения UltraHDR

Android 16 continues our work to deliver dazzling image quality with UltraHDR
images. It adds support for UltraHDR images in the HEIC file
format. These images will get ImageFormat type
HEIC_ULTRAHDR and will contain an embedded gainmap similar
to the existing UltraHDR JPEG format. We're working on AVIF support for UltraHDR
as well, so stay tuned.
In addition, Android 16 implements additional parameters in UltraHDR from the ISO 21496-1 draft standard, including the ability to get and set the colorspace that gainmap math should be applied in, as well as support for HDR encoded base images with SDR gainmaps.
Графика
Android 16 включает в себя новейшие графические улучшения, такие как пользовательские графические эффекты с AGSL.
Пользовательские графические эффекты с AGSL
В Android 16 добавлены RuntimeColorFilter и RuntimeXfermode , позволяющие создавать сложные эффекты, такие как «Порог», «Сепия» и «Насыщенность оттенка», и применять их для рисования вызовов. Начиная с Android 13, вы можете использовать AGSL для создания пользовательских RuntimeShaders , расширяющих Shader . Новый API отражает это, добавляя RuntimeColorFilter на базе AGSL, который расширяет ColorFilter , и эффект Xfermode , который позволяет реализовать настраиваемую компоновку и смешивание на основе AGSL между исходными и целевыми пикселями.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
Связность
Android 16 обновляет платформу, предоставляя вашему приложению доступ к новейшим достижениям в области коммуникационных и беспроводных технологий.
С повышенной безопасностью
Android 16 adds support for robust security features in Wi-Fi location on supported devices with Wi-Fi 6's 802.11az, allowing apps to combine the higher accuracy, greater scalability, and dynamic scheduling of the protocol with security enhancements including AES-256-based encryption and protection against MITM attacks. This allows it to be used more safely in proximity use cases, such as unlocking a laptop or a vehicle door. 802.11az is integrated with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, leveraging its infrastructure and capabilities for wider adoption and easier deployment.
Общие API ранжирования
Android 16 includes the new RangingManager, which provides
ways to determine the distance and angle on supported hardware between the local
device and a remote device. RangingManager supports the usage of a variety of
ranging technologies such as BLE channel sounding, BLE RSSI-based ranging, Ultra
Wideband, and Wi-Fi round trip time.
Наличие устройства в диспетчере сопутствующих устройств
In Android 16, new APIs are being introduced for binding your companion app
service. Service will be bound when BLE is in range and Bluetooth is connected
and service will be unbound when BLE is out of range or Bluetooth is
disconnected. App will receives a new
'onDevicePresenceEvent()' callback based on various
of DevicePresenceEvent.
More details can be found in
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
СМИ
Android 16 включает в себя ряд функций, улучшающих возможности мультимедиа.
Улучшения в выборе фотографий
The photo picker provides a safe, built-in way for users to grant your app access to selected images and videos from both local and cloud storage, instead of their entire media library. Using a combination of Modular System Components through Google System Updates and Google Play services, it's supported back to Android 4.4 (API level 19). Integration requires just a few lines of code with the associated Android Jetpack library.
Android 16 includes the following improvements to the photo picker:
- Embedded photo picker: New APIs that enable apps to embed the photo picker into their view hierarchy. This allows it to feel like a more integrated part of the app while still leveraging the process isolation that allows users to select media without the app needing overly broad permissions. To maximize compatibility across platform versions and simplify your integration, you'll want to use the forthcoming Android Jetpack library if you want to integrate the embedded photo picker.
- Cloud search in photo picker: New APIs that enable searching from the cloud media provider for the Android photo picker. Search functionality in the photo picker is coming soon.
Продвинутое профессиональное видео
Android 16 introduces support for the Advanced Professional Video (APV) codec which is designed to be used for professional level high quality video recording and post production.
The APV codec standard has the following features:
- Perceptually lossless video quality (close to raw video quality)
- Low complexity and high throughput intra-frame-only coding (without pixel domain prediction) to better support editing workflows
- Support for high bit-rate range up to a few Gbps for 2K, 4K and 8K resolution content, enabled by a lightweight entropy coding scheme
- Frame tiling for immersive content and for enabling parallel encoding and decoding
- Support for various chroma sampling formats and bit-depths
- Support for multiple decoding and re-encoding without severe visual quality degradation
- Support multi-view video and auxiliary video like depth, alpha, and preview
- Support for HDR10/10+ and user-defined metadata
A reference implementation of APV is provided through the OpenAPV project. Android 16 will implement support for the APV 422-10 Profile that provides YUV 422 color sampling along with 10-bit encoding and for target bitrates of up to 2Gbps.
Конфиденциальность
Android 16 включает в себя ряд функций, которые помогают разработчикам приложений защищать конфиденциальность пользователей.
Обновления Health Connect
Health Connect adds ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, a data type defined according to World
Health Organization guidelines around moderate and vigorous activity. Each
record requires the start time, the end time, and whether the activity intensity
is moderate or vigorous.
Health Connect also contains updated APIs supporting medical records. This allows apps to read and write medical records in FHIR format with explicit user consent.
Privacy Sandbox на Android
Android 16 включает в себя последнюю версию Privacy Sandbox для Android , что является частью нашей постоянной работы по разработке технологий, позволяющих пользователям знать, что их конфиденциальность защищена. На нашем веб-сайте вы найдете дополнительную информацию о бета-программе Privacy Sandbox для разработчиков Android, которая поможет вам начать работу. Ознакомьтесь со средой выполнения SDK , которая позволяет SDK запускаться в выделенной среде выполнения отдельно от приложения, которое они обслуживают, обеспечивая более надежную защиту при сборе и обмене пользовательскими данными.
Безопасность
Android 16 включает функции, которые помогут вам повысить безопасность вашего приложения и защитить его данные.
API обмена ключами
Android 16 adds APIs that support sharing access to
Android Keystore keys with other apps. The new
KeyStoreManager class supports
granting and revoking access to keys
by app uid, and includes an API for apps to access shared
keys.
Форм-факторы устройств
Android 16 позволяет вашим приложениям максимально эффективно использовать возможности форм-факторов Android.
Стандартизированная структура качества изображения и звука для телевизоров
The new MediaQuality
package in Android 16 exposes
a set of standardized APIs for access to audio and picture profiles and
hardware-related settings. This allows streaming apps to query profiles and
apply them to media dynamically:
- Movies mastered with a wider dynamic range require greater color accuracy to see subtle details in shadows and adjust to ambient light, so a profile that prefers color accuracy over brightness may be appropriate.
- Live sporting events are often mastered with a narrow dynamic range, but are often watched in daylight, so a profile that preferences brightness over color accuracy can give better results.
- Fully interactive content wants minimal processing to reduce latency, and wants higher frame rates, which is why many TV's ship with a game profile.
The API allows apps to switch between profiles and users to enjoy tuning supported TVs to best suit their content.
Интернационализация
В Android 16 добавлены функции и возможности, которые дополняют пользовательский опыт при использовании устройства на разных языках.
Вертикальный текст
Android 16 adds low-level support for rendering and measuring text vertically to
provide foundational vertical writing support for library developers. This is
particularly useful for languages like Japanese that commonly use vertical
writing systems. A new flag,
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG,
has been added to the Paint class. When
this flag is set using
Paint.setFlags, Paint's
text measurement APIs will report vertical advances instead of horizontal
advances, and Canvas will draw text
vertically.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
Настройка системы измерений
Users can now customize their measurement system in regional preferences within
Settings. The user preference is included as part of the locale code, so you can
register a BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED to handle locale configuration changes when
regional preferences change.
Using formatters can help match the local experience. For example, "0.5 in" in English (United States), is "12,7 mm" for a user who has set their phone to English (Denmark) or who uses their phone in English (United States) with the metric system as the measurement system preference.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & region.

