يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة رائعة للمطوّرين. توضّح الأقسام التالية هذه الميزات لمساعدتك على البدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة والمعدَّلة والمحذوفة، يُرجى قراءة تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهات برمجة تطبيقات Android، حيث يتم تمييز واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة لتسهيل العثور عليها.عليك أيضًا مراجعة الأقسام التي قد تؤثر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على الصفحات التالية:
- التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثّر في التطبيقات عند استهدافها الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android
- تغييرات في السلوك تؤثر في جميع التطبيقات بغض النظر عن
targetSdkVersion
الوظيفة الأساسية
يتضمّن Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة توسّع الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android.
إصداران من واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Android في 2025
- This preview is for the next major release of Android with a planned launch in Q2 of 2025. This release is similar to all of our API releases in the past, where we can have planned behavior changes that are often tied to a targetSdkVersion.
- We're planning the major release a quarter earlier (Q2 rather than Q3 in prior years) to better align with the schedule of device launches across our ecosystem, so more devices can get the major release of Android sooner. With the major release coming in Q2, you'll need to do your annual compatibility testing a few months earlier than in previous years to make sure your apps are ready.
- We plan to have another release in Q4 of 2025 which also will include new developer APIs. The Q2 major release will be the only release in 2025 to include planned behavior changes that could affect apps.
In addition to new developer APIs, the Q4 minor release will pick up feature updates, optimizations, and bug fixes; it will not include any app-impacting behavior changes.
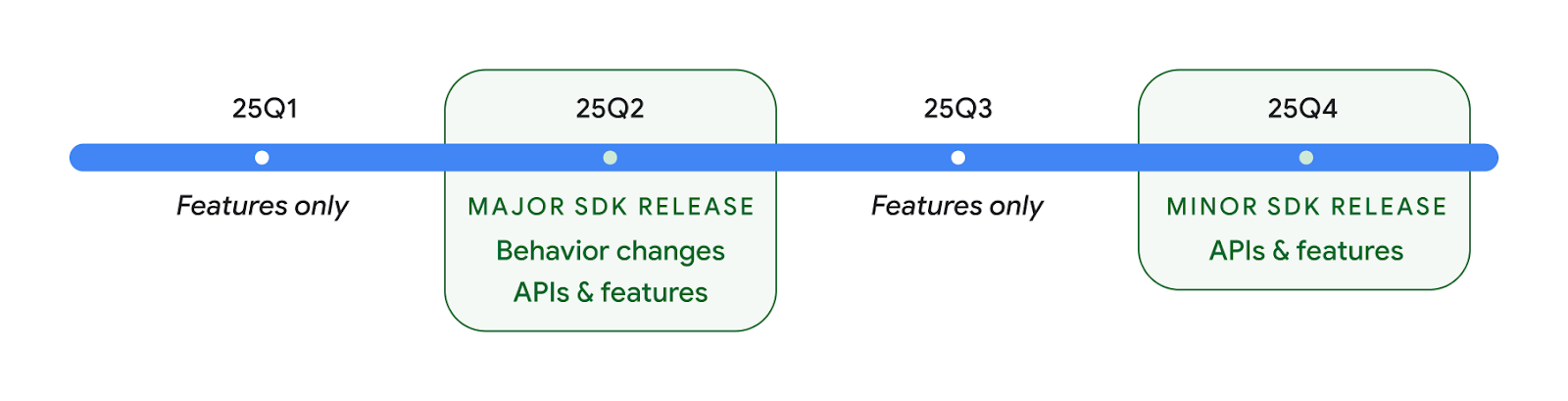
We'll continue to have quarterly Android releases. The Q1 and Q3 updates in-between the API releases will provide incremental updates to help ensure continuous quality. We're actively working with our device partners to bring the Q2 release to as many devices as possible.
Using new APIs with major and minor releases
Guarding a code block with a check for API level is done today using
the SDK_INT constant with
VERSION_CODES. This will continue
to be supported for major Android releases.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
The new SDK_INT_FULL
constant can be used for API checks against both major and minor versions with
the new VERSION_CODES_FULL
enumeration.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
You can also use the
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
method to get just the minor SDK version.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
These APIs have not yet been finalized and are subject to change, so please send us feedback if you have any concerns.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يمنح نظام التشغيل Android 16 مطوّري التطبيقات والمستخدمين المزيد من التحكّم والمرونة في إعداد أجهزتهم بما يتناسب مع احتياجاتهم.
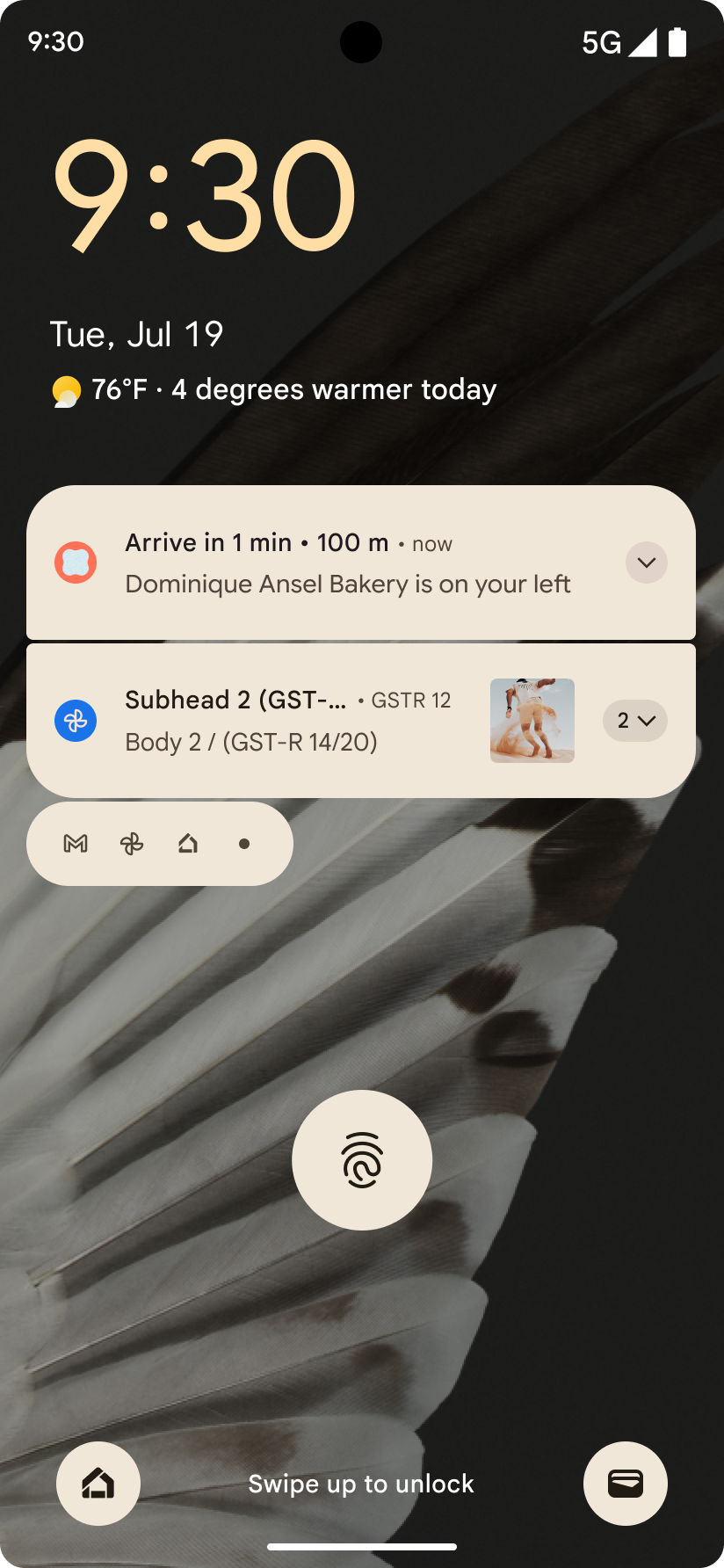
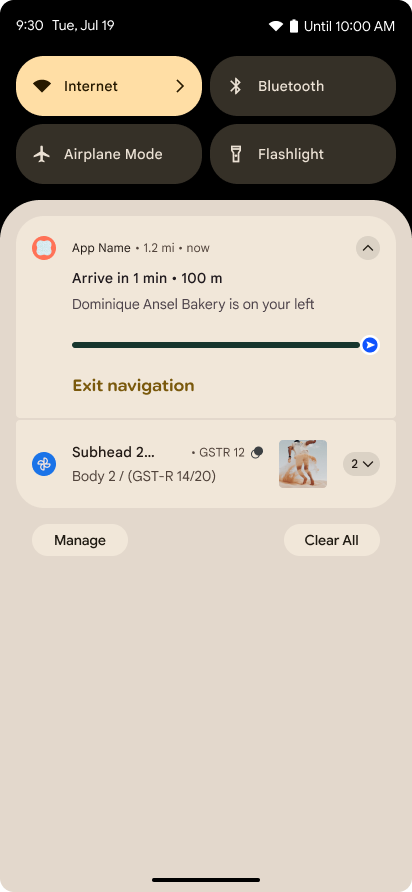
الإشعارات التي تركّز على مستوى التقدّم
يقدّم الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android إشعارات تركّز على مستوى التقدّم لمساعدة المستخدمين في تتبُّع الرحلات التي يبدأها المستخدمون من البداية إلى النهاية بسلاسة.
Notification.ProgressStyle هو أسلوب إشعار
جديد يتيح لك إنشاء إشعارات تركّز على مستوى التقدّم. تشمل حالات الاستخدام الرئيسية
خدمات النقل المشترك والتوصيل والملاحة. ضمن Notification.ProgressStyle
الفئة، يمكنك الإشارة إلى الحالات والمحطّات الرئيسية في رحلة المستخدِم باستخدام
النقاط والشريح.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على صفحة مستندات الإشعارات التي تركّز على مستوى التقدّم.
تعديلات على إيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية
يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة لمساعدتك في تفعيل الصور المتحركة في النظام لإيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية في أثناء التنقّل باستخدام الإيماءات، مثل الصورة المتحركة للرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية. من خلال تسجيل
onBackInvokedCallback باستخدام الرمز الجديد
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER، يمكن لتطبيقكتلقّي طلب onBackInvoked العادي كلما تعامل النظام مع عملية الرجوع بدون التأثير في سير عملية الرجوع العادي.
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 أيضًا رمزَي
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() و
moveTaskToBackCallback. من خلال تسجيل عمليات الاستدعاء هذه
باستخدام OnBackInvokedDispatcher، يمكن للنظام بدء
سلوكيات معيّنة وتشغيل الصور المتحركة المقابلة مسبقًا عند تنفيذ رمز الإيماءة
للرجوع.
تجاوب حسّي أكثر ثراءً
Android has exposed control over the haptic actuator ever since its inception.
Android 11 added support for more complex haptic effects that more advanced
actuators could support through
VibrationEffect.Compositions of device-defined semantic
primitives.
Android 16 adds haptic APIs that let apps define the amplitude and frequency curves of a haptic effect while abstracting away differences between device capabilities.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مع أنّ معظم جهودنا لتحسين إنتاجيتك تركّز على أدوات مثل استوديو Android وJetpack Compose ومكتبات Android Jetpack، إلا أنّنا نبحث دائمًا عن طرق في المنصة لمساعدتك في تحقيق أهدافك.
التعامل مع المحتوى في الخلفيات المتحركة
في الإصدار 16 من Android، سيحصل إطار عمل الخلفيات المتحركة على واجهة برمجة تطبيقات جديدة للمحتوى بهدف
معالجة تحديات الخلفيات الديناميكية التي ينشئها المستخدمون. في الوقت الحالي، تتطلّب
خلفيات الشاشة النشطة التي تتضمّن محتوى يقدّمه المستخدم تنفيذًا معقدًا
خاصًا بالخدمة. يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 رمزَي emoji
WallpaperDescription و
WallpaperInstance. يتيح لك WallpaperDescription معرفة
حالات مختلفة من خلفية متحركة من الخدمة نفسها. على سبيل المثال، قد تتضمّن الخلفية التي تظهر على كل من الشاشة الرئيسية وشاشة القفل محتوًى فريدًا في كلا المكانَين. يستخدم أداة اختيار الخلفية وWallpaperManager هذه البيانات الوصفية لعرض
الخلفيات بشكل أفضل للمستخدمين، ما يسهّل عليك إنشاء تجارب متنوعة
ومخصَّصة للخلفيات الحية.
الأداء والبطارية
يقدّم الإصدار Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تساعد في جمع إحصاءات حول تطبيقاتك.
تحديد المواصفات الشخصية لصاحب البيانات من خلال النظام
ProfilingManager was
added in Android 15, giving apps the ability to
request profiling data collection using Perfetto on public devices in the field.
However, since this profiling must be started from the app, critical flows such
as startups or ANRs would be difficult or impossible for apps to capture.
To help with this, Android 16 introduces system-triggered profiling to
ProfilingManager. Apps can register interest in receiving traces for certain
triggers such as cold start reportFullyDrawn
or ANRs, and then the system starts and stops a trace on the app's behalf. After
the trace completes, the results are delivered to the app's data directory.
بدء المكوّن في ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo was added in Android
15, allowing an app to see reasons
for process start, start type, start times, throttling, and other useful
diagnostic data. Android 16 adds
getStartComponent()
to distinguish what component type triggered the start, which can be helpful for
optimizing the startup flow of your app.
تحسين فحص المهام
تعرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() سبب احتمال أن تكون إحدى المهام في انتظار المراجعة. ومع ذلك، قد تكون المهمة في انتظار المراجعة لعدة أسباب.
في Android 16، نقدّم واجهة برمجة تطبيقات جديدة
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId)، وهي تعرض عدة
أسباب لتعليق إحدى المهام، وذلك بسبب القيود الصريحة التي يحدّدها المطوّر والقيود الضمنية التي يحدّدها النظام.
نقدّم أيضًا الرمز
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId) الذي يعرض قائمة
بأحدث تغييرات القيود.
ننصحك باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لمساعدتك في تصحيح الأخطاء المتعلّقة بعدم تنفيذ مهامك، خاصةً إذا لاحظت انخفاضًا في معدّلات نجاح مهام معيّنة أو إذا واجهت أخطاء تتعلّق بالوقت المستغرَق لإكمال مهام معيّنة. على سبيل المثال، تعذّر تعديل التطبيقات المصغّرة في الخلفية أو تعذّر استدعاء مهمة التحميل المُسبَق قبل بدأ التطبيق.
ويمكن أن يساعدك ذلك أيضًا في معرفة ما إذا كانت بعض المهام لا تكتمل بسبب قيود محدّدة من النظام مقارنةً بالقيود المحدّدة بوضوح.
معدّل التحديث التكيّفي
إنّ معدل إعادة التحميل التكيُّفي (ARR) الذي تم تقديمه في Android 15 يتيح لمعدل إعادة تحميل الشاشة على الأجهزة المتوافقة التكيُّف مع معدل عرض اللقطات للمحتوى باستخدام خطوات فاصل عرض اللقطات المنفصلة. ويؤدي ذلك إلى تقليل استهلاك الطاقة مع التخلص من الحاجة إلى التبديل بين الأوضاع الذي قد يؤدي إلى حدوث تقطُّع في الأداء.
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 hasArrSupport() و
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) مع استعادة
getSupportedRefreshRates() لتسهيل استفادة تطبيقاتك من ميزة ARR. يتيح RecyclerView
1.4 استخدام ميزة ARR داخليًا عند الانتقال من التمرير السريع أو
الانتقال السلس، ونحن نواصل عملنا لإضافة ميزة ARR
إلى المزيد من مكتبات Jetpack. تتناول مقالة معدّل عرض اللقطات هذه
العديد من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي يمكنك استخدامها لضبط معدّل عرض اللقطات كي يتمكّن تطبيقك من استخدام ميزة "معدل عرض الإعلانات" مباشرةً.
واجهات برمجة تطبيقات Headroom في ADPF
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
تسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف Android 16 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة لتسهيل الاستخدام يمكن أن تساعدك في توفير تطبيقك لجميع المستخدمين.
واجهات برمجة تطبيقات محسَّنة لتسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات إضافية لتحسين دلالات واجهة المستخدم التي تساعد في تحسين الاتساق للمستخدمين الذين يعتمدون على خدمات تسهيل الاستخدام، مثل TalkBack.
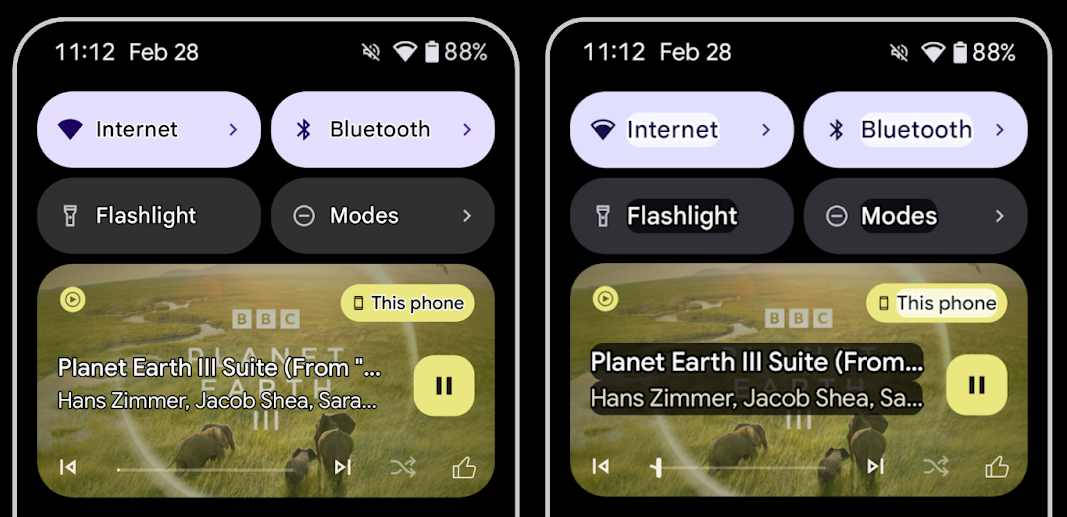
النص المفرّغ لزيادة تباين النص إلى أقصى حد
غالبًا ما يعاني المستخدمون الذين يعانون من ضعف في النظر من انخفاض في حساسية التباين، ما يجعل من الصعوبة بمكان تمييز الأجسام عن الخلفيات. لمساعدة هؤلاء المستخدمين، يقدّم الإصدار 16 من Android ميزة "النص المخطّط" الذي يحلّ محلّ ميزة "النص العالي التباين"، والذي يرسم منطقة أكبر ذات تباين أعلى حول النص لتحسين قراءته بشكل كبير.
يحتوي Android 16 على واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة AccessibilityManager للسماح لتطبيقاتك بالتحقّق أو تسجيل مستمع لتحديد ما إذا كان هذا الوضع مفعّلاً. يُستخدم هذا الأسلوب بشكل أساسي في حِزم أدوات واجهة المستخدم، مثل Compose، لتوفير تجربة مرئية مشابهة. إذا كنت تحافظ على مكتبة UI Toolkit أو كان
تطبيقك يُجري عرضًا مخصّصًا للنص يتجاوز فئة
android.text.Layout، يمكنك استخدام هذا الإجراء لمعرفة
حالات تفعيل النص المخطّط.
تمت إضافة المدة إلى TtsSpan
يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android TtsSpan TYPE_DURATION،
المكوّن من ARG_HOURS وARG_MINUTES
وARG_SECONDS. يتيح لك ذلك إضافة تعليقات توضيحية مباشرةً إلى مدّة المحتوى، ما يضمن تحويلًا دقيقًا ومتسقًا للنص إلى كلام باستخدام خدمات مثل TalkBack.
إتاحة العناصر التي تحتوي على تصنيفات متعددة
يسمح Android حاليًا لعناصر واجهة المستخدم بالحصول على تصنيف تسهيل الاستخدام من عنصر آخر، كما يتيح الآن إمكانية ربط تصنيفات متعددة، وهو سيناريو شائع في محتوى الويب. من خلال تقديم واجهة برمجة تطبيقات مستندة إلى قائمة في
AccessibilityNodeInfo، يمكن لنظام التشغيل Android إتاحة
هذه العلاقات المتعدّدة التصنيفات مباشرةً. وكجزء من هذا التغيير، أوقفنا نهائيًا استخدام
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy و
#getLabeledBy واستبدلناهما برمزَي
#addLabeledBy و#removeLabeledBy و
#getLabeledByList.
تحسين التوافق مع العناصر القابلة للتوسيع
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تسهيل الاستخدام تتيح لك الإشارة إلى الحالة الموسّعة أو
المجمّعة للعناصر التفاعلية، مثل القوائم والقوائم القابلة للتوسيع. من خلال
ضبط الحالة الموسّعة باستخدام setExpandedState و
إرسال TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
باستخدام نوع تغيير المحتوى CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED،
يمكنك التأكّد من أنّ برامج قراءة الشاشة، مثل TalkBack، تعلن عن
تغييرات الحالة، ما يقدّم تجربة مستخدم أكثر سهولة وشمولية.
أشرطة تقدّم غير محدّدة
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 رمز RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE، ما يتيح لك
عرض RangeInfo لكل من التطبيقات المصغّرةProgressBar المحددة وغير المحددة، ما يسمح لخدمات مثل
TalkBack بتقديم ملاحظات بشكل أكثر اتساقًا لمؤشرات التقدّم.
مربّع اختيار ثلاثي الحالات
تتيح الطريقتان الجديدتان AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked وsetChecked(int)
في Android 16 الآن حالة "تم وضع علامة جزئية" بالإضافة إلى
"تم وضع علامة" و "لم يتم وضع علامة". ويحلّ هذا النوع محلّ النوعَين المنطقيَين المتوقفَين نهائيًا
isChecked وsetChecked(boolean).
الأوصاف التكميلية
عندما تصف الخدمة المخصّصة لتسهيل الاستخدام عنصر ViewGroup، فإنّها
تضمّن تصنيفات المحتوى من عناصر العرض الثانوية. في حال تقديم contentDescription لعنصر ViewGroup، تفترض خدمات تسهيل الاستخدام أنّك تريد
أيضًا إلغاء وصف عناصر العرض الثانوية غير القابلة للتركيز. قد يتسبب ذلك في
مشاكل إذا أردت تصنيف عناصر مثل القائمة المنسدلة (على سبيل المثال، "عائلة
الخط") مع الحفاظ على الاختيار الحالي لتسهيل الاستخدام (على سبيل المثال،
"Roboto"). يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android setSupplementalDescription حتى تتمكّن من تقديم نص يقدّم معلومات عن ViewGroup بدون
إلغاء المعلومات الواردة من العناصر الفرعية.
حقول النموذج المطلوبة
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 الرمز setFieldRequired إلى
AccessibilityNodeInfo حتى تتمكّن التطبيقات من إبلاغ خدمة تسهيل الاستخدام بأنّ إدخال البيانات في حقل النموذج مطلوب. هذا سيناريو مهم
للمستخدمين الذين يملؤون العديد من أنواع النماذج، حتى الأشياء البسيطة مثل مربّع الاختيار المطلوب
لأحكام وشروط الاستخدام، ما يساعد المستخدمين في التعرّف على الحقول المطلوبة باستمرار
والتنقّل بينها بسرعة.
استخدام الهاتف كميكروفون لإجراء مكالمات صوتية باستخدام سماعات الأذن الطبية المزودة بتقنية LEA
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 إمكانية السماح لمستخدمي سمّاعات الأذن الطبية المزوّدة بتقنية LE Audio بالتبديل بين الميكروفونات المدمجة في سمّاعات الأذن الطبية والميكروفون في الهاتف لإجراء المكالمات الصوتية. يمكن أن يكون ذلك مفيدًا في البيئات الصاخبة أو في حالات أخرى قد لا تعمل فيها ميكروفونات سماعة الأذن الطبية بشكل جيد.
عناصر التحكّم في مستوى الصوت المحيط لسماعات الأذن الطبية المتوافقة مع LEA
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to adjust the volume of ambient sound that is picked up by the hearing aid's microphones. This can be helpful in situations where background noise is too loud or too quiet.
الكاميرا
يحسِّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 إمكانية استخدام الكاميرات الاحترافية، ما يتيح التعريض التلقائي المختلط إلى جانب التعديلات الدقيقة لدرجة حرارة الألوان ودرجة اللون. يساعد مؤشر وضع التصوير الليلي الجديد تطبيقك في معرفة الوقت المناسب للتبديل إلى جلسة تصوير في وضع التصوير الليلي أو إيقافها. تسهّل الإجراءات الجديدة Intent التقاط صور متحركة،
ونواصل تحسين صور UltraHDR من خلال توفير توافق مع ترميز HEIC
ومَعلمات جديدة من مسودة معيار ISO 21496-1.
التعرّض التلقائي المختلط للضوء
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 أوضاعًا جديدة مختلطة للتعريض التلقائي إلى Camera2، ما يتيح لك التحكّم يدويًا في جوانب معيّنة من التعريض مع السماح لخوارزمية التعريض التلقائي (AE) بالتعامل مع الباقي. يمكنك التحكّم في درجة ISO + التعريض التلقائي ووقت التعريض + التعريض التلقائي، ما يوفّر مزيدًا من المرونة مقارنةً بالنهج الحالي الذي يتيح لك التحكّم يدوياً بالكامل أو الاعتماد بالكامل على التعريض التلقائي.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
تعديلات دقيقة على درجة حرارة الألوان ودرجة اللون
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





رصد المشاهد في "الوضع الليلي" للكاميرا
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
إجراءات intent لالتقاط صور حيّة
Android 16 adds standard Intent actions —
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE, and
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE — which request that
the camera application capture a motion photo and return
it.
You must either pass an extra EXTRA_OUTPUT to control
where the image will be written, or a Uri through
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). If you don't set a
ClipData, it will be copied there for you when calling
Context.startActivity(Intent).
تحسينات على صور UltraHDR

يواصل نظام Android 16 جهودنا لتوفير جودة صور مذهلة باستخدام صور UltraHDR. تمت إضافة إمكانية استخدام صور UltraHDR بتنسيق ملف HEIC. ستحصل هذه الصور على نوع ImageFormat
HEIC_ULTRAHDR وستحتوي على خريطة مكاسب مضمّنة مشابهة
لتنسيق UltraHDR JPEG الحالي. نحن نعمل أيضًا على إتاحة تنسيق AVIF لميزة UltraHDR، لذا يُرجى متابعتنا باستمرار.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، ينفِّذ الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android مَعلمات إضافية في ميزة "دقة HDR الفائقة" من مسودة معيار ISO 21496-1، بما في ذلك إمكانية الحصول على مساحة الألوان التي يجب تطبيق العمليات الحسابية لخريطة الكسب فيها وضبطها، بالإضافة إلى إتاحة الصور الأساسية المُشفَّرة بتقنية النطاق العالي الديناميكية (HDR) مع خرائط الكسب بتقنية النطاق العادي الديناميكية (SDR).
الرسومات
يتضمّن Android 16 أحدث التحسينات على الرسومات، مثل التأثيرات المخصّصة للرسومات باستخدام AGSL.
تأثيرات رسومية مخصّصة باستخدام AGSL
Android 16 adds RuntimeColorFilter and
RuntimeXfermode, allowing you to author complex effects like
Threshold, Sepia, and Hue Saturation and apply them to draw calls. Since Android
13, you've been able to use AGSL to create custom
RuntimeShaders that extend Shader. The new API
mirrors this, adding an AGSL-powered RuntimeColorFilter that
extends ColorFilter, and a Xfermode effect that
lets you implement AGSL-based custom compositing and blending between source and
destination pixels.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
إمكانية الاتصال
يحدِّث Android 16 النظام الأساسي لمنح تطبيقك إمكانية الوصول إلى أحدث التطورات في تكنولوجيات الاتصال والشبكات اللاسلكية.
تحديد المدى مع مستوى أمان محسّن
Android 16 adds support for robust security features in Wi-Fi location on supported devices with Wi-Fi 6's 802.11az, allowing apps to combine the higher accuracy, greater scalability, and dynamic scheduling of the protocol with security enhancements including AES-256-based encryption and protection against MITM attacks. This allows it to be used more safely in proximity use cases, such as unlocking a laptop or a vehicle door. 802.11az is integrated with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, leveraging its infrastructure and capabilities for wider adoption and easier deployment.
واجهات برمجة التطبيقات العامة لتحديد النطاق
Android 16 includes the new RangingManager, which provides
ways to determine the distance and angle on supported hardware between the local
device and a remote device. RangingManager supports the usage of a variety of
ranging technologies such as BLE channel sounding, BLE RSSI-based ranging, Ultra
Wideband, and Wi-Fi round trip time.
توفّر الجهاز المصاحب في "أداة إدارة الأجهزة المصاحبة"
In Android 16, new APIs are being introduced for binding your companion app
service. Service will be bound when BLE is in range and Bluetooth is connected
and service will be unbound when BLE is out of range or Bluetooth is
disconnected. App will receives a new
'onDevicePresenceEvent()' callback based on various
of DevicePresenceEvent.
More details can be found in
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
الوسائط
يتضمّن Android 16 مجموعة متنوعة من الميزات التي تحسّن تجربة استخدام الوسائط.
تحسينات على أداة اختيار الصور
The photo picker provides a safe, built-in way for users to grant your app access to selected images and videos from both local and cloud storage, instead of their entire media library. Using a combination of Modular System Components through Google System Updates and Google Play services, it's supported back to Android 4.4 (API level 19). Integration requires just a few lines of code with the associated Android Jetpack library.
Android 16 includes the following improvements to the photo picker:
- Embedded photo picker: New APIs that enable apps to embed the photo picker into their view hierarchy. This allows it to feel like a more integrated part of the app while still leveraging the process isolation that allows users to select media without the app needing overly broad permissions. To maximize compatibility across platform versions and simplify your integration, you'll want to use the forthcoming Android Jetpack library if you want to integrate the embedded photo picker.
- Cloud search in photo picker: New APIs that enable searching from the cloud media provider for the Android photo picker. Search functionality in the photo picker is coming soon.
فيديو احترافي متقدّم
Android 16 introduces support for the Advanced Professional Video (APV) codec which is designed to be used for professional level high quality video recording and post production.
The APV codec standard has the following features:
- Perceptually lossless video quality (close to raw video quality)
- Low complexity and high throughput intra-frame-only coding (without pixel domain prediction) to better support editing workflows
- Support for high bit-rate range up to a few Gbps for 2K, 4K and 8K resolution content, enabled by a lightweight entropy coding scheme
- Frame tiling for immersive content and for enabling parallel encoding and decoding
- Support for various chroma sampling formats and bit-depths
- Support for multiple decoding and re-encoding without severe visual quality degradation
- Support multi-view video and auxiliary video like depth, alpha, and preview
- Support for HDR10/10+ and user-defined metadata
A reference implementation of APV is provided through the OpenAPV project. Android 16 will implement support for the APV 422-10 Profile that provides YUV 422 color sampling along with 10-bit encoding and for target bitrates of up to 2Gbps.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن Android 16 مجموعة متنوّعة من الميزات التي تساعد مطوّري التطبيقات في حماية خصوصية المستخدمين.
تحديثات Health Connect
Health Connect adds ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, a data type defined according to World
Health Organization guidelines around moderate and vigorous activity. Each
record requires the start time, the end time, and whether the activity intensity
is moderate or vigorous.
Health Connect also contains updated APIs supporting medical records. This allows apps to read and write medical records in FHIR format with explicit user consent.
"مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" على Android
Android 16 incorporates the latest version of the Privacy Sandbox on Android, part of our ongoing work to develop technologies where users know their privacy is protected. Our website has more about the Privacy Sandbox on Android developer beta program to help you get started. Check out the SDK Runtime which allows SDKs to run in a dedicated runtime environment separate from the app they are serving, providing stronger safeguards around user data collection and sharing.
الأمان
يتضمّن Android 16 ميزات تساعدك في تعزيز أمان تطبيقك وحماية بياناته.
Key sharing API
Android 16 adds APIs that support sharing access to
Android Keystore keys with other apps. The new
KeyStoreManager class supports
granting and revoking access to keys
by app uid, and includes an API for apps to access shared
keys.
أشكال الأجهزة
يوفّر Android 16 لتطبيقاتك إمكانية الاستفادة إلى أقصى حد من أشكال أجهزة Android.
إطار عمل موحّد لجودة الصورة والصوت في أجهزة التلفزيون
توفّر MediaQuality
الحزمة الجديدة في Android 16 مجموعة من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الموحدة للوصول إلى الملفات الصوتية والملفات الصوتية والصور والإعدادات المتعلّقة بالأجهزة. يتيح ذلك لتطبيقات البث الاستعلام عن الملفات الشخصية
وتطبيقها على الوسائط ديناميكيًا:
- تتطلّب الأفلام التي تمّت إتقانها بنطاق ديناميكي أوسع دقة ألوان أكبر لتمييز التفاصيل الدقيقة في الظلال والتكيّف مع الإضاءة المحيطة، لذا قد يكون من المناسب استخدام ملف شخصي يفضّل دقة الألوان على السطوع.
- غالبًا ما يتم ضبط الفعاليات الرياضية المباشرة باستخدام نطاق ديناميكي ضيّق، ولكن يتم مشاهدتها غالبًا في ضوء النهار، لذا يمكن أن يقدّم الملف الشخصي الذي يفضّل السطوع على دقة الألوان نتائج أفضل.
- يتطلب المحتوى التفاعلي بالكامل الحد الأدنى من المعالجة لتقليل وقت الاستجابة، ويتطلب معدلات عرض صور أعلى، ولهذا السبب يتم شحن العديد من أجهزة التلفزيون مع ملف ألعاب.
تسمح واجهة برمجة التطبيقات للتطبيقات بالتبديل بين الملفات الشخصية والمستخدمين للاستفادة من ضبط أجهزة التلفزيون المتوافقة بما يناسب المحتوى على أفضل نحو.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وإمكانات تكمل تجربة المستخدم عند استخدام الجهاز بلغات مختلفة.
نص عمودي
يضيف نظام Android 16 دعمًا من المستوى الأدنى لعرض النص وقياسه عموديًا بهدف
توفير دعم أساسي للكتابة العمودية لمطوّري المكتبات. ويفيد ذلك
بشكل خاص في اللغات التي تستخدم عادةً أنظمة كتابة عمودية، مثل اليابانية. تمت إضافة علامة جديدة،
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG،
إلى فئة Paint. عند ضبط
هذا الإعداد باستخدام
Paint.setFlags، ستحدّد واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
لقياس النصوص في Paint التقدّم في الرسم بالاتجاه العمودي بدلاً من التقدّم في الرسم بالاتجاه الأفقي، وسيرسم Canvas النص
بالاتجاه العمودي.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
تخصيص نظام القياس
Users can now customize their measurement system in regional preferences within
Settings. The user preference is included as part of the locale code, so you can
register a BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED to handle locale configuration changes when
regional preferences change.
Using formatters can help match the local experience. For example, "0.5 in" in English (United States), is "12,7 mm" for a user who has set their phone to English (Denmark) or who uses their phone in English (United States) with the metric system as the measurement system preference.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & region.

