Android 16 プラットフォームには、アプリに影響を与える可能性のある動作変更が含まれています。下記の動作変更は、targetSdkVersion に関係なく、Android 16 上で稼働するすべてのアプリに適用されます。該当する場合は、アプリをテストし、必要に応じて修正して、これらの変更に対応する必要があります。
Android 16 をターゲットとするアプリにのみ影響する動作変更のリストも必ずご確認ください。
コア機能
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、Android システムのさまざまなコア機能を変更または拡張する以下の変更が含まれています。
JobScheduler の割り当ての最適化
Android 16 以降では、次の要素に基づいて、通常のジョブと迅速なジョブの実行ランタイム割り当てを調整しています。
- アプリケーションが属するアプリ スタンバイ バケット: Android 16 では、アクティブなスタンバイ バケットは、十分なランタイム割り当てによって適用されるようになります。
- アプリが最上位の状態のときにジョブの実行が開始された場合: Android 16 では、アプリがユーザーに表示されている間に開始され、アプリが非表示になった後も継続されるジョブは、ジョブの実行時間割り当てに準拠します。
- フォアグラウンド サービスの実行中にジョブが実行されている場合: Android 16 では、フォアグラウンド サービスと同時に実行されているジョブは、ジョブの実行時間割り当てに準拠します。ジョブをユーザー開始型データ転送に活用している場合は、代わりにユーザー開始型データ転送ジョブの使用を検討してください。
この変更は、WorkManager、JobScheduler、DownloadManager を使用してスケジュール設定されたタスクに影響します。ジョブが停止した理由をデバッグするには、WorkInfo.getStopReason() を呼び出してジョブが停止した理由をロギングすることをおすすめします(JobScheduler ジョブの場合は JobParameters.getStopReason() を呼び出します)。
アプリの状態が使用できるリソースに与える影響については、電源管理のリソース制限をご覧ください。バッテリーを最適化するためのベスト プラクティスについて詳しくは、タスク スケジューリング API のバッテリー使用量を最適化するをご覧ください。
また、Android 16 で導入された新しい JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API を活用して、ジョブが実行されなかった理由を把握することをおすすめします。
テスト
アプリの動作をテストするには、アプリが Android 16 デバイスで実行されている場合に限り、特定のジョブ割り当ての最適化のオーバーライドを有効にできます。
「トップ状態はジョブ ランタイム割り当てに準拠する」の適用を無効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
「フォアグラウンド サービスと同時に実行されるジョブはジョブ ランタイム割り当てに準拠する」の適用を無効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
特定のアプリ スタンバイ バケットの動作をテストするには、次の adb コマンドを使用してアプリのアプリ スタンバイ バケットを設定します。
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
アプリが属するアプリ スタンバイ バケットを把握するには、次の adb コマンドを使用して、アプリのアプリ スタンバイ バケットを取得します。
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
空のジョブが破棄された停止理由
放棄されたジョブは、ジョブに関連付けられた JobParameters オブジェクトがガベージ コレクションされたものの、JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) が呼び出されず、ジョブの完了が通知されていない場合に発生します。これは、アプリが認識せずにジョブが実行され、スケジュールが変更されている可能性があることを示します。
JobScheduler に依存するアプリは、JobParameters オブジェクトへの強参照を維持しないため、タイムアウトには STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT ではなく、新しいジョブ停止理由 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED が付与されます。
新しい放棄された停止理由が頻繁に発生する場合、システムは緩和策を講じてジョブの頻度を減らします。
アプリは、新しい停止理由を使用して、放棄されたジョブを検出して削減する必要があります。
WorkManager、AsyncTask、DownloadManager を使用している場合、これらの API はアプリに代わってジョブのライフサイクルを管理するため、影響を受けません。
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground のサポートを完全に終了
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) メソッドは、スケジュール設定アプリがフォアグラウンドにある間、またはバックグラウンドの制限を一時的に免除されている間のジョブの重要度を示します。
このメソッドは、Android 12(API レベル 31)で非推奨になりました。Android 16 以降では、このメソッドは効果的に機能しなくなり、このメソッドの呼び出しは無視されます。
この機能の削除は JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground() にも適用されます。Android 16 以降では、メソッドが呼び出されると、メソッドは false を返します。
順序付きブロードキャストの優先度のスコープがグローバルではなくなった
Android アプリでは、ブロードキャスト レシーバの優先度を定義して、レシーバがブロードキャストを受信して処理する順序を制御できます。マニフェストで宣言されたレシーバの場合、アプリは android:priority 属性を使用して優先度を定義できます。コンテキストで登録されたレシーバの場合、アプリは IntentFilter#setPriority() API を使用して優先度を定義できます。ブロードキャストが送信されると、システムは優先度の高い順にレシーバにブロードキャストを配信します。
Android 16 では、異なるプロセス間で android:priority 属性または IntentFilter#setPriority() を使用してブロードキャスト配信順序を指定しても、その順序が保証されることはありません。ブロードキャストの優先度は、すべてのプロセスではなく、同じアプリケーション プロセス内でのみ考慮されます。
また、ブロードキャストの優先度は、(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1、SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1)の範囲に自動的に制限されます。SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY、SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY をブロードキャスト優先度として設定できるのは、システム コンポーネントのみです。
アプリが次のいずれかを行うと、影響を受ける可能性があります。
- アプリで同じブロードキャスト インテントを持つ複数のプロセスが宣言されており、優先度に基づいて特定の順序でそれらのインテントを受信することが想定されています。
- アプリのプロセスが他のプロセスとやり取りし、特定の順序でブロードキャスト インテントを受信することを想定している。
プロセスが相互に調整する必要がある場合は、他の調整チャネルを使用して通信する必要があります。
ART の内部変更
Android 16 には、Android ランタイム(ART)の最新のアップデートが含まれています。これにより、Android ランタイム(ART)のパフォーマンスが向上し、追加の Java 機能をサポートしています。Google Play システム アップデートにより、Android 12(API レベル 31)以降を搭載した 10 億台を超えるデバイスでもこれらの改善を利用できます。
これらの変更がリリースされると、ART の内部構造に依存するライブラリとアプリコードは、Android 16 を搭載したデバイスや、Google Play システム アップデートを通じて ART モジュールを更新する以前の Android バージョンで正しく動作しない可能性があります。
内部構造(SDK 以外のインターフェースなど)に依存すると、常に互換性の問題が発生する可能性がありますが、内部 ART 構造を利用するコード(またはコードを含むライブラリ)に依存しないようにすることが特に重要です。ART の変更は、デバイスが実行しているプラットフォーム バージョンに関連付けられておらず、Google Play システム アップデートを通じて 10 億台を超えるデバイスに配信されるためです。
すべてのデベロッパーは、Android 16 でアプリを徹底的にテストして、アプリに影響があるかどうかを確認する必要があります。また、既知の問題をチェックして、アプリが内部 ART 構造に依存していることが判明したライブラリに依存しているかどうかを確認します。影響を受けるアプリコードまたはライブラリの依存関係がある場合は、可能な限り公開 API の代替手段を探し、新しいユースケース用の公開 API をリクエストしてください。リクエストは、Issue Tracker で機能リクエストを作成して行います。
16 KB ページサイズの互換モード
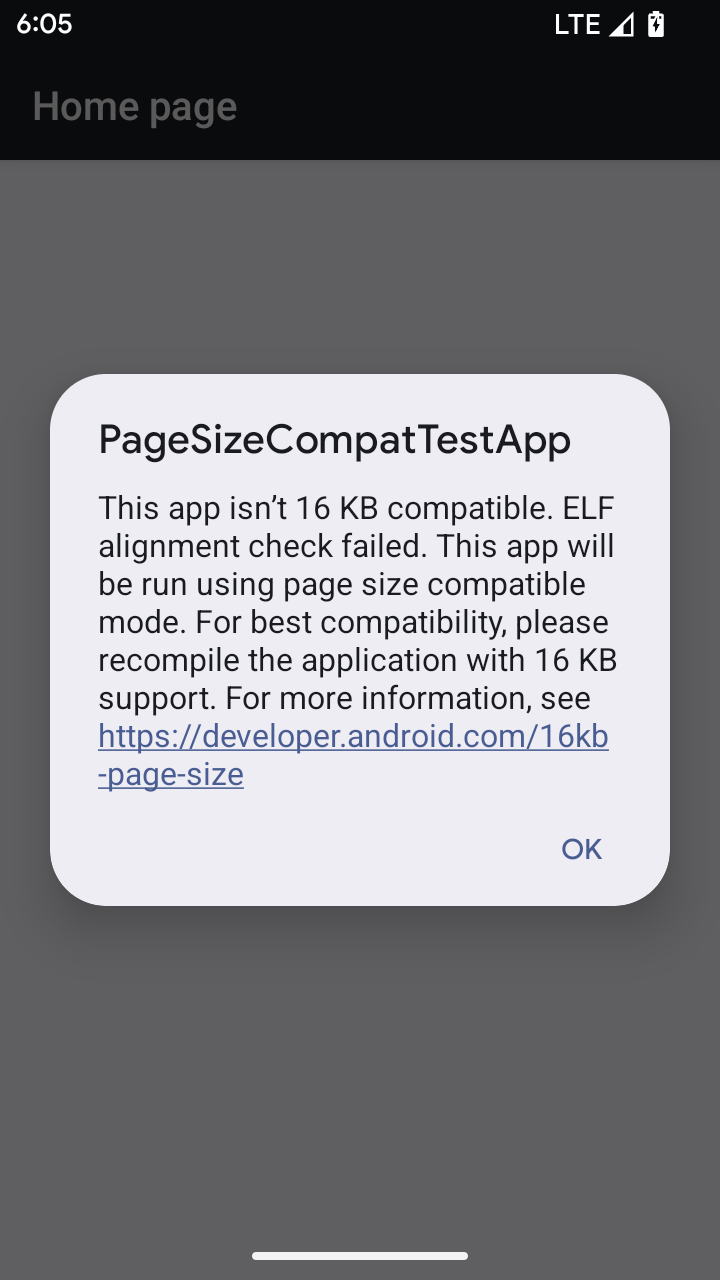
Android 15 では、プラットフォームのパフォーマンスを最適化するために、16 KB メモリページのサポートが導入されました。Android 16 では互換モードが追加され、4 KB メモリページ用にビルドされた一部のアプリを、16 KB メモリページ用に構成されたデバイスで実行できるようになりました。
Android 16 以降を搭載したデバイスでアプリが実行されているときに、アプリに 4 KB アライメントのメモリページがあることが検出されると、Android は自動的に互換モードを使用し、ユーザーに通知ダイアログを表示します。AndroidManifest.xml で android:pageSizeCompat プロパティを設定して後方互換モードを有効にすると、アプリの起動時にダイアログが表示されなくなります。android:pageSizeCompat プロパティを使用するには、Android 16 SDK を使用してアプリをコンパイルします。
パフォーマンス、信頼性、安定性を最大限に高めるには、アプリを 16 KB アライメントにする必要があります。詳しくは、16 KB メモリページをサポートするようにアプリを更新する方法に関する最新のブログ投稿をご覧ください。
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、より一貫性のある直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するための以下の変更が含まれています。
妨げになるユーザー補助の読み上げの非推奨化
Android 16 では、announceForAccessibility の使用や TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT ユーザー補助イベントのディスパッチを特徴とするユーザー補助通知が非推奨になりました。これにより、TalkBack と Android のスクリーン リーダーのユーザーに対して一貫性のないユーザー エクスペリエンスが生じる可能性があります。代替手段を使用すると、さまざまな Android 支援技術で幅広いユーザーのニーズに対応できます。
代替手段の例:
- ウィンドウの変更など、UI の大幅な変更の場合は、
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)とsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)を使用します。Compose でModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" }を使用する - 重要な UI の変更をユーザーに通知するには、
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)を使用します。Compose では、Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}を使用します。ビューが更新されるたびにお知らせが生成される可能性があるため、これらの関数は慎重に使用する必要があります。 - エラーをユーザーに通知するには、タイプ
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORのAccessibilityEventを送信し、AccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)を設定するか、TextView#setError(CharSequence)を使用します。
非推奨の announceForAccessibility API のリファレンス ドキュメントには、推奨される代替方法の詳細が記載されています。
3 ボタン ナビゲーションのサポート
Android 16 では、予測型「戻る」に適切に移行したアプリの 3 ボタン ナビゲーションに、予測型「戻る」のサポートが追加されています。戻るボタンを長押しすると、予測型「戻る」アニメーションが開始され、戻るスワイプで移動する先のプレビューが表示されます。
この動作は、システム アニメーション(ホームに戻る、タスク間、アクティビティ間)など、予測型「戻る」アニメーションをサポートするシステムのすべての領域に適用されます。
テーマ別アプリアイコンの自動生成
Android 16 QPR 2 以降では、Android がアプリ アイコンにテーマを自動的に適用し、一貫性のあるホーム画面を実現します。これは、アプリに独自のテーマ別アプリアイコンが用意されていない場合に発生します。アプリは、アダプティブ アイコン内にモノクローム レイヤを含め、Android Studio でアプリアイコンがどのように表示されるかをプレビューすることで、テーマ設定されたアプリアイコンのデザインを制御できます。
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、仮想デバイスの所有者がディスプレイに投影するアプリに対して、次の変更が加えられています。
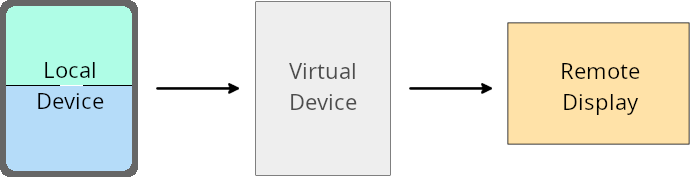
仮想デバイス所有者のオーバーライド
仮想デバイス オーナーは、仮想デバイスを作成して管理する信頼できる特権アプリです。仮想デバイスの所有者は、仮想デバイスでアプリを実行し、パソコン、仮想現実デバイス、自動車のインフォテインメント システムなどのリモート デバイスのディスプレイにアプリを投影します。仮想デバイスの所有者が、スマートフォンなどのローカル デバイスにいる。
アプリごとのオーバーライド
Android 16(API レベル 36)を搭載したデバイスでは、仮想デバイスの所有者は、仮想デバイスの所有者が管理する一部の仮想デバイスでアプリの設定をオーバーライドできます。たとえば、アプリのレイアウトを改善するために、仮想デバイスの所有者は、アプリを外部ディスプレイに投影する際に、向き、アスペクト比、サイズ変更の制限を無視できます。
一般的な互換性を破る変更
Android 16 の動作は、車載ディスプレイや Chromebook などの大画面フォーム ファクタのアプリの UI に影響する可能性があります。特に、縦向きの小さなディスプレイ向けに設計されたレイアウトに影響する可能性があります。すべてのデバイスのフォーム ファクタに対応するようにアプリをアダプティブにする方法については、アダプティブ レイアウトについてをご覧ください。
参照
セキュリティ
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、システム セキュリティを強化し、アプリとユーザーを悪意のあるアプリから保護するための変更が含まれています。
インテント リダイレクト攻撃に対するセキュリティの強化
Android 16 では、一般的な Intent リダイレクト攻撃に対するデフォルトのセキュリティが提供され、互換性とデベロッパーの変更が最小限で済みます。
Intent リダイレクト エクスプロイトに対するデフォルトのセキュリティ強化ソリューションを導入します。ほとんどの場合、インテントを使用するアプリで互換性の問題が発生することはありません。Google は開発プロセス全体で指標を収集し、どのアプリで破損が発生する可能性があるかをモニタリングしています。
Android のインテント リダイレクトは、脆弱なアプリに関連して新しいコンポーネントの起動に使用されるインテントの内容を攻撃者が部分的または完全に制御できる場合に発生します。一方、被害者のアプリは(「トップレベル」の)インテントの Extras フィールドで信頼できないサブレベルのインテントを起動します。これにより、攻撃者のアプリが被害者のアプリのコンテキストで非公開コンポーネントを起動し、特権アクションをトリガーしたり、機密データへの URI アクセス権を取得したりする可能性があります。これにより、データ窃盗や任意のコード実行につながるおそれがあります。
インテント リダイレクト処理をオプトアウトする
Android 16 では、アプリが起動時のセキュリティ保護をオプトアウトできる新しい API が導入されています。これは、デフォルトのセキュリティ動作が正当なアプリのユースケースを妨げる特定のケースで必要になることがあります。
Android 16(API レベル 36)以降の SDK を対象にコンパイルするアプリの場合
Intent オブジェクトで removeLaunchSecurityProtection() メソッドを直接使用できます。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Android 15(API レベル 35)以下を対象にコンパイルするアプリの場合
推奨はされませんが、リフレクションを使用して removeLaunchSecurityProtection() メソッドにアクセスできます。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
コンパニオン アプリに検出タイムアウトが通知されなくなった
Android 16 では、コンパニオン デバイスのペア設定フロー中に新しい動作が導入され、悪意のあるアプリからユーザーの位置情報のプライバシーを保護します。Android 16 で実行されているすべてのコンパニオン アプリは、RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT を使用して検出タイムアウトを直接通知されなくなりました。代わりに、タイムアウト イベントが視覚的なダイアログでユーザーに通知されます。ユーザーがダイアログを閉じると、アプリは RESULT_USER_REJECTED で関連付けの失敗をアラートします。
検索時間も元の 20 秒から延長され、検索中にユーザーがいつでもデバイス検出を停止できるようになりました。検索開始から 20 秒以内に 1 台以上のデバイスが検出されると、CDM は追加のデバイスの検索を停止します。
接続
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、周辺機器との接続性を改善するために、Bluetooth スタックに次の変更が加えられています。
債券損失の処理を改善
Android 16 以降、Bluetooth スタックが更新され、リモート ボンディングの損失が検出されたときのセキュリティとユーザー エクスペリエンスが改善されました。以前は、システムが自動的にボンディングを削除し、新しいペア設定プロセスを開始していたため、意図しない再ペア設定が発生する可能性がありました。多くのアプリで、債券の損失イベントが一貫した方法で処理されていないことが確認されています。
エクスペリエンスを統一するため、Android 16 ではシステムへのボンディング損失の処理が改善されました。以前にペア設定した Bluetooth デバイスを再接続時に認証できなかった場合、システムはリンクを切断し、ローカルのペア設定情報を保持します。また、ペア設定が解除されたことをユーザーに通知し、ペア設定をやり直すよう求めるシステム ダイアログを表示します。
