يتضمّن الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android تغييرات في السلوك قد تؤثّر في تطبيقك.
تنطبق تغييرات السلوك التالية على جميع التطبيقات عند تشغيلها على الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android،
بغض النظر عن targetSdkVersion. عليك اختبار تطبيقك ثم تعديله حسب الحاجة ليتوافق مع هذه التغييرات، حيثما ينطبق ذلك.
احرص أيضًا على مراجعة قائمة التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثّر فقط في التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android.
الوظيفة الأساسية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تعدّل أو توسّع العديد من الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android.
تحسينات حصص JobScheduler
اعتبارًا من Android 16، سنعدّل حصة وقت التشغيل المخصّصة لتنفيذ المهام العادية والمستعجلة استنادًا إلى العوامل التالية:
- حزمة التطبيق الاحتياطية التي يندرج فيها التطبيق: في Android 16، سيتم فرض حِزم التطبيقات الاحتياطية النشطة من خلال حصة سخية لوقت التشغيل.
- إذا بدأ تنفيذ المهمة بينما يكون التطبيق في حالة نشطة: في نظام التشغيل Android 16، ستلتزم المهام التي تبدأ أثناء ظهور التطبيق للمستخدم وتستمر بعد أن يصبح التطبيق غير مرئي بحصة وقت تشغيل المهمة.
- إذا كانت المهمة قيد التنفيذ أثناء تشغيل خدمة تعمل في المقدّمة: في Android 16، ستلتزم المهام التي يتم تنفيذها بشكل متزامن مع خدمة تعمل في المقدّمة بحصة وقت تشغيل المهمة. إذا كنت تستخدم المهام لنقل البيانات التي يبدأها المستخدم، ننصحك باستخدام مهام نقل البيانات التي يبدأها المستخدم بدلاً من ذلك.
يؤثّر هذا التغيير في المهام المُجدوَلة باستخدام WorkManager وJobScheduler وDownloadManager. لتحديد سبب إيقاف مهمة، ننصح بتسجيل سبب إيقاف مهمتك من خلال استدعاء WorkInfo.getStopReason() (بالنسبة إلى مهام JobScheduler، استدعِ JobParameters.getStopReason()).
للحصول على معلومات حول كيفية تأثير حالة تطبيقك في الموارد التي يمكنه استخدامها، اطّلِع على حدود موارد إدارة الطاقة. لمزيد من المعلومات حول أفضل الممارسات المتعلقة بتحسين استهلاك البطارية، يُرجى الرجوع إلى الإرشادات حول تحسين استخدام البطارية لواجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بجدولة المهام.
ننصحك أيضًا بالاستفادة من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory التي تم طرحها في Android 16 لمعرفة سبب عدم تنفيذ مهمة.
الاختبار
لاختبار سلوك تطبيقك، يمكنك تفعيل إلغاء بعض تحسينات حصة المهام طالما أنّ التطبيق يعمل على جهاز Android 16.
لإيقاف فرض "الالتزام بحصة وقت التشغيل المخصّصة للوظيفة"، نفِّذ الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
لإيقاف فرض "المهام التي يتم تنفيذها بشكل متزامن مع خدمة تعمل في المقدّمة ستلتزم بحصة وقت تشغيل المهمة"، شغِّل الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
لاختبار سلوك معيّن لحزمة التطبيق في وضع الاستعداد، يمكنك ضبط حزمة التطبيق في وضع الاستعداد باستخدام الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
لمعرفة فئة وضع الاستعداد التي يندرج فيها تطبيقك، يمكنك الحصول على فئة وضع الاستعداد لتطبيقك باستخدام الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
سبب إيقاف المهام الفارغة التي تم التخلي عنها
تحدث المهمة المهجورة عندما يتم جمع المهملات من عنصر JobParameters المرتبط بالمهمة
، ولكن لم يتم استدعاء JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) للإشارة إلى اكتمال المهمة. يشير ذلك إلى أنّه
قد يكون المهام قيد التشغيل ويتم إعادة جدولتها بدون علم التطبيق.
لا تحافظ التطبيقات التي تعتمد على JobScheduler على إشارة قوية إلى ملف برمجي
JobParameters، وسيتم الآن منح مهلة سبب إيقاف المهمة الجديد
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED بدلاً من STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
إذا تكرّر سبب الإيقاف الجديد، سيتّخذ النظام خطوات لتخفيف المشكلة من خلال تقليل تكرار المهام.
على التطبيقات استخدام سبب الإيقاف الجديد لرصد المهام المتوقفة عن العمل والحدّ منها.
إذا كنت تستخدم WorkManager أو AsyncTask أو DownloadManager، لن تتأثر بهذه التغييرات، لأنّ واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه تدير دورة حياة المهام نيابةً عن تطبيقك.
إيقاف JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground نهائيًا
تشير طريقة JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
إلى أهمية إحدى المهام عندما يكون تطبيق تحديد الموعد في
المقدّمة أو عندما يتم إعفاؤه مؤقتًا من القيود المفروضة على التطبيقات التي تعمل في الخلفية.
تم إيقاف هذه الطريقة نهائيًا منذ الإصدار 12 من Android (المستوى 31 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات). اعتبارًا من الإصدار Android 16، لم تعُد هذه الطريقة تعمل بفعالية، وسيتم تجاهل استدعاء هذه الطريقة.
تنطبق إزالة هذه الوظيفة أيضًا على
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). بدءًا من الإصدار Android
16، إذا تم استدعاء الطريقة، ستُرجع الطريقة false.
لم يعُد نطاق أولوية البث المنظَّم عامًا
يُسمح لتطبيقات Android بتحديد الأولويات في أجهزة استقبال البث للتحكّم في
الترتيب الذي تتلقّى به أجهزة الاستقبال البث وتعالجه. بالنسبة إلى تطبيقات معالجة الإشعارات المُعلَن عنها في البيان، يمكنها استخدام السمة
android:priority لتحديد الأولوية، وبالنسبة إلى تطبيقات معالجة الإشعارات المسجَّلة في السياق، يمكنها استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
IntentFilter#setPriority() لتحديد الأولوية. عند إرسال بث، يرسله النظام إلى المستلِمين حسب تصاعد
أولويتهم، من الأعلى إلى الأدنى.
في الإصدار Android 16، لن يتم ضمان ترتيب إرسال البث باستخدام سمة android:priority
أو IntentFilter#setPriority() في عمليات مختلفة. سيتم الالتزام بأولويات البث فقط في عملية التقديم نفسها وليس في جميع العمليات.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، سيتم تلقائيًا حصر أولويات البث في النطاق (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1،
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). سيتم السماح فقط لمكونات النظام
بضبط SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY وSYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY كأولوية
البث.
قد يتأثر تطبيقك إذا كان ينفّذ أيًا مما يلي:
- أعلن تطبيقك عن عمليات متعدّدة باستخدام نية البث نفسها، ولديه توقّعات بشأن تلقّي هذه النوايا بترتيب معين استنادًا إلى الأولوية.
- تتفاعل عملية تقديم الطلب مع عمليات أخرى وتتوقّع تلقّي نية بثّ بترتيب معيّن.
إذا كانت العمليات بحاجة إلى التنسيق مع بعضها، يجب أن تتواصل باستخدام قنوات تنسيق أخرى.
التغييرات الداخلية في ART
يتضمّن Android 16 أحدث التحديثات لنظام التشغيل Android Runtime (ART) التي تحسِّن أداء Android Runtime (ART) وتوفّر دعمًا لمزيد من ميزات Java. من خلال تحديثات نظام Google Play، تصبح هذه التحسينات متوفرة أيضًا لـ أكثر من مليار جهاز يعمل بالإصدار 12 من نظام Android (المستوى 31 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث.
عند طرح هذه التغييرات، قد لا تعمل المكتبات ورموز التطبيقات التي تعتمد على البنى الداخلية لـ ART بشكل صحيح على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 16 من Android، بالإضافة إلى إصدارات Android الأقدم التي تعمل على تحديث وحدة ART من خلال تحديثات نظام Google Play.
يمكن أن يؤدي الاعتماد على البنى الداخلية (مثل واجهات غير حِزم تطوير البرامج (SDK)) دائمًا إلى مشاكل في التوافق، ولكن من المهم بشكل خاص تجنُّب الاعتماد على الرموز البرمجية (أو المكتبات التي تحتوي على رموز برمجية) التي تستفيد من بنى ART الداخلية، لأنّ تغييرات ART لا تكون مرتبطة بإصدار النظام الذي يعمل عليه الجهاز وتصل إلى أكثر من مليار جهاز من خلال تحديثات نظام Google Play.
على جميع المطوّرين التحقّق مما إذا كان تطبيقاتهم متأثرة من خلال اختبارها بدقة على Android 16. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكنك الاطّلاع على المشاكل المعروفة لتحديد ما إذا كان تطبيقك يعتمد على أي مكتبات رصدناها تعتمد بدورها على بنى ART الداخلية. إذا كان لديك رموز برمجية للتطبيقات أو مكتبات متأثرة ، ابحث عن بدائل لواجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتاحة للجميع كلما أمكن ذلك واطلِب واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتاحة للجميع لحالات الاستخدام الجديدة من خلال إنشاء طلب ميزة في أداة تتبُّع الصعوبات.
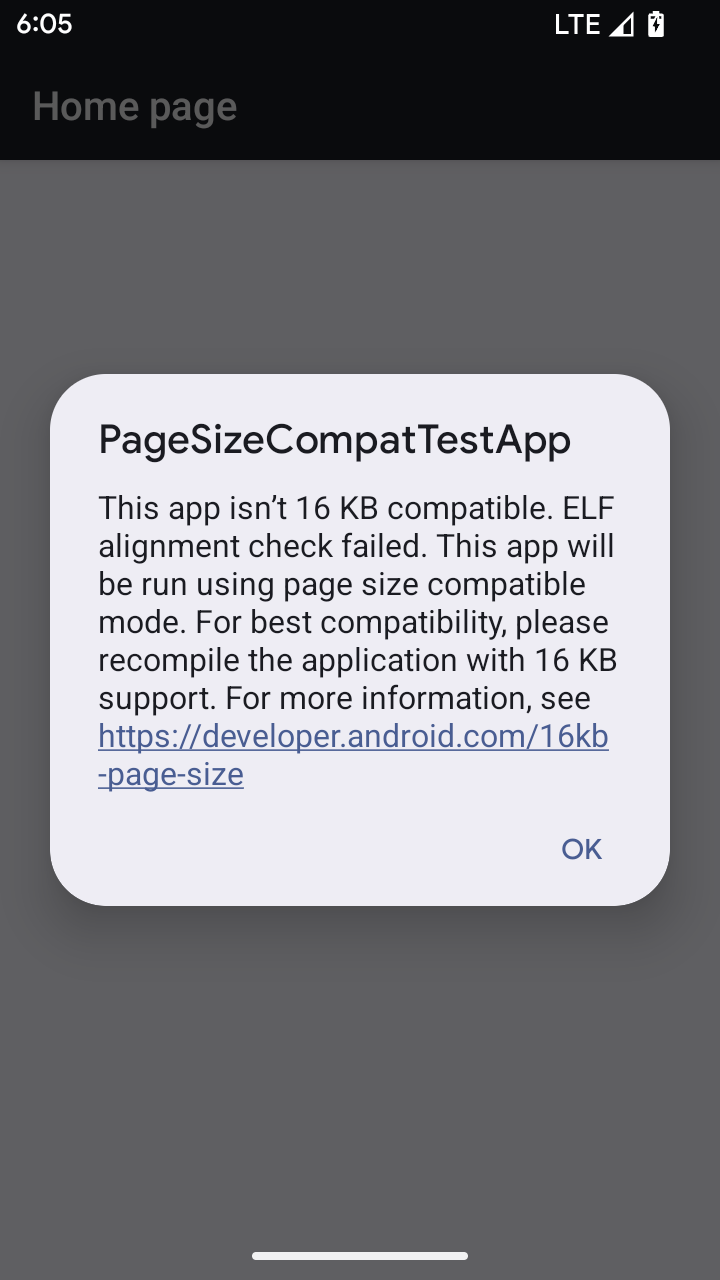
وضع التوافق مع حجم الصفحة البالغ 16 كيلوبايت
وفّر الإصدار 15 من Android إمكانية استخدام صفحات ذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت لتحسين أداء المنصة. يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android وضع ملف شخصي متوافقًا، ما يسمح بتشغيل بعض التطبيقات المُنشأة لصفحات ذاكرة بحجم 4 كيلوبايت على جهاز تم ضبطه لصفحات ذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت.
عندما يكون تطبيقك قيد التشغيل على جهاز يعمل بنظام Android 16 أو إصدار أحدث، إذا رصد نظام Android أنّ تطبيقك يحتوي على صفحات ذاكرة بحجم 4 كيلوبايت، سيستخدم تلقائيًا وضع التوافق ويعرض مربّع حوار إشعار للمستخدم. سيؤدي ضبط سمة
android:pageSizeCompat في AndroidManifest.xml لتفعيل
وضع التوافق مع الإصدارات القديمة إلى منع عرض مربّع الحوار عند
تشغيل تطبيقك. لاستخدام السمة android:pageSizeCompat، عليك تجميع تطبيقك
باستخدام حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) لنظام التشغيل Android 16.
لتحقيق أفضل أداء وموثوقية وثبات، يجب أن يظل تطبيقك متوافقًا مع حجم الصفحة الذي يبلغ 16 كيلوبايت. يمكنك الاطّلاع على مزيد من التفاصيل في مقالتنا الأخيرة في المدونة التي تتناول تحديث تطبيقاتك لتتوافق مع صفحات الذاكرة التي تبلغ سعة كل منها 16 كيلوبايت.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تهدف إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر اتساقًا وسهولة.
إيقاف الإشعارات الخطيرة المتعلّقة بإمكانية الوصول نهائيًا
يوقف نظام التشغيل Android 16 نهائيًا إعلانات تسهيل الاستخدام التي تتميز باستخدام
announceForAccessibility أو إرسال
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT أحداث تسهيل الاستخدام. ويمكن أن تؤدي هذه العناصر إلى اختلاف تجربتَي المستخدمين في TalkBack وقارئ شاشة Android،
وتعمل العناصر البديلة بشكل أفضل على تلبية مجموعة أوسع من احتياجات المستخدمين في مجموعة متنوعة من
التكنولوجيات المساعِدة في Android.
أمثلة على الحلول البديلة:
- بالنسبة إلى التغييرات المهمة في واجهة المستخدم، مثل التغييرات في النوافذ، استخدِم
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)وsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). في الكتابة، استخدِمModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - لإعلام المستخدم بالتغييرات في واجهة المستخدم المهمة، استخدِم رمز
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). في ميزة "إنشاء"، استخدِم رمزModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. يجب استخدام هذه الإعدادات بقدر معقول، لأنّها قد تؤدي إلى إنشاء إشعارات في كل مرة يتم فيها تعديل أحد "المشاهدات". - لإعلام المستخدمين بالأخطاء، أرسِل
AccessibilityEventمن النوعAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORواضبطAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)، أو استخدِمTextView#setError(CharSequence).
تتضمّن المستندات المرجعية لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات
announceForAccessibility المتوقّفة نهائيًا مزيدًا من التفاصيل حول
البدائل المقترَحة.
إتاحة التنقّل باستخدام ثلاثة أزرار
يتيح نظام Android 16 ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي" في ميزة التنقّل باستخدام 3 أزرار للتطبيقات التي تم نقلها بشكل صحيح إلى ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي". يؤدي الضغط مع الاستمرار على زر الرجوع إلى تشغيل صورة متحركة تنبؤية للرجوع، ما يمنحك معاينة للصفحة التي يؤدي التمرير السريع للخلف إلى عرضها.
ينطبق هذا السلوك على جميع أقسام النظام التي تتيح استخدام الصور المتحركة التنبؤية للرجوع، بما في ذلك الصور المتحركة في النظام (للرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية والتنقّل بين المهام وتنفيذ عدة أنشطة في الوقت نفسه).
رموز تطبيقات مستوحاة من موضوع معيّن تلقائيًا
بدءًا من الإصدار الثاني من Android 16 QPR، يطبّق Android تلقائيًا المظاهر على رموز التطبيقات لتوفير تجربة متسقة على الشاشة الرئيسية. يحدث ذلك إذا لم يوفّر التطبيق رمزًا مستوحى من موضوع معيّن. يمكن للتطبيقات التحكّم في تصميم رمز التطبيق المتوافق مع المظهر من خلال تضمين طبقة أحادية اللون في الرمز التكيّفي ومعاينة الشكل الذي سيبدو عليه رمز التطبيق في استوديو Android.
أشكال الأجهزة
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية للتطبيقات عند عرضها على الشاشات من قِبل مالكي الأجهزة الافتراضية.
تجاهل مالك الجهاز الافتراضي
مالك الجهاز الافتراضي هو تطبيق موثوق به أو لديه امتيازات، وهو ينشئ جهازًا افتراضيًا ويديره. يشغّل مالكو الأجهزة الافتراضية التطبيقات على جهاز افتراضي ثم يعرضونها على شاشة جهاز بعيد، مثل جهاز كمبيوتر شخصي أو جهاز واقع افتراضي أو نظام معلومات وترفيه في السيارة. يكون مالك الجهاز الافتراضي على جهاز محلي، مثل هاتف جوّال.
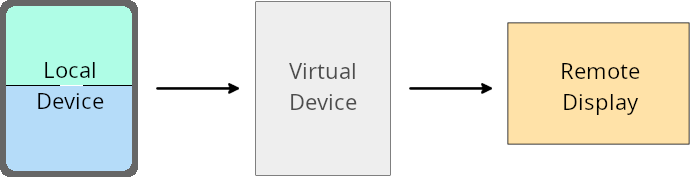
عمليات التجاوز على مستوى التطبيق
على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، يمكن لمالكي الأجهزة الافتراضية إلغاء إعدادات التطبيقات على أجهزة افتراضية محدّدة يديرها مالكو الأجهزة الافتراضية. على سبيل المثال، لتحسين تخطيط التطبيق، يمكن لمالك جهاز افتراضي تجاهل القيود المتعلقة بالاتجاه ونسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع وإمكانية تغيير الحجم عند عرض التطبيقات على شاشة خارجية.
التغييرات الشائعة التي قد تؤدي إلى أعطال
قد يؤثّر سلوك Android 16 في واجهة المستخدم لتطبيقك على أجهزة ذات شاشات كبيرة، مثل شاشات السيارات أو أجهزة Chromebook، خاصةً التصاميم التي تم إنشاؤها لشاشات صغيرة في الوضع العمودي. للتعرّف على كيفية جعل تطبيقك متوافقًا مع جميع أشكال الأجهزة، يمكنك الاطّلاع على لمحة عن التصاميم المتجاوبة.
المراجع
الأمان
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) تغييرات تعزّز أمان النظام للمساعدة في حماية التطبيقات والمستخدمين من التطبيقات الضارة.
تحسين الأمان ضد هجمات إعادة توجيه Intent
يوفر نظام التشغيل Android 16 حماية تلقائية من هجمات إعادة التوجيه العامة Intent، مع الحد الأدنى من التوافق والتغييرات المطلوبة من المطوّرين.
نحن بصدد طرح حلول لتعزيز الأمان بشكل تلقائي بهدف الحماية من استغلال عمليات إعادة التوجيه.Intent في معظم الحالات، لن تواجه التطبيقات التي تستخدم الأهداف أي مشاكل في التوافق، إذ جمعنا مقاييس خلال عملية التطوير لمراقبة التطبيقات التي قد تواجه مشاكل.
تحدث عملية إعادة توجيه Intent في نظام التشغيل Android عندما يتمكّن أحد المهاجمين من التحكّم جزئيًا أو كليًا في محتوى Intent المستخدَم لإطلاق مكوِّن جديد في سياق تطبيق معرَّض للخطر، بينما يطلق تطبيق الضحية Intent غير موثوق به على مستوى فرعي في حقل التطبيقات الإضافية من Intent ("على المستوى الأعلى"). ويمكن أن يؤدي ذلك إلى أن يطلق تطبيق المهاجم مكوّنات خاصة في سياق تطبيق الضحية، أو أن يؤدي إلى تشغيل إجراءات ذات امتيازات، أو الحصول على إذن الوصول إلى بيانات حساسة باستخدام معرّف الموارد الموحّد (URI)، ما قد يؤدي إلى سرقة البيانات وتنفيذ رموز برمجية عشوائية.
إيقاف معالجة إعادة التوجيه المستندة إلى Intent
يقدّم Android 16 واجهة برمجة تطبيقات جديدة تتيح للتطبيقات إيقاف ميزات الحماية الأمنية عند التشغيل. وقد يكون ذلك ضروريًا في حالات معيّنة يتداخل فيها السلوك الأمني التلقائي مع حالات استخدام التطبيق المشروعة.
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي يتم تجميعها باستخدام حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) لنظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأحدث
يمكنك استخدام طريقة removeLaunchSecurityProtection() مباشرةً في عنصر Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي يتم تجميعها باستخدام الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأقدم
مع أنّنا لا ننصح بذلك، يمكنك استخدام الانعكاس للوصول إلى الطريقة removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
لم تعُد التطبيقات المصاحبة تتلقّى إشعارات بانتهاء مهلة البحث عن الأجهزة
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 سلوكًا جديدًا أثناء
عملية إقران الجهاز المصاحب لحماية خصوصية
الموقع الجغرافي للمستخدم من التطبيقات الضارّة. لم يعُد يتم إعلام جميع التطبيقات المصاحبة التي تعمل على الإصدار 16 من Android
بشكل مباشر بوقت الاستراحة في عملية الاكتشاف باستخدام
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. بدلاً من ذلك، يتم إعلام المستخدم
بأحداث انتهاء مهلة باستخدام مربّع حوار مرئي. عندما يغلِق المستخدم
مربّع الحوار، يتم تنبيه التطبيق بتعذُّر الربط بحساب
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
تم أيضًا تمديد مدة البحث من 20 ثانية الأصلية، ويمكن للمستخدم إيقاف اكتشاف الجهاز في أي وقت أثناء البحث. إذا تم العثور على جهاز واحد على الأقل خلال أوّل 20 ثانية من بدء البحث، يتوقف "مدير خدمات الطباعة في السحابة الإلكترونية" عن البحث عن أجهزة إضافية.
إمكانية الاتصال
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية في حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث لتحسين إمكانية الاتصال بالأجهزة الطرفية.
تحسين معالجة فقدان الاتصال
بدءًا من Android 16، تم تعديل حِزمة البلوتوث لتحسين الأمان وتجربة المستخدم عند رصد فقدان الربط عن بُعد. في السابق، كان النظام يزيل الربط تلقائيًا ويُطلق عملية إقران جديدة، ما قد يؤدي إلى إعادة إقران غير مقصودة. لقد لاحظنا في العديد من الحالات أنّ التطبيقات لا تهتم بحدث فقدان الارتباط بطريقة متّسقة.
لتوحيد التجربة، حسّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 معالجة فقدان الربط في النظام. إذا تعذّر مصادقة جهاز بلوتوث سبق ربطه عند إعادة الربط، سيقطع النظام الرابط ويحتفظ بمعلومات الربط المحلية ويعرض مربّع حوار للنظام يُعلم المستخدمين بفقدان الربط ويوجّههم إلى إعادة الإقران.
