Platform Android 16 menyertakan perubahan perilaku yang dapat memengaruhi aplikasi Anda.
Perubahan perilaku berikut berlaku untuk semua aplikasi saat dijalankan di Android 16,
terlepas dari targetSdkVersion. Sebaiknya uji aplikasi Anda, lalu ubah
sesuai kebutuhan untuk mendukung perubahan ini, jika memungkinkan.
Selain itu, pastikan Anda meninjau daftar perubahan perilaku yang hanya memengaruhi aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16.
Fungsi inti
Android 16 (API level 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut yang mengubah atau memperluas berbagai kemampuan inti sistem Android.
Pengoptimalan kuota JobScheduler
Starting in Android 16, we're adjusting regular and expedited job execution runtime quota based on the following factors:
- Which app standby bucket the application is in: in Android 16, active standby buckets will start being enforced by a generous runtime quota.
- If the job starts execution while the app is in a top state: in Android 16, Jobs started while the app is visible to the user and continues after the app becomes invisible, will adhere to the job runtime quota.
- If the job is executing while running a Foreground Service: in Android 16, jobs that are executing while concurrently with a foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota. If you're leveraging jobs for user initiated data transfer, consider using user initiated data transfer jobs instead.
This change impacts tasks scheduled using WorkManager, JobScheduler, and
DownloadManager. To debug why a job was stopped, we recommend logging why your
job was stopped by calling WorkInfo.getStopReason() (for
JobScheduler jobs, call JobParameters.getStopReason()).
For more information on battery-optimal best practices, refer to guidance on optimize battery use for task scheduling APIs.
We also recommend leveraging the new
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API introduced in
Android 16 to understand why a job has not executed.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable override of certain job quota optimizations as long as the app is running on an Android 16 device.
To disable enforcement of "top state will adhere to job runtime quota", run the
following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To disable enforcement of "jobs that are executing while concurrently with a
foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota", run the following
adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To test certain app standby bucket behavior, you can set the app standby bucket
of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
To understand the app standby bucket your app is in, you can get the app standby
bucket of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Alasan penghentian tugas kosong yang ditinggalkan
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
Tidak lagi menggunakan JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground sepenuhnya
The JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
method indicates the importance of a job while the scheduling app is in the
foreground or when temporarily exempted from background restrictions.
This method has been deprecated since Android 12 (API level 31). Starting in Android 16, it no longer functions effectively and calling this method will be ignored.
This removal of functionality also applies to
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). Starting in Android
16, if the method is called, the method returns false.
Cakupan prioritas siaran yang diurutkan tidak lagi bersifat global
Aplikasi Android diizinkan untuk menentukan prioritas pada penerima siaran untuk mengontrol
urutan penerima menerima dan memproses siaran. Untuk
penerima yang dideklarasikan dalam manifes, aplikasi dapat menggunakan
atribut android:priority untuk menentukan prioritas dan untuk
penerima yang terdaftar dalam konteks, aplikasi dapat menggunakan
IntentFilter#setPriority() API untuk menentukan prioritas. Saat
siaran dikirim, sistem akan mengirimkannya ke penerima sesuai urutan
prioritasnya, dari yang tertinggi ke yang terendah.
Di Android 16, urutan pengiriman siaran menggunakan atribut android:priority
atau IntentFilter#setPriority() di berbagai proses tidak akan
dijamin. Prioritas siaran hanya akan dihormati dalam proses
aplikasi yang sama, bukan di semua proses.
Selain itu, prioritas siaran akan otomatis dibatasi pada rentang
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Hanya komponen sistem yang akan
diizinkan untuk menetapkan SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY sebagai
prioritas siaran.
Aplikasi Anda mungkin terpengaruh jika melakukan salah satu hal berikut:
- Aplikasi Anda telah mendeklarasikan beberapa proses dengan intent siaran yang sama, dan memiliki ekspektasi seputar penerimaan intent tersebut dalam urutan tertentu berdasarkan prioritas.
- Proses aplikasi Anda berinteraksi dengan proses lain dan memiliki ekspektasi tentang menerima intent siaran dalam urutan tertentu.
Jika proses perlu berkoordinasi satu sama lain, proses tersebut harus berkomunikasi menggunakan saluran koordinasi lain.
Perubahan internal ART
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
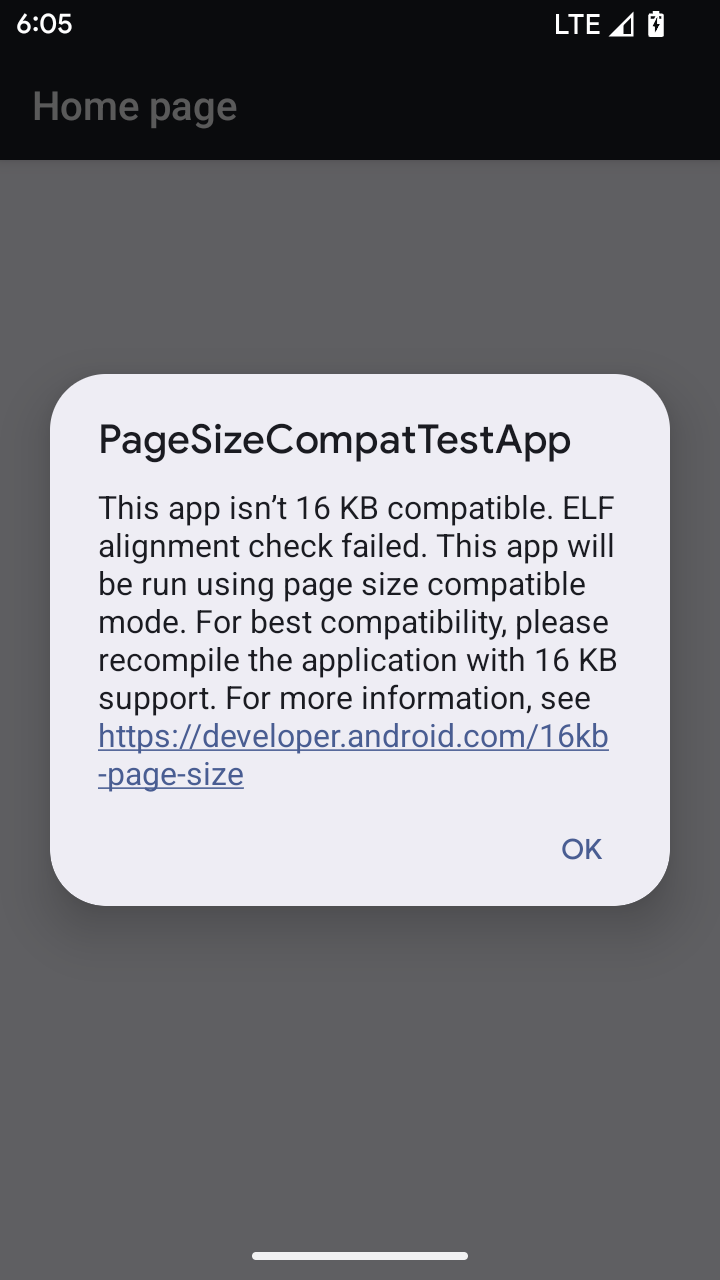
Mode kompatibilitas ukuran halaman 16 KB
Android 15 memperkenalkan dukungan untuk halaman memori 16 KB guna mengoptimalkan performa platform. Android 16 menambahkan mode kompatibilitas, yang memungkinkan beberapa aplikasi yang di-build untuk halaman memori 4 KB berjalan di perangkat yang dikonfigurasi untuk halaman memori 16 KB.
Saat aplikasi Anda berjalan di perangkat dengan Android 16 atau yang lebih tinggi, jika Android
mendeteksi bahwa aplikasi Anda memiliki halaman memori yang diselaraskan 4 KB, aplikasi akan otomatis menggunakan
mode kompatibilitas dan menampilkan dialog notifikasi kepada pengguna. Menetapkan
properti android:pageSizeCompat di AndroidManifest.xml untuk mengaktifkan
mode kompatibilitas mundur akan mencegah tampilan dialog saat
aplikasi diluncurkan. Untuk menggunakan properti android:pageSizeCompat, kompilasi aplikasi Anda
menggunakan Android 16 SDK.
Untuk performa, keandalan, dan stabilitas terbaik, aplikasi Anda harus tetap selaras dengan 16 KB. Lihat postingan blog terbaru kami tentang mengupdate aplikasi Anda untuk mendukung halaman memori 16 KB guna mengetahui detail selengkapnya.
Pengalaman pengguna dan UI sistem
Android 16 (API level 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut yang dimaksudkan untuk menciptakan pengalaman pengguna yang lebih konsisten dan intuitif.
Penghentian pengumuman aksesibilitas yang mengganggu
Android 16 deprecates accessibility announcements, characterized by the use of
announceForAccessibility or the dispatch of
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT accessibility events. These can create
inconsistent user experiences for users of TalkBack and Android's screen reader,
and alternatives better serve a broader range of user needs across a variety of
Android's assistive technologies.
Examples of alternatives:
- For significant UI changes like window changes, use
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)andsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - To inform the user of changes to critical UI, use
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. These should be used sparingly as they may generate announcements every time a View is updated. - To notify users about errors, send an
AccessibilityEventof typeAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORand setAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), or useTextView#setError(CharSequence).
The reference documentation for the deprecated
announceForAccessibility API includes more details about
suggested alternatives.
Dukungan untuk navigasi 3 tombol
Android 16 menghadirkan dukungan kembali prediktif ke navigasi 3 tombol untuk aplikasi yang telah dimigrasikan dengan benar ke kembali prediktif. Menekan lama tombol kembali akan memulai animasi kembali prediktif, yang memberi Anda pratinjau tempat geser kembali akan membawa Anda.
Perilaku ini berlaku di semua area sistem yang mendukung animasi kembali prediktif, termasuk animasi sistem (kembali ke layar utama, lintas tugas, dan lintas aktivitas).
Faktor bentuk perangkat
Android 16 (API level 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut untuk aplikasi saat diproyeksikan ke layar oleh pemilik perangkat virtual.
Penggantian pemilik perangkat virtual
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that creates and manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners run apps on a virtual device and then project the apps to the display of a remote device, such as a personal computer, virtual reality device, or car infotainment system. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a mobile phone.
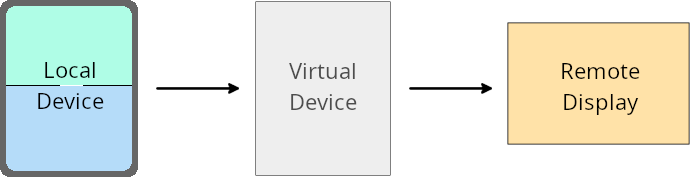
Per-app overrides
On devices running Android 16 (API level 36), virtual device owners can override app settings on select virtual devices that the virtual device owners manage. For example, to improve app layout, a virtual device owner can ignore orientation, aspect ratio, and resizability restrictions when projecting apps onto an external display.
Common breaking changes
The Android 16 behavior might impact your app's UI on large screen form factors such as car displays or Chromebooks, especially layouts that were designed for small displays in portrait orientation. To learn how to make your app adaptive for all device form factors, see About adaptive layouts.
References
Keamanan
Android 16 (API level 36) menyertakan perubahan yang meningkatkan keamanan sistem untuk membantu melindungi aplikasi dan pengguna dari aplikasi berbahaya.
Peningkatan keamanan terhadap serangan pengalihan Intent
Android 16 provides default security against general Intent redirection
attacks, with minimum compatibility and developer changes required.
We are introducing by-default security hardening solutions to Intent
redirection exploits. In most cases, apps that use intents normally won't
experience any compatibility issues; we've gathered metrics throughout our
development process to monitor which apps might experience breakages.
Intent redirection in Android occurs when an attacker can partly or fully control the contents of an intent used to launch a new component in the context of a vulnerable app, while the victim app launches an untrusted sub-level intent in an extras field of an ("top-level") Intent. This can lead to the attacker app launching private components in the context of the victim app, triggering privileged actions, or gaining URI access to sensitive data, potentially leading to data theft and arbitrary code execution.
Opt out of Intent redirection handling
Android 16 introduces a new API that allows apps to opt out of launch security protections. This might be necessary in specific cases where the default security behavior interferes with legitimate app use cases.
For applications compiling against Android 16 (API level 36) SDK or higher
You can directly use the removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method on the Intent
object.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
For applications compiling against Android 15 (API level 35) or lower
While not recommended, you can use reflection to access the
removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Konektivitas
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut dalam stack Bluetooth untuk meningkatkan konektivitas dengan perangkat periferal.
Peningkatan penanganan kerugian obligasi
Mulai Android 16, stack Bluetooth telah diupdate untuk meningkatkan keamanan dan pengalaman pengguna saat kehilangan ikatan jarak jauh terdeteksi. Sebelumnya, sistem akan otomatis menghapus ikatan dan memulai proses penyambungan baru, yang dapat menyebabkan penyambungan ulang yang tidak disengaja. Kami telah melihat dalam banyak kasus aplikasi tidak menangani peristiwa kehilangan ikatan secara konsisten.
Untuk menyatukan pengalaman, Android 16 meningkatkan penanganan kehilangan ikatan ke sistem. Jika perangkat Bluetooth yang sebelumnya tersambung tidak dapat diautentikasi setelah terhubung kembali, sistem akan memutuskan hubungan link, mempertahankan informasi ikatan lokal, dan menampilkan dialog sistem yang memberi tahu pengguna tentang hilangnya ikatan dan mengarahkan mereka untuk menyambungkan kembali.

