Как и в предыдущих версиях, Android 16 включает изменения в поведении, которые могут повлиять на ваше приложение. Следующие изменения в поведении применяются исключительно к приложениям, ориентированным на Android 16 или выше. Если ваше приложение ориентировано на Android 16 или выше, вам следует внести в него изменения для поддержки этих изменений, где это применимо.
Обязательно ознакомьтесь также со списком изменений в поведении, которые затрагивают все приложения, работающие на Android 16, независимо от targetSdkVersion вашего приложения.
Пользовательский опыт и пользовательский интерфейс системы
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения, призванные обеспечить более согласованный и интуитивно понятный пользовательский интерфейс.
Возможность отказа от участия на всех этапах исчезает.
В Android 15 для приложений, ориентированных на Android 15 (уровень API 35), принудительно используется режим отображения от края до края экрана , но ваше приложение может отказаться от него, установив R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement в значение true . Для приложений, ориентированных на Android 16 (уровень API 36), R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement устарел и отключен, и ваше приложение не может отказаться от режима отображения от края до края экрана.
- Если ваше приложение ориентировано на Android 16 (уровень API 36) и работает на устройстве с Android 15,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementпродолжает работать. - Если ваше приложение ориентировано на Android 16 (уровень API 36) и работает на устройстве Android 16,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementбудет отключен.
Для тестирования на Android 16 убедитесь, что ваше приложение поддерживает режим «от края до края», и удалите любое использование R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement , чтобы ваше приложение также поддерживало режим «от края до края» на устройстве Android 15. Для поддержки режима «от края до края» см. руководство по Compose и Views .
Для использования функции прогнозирования требуется миграция или отказ от нее.
Для приложений, ориентированных на Android 16 (уровень API 36) или выше и работающих на устройствах с Android 16 или выше, предиктивные анимации возврата (возврат на главный экран, межзадачные и межактивные) включены по умолчанию. Кроме того, onBackPressed больше не вызывается, и KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK больше не отправляется.
Если ваше приложение перехватывает событие «Назад», и вы еще не перешли на предиктивную навигацию «Назад», обновите приложение, чтобы использовать поддерживаемые API навигации «Назад» , или временно отключите эту функцию, установив атрибут android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback в значение false в теге <application> или <activity> файла AndroidManifest.xml вашего приложения.
API-интерфейсы Elegant Font устарели и отключены.
В приложениях для Android 15 (уровень API 35) атрибут elegantTextHeight TextView по умолчанию установлен в true , что заменяет компактный шрифт на более читабельный. Вы можете переопределить это, установив атрибут elegantTextHeight в false .
В Android 16 атрибут elegantTextHeight устарел, и он будет игнорироваться, как только ваше приложение перейдет на Android 16. Поддержка «шрифтов пользовательского интерфейса», контролируемых этими API, прекращается, поэтому вам следует адаптировать все макеты для обеспечения единообразного и перспективного отображения текста на арабском, лаосском, мьянманском, тамильском, гуджарати, каннада, малаялам, ория, телугу и тайском языках.
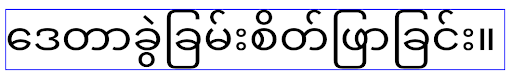
elegantTextHeight для приложений, ориентированных на Android 14 (уровень API 34) и ниже, или для приложений, ориентированных на Android 15 (уровень API 35), которые переопределяют значение по умолчанию, устанавливая атрибут elegantTextHeight в false . 
elegantTextHeight для приложений, ориентированных на Android 16 (уровень API 36), или для приложений, ориентированных на Android 15 (уровень API 35), которые не переопределяют значение по умолчанию путем установки атрибута elegantTextHeight в false .Основная функциональность
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения, которые модифицируют или расширяют различные основные возможности системы Android.
Оптимизация планирования работ по фиксированной ставке
До ориентации на Android 16, когда scheduleAtFixedRate пропускало выполнение задачи из-за того, что оно находилось за пределами допустимого жизненного цикла процесса , все пропущенные выполнения выполнялись немедленно, когда приложение возвращалось к допустимому жизненному циклу.
При настройке Android 16 не более одного пропущенного выполнения scheduleAtFixedRate выполняется немедленно, когда приложение возвращается к допустимому жизненному циклу. Ожидается, что это изменение поведения улучшит производительность приложения. Проверьте это поведение в своем приложении, чтобы проверить, не затронуто ли оно ваше приложение. Вы также можете протестировать, используя платформу совместимости приложений и включив флаг совместимости STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS .
форм-факторы устройств
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения для приложений при отображении на устройствах с большими экранами.
Адаптивные макеты
В условиях, когда приложения для Android работают на самых разных устройствах (таких как телефоны, планшеты, складные устройства, настольные компьютеры, автомобили и телевизоры) и доступны оконные режимы на больших экранах (например, разделенный экран и оконный режим рабочего стола), разработчикам следует создавать приложения для Android, которые адаптируются к любому размеру экрана и окна, независимо от ориентации устройства. Такие парадигмы, как ограничение ориентации и возможности изменения размера, слишком ограничительны в современном мире, где используется множество устройств.
Игнорируйте ограничения по ориентации, изменению размера и соотношению сторон.
Для приложений, ориентированных на Android 16 (уровень API 36), ограничения по ориентации, изменению размера и соотношению сторон больше не применяются на дисплеях с минимальной шириной >= 600dp. Приложения заполняют все окно дисплея независимо от соотношения сторон или предпочтительной ориентации пользователя, и черные полосы по бокам (pillarboxing) не используются.
Это изменение вводит новый стандарт поведения платформы. Android движется к модели , в которой от приложений ожидается адаптация к различным ориентациям экрана, размерам дисплея и соотношениям сторон. Ограничения, такие как фиксированная ориентация или ограниченная возможность изменения размера, препятствуют адаптивности приложений. Сделайте ваше приложение адаптивным, чтобы обеспечить наилучший пользовательский опыт.
Вы также можете проверить это поведение, используя фреймворк совместимости приложений и включив флаг совместимости UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT .
Распространенные изменения, нарушающие обратную связь
Игнорирование ограничений по ориентации, масштабируемости и соотношению сторон может повлиять на пользовательский интерфейс вашего приложения на некоторых устройствах, особенно на элементы, разработанные для небольших макетов, заблокированных в портретной ориентации: например, могут возникнуть проблемы с растянутыми макетами, анимацией и компонентами, выходящими за пределы экрана. Любые предположения о соотношении сторон или ориентации могут вызвать визуальные проблемы в вашем приложении. Узнайте больше о том, как избежать их и улучшить адаптивное поведение вашего приложения.
Разрешение поворота устройства приводит к более частому повторному созданию активности, что может привести к потере состояния пользователя, если оно не будет должным образом сохранено. Узнайте, как правильно сохранять состояние пользовательского интерфейса в разделе «Сохранение состояний пользовательского интерфейса» .
Детали реализации
Следующие атрибуты манифеста и API среды выполнения игнорируются на устройствах с большими экранами в полноэкранном и многооконном режимах:
-
screenOrientation -
resizableActivity -
minAspectRatio -
maxAspectRatio -
setRequestedOrientation() -
getRequestedOrientation()
Следующие значения для screenOrientation , setRequestedOrientation() и getRequestedOrientation() игнорируются:
-
portrait -
reversePortrait -
sensorPortrait -
userPortrait -
landscape -
reverseLandscape -
sensorLandscape -
userLandscape
Что касается возможности изменения размера экрана, android:resizeableActivity="false" , android:minAspectRatio и android:maxAspectRatio не оказывают никакого эффекта.
Для приложений, ориентированных на Android 16 (уровень API 36), ограничения по ориентации, изменению размера и соотношению сторон приложения по умолчанию игнорируются на больших экранах, но любое приложение, которое еще не полностью готово, может временно изменить это поведение, отказавшись от него (что приводит к предыдущему поведению — переходу в режим совместимости).
Исключения
Ограничения Android 16 на ориентацию, изменение размера и соотношение сторон не применяются в следующих ситуациях:
- Игры (на основе флага
android:appCategory) - Пользователи явно соглашаются на поведение приложения по умолчанию в настройках соотношения сторон устройства.
- Экраны меньше, чем
sw600dp
Временно отказаться от участия
Чтобы отказаться от выполнения определенного действия, объявите свойство манифеста PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY :
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
Если слишком много частей вашего приложения не готовы к Android 16, вы можете полностью отказаться от их поддержки, применив то же свойство на уровне приложения:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Здоровье и фитнес
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения, касающиеся данных о здоровье и физической активности.
Разрешения на занятия спортом и поддержание физической формы
Для приложений, ориентированных на Android 16 (уровень API 36) или выше, разрешения BODY_SENSORS используют более детальные разрешения в рамках android.permissions.health , которые также используются в Health Connect . Начиная с Android 16, любой API, ранее требувший BODY_SENSORS или BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND теперь требует соответствующего разрешения android.permissions.health . Это затрагивает следующие типы данных, API и типы служб переднего плана:
-
HEART_RATE_BPMиз раздела «Медицинские услуги» на Wear OS. -
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEиз Android Sensor Manager -
heartRateAccuracyиheartRateBpmизProtoLayoutна Wear OS -
FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH, где вместоBODY_SENSORSтребуется соответствующее разрешениеandroid.permission.health
Если ваше приложение использует эти API, оно должно запросить соответствующие детализированные разрешения:
- Для мониторинга частоты сердечных сокращений, уровня насыщения крови кислородом (SpO2) или температуры кожи во время использования: запросите более детальное разрешение в файле
android.permissions.health, например,READ_HEART_RATEвместоBODY_SENSORS. - Для доступа к датчикам в фоновом режиме: вместо
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDиспользуйтеREAD_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND.
Эти разрешения аналогичны тем, которые защищают доступ к чтению данных из Health Connect , хранилища данных Android, содержащего информацию о здоровье, фитнесе и самочувствии.
Мобильные приложения
Мобильные приложения, переходящие на использование разрешения READ_HEART_RATE и других детализированных разрешений, также должны объявить об активности для отображения политики конфиденциальности приложения. Это то же самое требование, что и в Health Connect.
Подключение
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения в стек Bluetooth для улучшения связи с периферийными устройствами.
Новые намерения по обработке убытков по облигациям и изменения в шифровании
В рамках улучшенной обработки потери облигаций в Android 16 также представлены 2 новых намерения, которые предоставляют приложениям более подробную информацию об изменениях в потере облигаций и шифровании.
Приложения для Android 16 теперь могут:
- Получать намерение
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGпри обнаружении удаленной потери связи, что позволяет им предоставлять более информативную обратную связь пользователю и предпринимать соответствующие действия. - Получайте намерение
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEвсякий раз, когда изменяется статус шифрования ссылки. Это включает изменение статуса шифрования, изменение алгоритма шифрования и изменение размера ключа шифрования. Приложения должны считать связь восстановленной, если ссылка успешно зашифрована при получении намеренияACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEпозже.
Адаптация к различным реализациям OEM
Хотя Android 16 представляет эти новые намерения, их реализация и трансляция могут различаться у разных производителей устройств (OEM). Чтобы гарантировать, что ваше приложение обеспечивает единообразный и надежный опыт на всех устройствах, разработчикам следует разработать обработку потери связи, чтобы изящно адаптироваться к этим потенциальным изменениям.
Мы рекомендуем следующее поведение приложения:
Если транслируется намерение
ACTION_KEY_MISSING:Система отключит соединение ACL (асинхронное соединение без установления соединения), но информация о соединении для устройства будет сохранена (как описано здесь ).
Ваше приложение должно использовать это намерение в качестве основного сигнала для обнаружения потери связи и предоставления пользователю указания подтвердить, что удаленное устройство находится в зоне действия, прежде чем инициировать процедуру забывания устройства или его повторного сопряжения.
Если устройство отключается после получения
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, вашему приложению следует с осторожностью выполнять повторное подключение, поскольку устройство может быть больше не связано с системой.Если намерение
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGНЕ транслируется:Ссылка ACL останется подключенной, а информация о связи для устройства будет удалена системой, аналогично поведению в Android 15.
В этом случае ваше приложение должно продолжать использовать существующие механизмы обработки потерь облигаций, как и в предыдущих версиях Android, для обнаружения и управления событиями потери облигаций.
Новый способ устранения проблемы с Bluetooth.
Все приложения, ориентированные на Android 16, теперь могут отключать сопряжение устройств Bluetooth с помощью общедоступного API в CompanionDeviceManager . Если сопутствующее устройство управляется как ассоциация CDM, то приложение может инициировать удаление связи Bluetooth с помощью нового API removeBond(int) на связанном устройстве. Приложение может отслеживать изменения состояния связи, прослушивая событие широковещательной передачи устройства Bluetooth ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED .
Безопасность
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения в систему безопасности.
Блокировка версий MediaStore
Для приложений, предназначенных для Android 16 или более поздних версий, MediaStore#getVersion() теперь будет уникальным для каждого приложения. Это исключает идентификацию свойств из строки версии, чтобы предотвратить злоупотребление и использование методов снятия отпечатков пальцев. Приложения не должны делать никаких предположений относительно формата этой версии. Приложения уже должны обрабатывать изменения версий при использовании этого API, и в большинстве случаев им не нужно менять свое текущее поведение, если только разработчик не попытался получить дополнительную информацию, выходящую за рамки предполагаемой области действия этого API.
Более безопасные намерения
Функция Safer Intents — это многоэтапная инициатива в области безопасности, призванная повысить защиту механизма распознавания намерений в Android. Цель состоит в защите приложений от вредоносных действий путем добавления проверок во время обработки намерений и фильтрации намерений, не соответствующих определенным критериям.
В Android 15 эта функция была ориентирована на отправляющее приложение, а в Android 16 управление переходит к принимающему приложению, позволяя разработчикам использовать строгую процедуру разрешения намерений с помощью манифеста приложения.
Внедряются два ключевых изменения:
Явно заданные намерения должны соответствовать фильтру намерений целевого компонента: если намерение явно нацелено на компонент, оно должно соответствовать фильтру намерений этого компонента.
Интенты без указанного действия не могут соответствовать ни одному фильтру интентов: Интенты, у которых не указано действие, не должны обрабатываться ни одним фильтром интентов.
Эти изменения применяются только при участии нескольких приложений и не влияют на обработку намерений в рамках одного приложения.
Влияние
Поскольку эта функция является добровольной, разработчики должны явно включить её в манифесте своего приложения, чтобы она вступила в силу. В результате, влияние этой функции будет ограничено приложениями, разработчики которых:
- Осведомлены о функции «Безопасные намерения» и ее преимуществах.
- Активно внедрять более строгие методы обработки намерений в свои приложения.
Такой подход, предполагающий добровольное участие, минимизирует риск нарушения работы существующих приложений, которые могут полагаться на нынешнее менее безопасное поведение разрешения намерений.
Хотя первоначальное влияние в Android 16 может быть ограниченным, инициатива Safer Intents имеет дорожную карту для более широкого воздействия в будущих версиях Android. План состоит в том, чтобы в конечном итоге сделать строгое разрешение намерений поведением по умолчанию.
Функция Safer Intents потенциально может значительно повысить безопасность экосистемы Android, затруднив использование вредоносными приложениями уязвимостей в механизме разрешения намерений.
Однако переход к системе с возможностью отказа от участия и обязательному применению должен осуществляться тщательно, чтобы устранить потенциальные проблемы совместимости с существующими приложениями.
Выполнение
Разработчикам необходимо явно включить более строгий поиск намерений, используя атрибут intentMatchingFlags в манифесте приложения. Вот пример, где эта функция является необязательной для всего приложения, но отключена/отключена для получателя:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
Подробнее о поддерживаемых флагах:
| Название флага | Описание |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Применяет более строгий контроль соответствия для входящих запросов. |
| никто | Отключает все специальные правила сопоставления для входящих интентов. При указании нескольких флагов конфликтующие значения разрешаются путем отдачи приоритета флагу «none». |
| allowNullAction | Смягчает правила сопоставления, позволяя сопоставлять намерения без действия. Этот флаг используется совместно с "enforceIntentFilter" для достижения определенного поведения. |
Тестирование и отладка
Когда функция принудительного применения включена, приложения должны работать корректно, если вызывающий интент правильно заполнил свой интент. Однако заблокированные интенты будут вызывать предупреждающие сообщения в журнале, такие как "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" и "Access blocked:" с тегом "PackageManager." Это указывает на потенциальную проблему, которая может повлиять на работу приложения и требует внимания.
Фильтр Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
Фильтрация системных вызовов графического процессора
Для повышения безопасности графического процессора Mali, в производственных сборках заблокированы IOCTL-операции Mali GPU, которые устарели или предназначены исключительно для разработки под GPU. Кроме того, использование IOCTL-операций для профилирования GPU ограничено процессом оболочки или отлаживаемыми приложениями. Более подробную информацию о политике на уровне платформы см. в обновлении SAC.
Это изменение затрагивает устройства Pixel, использующие графический процессор Mali (Pixel 6-9). Компания Arm предоставила официальную классификацию своих IOCTL в Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst в своем релизе r54p2 . Этот список будет поддерживаться в будущих версиях драйверов.
Это изменение не затронет поддерживаемые графические API (включая Vulkan и OpenGL) и, как ожидается, не повлияет на разработчиков или существующие приложения. Инструменты профилирования графического процессора, такие как Streamline Performance Analyzer и Android GPU Inspector, останутся без изменений.
Тестирование
Если вы видите сообщение об отказе SELinux, подобное приведенному ниже, вероятно, ваше приложение пострадало от этого изменения:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
Если вашему приложению необходимо использовать заблокированные IOCTL, пожалуйста, сообщите об ошибке и назначьте ответственного за ее исправление по адресу android-partner-security@google.com.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Распространяется ли это изменение политики на всех производителей оригинального оборудования (OEM)? Это изменение будет добровольным, но доступным для любых OEM-производителей, желающих использовать этот метод повышения безопасности. Инструкции по внедрению изменения можно найти в документации по внедрению.
Обязательно ли вносить изменения в код OEM-производителя для реализации этого, или это будет включено в новый релиз AOSP по умолчанию? Изменение на уровне платформы будет включено в новый релиз AOSP по умолчанию. Поставщики могут включить это изменение в свой код, если хотят его применить.
Несут ли производители SoC ответственность за поддержание актуальности списка IOCTL? Например, если в моем устройстве используется графический процессор ARM Mali, нужно ли мне обращаться в ARM по поводу каких-либо изменений? Каждый SoC должен обновлять свой список IOCTL для каждого устройства после выпуска драйверов. Например, ARM обновляет свой опубликованный список IOCTL при обновлении драйверов. Однако производители оборудования должны убедиться, что они включают обновления в свою политику SEPolicy и добавляют любые выбранные пользовательские IOCTL в списки по мере необходимости.
Применяется ли это изменение автоматически ко всем устройствам Pixel, представленным на рынке, или для его применения требуется какое-либо действие со стороны пользователя? Это изменение применяется ко всем устройствам Pixel, представленным на рынке, использующим графический процессор Mali (Pixel 6-9). Для применения этого изменения никаких действий со стороны пользователя не требуется.
Повлияет ли использование этой политики на производительность драйвера ядра? Эта политика была протестирована на графическом процессоре Mali с помощью GFXBench, и никаких измеримых изменений в производительности графического процессора не наблюдалось.
Необходимо ли, чтобы список IOCTL соответствовал текущим версиям драйверов пользовательского пространства и ядра? Да, список разрешенных IOCTL должен быть синхронизирован с IOCTL, поддерживаемыми как драйверами пользовательского пространства, так и драйверами ядра. Если IOCTL в драйвере пользовательского пространства или ядра обновляются, список IOCTL SEPolicy также должен быть обновлен в соответствии с ними.
ARM классифицировала IOCTL как «ограниченные» / «инструментальные», но мы хотим использовать некоторые из них в производственных сценариях и/или запретить другие. Отдельные OEM-производители/SoC несут ответственность за определение классификации используемых ими IOCTL на основе конфигурации своих пользовательских библиотек Mali. Список ARM может помочь в принятии этих решений, но сценарий использования для каждого OEM-производителя/SoC может быть разным.
Конфиденциальность
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения, касающиеся конфиденциальности.
Права доступа в локальной сети
Любое приложение, имеющее разрешение на доступ INTERNET , может получить доступ к устройствам в локальной сети. Это упрощает подключение приложений к локальным устройствам, но также имеет последствия для конфиденциальности, например, формирование «отпечатка пальца» пользователя и использование его в качестве прокси-сервера для определения местоположения.
Проект Local Network Protections направлен на защиту конфиденциальности пользователей путем ограничения доступа к локальной сети с помощью нового механизма разрешений во время выполнения.
План выпуска
Это изменение будет внедрено между двумя релизами: 25-м кварталом 2025 года и 26-м кварталом 2026 года соответственно. Разработчикам крайне важно следовать этим рекомендациям для 25-го квартала 2025 года и делиться отзывами, поскольку эти меры защиты будут внедрены в более позднем релизе Android . Кроме того, им потребуется обновить сценарии, зависящие от неявного доступа к локальной сети, используя следующие рекомендации, и подготовиться к отклонению и аннулированию пользователем нового разрешения.
Влияние
На данном этапе LNP — это функция, требующая добровольного участия, то есть она затронет только те приложения, которые согласятся на её использование. Цель этапа добровольного участия — помочь разработчикам приложений понять, какие части их приложения зависят от неявного доступа к локальной сети, чтобы они могли подготовиться к защите этих разрешений в следующем релизе.
Приложения будут затронуты, если они получают доступ к локальной сети пользователя с помощью следующих способов:
- Прямое или библиотечное использование необработанных сокетов по локальным сетевым адресам (например, протокол обнаружения служб mDNS или SSDP).
- Использование классов уровня фреймворка, которые обращаются к локальной сети (например, NsdManager).
Для передачи данных в локальную сеть и из нее требуются разрешения на доступ к локальной сети. В таблице ниже перечислены некоторые распространенные случаи:
| Низкоуровневое управление сетью приложения | Требуется разрешение для локальной сети. |
|---|---|
| Установление исходящего TCP-соединения | да |
| Приём входящих TCP-соединений | да |
| Отправка UDP-сообщений в одноадресной, многоадресной или широковещательной рассылке. | да |
| Приём входящего UDP-сообщения (одноадресная, многоадресная, широковещательная передача) | да |
Эти ограничения реализованы глубоко в сетевом стеке и, следовательно, применяются ко всем сетевым API . Это включает в себя сокеты, созданные в нативном или управляемом коде, сетевые библиотеки, такие как Cronet и OkHttp, и любые API, реализованные поверх них. Попытка разрешения доступа к службам в локальной сети (т.е. к службам с суффиксом .local) потребует разрешения доступа к локальной сети.
Исключения из вышеуказанных правил:
- Если DNS-сервер устройства находится в локальной сети, то для передачи данных к нему или от него (через порт 53) не требуется разрешение на доступ к локальной сети.
- Приложениям, использующим Output Switcher в качестве встроенного средства выбора, не потребуются разрешения на доступ к локальной сети (более подробная информация появится в 4 квартале 2025 года).
Руководство для разработчиков (с возможностью добровольного участия)
Чтобы включить ограничения локальной сети, выполните следующие действия:
- Прошейте устройство версией прошивки 25Q2 Beta 3 или более поздней.
- Установите тестируемое приложение.
Переключите флаг Appcompat в adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Перезагрузите устройство.
Теперь доступ вашего приложения к локальной сети ограничен, и любая попытка доступа к ней приведет к ошибкам сокета. Если вы используете API, выполняющие операции в локальной сети вне процесса вашего приложения (например, NsdManager), на этапе включения этой функции на них это не повлияет.
Для восстановления доступа необходимо предоставить приложению разрешение на использование NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES .
- Убедитесь, что приложение указывает разрешение
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESв своем манифесте. - Перейдите в Настройки > Приложения > [Название приложения] > Разрешения > Ближайшие устройства > Разрешить .
Теперь доступ вашего приложения к локальной сети должен быть восстановлен, и все ваши сценарии должны работать так же, как и до включения приложения в систему.
После начала применения мер по защите локальной сети, вот как это повлияет на сетевой трафик приложений.
| Разрешение | Исходящий запрос по локальной сети | Исходящий/входящий интернет-запрос | Входящий запрос локальной сети |
|---|---|---|---|
| Предоставленный | Работы | Работы | Работы |
| Не предоставлено | Неудачи | Работы | Неудачи |
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы отключить флаг совместимости приложений.
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Ошибки
Ошибки, возникающие из-за этих ограничений, будут возвращаться вызывающему сокету всякий раз, когда он вызывает функцию send или её вариант для отправки по локальному сетевому адресу.
Примеры ошибок:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Определение локальной сети
В данном проекте под локальной сетью понимается IP-сеть, использующая сетевой интерфейс с возможностью широковещательной передачи, такой как Wi-Fi или Ethernet, но исключающая сотовые (WWAN) или VPN-соединения.
К локальным сетям относятся следующие:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Локальная ссылка
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Локальная ссылка
- Маршруты, имеющие прямое соединение
- Заглушки сетей, такие как Thread
- Несколько подсетей (будет определено позже)
Кроме того, как многоадресные адреса (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8), так и широковещательные адреса IPv4 (255.255.255.255) классифицируются как адреса локальной сети.

