Podobnie jak w przypadku poprzednich wersji, Android 16 wprowadza zmiany w działaniu, które mogą mieć wpływ na Twoją aplikację. Poniższe zmiany dotyczą wyłącznie aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 lub nowszego. Jeśli Twoja aplikacja jest kierowana na Androida 16 lub nowszego, zmodyfikuj ją tak, aby obsługiwała te zachowania w odpowiednich przypadkach.
Zapoznaj się też z listą zmian w zachowaniu, które mają wpływ na wszystkie aplikacje działające na Androidzie 16, niezależnie od targetSdkVersion aplikacji.
Wrażenia użytkowników i interfejs systemu
Android 16 (poziom API 36) zawiera te zmiany, które mają na celu zapewnienie bardziej spójnego i intuicyjnego interfejsu użytkownika.
Wyłączenie wyświetlania bez ramki
Android 15 wymusza wyświetlanie bez ramki w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15 (API na poziomie 35), ale możesz zrezygnować z tej funkcji, ustawiając R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement na true. W przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 (poziom API 36) interfejs R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement jest wycofany i wyłączony, a aplikacja nie może zrezygnować z wyświetlania bez ramki.
- Jeśli Twoja aplikacja jest kierowana na Androida 16 (API na poziomie 36) i działa na urządzeniu z Androidem 15, funkcja
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementnadal działa. - Jeśli Twoja aplikacja jest kierowana na Androida 16 (API na poziomie 36) i działa na urządzeniu z Androidem 16, funkcja
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementjest wyłączona.
Aby przetestować aplikację na Androidzie 16, upewnij się, że obsługuje ona wyświetlanie od krawędzi do krawędzi, i usuń wszystkie wystąpienia R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement, aby aplikacja obsługiwała wyświetlanie od krawędzi do krawędzi również na urządzeniu z Androidem 15. Aby obsługiwać wyświetlanie od krawędzi do krawędzi, zapoznaj się z wytycznymi dotyczącymi Compose i widoków.
Wymagana migracja lub rezygnacja z funkcji przewidywania powrotu
W przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 (API na poziomie 36) lub nowszego i uruchamianych na urządzeniu z Androidem 16 lub nowszym domyślnie włączone są animacje systemowe przewidywanego powrotu (powrót do ekranu głównego, przełączanie między zadaniami i przełączanie między aktywnościami).
Dodatkowo wywołanie onBackPressed i wysyłanie KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK nie są już wykonywane.
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja przechwytuje zdarzenie powrotu i nie została jeszcze przeniesiona do przewidywanego powrotu, zaktualizuj ją, aby korzystała z obsługiwanych interfejsów API nawigacji wstecz, lub tymczasowo zrezygnuj z tej funkcji, ustawiając atrybut android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback na false w tagu <application> lub <activity> w pliku AndroidManifest.xml aplikacji.
Wycofanie i wyłączenie interfejsów API czcionek Elegant
Aplikacje kierowane na Androida 15 (API na poziomie 35) mają atrybut elegantTextHeight
TextView domyślnie ustawiony na true, co powoduje zastąpienie czcionki kompaktowej czcionką znacznie bardziej czytelną. Możesz to zmienić, ustawiając atrybut elegantTextHeight na false.
Android 16 wycofuje atrybut elegantTextHeight. Gdy aplikacja będzie kierowana na Androida 16, atrybut ten będzie ignorowany. Interfejsy API kontrolujące „czcionki interfejsu” zostaną wycofane, więc musisz dostosować układy, aby zapewnić spójne i przyszłościowe renderowanie tekstu w językach arabskim, laotańskim, birmańskim, tamilskim, gudżarati, kannada, malajalam, odia, telugu i tajskim.
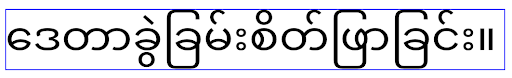
elegantTextHeight w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 14 (API na poziomie 34) lub starszego albo aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15 (API na poziomie 35), które zastąpiły domyślne ustawienie, ustawiając atrybut elegantTextHeight na false.
elegantTextHeight w przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 (API na poziomie 36) lub aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 15 (API na poziomie 35), które nie zastąpiły domyślnego ustawienia atrybutu elegantTextHeight wartością false.Główna funkcja
Android 16 (API na poziomie 36) zawiera te zmiany, które modyfikują lub rozszerzają różne podstawowe funkcje systemu Android.
Optymalizacja harmonogramu pracy przy stałej stawce
Przed kierowaniem na Androida 16, gdy scheduleAtFixedRate
nie udało się wykonać zadania, ponieważ nie było ono dostępne w ramach prawidłowego cyklu życia procesu, wszystkie niewykonane zadania są natychmiast wykonywane, gdy aplikacja wraca do prawidłowego cyklu życia.
W przypadku kierowania na Androida 16 maksymalnie 1 niewykonany wcześniej element scheduleAtFixedRate jest natychmiast wykonywany, gdy aplikacja wraca do prawidłowego cyklu życia. Ta zmiana zachowania powinna poprawić działanie aplikacji. Przetestuj to zachowanie w aplikacji, aby sprawdzić, czy na nią wpływa.
Możesz też przeprowadzić testy za pomocą ramy kompatybilności aplikacji i włączenia flagi zgodności STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS.
Formaty urządzeń
Android 16 (poziom interfejsu API 36) wprowadza te zmiany w aplikacjach wyświetlanych na urządzeniach z dużym ekranem:
Układy adaptacyjne
Aplikacje na Androida działają teraz na wielu różnych urządzeniach (takich jak telefony, tablety, urządzenia składane, komputery, samochody i telewizory) oraz w różnych trybach okien na dużych ekranach (takich jak tryb podzielonego ekranu i tryb okien na pulpicie). Deweloperzy powinni tworzyć aplikacje na Androida, które dostosowują się do dowolnego rozmiaru ekranu i okna, niezależnie od orientacji urządzenia. Paradygmaty takie jak ograniczenie orientacji i możliwości zmiany rozmiaru są zbyt restrykcyjne w dzisiejszym świecie wielu urządzeń.
Ignorowanie ograniczeń dotyczących orientacji, zmiany rozmiaru i współczynnika proporcji
W przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 (API na poziomie 36) ograniczenia dotyczące orientacji, możliwości zmiany rozmiaru i formatu obrazu nie obowiązują już na wyświetlaczach o najmniejszej szerokości ≥ 600 dp. Aplikacje wypełniają całe okno wyświetlania niezależnie od formatu obrazu czy preferowanej orientacji użytkownika. Nie stosuje się efektu pillarboxing.
Ta zmiana wprowadza nowe standardowe działanie platformy. Android zmierza w kierunku modelu, w którym aplikacje powinny dostosowywać się do różnych orientacji, rozmiarów wyświetlacza i proporcji. Ograniczenia takie jak stała orientacja lub ograniczona możliwość zmiany rozmiaru utrudniają dostosowanie aplikacji. Dostosuj aplikację, aby zapewnić użytkownikom jak najlepsze wrażenia.
Możesz też przetestować to zachowanie, korzystając z platformy zgodności aplikacji i włączając flagę zgodności UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT.
Typowe zmiany powodujące niezgodność
Ignorowanie ograniczeń dotyczących orientacji, zmiany rozmiaru i proporcji może mieć wpływ na interfejs aplikacji na niektórych urządzeniach, zwłaszcza na elementy zaprojektowane z myślą o małych układach zablokowanych w orientacji pionowej. Może to powodować problemy takie jak rozciągnięte układy oraz animacje i komponenty poza ekranem. Wszelkie założenia dotyczące proporcji lub orientacji mogą powodować problemy wizualne w aplikacji. Dowiedz się więcej o tym, jak ich unikać i poprawić adaptacyjne działanie aplikacji.
Zezwolenie na obracanie urządzenia powoduje częstsze ponowne tworzenie aktywności, co może prowadzić do utraty stanu użytkownika, jeśli nie zostanie on prawidłowo zachowany. Dowiedz się, jak prawidłowo zapisywać stan interfejsu w sekcji Zapisywanie stanów interfejsu.
Szczegóły implementacji
Na urządzeniach z dużym ekranem w trybie pełnoekranowym i wielookienkowym ignorowane są te atrybuty manifestu i interfejsy API środowiska wykonawczego:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
Te wartości w przypadku screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() i getRequestedOrientation() są ignorowane:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
W przypadku zmiany rozmiaru wyświetlacza elementy android:resizeableActivity="false", android:minAspectRatio i android:maxAspectRatio nie mają wpływu.
W przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 (API na poziomie 36) ograniczenia dotyczące orientacji, możliwości zmiany rozmiaru i formatu obrazu są domyślnie ignorowane na dużych ekranach, ale każda aplikacja, która nie jest w pełni gotowa, może tymczasowo zastąpić to zachowanie, rezygnując z tej funkcji (co spowoduje powrót do poprzedniego zachowania, czyli umieszczenia w trybie zgodności).
Wyjątki
Ograniczenia dotyczące orientacji, zmiany rozmiaru i proporcji w Androidzie 16 nie obowiązują w tych sytuacjach:
- Gry (na podstawie flagi
android:appCategory) - użytkownicy, którzy wyraźnie zgodzili się na domyślne działanie aplikacji w ustawieniach proporcji obrazu na urządzeniu;
- ekrany mniejsze niż
sw600dp,
Tymczasowa rezygnacja
Aby zrezygnować z określonej aktywności, zadeklaruj właściwość manifestu:PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
Jeśli zbyt wiele części aplikacji nie jest gotowych na Androida 16, możesz całkowicie zrezygnować z tej funkcji, stosując tę samą właściwość na poziomie aplikacji:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Zdrowie i fitness
Android 16 (poziom API 36) zawiera te zmiany związane z danymi o zdrowiu i aktywności fizycznej:
Uprawnienia dotyczące zdrowia i aktywności fizycznej
W przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 (API na poziomie 36) lub nowszego uprawnieniaBODY_SENSORS korzystają z bardziej szczegółowych uprawnieńandroid.permissions.health, które są też używane na platformie Health Connect. Od Androida 16 interfejsy API, które wcześniej wymagały uprawnień BODY_SENSORS lub BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND, wymagają teraz odpowiednich uprawnień android.permissions.health. Ma to wpływ na te typy danych, interfejsy API i rodzaje usług działających na pierwszym planie:
HEART_RATE_BPMz usług zdrowotnych na Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEz Menedżera czujników Androida.heartRateAccuracyiheartRateBpmzProtoLayoutna Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH, gdzie zamiastBODY_SENSORSwymagane jest odpowiednie uprawnienieandroid.permission.health.
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja korzysta z tych interfejsów API, powinna prosić o odpowiednie szczegółowe uprawnienia:
- W przypadku monitorowania tętna, SpO2 lub temperatury skóry podczas korzystania z urządzenia:
poproś o szczegółowe uprawnienie w sekcji
android.permissions.health, np.READ_HEART_RATEzamiastBODY_SENSORS. - W przypadku dostępu do czujnika w tle użyj request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDzamiastBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
Są one takie same jak uprawnienia, które chronią dostęp do odczytywania danych z Health Connect, czyli magazynu danych Androida dotyczących zdrowia, aktywności fizycznej i samopoczucia.
Aplikacjach mobilnych
Aplikacje mobilne, które przechodzą na korzystanie z READ_HEART_RATE i innych szczegółowych uprawnień, muszą też zgłosić aktywność, aby wyświetlać politykę prywatności aplikacji. Jest to takie samo wymaganie jak w przypadku Health Connect.
Łączność
Android 16 (poziom API 36) zawiera te zmiany w stosie Bluetootha, które poprawiają łączność z urządzeniami peryferyjnymi:
Nowe intencje do obsługi utraty połączenia i zmian szyfrowania
W ramach ulepszonej obsługi utraty połączenia Android 16 wprowadza 2 nowe intencje, które zwiększają świadomość aplikacji na temat utraty połączenia i zmian szyfrowania.
Aplikacje kierowane na Androida 16 mogą teraz:
- Otrzymywać intencję
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, gdy wykryje utratę połączenia zdalnego, aby móc udzielić użytkownikowi bardziej szczegółowej odpowiedzi i podjąć odpowiednie działania. - Otrzymywać intencję
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEza każdym razem, gdy zmienia się stan szyfrowania linku. Obejmuje to zmianę stanu szyfrowania, zmianę algorytmu szyfrowania i zmianę rozmiaru klucza szyfrowania. Aplikacje muszą uznać, że połączenie zostało przywrócone, jeśli link zostanie zaszyfrowany po otrzymaniu intencjiACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE.
Dostosowanie do różnych implementacji OEM
Chociaż Android 16 wprowadza te nowe intencje, ich implementacja i transmisja mogą się różnić w zależności od producenta urządzenia (OEM). Aby zapewnić spójne i niezawodne działanie aplikacji na wszystkich urządzeniach, deweloperzy powinni zaprojektować obsługę utraty zabezpieczeń w sposób umożliwiający dostosowanie się do tych potencjalnych różnic.
Zalecamy takie zachowanie aplikacji:
Jeśli intencja
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGjest nadawana:System rozłączy połączenie ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less), ale informacje o połączeniu urządzenia zostaną zachowane (jak opisano tutaj).
Aplikacja powinna używać tego zamiaru jako głównego sygnału do wykrywania utraty połączenia i prowadzenia użytkownika przez proces potwierdzania, że urządzenie zdalne znajduje się w zasięgu, zanim rozpocznie się zapominanie urządzenia lub ponowne parowanie.
Jeśli urządzenie rozłączy się po otrzymaniu
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, aplikacja powinna zachować ostrożność podczas ponownego nawiązywania połączenia, ponieważ urządzenie może nie być już połączone z systemem.Jeśli intencja
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGNIE JEST transmitowana:Połączenie ACL pozostanie aktywne, a system usunie informacje o połączeniu urządzenia. To zachowanie jest takie samo jak w Androidzie 15.
W takim przypadku aplikacja powinna nadal używać dotychczasowych mechanizmów obsługi utraty połączenia, tak jak w poprzednich wersjach Androida, aby wykrywać zdarzenia utraty połączenia i nimi zarządzać.
Nowy sposób usuwania powiązania Bluetooth
Wszystkie aplikacje kierowane na Androida 16 mogą teraz odłączać urządzenia Bluetooth za pomocą publicznego interfejsu API w CompanionDeviceManager. Jeśli urządzenie towarzyszące jest zarządzane jako powiązanie CDM, aplikacja może wywołać usunięcie połączenia Bluetooth, używając nowego interfejsu removeBond(int) na powiązanym urządzeniu. Aplikacja może monitorować zmiany stanu połączenia, nasłuchując zdarzenia przesyłania danych z urządzenia Bluetooth ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
Bezpieczeństwo
Android 16 (poziom API 36) zawiera te zmiany dotyczące bezpieczeństwa:
Blokowanie wersji MediaStore
W przypadku aplikacji kierowanych na Androida 16 lub nowszego ciąg MediaStore#getVersion() będzie teraz niepowtarzalny dla każdej aplikacji. Pozwoli to wyeliminować z ciągu wersji właściwości identyfikujące, aby zapobiec nadużyciom i użyciu w ramach technik odciskania palca. Aplikacje nie powinny zakładać niczego w stosunku do formatu tej wersji. Aplikacje powinny już obsługiwać zmiany wersji podczas korzystania z tego interfejsu API i w większości przypadków nie trzeba zmieniać ich bieżącego działania, chyba że deweloper próbował wywnioskować dodatkowe informacje wykraczające poza zamierzony zakres tego interfejsu API.
Bezpieczniejsze intencje
Funkcja Safer Intents to wieloetapowa inicjatywa dotycząca bezpieczeństwa, która ma na celu zwiększenie bezpieczeństwa mechanizmu rozpoznawania intencji w Androidzie. Celem jest ochrona aplikacji przed złośliwymi działaniami przez dodanie kontroli podczas przetwarzania intencji i filtrowanie intencji, które nie spełniają określonych kryteriów.
W Androidzie 15 funkcja ta była skoncentrowana na aplikacji wysyłającej, a w Androidzie 16 przenosi kontrolę na aplikację odbierającą, co pozwala programistom włączyć ścisłe rozpoznawanie intencji za pomocą manifestu aplikacji.
Wprowadzamy 2 kluczowe zmiany:
Intencje bezpośrednie muszą pasować do filtra intencji komponentu docelowego: Jeśli intencja jest kierowana bezpośrednio na komponent, powinna pasować do filtra intencji tego komponentu.
Intencje bez działania nie mogą pasować do żadnego filtra intencji: intencje, które nie mają określonego działania, nie powinny być rozwiązywane w żadnym filtrze intencji.
Te zmiany mają zastosowanie tylko w przypadku wielu aplikacji i nie wpływają na obsługę intencji w ramach jednej aplikacji.
Wpływ
Oznacza to, że deweloperzy muszą jawnie włączyć tę funkcję w pliku manifestu aplikacji, aby zaczęła działać. W związku z tym wpływ tej funkcji będzie ograniczony do aplikacji, których deweloperzy:
- znają funkcję bezpieczniejszych intencji i jej zalety;
- aktywne wdrażanie w aplikacjach bardziej rygorystycznych praktyk obsługi intencji.
Takie podejście minimalizuje ryzyko uszkodzenia istniejących aplikacji, które mogą polegać na obecnym, mniej bezpiecznym sposobie rozpoznawania intencji.
Początkowy wpływ w Androidzie 16 może być ograniczony, ale inicjatywa Safer Intents ma plan działania, który pozwoli na szersze zastosowanie w przyszłych wersjach Androida. Planujemy, że w przyszłości ścisłe rozpoznawanie intencji stanie się domyślnym zachowaniem.
Funkcja bezpieczniejszych intencji może znacznie zwiększyć bezpieczeństwo ekosystemu Androida, ponieważ utrudnia złośliwym aplikacjom wykorzystywanie luk w mechanizmie rozpoznawania intencji.
Przejście na rezygnację i obowiązkowe egzekwowanie musi być jednak starannie zarządzane, aby rozwiązać potencjalne problemy ze zgodnością z istniejącymi aplikacjami.
Implementacja
Deweloperzy muszą wyraźnie włączyć bardziej rygorystyczne dopasowywanie intencji za pomocą atrybutu intentMatchingFlags w pliku manifestu aplikacji.
Oto przykład, w którym funkcja jest opcjonalna w przypadku całej aplikacji, ale wyłączona lub opcjonalna w przypadku odbiornika:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
Więcej informacji o obsługiwanych flagach:
| Nazwa flagi | Opis |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Wymusza bardziej rygorystyczne dopasowywanie przychodzących intencji |
| brak | Wyłącza wszystkie specjalne reguły dopasowywania w przypadku przychodzących intencji. Jeśli podasz kilka flag, sprzeczne wartości zostaną rozwiązane przez nadanie priorytetu fladze „none”. |
| allowNullAction | Zmienia reguły dopasowywania, aby umożliwić dopasowywanie intencji bez działania. Ta flaga jest używana w połączeniu z parametrem „enforceIntentFilter” w celu uzyskania określonego działania. |
Testowanie i debugowanie
Gdy egzekwowanie jest aktywne, aplikacje powinny działać prawidłowo, jeśli wywołujący intencję prawidłowo ją wypełnił.
Zablokowane intencje będą jednak wywoływać komunikaty ostrzegawcze w dzienniku, np. "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" i "Access blocked:"
z tagiem "PackageManager.".
Wskazuje to potencjalny problem, który może mieć wpływ na aplikację i wymaga uwagi.
Filtr Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
Filtrowanie wywołań systemowych GPU
Aby zwiększyć bezpieczeństwo interfejsu GPU Mali, w wersjach produkcyjnych zablokowaliśmy wycofane lub przeznaczone wyłącznie do programowania GPU wywołania IOCTL GPU Mali. Dodatkowo IOCTL używane do profilowania GPU zostały ograniczone do procesu powłoki lub aplikacji, które można debugować. Więcej informacji o zasadach na poziomie platformy znajdziesz w aktualizacji SAC.
Zmiana ta dotyczy urządzeń Pixel z procesorem graficznym Mali (Pixel 6–9). Firma Arm
udostępniła oficjalną klasyfikację swoich IOCTL w Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst wersji r54p2. Ta lista będzie aktualizowana w kolejnych wersjach sterowników.
Ta zmiana nie ma wpływu na obsługiwane interfejsy API grafiki (w tym Vulkan i OpenGL) i nie powinna mieć wpływu na deweloperów ani istniejące aplikacje. Nie ma to wpływu na narzędzia do profilowania GPU, takie jak Streamline Performance Analyzer i Android GPU Inspector.
Testowanie
Jeśli widzisz odmowę SELinux podobną do tej poniżej, prawdopodobnie ta zmiana wpłynęła na Twoją aplikację:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
Jeśli Twoja aplikacja musi używać zablokowanych kodów IOCTL, zgłoś błąd i przypisz go do android-partner-security@google.com.
Najczęstsze pytania
Czy ta zmiana zasad dotyczy wszystkich producentów OEM? Ta zmiana będzie opcjonalna, ale dostępna dla wszystkich producentów OEM, którzy chcą korzystać z tej metody zabezpieczeń. Instrukcje wdrażania zmian znajdziesz w dokumentacji implementacji.
Czy aby wdrożyć tę funkcję, trzeba wprowadzić zmiany w bazie kodu OEM, czy jest ona domyślnie dostępna w nowej wersji AOSP? Zmiana na poziomie platformy będzie domyślnie wprowadzana w nowej wersji AOSP. Jeśli dostawcy chcą zastosować tę zmianę, mogą ją wprowadzić w swoim kodzie.
Czy zespoły ds. SoC odpowiadają za aktualizowanie listy IOCTL? Jeśli na przykład moje urządzenie korzysta z procesora graficznego ARM Mali, czy muszę się skontaktować z firmą ARM w sprawie tych zmian? Poszczególne firmy SoC muszą aktualizować listy IOCTL dla każdego urządzenia po wydaniu sterownika. Na przykład ARM zaktualizuje opublikowaną listę IOCTL po aktualizacji sterowników. Producenci OEM powinni jednak upewnić się, że uwzględnili aktualizacje w swojej polityce SELinux i w razie potrzeby dodali wybrane niestandardowe wywołania IOCTL do list.
Czy ta zmiana zostanie automatycznie zastosowana na wszystkich dostępnych na rynku urządzeniach Pixel, czy też użytkownik musi coś przełączyć, aby ją zastosować? Ta zmiana dotyczy wszystkich urządzeń Pixel dostępnych na rynku, które korzystają z procesora graficznego Mali (Pixel 6–9). Aby zastosować tę zmianę, użytkownik nie musi podejmować żadnych działań.
Czy użycie tej zasady wpłynie na wydajność sterownika jądra? Zasady te zostały przetestowane na procesorze graficznym Mali za pomocą GFXBench i nie zaobserwowano żadnych mierzalnych zmian w wydajności procesora graficznego.
Czy lista IOCTL musi być zgodna z bieżącymi wersjami przestrzeni użytkownika i sterownika jądra? Tak, lista dozwolonych kodów IOCTL musi być zsynchronizowana z kodami IOCTL obsługiwanymi przez sterowniki przestrzeni użytkownika i sterowniki jądra. Jeśli IOCTL w przestrzeni użytkownika lub sterowniku jądra zostaną zaktualizowane, lista IOCTL w SEPolicy musi zostać zaktualizowana, aby była zgodna z tymi zmianami.
Firma ARM sklasyfikowała IOCTL jako „ograniczone” lub „instrumentacyjne”, ale chcemy używać niektórych z nich w przypadkach produkcyjnych lub odmawiać dostępu do innych. Poszczególni producenci OEM/SoC odpowiadają za decyzję o sposobie kategoryzacji używanych przez nich IOCTL na podstawie konfiguracji bibliotek Mali w przestrzeni użytkownika. Lista ARM może pomóc w podjęciu decyzji, ale zastosowanie w przypadku każdego producenta OEM lub SoC może być inne.
Prywatność
Android 16 (poziom API 36) zawiera te zmiany dotyczące prywatności:
Dostęp do sieci lokalnej
Urządzenia w sieci LAN są dostępne dla każdej aplikacji, która ma uprawnienie INTERNET.
Ułatwia to aplikacjom łączenie się z urządzeniami lokalnymi, ale ma też wpływ na prywatność, np. tworzenie odcisku cyfrowego użytkownika i pełnienie funkcji serwera proxy dla lokalizacji.
Projekt Local Network Protections ma na celu ochronę prywatności użytkowników poprzez ograniczenie dostępu do sieci lokalnej za pomocą nowego uprawnienia środowiska wykonawczego.
Plan wydania
Ta zmiana zostanie wprowadzona w 2 wersjach: 25Q2 i 26Q2. Deweloperzy muszą postępować zgodnie z tymi wytycznymi w II kwartale 2025 r. i przesyłać opinie, ponieważ te zabezpieczenia zostaną wprowadzone w późniejszej wersji Androida. Ponadto będą musieli zaktualizować scenariusze, które zależą od domyślnego dostępu do sieci lokalnej, korzystając z tych wskazówek, i przygotować się na odrzucenie przez użytkownika nowych uprawnień lub ich cofnięcie.
Wpływ
Na obecnym etapie LNP jest funkcją, którą można włączyć. Oznacza to, że będzie ona miała wpływ tylko na aplikacje, które ją włączą. Celem fazy wyrażania zgody jest umożliwienie deweloperom aplikacji sprawdzenia, które części ich aplikacji zależą od domyślnego dostępu do sieci lokalnej, aby mogli przygotować się do ochrony tych części w kolejnej wersji.
Aplikacje będą miały wpływ na dostęp do sieci lokalnej użytkownika za pomocą:
- Bezpośrednie lub biblioteczne użycie surowych gniazd na adresach sieci lokalnej (np. protokół wykrywania usług mDNS lub SSDP)
- Używanie klas na poziomie platformy, które mają dostęp do sieci lokalnej (np. NsdManager)
Ruch do i z adresu sieci lokalnej wymaga zgody na dostęp do sieci lokalnej. W tabeli poniżej znajdziesz kilka typowych przypadków:
| Operacja sieciowa niskiego poziomu aplikacji | Wymagany jest dostęp do sieci lokalnej |
|---|---|
| Nawiązywanie wychodzącego połączenia TCP | tak |
| Akceptowanie przychodzących połączeń TCP | tak |
| Wysyłanie transmisji pojedynczej, grupowej lub rozgłoszeniowej UDP | tak |
| Odbieranie przychodzących pakietów UDP unicast, multicast i broadcast | tak |
Te ograniczenia są zaimplementowane głęboko w stosie sieciowym, dlatego dotyczą wszystkich interfejsów API sieci. Dotyczy to gniazd utworzonych w kodzie natywnym lub zarządzanym, bibliotek sieciowych takich jak Cronet i OkHttp oraz wszystkich interfejsów API zaimplementowanych na ich podstawie. Próba rozpoznania usług w sieci lokalnej (czyli tych z sufiksem .local) będzie wymagać uprawnień do sieci lokalnej.
Wyjątki od powyższych reguł:
- Jeśli serwer DNS urządzenia znajduje się w sieci lokalnej, ruch do niego lub z niego (na porcie 53) nie wymaga uprawnień dostępu do sieci lokalnej.
- Aplikacje, które używają przełącznika wyjścia jako selektora w aplikacji, nie będą potrzebować uprawnień do sieci lokalnej (więcej wskazówek pojawi się w IV kwartale 2025 r.).
Wskazówki dla programistów (włącz)
Aby włączyć ograniczenia dotyczące sieci lokalnej, wykonaj te czynności:
- Wgraj na urządzenie kompilację w wersji 25Q2 Beta 3 lub nowszej.
- Zainstaluj aplikację, która ma zostać przetestowana.
Przełącz flagę zgodności aplikacji w adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Uruchom ponownie urządzenie
Dostęp aplikacji do sieci lokalnej jest teraz ograniczony, a każda próba uzyskania dostępu do sieci lokalnej spowoduje błędy gniazda. Jeśli używasz interfejsów API, które wykonują operacje w sieci lokalnej poza procesem aplikacji (np. NsdManager), nie będą one miały wpływu na fazę wyrażania zgody.
Aby przywrócić dostęp, musisz przyznać aplikacji uprawnienia do NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Sprawdź, czy aplikacja deklaruje uprawnienie
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESw pliku manifestu. - Otwórz Ustawienia > Aplikacje > [Nazwa aplikacji] > Uprawnienia > Urządzenia w pobliżu > Zezwól.
Dostęp aplikacji do sieci lokalnej powinien zostać przywrócony, a wszystkie scenariusze powinny działać tak jak przed włączeniem aplikacji.
Gdy zaczniemy egzekwować ochronę sieci lokalnej, ruch sieciowy aplikacji będzie wyglądać tak:
| Uprawnienia | Żądanie wychodzące z sieci LAN | Żądanie internetowe wychodzące/przychodzące | Żądanie przychodzące z sieci LAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Przyznano | Works | Works | Works |
| Nie przyznano | Wpadki | Works | Wpadki |
Aby wyłączyć flagę zgodności aplikacji, użyj tego polecenia:
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Błędy
Błędy wynikające z tych ograniczeń będą zwracane do gniazda wywołującego, gdy tylko wywoła ono funkcję send lub jej wariant w odniesieniu do lokalnego adresu sieciowego.
Przykładowe błędy:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Definicja sieci lokalnej
Sieć lokalna w tym projekcie to sieć IP, która korzysta z interfejsu sieciowego obsługującego transmisję, takiego jak Wi-Fi lub Ethernet, ale nie obejmuje połączeń komórkowych (WWAN) ani VPN.
Za sieci lokalne uznaje się:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Trasy połączone bezpośrednio
- sieci typu stub, takie jak Thread,
- Wiele podsieci (do ustalenia)
Adresy multiemisji (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) i adres rozgłoszeniowy IPv4 (255.255.255.255) są klasyfikowane jako adresy sieci lokalnej.
Zdjęcia należące do aplikacji
Gdy aplikacja kierowana na pakiet SDK 36 lub nowszy na urządzeniach z Androidem 16 lub nowszym poprosi o uprawnienia do zdjęć i filmów, użytkownicy, którzy zdecydują się na ograniczenie dostępu do wybranych multimediów, zobaczą wszystkie zdjęcia należące do aplikacji wstępnie wybrane w selektorze zdjęć. Użytkownicy mogą odznaczyć dowolne z tych wstępnie wybranych elementów, co spowoduje cofnięcie dostępu aplikacji do tych zdjęć i filmów.
