これまでのリリースと同様、Android 16 には、アプリに影響する可能性がある動作変更が含まれています。下記の動作変更は、Android 16 以上をターゲットとするアプリにのみ適用されます。アプリが Android 16 以上をターゲットとする場合は、必要に応じてアプリを変更し、下記の動作に対応できるようにしてください。
アプリの targetSdkVersion に関係なく、Android 16 で実行されるすべてのアプリに影響する動作変更のリストも必ずご確認ください。
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、より一貫性のある直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するための以下の変更が含まれています。
エッジ ツー エッジのオプトアウトの廃止
Android 15 では、Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリに対してエッジ ツー エッジが強制適用されましたが、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement を true に設定することで、アプリはエッジ ツー エッジを無効にできます。Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとするアプリの場合、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement は非推奨となり無効化されます。アプリでエッジ ツー エッジを無効にすることはできません。
- アプリが Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとしており、Android 15 デバイスで実行されている場合、
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementは引き続き動作します。 - アプリが Android 16(API レベル 36)をターゲットとしており、Android 16 デバイスで実行されている場合、
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementは無効になります。
Android 16 でテストする場合は、アプリがエッジ ツー エッジに対応していることを確認し、R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement の使用をすべて削除して、Android 15 デバイスでもエッジ ツー エッジに対応するようにします。エッジ ツー エッジをサポートするには、Compose と Views のガイダンスをご覧ください。
予測型「戻る」には移行またはオプトアウトが必要
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher and running on an
Android 16 or higher device, the predictive back system animations
(back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity) are enabled by default.
Additionally, onBackPressed is not called and
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK is not dispatched anymore.
If your app intercepts the back event and you haven't migrated to predictive
back yet, update your app to use supported back navigation APIs, or
temporarily opt out by setting the
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback attribute to false in the
<application> or <activity> tag of your app's AndroidManifest.xml file.
Elegant font API のサポート終了と無効化
Apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) have the
elegantTextHeight
TextView attribute set to true by
default, replacing the compact font with one that is much more readable. You
could override this by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to false.
Android 16 deprecates the
elegantTextHeight attribute,
and the attribute will be ignored once your app targets Android 16. The "UI
fonts" controlled by these APIs are being discontinued, so you should adapt any
layouts to ensure consistent and future proof text rendering in Arabic, Lao,
Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu or Thai.
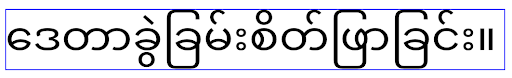
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
14 (API level 34) and lower, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35)
that overrode the default by setting the elegantTextHeight
attribute to false.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
16 (API level 36), or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) that didn't
override the default by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute
to false.コア機能
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、Android システムのさまざまなコア機能を変更または拡張する以下の変更が含まれています。
固定レートの作業スケジュールの最適化
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、大画面デバイスに表示されるアプリに対して次の変更が加えられています。
アダプティブ レイアウト
With Android apps now running on a variety of devices (such as phones, tablets, foldables, desktops, cars, and TVs) and windowing modes on large screens (such as split screen and desktop windowing), developers should build Android apps that adapt to any screen and window size, regardless of device orientation. Paradigms like restricting orientation and resizability are too restrictive in today's multidevice world.
Ignore orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions no longer apply on displays with smallest width >= 600dp. Apps fill the entire display window, regardless of aspect ratio or a user's preferred orientation, and pillarboxing isn't used.
This change introduces a new standard platform behavior. Android is moving toward a model where apps are expected to adapt to various orientations, display sizes, and aspect ratios. Restrictions like fixed orientation or limited resizability hinder app adaptability. Make your app adaptive to deliver the best possible user experience.
You can also test this behavior by using the
app compatibility framework and enabling the
UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag.
Common breaking changes
Ignoring orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions might impact your app's UI on some devices, especially elements that were designed for small layouts locked in portrait orientation: for example, issues like stretched layouts and off-screen animations and components. Any assumptions about aspect ratio or orientation can cause visual issues with your app. Learn more about how to avoid them and improve your app's adaptive behaviour.
Allowing device rotation results in more activity re-creation, which can result in losing user state if not properly preserved. Learn how to correctly save UI state in Save UI states.
Implementation details
The following manifest attributes and runtime APIs are ignored across large screen devices in full-screen and multi-window modes:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
The following values for screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), and
getRequestedOrientation() are ignored:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Regarding display resizability, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, and android:maxAspectRatio have no effect.
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), app orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio constraints are ignored on large screens by default, but every app that isn't fully ready can temporarily override this behavior by opting out (which results in the previous behavior of being placed in compatibility mode).
Exceptions
The Android 16 orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions don't apply in the following situations:
- Games (based on the
android:appCategoryflag) - Users explicitly opting in to the app's default behavior in aspect ratio settings of the device
- Screens that are smaller than
sw600dp
Opt out temporarily
To opt out a specific activity, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
If too many parts of your app aren't ready for Android 16, you can opt out completely by applying the same property at the application level:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
健康&フィットネス
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、健康とフィットネスに関するデータに関連して、以下の変更が加えられています。
健康とフィットネスの権限
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher,
BODY_SENSORS permissions use more granular permissions
under android.permissions.health, which Health Connect
also uses. As of Android 16, any API previously requiring BODY_SENSORS
or BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requires the corresponding
android.permissions.health permission instead. This affects the following data
types, APIs, and foreground service types:
HEART_RATE_BPMfrom Health Services on Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEfrom Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyandheartRateBpmfromProtoLayouton Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHwhere the respectiveandroid.permission.healthpermission is needed in place ofBODY_SENSORS
If your app uses these APIs, it should request the respective granular permissions:
- For while-in-use monitoring of Heart Rate, SpO2, or Skin Temperature:
request the granular permission under
android.permissions.health, such asREAD_HEART_RATEinstead ofBODY_SENSORS. - For background sensor access: request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDinstead ofBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
These permissions are the same as those that guard access to reading data from Health Connect, the Android datastore for health, fitness, and wellness data.
Mobile apps
Mobile apps migrating to use the READ_HEART_RATE and other granular
permissions must also declare an activity to display
the app's privacy policy. This is the same requirement as Health Connect.
接続
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、周辺機器との接続性を改善するために、Bluetooth スタックに次の変更が加えられています。
ボンドの損失と暗号化の変更を処理する新しいインテント
As part of the Improved bond loss handling, Android 16 also introduces 2 new intents to provide apps with greater awareness of bond loss and encryption changes.
Apps targeting Android 16 can now:
- Receive an
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent when remote bond loss is detected, allowing them to provide more informative user feedback and take appropriate actions. - Receive an
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent whenever encryption status of the link changes. This includes encryption status change, encryption algorithm change, and encryption key size change. Apps must consider the bond restored if the link is successfully encrypted upon receivingACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent later.
Adapting to varying OEM implementations
While Android 16 introduces these new intents, their implementation and broadcasting can vary across different device manufacturers (OEMs). To ensure your app provides a consistent and reliable experience across all devices, developers should design their bond loss handling to gracefully adapt to these potential variations.
We recommend the following app behaviors:
If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is broadcast:The ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) link will be disconnected by the system, but the bond information for the device will be retained (as described here).
Your app should use this intent as the primary signal for bond loss detection and guiding the user to confirm the remote device is in range before initiating device forgetting or re-pairing.
If a device disconnects after
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGis received, your app should be cautious about reconnecting, as the device may no longer be bonded with the system.If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is NOT broadcast:The ACL link will remain connected, and the bond information for the device will be removed by the system, same to behavior in Android 15.
In this scenario, your app should continue its existing bond loss handling mechanisms as in previous Android releases, to detect and manage bond loss events.
Bluetooth のペア設定を削除する新しい方法
All apps targeting Android 16 are now able to unpair bluetooth devices using a
public API in CompanionDeviceManager. If a companion device is
being managed as a CDM association, then the app can trigger
bluetooth bond removal by using the new removeBond(int) API
on the associated device. The app can monitor the bond state changes by
listening to the bluetooth device broadcast event
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
セキュリティ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、セキュリティが次のように変更されています。
MediaStore バージョンのロックダウン
Android 16 以降をターゲットとするアプリの場合、MediaStore#getVersion() はアプリごとに一意になります。これにより、バージョン文字列から識別プロパティが削除され、フィンガープリント手法の不正使用と使用が防止されます。アプリでは、このバージョンの形式について前提条件を設定しないでください。アプリは、この API を使用する際にバージョンの変更をすでに処理している必要があります。ほとんどの場合、デベロッパーがこの API の対象範囲を超える追加情報を推測しようとしない限り、現在の動作を変更する必要はありません。
Safer Intents
The Safer Intents feature is a multi-phase security initiative designed to improve the security of Android's intent resolution mechanism. The goal is to protect apps from malicious actions by adding checks during intent processing and filtering intents that don't meet specific criteria.
In Android 15 the feature focused on the sending app, now with Android 16, shifts control to the receiving app, allowing developers to opt-in to strict intent resolution using their app manifest.
Two key changes are being implemented:
Explicit Intents Must Match the Target Component's Intent Filter: If an intent explicitly targets a component, it should match that component's intent filter.
Intents Without an Action Cannot Match any Intent Filter: Intents that don't have an action specified shouldn't be resolved to any intent filter.
These changes only apply when multiple apps are involved and don't affect intent handling within a single app.
Impact
The opt-in nature means that developers must explicitly enable it in their app manifest for it to take effect. As a result, the feature's impact will be limited to apps whose developers:
- Are aware of the Safer Intents feature and its benefits.
- Actively choose to incorporate stricter intent handling practices into their apps.
This opt-in approach minimizes the risk of breaking existing apps that may rely on the current less-secure intent resolution behavior.
While the initial impact in Android 16 may be limited, the Safer Intents initiative has a roadmap for broader impact in future Android releases. The plan is to eventually make strict intent resolution the default behavior.
The Safer Intents feature has the potential to significantly enhance the security of the Android ecosystem by making it more difficult for malicious apps to exploit vulnerabilities in the intent resolution mechanism.
However, the transition to opt-out and mandatory enforcement must be carefully managed to address potential compatibility issues with existing apps.
Implementation
Developers need to explicitly enable stricter intent matching using the
intentMatchingFlags attribute in their app manifest.
Here is an example where the feature is opt-in for the entire app,
but disabled/opt-out on a receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
More on the supported flags:
| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Enforces stricter matching for incoming intents |
| none | Disables all special matching rules for incoming intents. When specifying multiple flags, conflicting values are resolved by giving precedence to the "none" flag |
| allowNullAction | Relaxes the matching rules to allow intents without an action to match. This flag to be used in conjunction with "enforceIntentFilter" to achieve a specific behavior |
Testing and Debugging
When the enforcement is active, apps should function correctly if the intent
caller has properly populated the intent.
However, blocked intents will trigger warning log messages like
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" and "Access blocked:"
with the tag "PackageManager."
This indicates a potential issue that could impact the app and requires
attention.
Logcat filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU システムコール フィルタリング
Mali GPU サーフェスを強化するため、非推奨になった Mali GPU IOCTL や GPU 開発専用の Mali GPU IOCTL は、本番環境ビルドでブロックされています。また、GPU プロファイリングに使用される IOCTL が、シェルプロセスまたはデバッグ可能なアプリに制限されました。プラットフォーム レベルのポリシーについて詳しくは、SAC の更新を参照してください。
この変更は、Mali GPU を使用する Google Pixel デバイス(Google Pixel 6 ~ 9)で実施されます。Arm は、r54p2 リリースの Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst で IOCTL の公式な分類を提供しています。このリストは、今後のドライバ リリースでも引き続き維持されます。
この変更は、サポートされているグラフィック API(Vulkan や OpenGL など)には影響しません。また、デベロッパーや既存のアプリケーションにも影響しないと見込まれます。Streamline Performance Analyzer や Android GPU Inspector などの GPU プロファイリング ツールは影響を受けません。
テスト
次のような SELinux の拒否が表示された場合は、アプリがこの変更の影響を受けている可能性があります。
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
アプリケーションでブロックされた IOCTL を使用する必要がある場合は、バグを報告して android-partner-security@google.com に割り当ててください。
よくある質問
このポリシーの変更はすべての OEM に適用されますか?この変更はオプトインですが、この強化方法を使用したい OEM は誰でも利用できます。変更の実装手順については、実装に関するドキュメントをご覧ください。
これを実装するには OEM コードベースで変更を行う必要がありますか?それとも、新しい AOSP リリースにデフォルトで含まれていますか?プラットフォーム レベルの変更は、デフォルトで新しい AOSP リリースに含まれます。ベンダーは、この変更を適用したい場合は、コードベースでこの変更を有効にできます。
SoC は IOCTL リストを最新の状態に保つ責任を負っていますか?たとえば、デバイスで ARM Mali GPU を使用している場合、変更について ARM に問い合わせる必要はありますか?個々の SoC は、ドライバのリリース時にデバイスごとに IOCTL リストを更新する必要があります。たとえば、ARM はドライバの更新時に公開済みの IOCTL リストを更新します。ただし、OEM は、SEPolicy に更新を組み込み、必要に応じて選択したカスタム IOCTL をリストに追加する必要があります。
この変更は、販売中のすべての Google Pixel に自動的に適用されますか?それとも、この変更を適用するためにユーザーが何かを切り替える必要がありますか?この変更は、Mali GPU(Google Pixel 6 ~ 9)を使用するすべての Google Pixel 販売中デバイスに適用されます。この変更を適用するためにユーザー側で必要な対応はありません。
このポリシーを使用すると、カーネル ドライバのパフォーマンスに影響しますか?このポリシーは GFXBench を使用して Mali GPU でテストされましたが、GPU パフォーマンスに測定可能な変化は見られませんでした。
IOCTL リストを現在のユーザースペースとカーネル ドライバのバージョンに合わせる必要がありますか?はい。許可される IOCTL のリストは、ユーザー空間とカーネル ドライバの両方でサポートされる IOCTL と同期する必要があります。ユーザー空間またはカーネル ドライバの IOCTL が更新された場合は、SEPolicy IOCTL リストも一致するように更新する必要があります。
ARM は IOCTL を「制限付き」 / 「計測」に分類していますが、一部を本番環境のユースケースで使用したり、一部を拒否したりしたいと考えています。個々の OEM/SoC は、ユーザー空間 Mali ライブラリの構成に基づいて、使用する IOCTL を分類する方法を決定する責任があります。ARM のリストは、これらの決定に役立ちますが、OEM/SoC のユースケースはそれぞれ異なる場合があります。
プライバシー
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、プライバシーが次のように変更されています。
ローカル ネットワークの権限
Devices on the LAN can be accessed by any app that has the INTERNET permission.
This makes it easy for apps to connect to local devices but it also has privacy
implications such as forming a fingerprint of the user, and being a proxy for
location.
The Local Network Protections project aims to protect the user's privacy by gating access to the local network behind a new runtime permission.
Release plan
This change will be deployed between two releases, 25Q2 and 26Q2 respectively. It is imperative that developers follow this guidance for 25Q2 and share feedback because these protections will be enforced at a later Android release. Moreover, they will need to update scenarios which depend on implicit local network access by using the following guidance and prepare for user rejection and revocation of the new permission.
Impact
At the current stage, LNP is an opt-in feature which means only the apps that opt in will be affected. The goal of the opt-in phase is for app developers to understand which parts of their app depend on implicit local network access such that they can prepare to permission guard them for the next release.
Apps will be affected if they access the user's local network using:
- Direct or library use of raw sockets on local network addresses (e.g. mDNS or SSDP service discovery protocol)
- Use of framework level classes that access the local network (e.g. NsdManager)
Traffic to and from a local network address requires local network access permission. The following table lists some common cases:
| App Low Level Network Operation | Local Network Permission Required |
|---|---|
| Making an outgoing TCP connection | yes |
| Accepting incoming TCP connections | yes |
| Sending a UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
| Receiving an incoming UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
These restrictions are implemented deep in the networking stack, and thus they apply to all networking APIs. This includes sockets created in native or managed code, networking libraries like Cronet and OkHttp, and any APIs implemented on top of those. Trying to resolve services on the local network (i.e. those with a .local suffix) will require local network permission.
Exceptions to the rules above:
- If a device's DNS server is on a local network, traffic to or from it (at port 53) doesn't require local network access permission.
- Applications using Output Switcher as their in-app picker won't need local network permissions (more guidance to come in 2025Q4).
Developer Guidance (Opt-in)
To opt into local network restrictions, do the following:
- Flash the device to a build with 25Q2 Beta 3 or later.
- Install the app to be tested.
Toggle the Appcompat flag in adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Reboot The device
Now your app's access to the local network is restricted and any attempt to access the local network will lead to socket errors. If you are using APIs that perform local network operations outside of your app process (ex: NsdManager), they won't be impacted during the opt-in phase.
To restore access, you must grant your app permission to NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Ensure the app declares the
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESpermission in its manifest. - Go to Settings > Apps > [Application Name] > Permissions > Nearby devices > Allow.
Now your app's access to the local network should be restored and all your scenarios should work as they did prior to opting the app in.
Once enforcement for local network protection begins, here is how the app network traffic will be impacted.
| Permission | Outbound LAN Request | Outbound/Inbound Internet Request | Inbound LAN Request |
|---|---|---|---|
| Granted | Works | Works | Works |
| Not Granted | Fails | Works | Fails |
Use the following command to toggle-off the App-Compat flag
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Errors
Errors arising from these restrictions will be returned to the calling socket whenever it invokes send or a send variant to a local network address.
Example errors:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Local Network Definition
A local network in this project refers to an IP network that utilizes a broadcast-capable network interface, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet, but excludes cellular (WWAN) or VPN connections.
The following are considered local networks:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Directly-connected routes
- Stub networks like Thread
- Multiple-subnets (TBD)
Additionally, both multicast addresses (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) and the IPv4 broadcast address (255.255.255.255) are classified as local network addresses.
アプリ所有の写真
When prompted for photo and video permissions by an app targeting SDK 36 or higher on devices running Android 16 or higher, users who choose to limit access to selected media will see any photos owned by the app pre-selected in the photo picker. Users can deselect any of these pre-selected items, which will revoke the app's access to those photos and videos.
