これまでのリリースと同様、Android 15 には、アプリに影響する可能性がある動作変更が含まれています。下記の動作変更は、Android 15 以上をターゲットとするアプリにのみ適用されます。アプリが Android 15 以上をターゲットとする場合は、必要に応じてアプリを変更し、下記の動作に適切に対応できるようにしてください。
アプリの targetSdkVersion に関係なく、Android 15 で実行されるすべてのアプリに影響する動作変更のリストも必ずご確認ください。
コア機能
Android 15 では、Android システムのさまざまなコア機能が変更または拡張されています。
フォアグラウンド サービスの変更
Android 15 では、フォアグラウンド サービスに次の変更を加えます。
- データ同期フォアグラウンド サービスのタイムアウト動作
- 新しいメディア処理フォアグラウンド サービスのタイプ
- フォアグラウンド サービスを起動する
BOOT_COMPLETEDブロードキャスト レシーバに関する制限 - アプリが
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW権限を保持しているときにフォアグラウンド サービスを起動する場合の制限
データ同期フォアグラウンド サービスのタイムアウト動作
Android 15 では、Android 15(API レベル 35)以降をターゲットとするアプリに対して、dataSync に新しいタイムアウト動作が導入されます。この動作は、新しい mediaProcessing フォアグラウンド サービス タイプにも適用されます。
システムは、アプリの dataSync サービスを 24 時間以内に合計 6 時間実行することを許可します。その後、システムは実行中のサービスの Service.onTimeout(int, int) メソッド(Android 15 で導入)を呼び出します。この時点で、サービスは Service.stopSelf() を呼び出すために数秒間待機します。Service.onTimeout() が呼び出されると、サービスはフォアグラウンド サービスと見なされなくなります。サービスが Service.stopSelf() を呼び出さない場合、システムは内部例外をスローします。例外は Logcat に次のメッセージとともに記録されます。
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
この動作の変更による問題を回避するには、次のいずれかを行います。
- サービスに新しい
Service.onTimeout(int, int)メソッドを実装します。アプリがコールバックを受信したら、数秒以内にstopSelf()を呼び出します。(アプリをすぐに停止しないと、システムは障害を生成します)。 - アプリの
dataSyncサービスが、24 時間で合計 6 時間を超えて実行されていないことを確認します(ユーザーがアプリを操作してタイマーをリセットする場合を除きます)。 dataSyncフォアグラウンド サービスは、直接のユーザー操作の結果としてのみ起動します。サービスの開始時にアプリはフォアグラウンドにあるため、サービスはバックグラウンドに移行してから 6 時間すべてかかります。dataSyncフォアグラウンド サービスを使用する代わりに、代替の API を使用してください。
アプリの dataSync フォアグラウンド サービスが過去 24 時間以内に 6 時間実行されている場合、ユーザーがアプリをフォアグラウンドに表示した(これによりタイマーがリセットされる)場合を除き、別の dataSync フォアグラウンド サービスを開始することはできません。別の dataSync フォアグラウンド サービスを開始しようとすると、システムは ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException をスローし、「フォアグラウンド サービス タイプ dataSync の制限時間はすでに経過しています」などのエラー メッセージを出力します。
テスト
アプリの動作をテストするには、アプリが Android 15 をターゲットとしていない場合でも、データ同期のタイムアウトを有効にできます(アプリが Android 15 デバイスで実行されている場合)。タイムアウトを有効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
タイムアウト期間を調整して、上限に達したときアプリの動作を簡単にテストすることもできます。新しいタイムアウト期間を設定するには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
新しいメディア処理フォアグラウンド サービス タイプ
Android 15 では、新しいフォアグラウンド サービス タイプ mediaProcessing が導入されています。このサービスタイプは、メディア ファイルのコード変換などのオペレーションに適しています。たとえば、メディアアプリが音声ファイルをダウンロードし、再生する前に別の形式に変換する必要がある場合があります。mediaProcessing フォアグラウンド サービスを使用すると、アプリがバックグラウンドにあっても変換を続行できます。
システムは、アプリの mediaProcessing サービスを 24 時間以内に合計 6 時間実行することを許可します。その後、システムは実行中のサービスの Service.onTimeout(int, int) メソッド(Android 15 で導入)を呼び出します。この時点で、サービスは Service.stopSelf() を呼び出すために数秒間待機します。サービスが Service.stopSelf() を呼び出さない場合、システムは内部例外をスローします。例外は Logcat に次のメッセージとともに記録されます。
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
この例外を回避するには、次のいずれかを行います。
- サービスに新しい
Service.onTimeout(int, int)メソッドを実装します。アプリがコールバックを受信したら、数秒以内にstopSelf()を呼び出します。(アプリをすぐに停止しないと、システムは障害を生成します)。 - アプリの
mediaProcessingサービスが 24 時間以内に合計 6 時間を超えて実行されないようにします(ユーザーがアプリを操作してタイマーをリセットする場合を除く)。 mediaProcessingフォアグラウンド サービスは、ユーザーが直接操作した結果としてのみ開始します。サービスが開始されたときにアプリはフォアグラウンドにあるため、アプリがバックグラウンドに移動した後も 6 時間間サービスは実行されます。mediaProcessingフォアグラウンド サービスを使用する代わりに、WorkManager などの代替 API を使用してください。
アプリの mediaProcessing フォアグラウンド サービスが過去 24 時間以内に 6 時間実行されている場合、ユーザーがアプリをフォアグラウンドに表示して(タイマーがリセットされる)場合を除き、別の mediaProcessing フォアグラウンド サービスを開始することはできません。別の mediaProcessing フォアグラウンド サービスを開始しようとすると、システムによって ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException がスローされ、「フォアグラウンド サービス タイプ mediaProcessing で時間制限がすでになくなりました」などのエラー メッセージが表示されます。
mediaProcessing サービスタイプについて詳しくは、Android 15 のフォアグラウンド サービス タイプの変更: メディア処理をご覧ください。
テスト
アプリの動作をテストするには、アプリが Android 15 をターゲットとしていない場合でも、メディア処理のタイムアウトを有効にできます(アプリが Android 15 デバイスで実行されている場合)。タイムアウトを有効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
タイムアウト期間を調整して、上限に達したときアプリの動作を簡単にテストすることもできます。新しいタイムアウト期間を設定するには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
フォアグラウンド サービスを起動する BOOT_COMPLETED ブロードキャスト レシーバの制限
BOOT_COMPLETED ブロードキャスト レシーバに対する新しい制限事項がリリースされます
フォアグラウンド サービスの場合。BOOT_COMPLETED レシーバーは、API 呼び出しを起動できない
フォアグラウンド サービスのタイプを使用できます。
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(この制限は、次の日付よりmicrophoneに適用されています) Android 14)
BOOT_COMPLETED レシーバーがこれらのタイプのフォアグラウンドのいずれかを起動しようとした場合
サービスの場合、システムは ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException をスローします。
テスト
アプリの動作をテストするには、アプリが Android 15 をターゲットとしていない場合でも、これらの新しい制限を有効にできます(アプリが Android 15 デバイスで実行されている場合)。次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
デバイスを再起動せずに BOOT_COMPLETED ブロードキャストを送信するには、次の操作を行います。
次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
アプリが SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 権限を保持しているときにフォアグラウンド サービスを開始する場合の制限
以前は、アプリが SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 権限を保持している場合、アプリが現在バックグラウンドで実行されている場合でも、フォアグラウンド サービスを起動できました(バックグラウンドでの起動制限の免除で説明しています)。
アプリが Android 15 をターゲットとしている場合、この免除はより限定的になりました。アプリには SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 権限が必要になり、また、表示可能なオーバーレイ ウィンドウも必要になります。つまり、フォアグラウンド サービスを開始する前に、アプリがまず TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY ウィンドウを起動し、そのウィンドウを表示する必要があります。
アプリがこれらの新しい要件を満たさずにバックグラウンドからフォアグラウンド サービスを起動しようとすると(他の例外がない限り)、システムは ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException をスローします。
アプリが SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 権限を宣言し、バックグラウンドからフォアグラウンド サービスを起動する場合、この変更の影響を受ける可能性があります。アプリが ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException を取得した場合は、アプリの処理順序を確認し、バックグラウンドからフォアグラウンド サービスを開始する前に、アプリにアクティブなオーバーレイ ウィンドウがすでに存在することを確認します。オーバーレイ ウィンドウが現在表示されているかどうかを確認するには、View.getWindowVisibility() を呼び出します。また、View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() を上書きして、可視性が変更されるたびに通知を受け取ることもできます。
テスト
アプリの動作をテストするには、アプリが Android 15 をターゲットとしていない場合でも、これらの新しい制限を有効にできます(アプリが Android 15 デバイスで実行されている場合)。バックグラウンドからフォアグラウンド サービスを起動する際の新しい制限を有効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
アプリがサイレント モードのグローバル状態を変更できるタイミングの変更
Android 15(API レベル 35)以降をターゲットとするアプリは、デバイスのサイレント(DND)モードのグローバル状態やポリシーを変更できなくなりました(ユーザー設定の変更や DND モードのオフによる変更も含みます)。代わりに、アプリは AutomaticZenRule を提供する必要がある。システムは、既存の最も制限の厳しいポリシーが優先されるスキームで、これをグローバル ポリシーに統合します。以前はグローバル状態に影響していた既存の API(setInterruptionFilter、setNotificationPolicy)を呼び出すと、暗黙的な AutomaticZenRule が作成または更新されます。この AutomaticZenRule は、API 呼び出しの呼び出しサイクルに応じてオンまたはオフに切り替わります。
この変更は、アプリが setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) を呼び出し、その呼び出しによって所有者によって以前に有効にされた AutomaticZenRule が無効になることを想定している場合にのみ、検出可能な動作に影響します。
OpenJDK API の変更
Android 15 では、最新の OpenJDK LTS リリースの機能に合わせて Android のコアライブラリを更新する取り組みが引き続き行われています。
これらの変更の一部は、Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリの互換性に影響する可能性があります。
String Formatting API を変更: 次の
String.format()API とFormatter.format()API を使用する場合、引数インデックス、フラグ、幅、精度の検証がより厳格になりました。String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
たとえば、引数インデックス 0(書式文字列の
%0)が使用されると、次の例外がスローされます。IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0この場合、引数インデックス 1(形式文字列の
%1)を使用することで問題を解決できます。Arrays.asList(...).toArray()のコンポーネント型の変更:Arrays.asList(...).toArray()を使用する場合、結果の配列のコンポーネント型は、基になる配列の要素の型ではなく、Objectになりました。したがって、次のコードはClassCastExceptionをスローします。String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();この場合、結果の配列でコンポーネント タイプとして
Stringを保持するには、代わりにCollection.toArray(Object[])を使用します。String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);言語コードの処理の変更:
LocaleAPI を使用する場合、ヘブライ語、イディッシュ語、インドネシア語の言語コードは、廃止された形式(ヘブライ語:iw、イディッシュ語:ji、インドネシア語:in)に変換されなくなりました。これらのロケールのいずれかの言語コードを指定する場合は、代わりに ISO 639-1 のコード(ヘブライ語:he、イディッシュ語:yi、インドネシア語:id)を使用してください。ランダムな整数シーケンスの変更: https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 で行われた変更に伴い、次の
Random.ints()メソッドはRandom.nextInt()メソッドとは異なる数値シーケンスを返すようになりました。一般に、この変更によってアプリの動作が損なわれることはありませんが、コードでは
Random.ints()メソッドから生成されたシーケンスがRandom.nextInt()と一致することを想定しないでください。
新しい SequencedCollection API は、アプリのビルド構成で compileSdk を更新して Android 15(API レベル 35)を使用すると、アプリの互換性に影響する可能性があります。
kotlin-stdlibのMutableList.removeFirst()拡張関数とMutableList.removeLast()拡張関数との競合Java の
List型は Kotlin のMutableList型にマッピングされます。List.removeFirst()API とList.removeLast()API は Android 15(API レベル 35)で導入されたため、Kotlin コンパイラは、関数呼び出し(list.removeFirst()など)をkotlin-stdlibの拡張関数ではなく、新しいListAPI に静的に解決します。compileSdkが35に設定され、minSdkが34以下に設定された状態でアプリが再コンパイルされ、Android 14 以下で実行されると、ランタイム エラーがスローされます。java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Android Gradle プラグインの既存の
NewApilint オプションで、これらの新しい API の使用を検出できます。./gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()ランタイム例外と lint エラーを修正するには、Kotlin で
removeFirst()関数呼び出しとremoveLast()関数呼び出しをそれぞれremoveAt(0)とremoveAt(list.lastIndex)に置き換えます。Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 以降を使用している場合は、これらのエラーに対するクイック フィックス オプションも提供されます。lint オプションが無効になっている場合は、
@SuppressLint("NewApi")とlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }の削除を検討してください。Java の他のメソッドとの衝突
既存の型(
List、Dequeなど)に新しいメソッドが追加されました。これらの新しいメソッドは、他のインターフェースやクラスの同じ名前と引数の型のメソッドと互換性がない可能性があります。互換性のないメソッド シグネチャの衝突が発生した場合、javacコンパイラはビルド時のエラーを出力します。次に例を示します。エラーの例 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface Listエラーの例 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorエラー 3 の例:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorこれらのビルドエラーを修正するには、これらのインターフェースを実装するクラスで、互換性のある戻り値の型を使用してメソッドをオーバーライドする必要があります。次に例を示します。
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
セキュリティ
Android 15 には、悪意のあるアプリからアプリとユーザーを保護するために、システムのセキュリティを強化する変更が含まれています。
制限付き TLS バージョン
Android 15 では、TLS バージョン 1.0 および 1.1 の使用が制限されています。これまではこれらのバージョンは Android で非推奨でしたが、現在は Android 15 をターゲットとするアプリで許可されないようになりました。
バックグラウンド アクティビティの安全な起動
Android 15 では、悪意のあるバックグラウンド アプリが他のアプリをフォアグラウンドに移動させたり、権限を昇格させたり、ユーザー インタラクションを悪用したりすることを防ぐ変更が加えられ、悪意のあるアプリからユーザーを保護し、デバイスの制御性を高めています。Android 10(API レベル 29)以降、バックグラウンド アクティビティの起動が制限されています。
その他の変更点
PendingIntentクリエイターのデフォルトをバックグラウンド アクティビティの起動をブロックに変更。これにより、アプリが誤ってPendingIntentを作成し、悪意のある行為者によって不正使用されるのを防ぐことができます。PendingIntent送信者が許可しない限り、アプリをフォアグラウンドに移動しないでください。この変更は、悪意のあるアプリがバックグラウンドでアクティビティを開始する機能を悪用することを防ぐことを目的としています。デフォルトでは、作成者がバックグラウンド アクティビティの起動権限を許可するか、送信者がバックグラウンド アクティビティの起動権限を持っている場合を除き、アプリがタスクスタックをフォアグラウンドに移動することは許可されません。- タスクスタックの最上位のアクティビティがタスクを完了する方法を制御します。最上位のアクティビティがタスクを終了すると、Android は最後にアクティブだったタスクに戻ります。また、最上位でないアクティビティがタスクを終了した場合、Android はホーム画面に戻ります。この最上位でないアクティビティの終了はブロックされません。
- 他のアプリから任意の Activity が自分のタスクに起動されるのを防ぎます。この変更により、悪意のあるアプリが他のアプリからのものに見せかけたアクティビティを作成してユーザーをフィッシングするのを防ぐことができます。
- 非表示のウィンドウがバックグラウンド アクティビティの起動の対象にならないようにブロック。これにより、悪意のあるアプリがバックグラウンド アクティビティの起動を不正使用して、ユーザーに不要なコンテンツや悪意のあるコンテンツを表示するのを防ぐことができます。
より安全なインテント
Android 15 では、インテント用に StrictMode が導入されています。
Intent の使用違反に関する詳細なログを表示するには、次の方法を使用します。
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 15 には、より一貫性のある直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するための変更が含まれています。
ウィンドウ インセットの変更
Android 15 では、ウィンドウの切り欠きに関連する 2 つの変更があります。エッジツーエッジがデフォルトで適用され、システムバーのデフォルト構成などの構成も変更されています。
エッジ ツー エッジの適用
アプリが Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとしている場合、Android 15 を搭載しているデバイスではデフォルトでエッジツーエッジ表示となります。
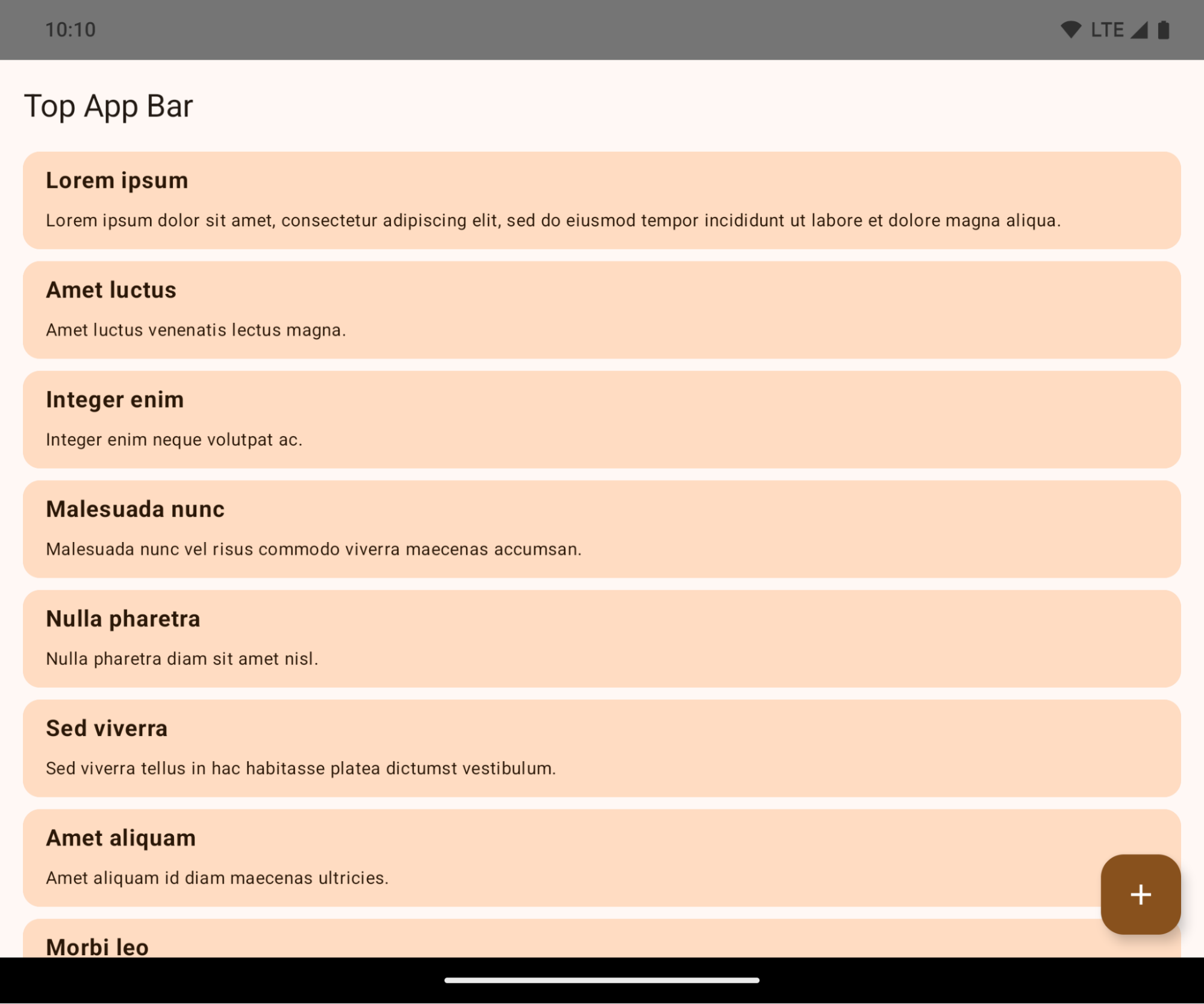
これは、アプリの UI に悪影響を与える可能性がある破壊的変更です。この 変更は、次の UI 領域に影響します。
- ジェスチャー ハンドル ナビゲーション バー
- デフォルトでは透明です。
- 下部のオフセットが無効になっているため、インセットが適用されない限り、コンテンツはシステム ナビゲーション バーの背後に描画されます。
setNavigationBarColorとR.attr#navigationBarColorは 非推奨であり、ジェスチャー ナビゲーションには影響しません。setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedとR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedは、引き続き ジェスチャー ナビゲーションに影響しません。
- 3 ボタン ナビゲーション
- デフォルトでは不透明度が 80% に設定され、ウィンドウの背景と色が一致する場合があります。
- 下部のオフセットが無効になっているため、コンテンツはシステム ナビゲーション バーの背後に描画されます。 インセットが適用されない限り。
setNavigationBarColorとR.attr#navigationBarColorは 、デフォルトでウィンドウの背景と一致するように設定されています。このデフォルトを適用するには、ウィンドウの背景 をカラー ドローアブルにする必要があります。この API は 非推奨ですが、3 ボタン ナビゲーションに引き続き影響します。setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedとR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedはデフォルトで true になっており、 80% の不透明度の背景が 3 ボタン ナビゲーション全体に追加されます。
- **ステータスバー**
- デフォルトでは透明です。
- 上部のオフセットが無効になっているため、 インセットが適用されない限り、コンテンツはステータスバーの背後に描画されます。
setStatusBarColorとR.attr#statusBarColorは 非推奨であり、Android 15 には影響しません。setStatusBarContrastEnforcedとR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedは非推奨ですが、Android 15 には引き続き影響します。
- ディスプレイ カットアウト
- フローティング ウィンドウ以外のウィンドウの
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeはLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSにする必要があります。SHORT_EDGES、NEVER、DEFAULTはALWAYSとして解釈されるため、ディスプレイ カットアウトによって黒い バーが表示されることはなく、エッジツーエッジで表示されます。
- フローティング ウィンドウ以外のウィンドウの
次の例は、 Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとする前後のアプリと、インセットを適用する前後のアプリを示しています。この例は 包括的なものではなく、Android Auto では表示が異なる場合があります。
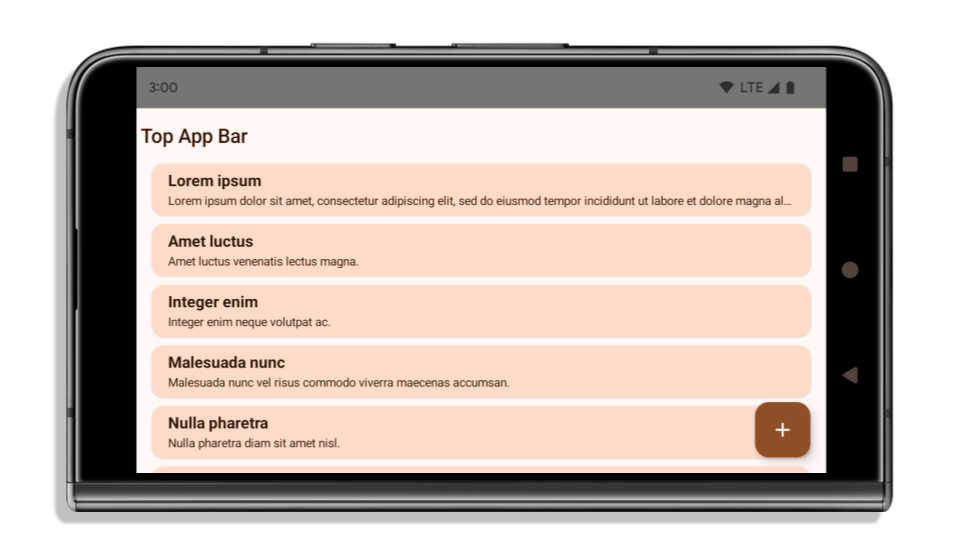

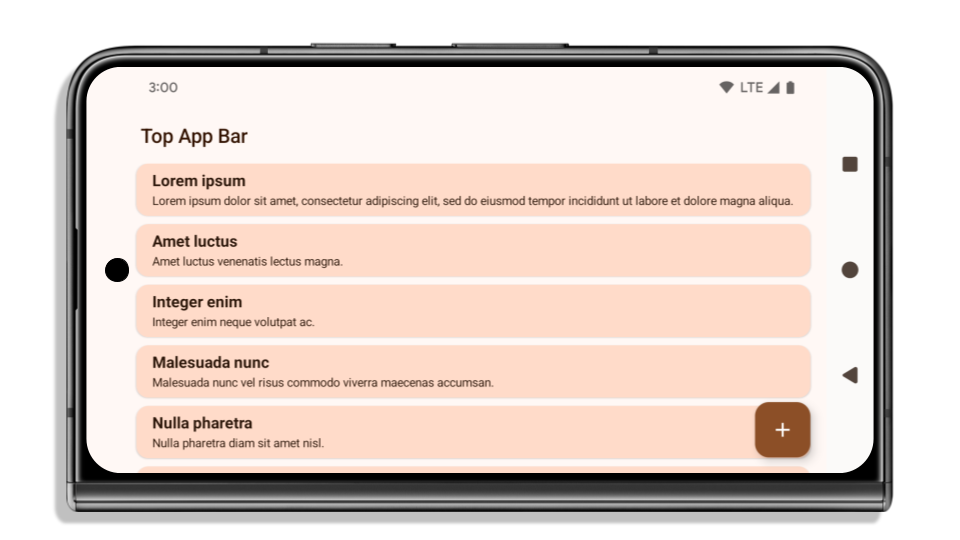
アプリがすでにエッジツーエッジになっている場合に確認すべきこと
アプリがすでにエッジツーエッジになっていて、インセットを適用している場合、次のシナリオを除き、 ほとんど影響はありません。影響がないと思われる場合でも、 アプリをテストすることをおすすめします。
Activityの代わりにLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYSを使用するSHORT_EDGES、NEVER、DEFAULTなど、フローティング ウィンドウ以外のウィンドウがある。アプリが起動時にクラッシュする場合は、これ はスプラッシュ画面が原因である可能性があります。core splashscreen の依存関係を 1.2.0-alpha01 以降にアップグレードするか、window.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.alwaysを設定します。- トラフィックの少ない画面で UI が隠れている可能性がある。アクセス数の少ない画面で UI が隠れていないことを確認します。トラフィックの少ない画面には、次のようなものがあります。
- オンボーディング画面またはログイン画面
- 設定ページ
アプリがまだエッジツーエッジになっていない場合に確認すべきこと
アプリがまだエッジツーエッジになっていない場合、影響を受ける可能性が非常に高くなります。すでにエッジツーエッジになっているアプリのシナリオに加えて、次の点を考慮する必要があります。
- アプリが Compose でマテリアル デザイン 3 のコンポーネント(
androidx.compose.material3)を使用している場合(TopAppBar、BottomAppBar、NavigationBarなど)、これらのコンポーネントはインセットを自動的に処理するため、影響を受けない 可能性があります。 - アプリが Compose でマテリアル デザイン 2 のコンポーネント(
androidx.compose.material)を使用している場合、コンポーネントはインセットを自動的には処理しません。ただし、インセットにアクセスして手動で適用することはできます。androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 以降では、windowInsetsパラメータを使用して、BottomAppBar、TopAppBar、BottomNavigation、およびNavigationRailにインセットを手動で適用します。 同様に、contentWindowInsetsパラメータをScaffoldに使用します。 - アプリがビューとマテリアル デザイン コンポーネント
(
com.google.android.material)を使用する場合、ビューベースのマテリアル デザイン コンポーネントの多く(BottomNavigationView、BottomAppBar、NavigationRailView、NavigationViewなど)はインセットを処理するため、追加の 作業は不要です。ただし、android:fitsSystemWindows="true"を使用する場合は、AppBarLayoutを追加する必要があります。 - カスタム コンポーザブルの場合は、インセットをパディングとして手動で適用します。コンテンツが
Scaffold内にある場合は、Scaffoldパディング値を使用してインセットを使用できます。それ以外の場合は、WindowInsetsのいずれかを使用してパディングを適用します。 - アプリがビューと
BottomSheet、SideSheet、またはカスタム コンテナを使用する場合、ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListenerを使用してパディングを適用します。RecyclerViewについては、このリスナーを使用してパディングを適用して、さらにclipToPadding="false"を追加します。
アプリでカスタムの背景保護を提供する必要がある場合に確認すべきこと
アプリで 3 ボタン ナビゲーションまたは
ステータスバーにカスタムの背景保護を提供する必要がある場合は、システムバーの背後にコンポーザブルまたはビューを配置する必要があります。
WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() を使用して 3 ボタン
ナビゲーション バーの高さを取得するか、WindowInsets.Type#statusBars を使用します。
エッジツーエッジに関するその他のリソース
インセットの適用に関するその他の考慮事項については、エッジツーエッジのビューとエッジツーエッジの Compose のガイドをご覧ください。
非推奨 API
次の API は非推奨ですが、無効にはなっていません。
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(3 ボタン ナビゲーション用、アルファ値 80% )Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(3 ボタン ナビゲーション用、 アルファ値 80%)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
次の API は非推奨であり、無効になっています。
R.attr#navigationBarColor(ジェスチャー ナビゲーション用)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(ジェスチャー ナビゲーション用)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
安定版の構成
アプリが Android 15(API レベル 35)以上をターゲットにしている場合、Configuration はシステムバーを除外しません。レイアウトの計算に Configuration クラスの画面サイズを使用している場合は、必要に応じて適切な ViewGroup、WindowInsets、WindowMetricsCalculator などのより良い代替手段に置き換える必要があります。
Configuration は API 1 以降で利用可能です。通常は Activity.onConfigurationChanged から取得します。ウィンドウの密度、向き、サイズなどの情報が提供されます。Configuration から返されるウィンドウ サイズの重要な特徴の 1 つは、以前はシステムバーが除外されていたことです。
構成サイズは通常、/res/layout-h500dp などのリソース選択に使用されますが、これは依然として有効なユースケースです。ただし、レイアウトの計算に使用することは常に推奨されていません。その場合は、今すぐ離れてください。ユースケースに応じて、Configuration の使用をより適切なものに置き換える必要があります。
レイアウトの計算に使用する場合は、CoordinatorLayout や ConstraintLayout などの適切な ViewGroup を使用します。システム ナビバーの高さを決定するために使用する場合は、WindowInsets を使用します。アプリ ウィンドウの現在のサイズを知りたい場合は、computeCurrentWindowMetrics を使用します。
この変更の影響を受けるフィールドは次のとおりです。
Configuration.screenWidthDpサイズとscreenHeightDpサイズでシステムバーが除外されなくなりました。Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpは、screenWidthDpとscreenHeightDpの変更の影響を間接的に受けます。Configuration.orientationは、正方形に近いデバイスのscreenWidthDpとscreenHeightDpの変更によって間接的に影響を受けます。Display.getSize(Point)は、Configurationの変更の影響を間接的に受けます。これは API レベル 30 以降で非推奨になりました。Display.getMetrics()は、API レベル 33 以降、すでにこの動作をしています。
elegantTextHeight 属性のデフォルトは true
Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリの場合、elegantTextHeight TextView 属性はデフォルトで true になります。これにより、デフォルトで使用されるコンパクトなフォントが、読みやすく大きな縦方向の測定値を持つスクリプトに置き換えられます。コンパクト フォントは、レイアウトの分割を防ぐために導入されました。Android 13(API レベル 33)では、fallbackLineSpacing 属性を使用してテキスト レイアウトの垂直方向の高さを伸ばすことで、このような分割の多くを防ぐことができます。
Android 15 では、コンパクト フォントは引き続きシステムに残るため、アプリで elegantTextHeight を false に設定して以前と同じ動作を実現できますが、今後のリリースでサポートされる可能性は低いです。そのため、アプリがアラビア語、ラオス語、ミャンマー語、タミル語、グジャラート語、カンナダ語、マラヤーラム語、オディア語、テルグ語、タイ語のスクリプトをサポートしている場合は、elegantTextHeight を true に設定してアプリをテストします。
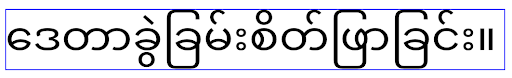 Android 14(API レベル 34)以前をターゲットとするアプリの
Android 14(API レベル 34)以前をターゲットとするアプリの elegantTextHeight の動作
elegantTextHeight の動作。複雑な文字の形状に対する TextView の幅の変更
Android の以前のバージョンでは、複雑なシェーピングを持つ一部の筆記体フォントや言語では、文字が前の文字または次の文字の領域に描画されることがあります。場合によっては、このような文字の開始位置や終了位置が切り詰められていました。Android 15 以降では、TextView はこのような文字に十分なスペースを描画するための幅を割り当て、アプリがクリッピングを防ぐために左側に追加の余白をリクエストできるようにします。
この変更は TextView が幅を決定する方法に影響するため、アプリが Android 15(API レベル 35)以降をターゲットとしている場合、TextView はデフォルトでより多くの幅を割り当てます。この動作を有効または無効にするには、TextView で setUseBoundsForWidth API を呼び出します。
左側の余白を追加すると、既存のレイアウトの位置がずれる可能性があるため、Android 15 以降をターゲットとするアプリでも、デフォルトでは余白は追加されません。ただし、setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang を呼び出すことで、クリッピングを防ぐためにパディングを追加できます。
次の例は、これらの変更によって、一部のフォントと言語のテキスト レイアウトがどのように改善されるかを示しています。

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
EditText の言語 / 地域対応のデフォルトの行の高さ
以前のバージョンの Android では、テキスト レイアウトは、現在の言語 / 地域に一致するフォントの行の高さに合うようにテキストの高さを伸ばしていました。たとえば、コンテンツが日本語の場合、日本語フォントの行間がラテン文字フォントよりも少し大きいため、テキストの高さが少し大きくなっていました。ただし、次の画像に示すように、このような行の高さの違いにもかかわらず、EditText 要素は、使用されている言語 / 地域に関係なく、均一にサイズ設定されていました。

EditText 要素を表す 3 つのボックス。これらの言語の行の高さは異なりますが、EditText の高さは同じです。Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリの場合、指定されたロケールの参照フォントに合わせて、EditText の最小行の高さが予約されるようになりました。これは次の図に示すとおりです。

EditText 要素を表す 3 つのボックス。EditText の高さに、これらの言語のフォントのデフォルトの行の高さに対応するスペースが追加されました。必要に応じて、useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum 属性を false に指定することで、以前の動作を復元できます。また、Kotlin と Java で setMinimumFontMetrics API を使用して、カスタムの最小垂直指標を設定することもできます。
カメラとメディア
Android 15 では、Android 15 以上をターゲットとするアプリのカメラとメディアの動作が次のように変更されています。
音声フォーカス リクエストの制限
Android 15(API レベル 35)をターゲットとするアプリが音声フォーカスをリクエストするには、最上位のアプリであるか、フォアグラウンド サービスを実行している必要があります。アプリがこれらの要件のいずれかを満たしていないときにフォーカスをリクエストしようとすると、呼び出しは AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED を返します。
音声フォーカスの詳細については、音声フォーカスを管理するをご覧ください。
非 SDK の制限の更新
Android 15 では、Android デベロッパーの協力と直近の内部テストに基づいて、制限を受ける非 SDK インターフェースのリストが更新されています。Google は、非 SDK インターフェースを制限する前に、可能な限り、その代わりとなる公開インターフェースを利用可能にしています。
Android 15 をターゲットとしないアプリでは、この変更の一部はすぐには影響しない可能性があります。ただし、アプリのターゲット API レベルに応じて、アプリが一部の非 SDK インターフェースにアクセスできる場合もありますが、非 SDK のメソッドまたはフィールドを使用すると、アプリが機能しなくなるリスクが高くなります。
アプリが非 SDK インターフェースを使用しているかどうか不明な場合は、アプリをテストして確認できます。アプリが非 SDK インターフェースに依存している場合は、SDK の代替インターフェースへの移行を計画してください。ただし Google も、一部のアプリには非 SDK インターフェースを使用する正当なユースケースがあると承知しています。アプリの機能に使用している非 SDK インターフェースの代わりが見つからない場合は、新しい公開 API をリクエストしてください。
Android の今回のリリースの変更について詳しくは、非 SDK インターフェースの制限に関する Android 15 での変更点をご覧ください。非 SDK インターフェース全般について詳しくは、非 SDK インターフェースの制限をご覧ください。
