مانند نسخههای قبلی، اندروید ۱۶ شامل تغییرات رفتاری است که ممکن است بر برنامه شما تأثیر بگذارد. تغییرات رفتاری زیر منحصراً برای برنامههایی اعمال میشود که اندروید ۱۶ یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهند. اگر برنامه شما اندروید ۱۶ یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهد، باید برنامه خود را برای پشتیبانی از این رفتارها، در صورت لزوم، اصلاح کنید.
حتماً فهرست تغییرات رفتاری که صرف نظر از targetSdkVersion برنامه شما، بر همه برنامههای در حال اجرا در اندروید ۱۶ تأثیر میگذارند را نیز بررسی کنید.
تجربه کاربری و رابط کاربری سیستم
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر است که برای ایجاد یک تجربه کاربری سازگارتر و شهودیتر در نظر گرفته شدهاند.
کنار رفتن گزینه انصراف از لبه تا لبه
اندروید ۱۵ برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۵ (سطح API ۳۵) را هدف قرار میدهند، پشتیبانی از لبه به لبه را اجباری کرده است ، اما برنامه شما میتواند با تنظیم R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement روی true ، از این قابلیت انصراف دهد. برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) را هدف قرار میدهند، R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement منسوخ و غیرفعال شده است و برنامه شما نمیتواند از پشتیبانی از لبه به لبه انصراف دهد.
- اگر برنامه شما اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) را هدف قرار داده و روی دستگاهی با اندروید ۱۵ اجرا میشود،
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementبه کار خود ادامه میدهد. - اگر برنامه شما اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) را هدف قرار داده و روی دستگاهی با اندروید ۱۶ اجرا میشود،
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementغیرفعال است.
برای آزمایش در اندروید ۱۶، مطمئن شوید که برنامه شما از لبه به لبه پشتیبانی میکند و هرگونه استفاده از R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement را حذف کنید تا برنامه شما از لبه به لبه در دستگاه اندروید ۱۵ نیز پشتیبانی کند. برای پشتیبانی از لبه به لبه، به راهنمای نوشتن و نمایشها مراجعه کنید.
مهاجرت یا انصراف برای بازگشت پیشبینیکننده الزامی است
برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهند و روی دستگاه اندروید ۱۶ یا بالاتر اجرا میشوند، انیمیشنهای سیستم بازگشت پیشبینیکننده (بازگشت به خانه، میانکاری و میانفعالیتی) به طور پیشفرض فعال هستند. علاوه بر این، onBackPressed فراخوانی نمیشود و KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK دیگر ارسال نمیشود.
اگر برنامه شما رویداد back را متوقف میکند و شما هنوز به حالت predictive back مهاجرت نکردهاید، برنامه خود را بهروزرسانی کنید تا از APIهای پشتیبانیشده برای ناوبری back استفاده کند ، یا با تنظیم ویژگی android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback به false در تگ <application> یا <activity> از فایل AndroidManifest.xml برنامه خود، موقتاً از این حالت خارج شوید.
APIهای فونت Elegant منسوخ و غیرفعال شدند
Apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) have the
elegantTextHeight
TextView attribute set to true by
default, replacing the compact font with one that is much more readable. You
could override this by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to false.
Android 16 deprecates the
elegantTextHeight attribute,
and the attribute will be ignored once your app targets Android 16. The "UI
fonts" controlled by these APIs are being discontinued, so you should adapt any
layouts to ensure consistent and future proof text rendering in Arabic, Lao,
Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu or Thai.
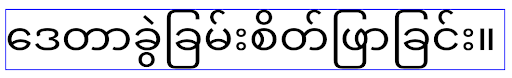
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
14 (API level 34) and lower, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35)
that overrode the default by setting the elegantTextHeight
attribute to false.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
16 (API level 36), or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) that didn't
override the default by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute
to false.عملکرد اصلی
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر است که قابلیتهای اصلی مختلف سیستم اندروید را اصلاح یا گسترش میدهد.
بهینهسازی زمانبندی کار با نرخ ثابت
قبل از هدف قرار دادن اندروید 16، زمانی که scheduleAtFixedRate اجرای یک کار را به دلیل خارج از چرخه حیات فرآیند معتبر از دست داد، همه اجراهای از دست رفته بلافاصله با بازگشت برنامه به چرخه حیات معتبر اجرا می شوند.
هنگام هدف قرار دادن Android 16، حداکثر یک اجرای از دست رفته scheduleAtFixedRate بلافاصله پس از بازگشت برنامه به چرخه حیات معتبر اجرا می شود. انتظار می رود این تغییر رفتار باعث بهبود عملکرد برنامه شود. این رفتار را در برنامه خود آزمایش کنید تا بررسی کنید آیا برنامه شما تحت تأثیر قرار گرفته است یا خیر. همچنین میتوانید با استفاده از چارچوب سازگاری برنامه و فعال کردن پرچم سازگار STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS آزمایش کنید.
فاکتورهای شکل دستگاه
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر برای برنامهها هنگام نمایش در دستگاههای صفحه نمایش بزرگ است.
طرحبندیهای تطبیقی
با توجه به اینکه برنامههای اندروید اکنون روی دستگاههای متنوعی (مانند تلفن، تبلت، دستگاههای تاشو، کامپیوترهای رومیزی، ماشین و تلویزیون) اجرا میشوند و حالتهای پنجرهای روی صفحه نمایشهای بزرگ (مانند تقسیم صفحه و پنجرهای کردن دسکتاپ)، توسعهدهندگان باید برنامههای اندرویدی بسازند که صرف نظر از جهتگیری دستگاه، با هر صفحه و اندازه پنجرهای سازگار شوند. الگوهایی مانند محدود کردن جهتگیری و قابلیت تغییر اندازه در دنیای چنددستگاهی امروز بسیار محدودکننده هستند.
محدودیتهای جهتگیری، تغییر اندازه و نسبت ابعاد را نادیده بگیرید
برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) را هدف قرار میدهند، محدودیتهای جهتگیری، تغییر اندازه و نسبت ابعاد دیگر در نمایشگرهایی با کوچکترین عرض >= ۶۰۰dp اعمال نمیشوند. برنامهها کل پنجره نمایشگر را صرف نظر از نسبت ابعاد یا جهتگیری ترجیحی کاربر پر میکنند و از ستونبندی استفاده نمیشود.
این تغییر، یک رفتار استاندارد جدید برای پلتفرم معرفی میکند. اندروید به سمت مدلی حرکت میکند که در آن انتظار میرود برنامهها با جهتگیریها، اندازههای نمایشگر و نسبتهای ابعاد مختلف سازگار شوند. محدودیتهایی مانند جهتگیری ثابت یا قابلیت تغییر اندازه محدود، مانع از سازگاری برنامه میشود. برنامه خود را سازگار کنید تا بهترین تجربه کاربری ممکن را ارائه دهید.
همچنین میتوانید این رفتار را با استفاده از چارچوب سازگاری برنامه و فعال کردن پرچم UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat آزمایش کنید.
تغییرات رایج در شکستن قفل
نادیده گرفتن محدودیتهای جهتگیری، تغییر اندازه و نسبت ابعاد ممکن است بر رابط کاربری برنامه شما در برخی دستگاهها تأثیر بگذارد، به خصوص عناصری که برای طرحبندیهای کوچک قفلشده در جهت عمودی طراحی شدهاند: برای مثال، مسائلی مانند طرحبندیهای کشیده و انیمیشنها و اجزای خارج از صفحه. هرگونه فرض در مورد نسبت ابعاد یا جهتگیری میتواند باعث مشکلات بصری در برنامه شما شود. درباره نحوه اجتناب از آنها و بهبود رفتار تطبیقی برنامه خود بیشتر بیاموزید .
فعال کردن چرخش دستگاه منجر به ایجاد مجدد فعالیتها میشود که در صورت عدم حفظ صحیح، میتواند منجر به از دست رفتن وضعیت کاربر شود. نحوه ذخیره صحیح وضعیت رابط کاربری را در بخش «ذخیره وضعیتهای رابط کاربری» بیاموزید.
جزئیات پیادهسازی
ویژگیهای مانیفست و APIهای زمان اجرا زیر در دستگاههای با صفحه نمایش بزرگ، در حالتهای تمام صفحه و چند پنجرهای نادیده گرفته میشوند:
-
screenOrientation -
resizableActivity -
minAspectRatio -
maxAspectRatio -
setRequestedOrientation() -
getRequestedOrientation()
مقادیر زیر برای screenOrientation ، setRequestedOrientation() و getRequestedOrientation() نادیده گرفته میشوند:
-
portrait -
reversePortrait -
sensorPortrait -
userPortrait -
landscape -
reverseLandscape -
sensorLandscape -
userLandscape
در مورد قابلیت تغییر اندازه صفحه نمایش، android:resizeableActivity="false" ، android:minAspectRatio و android:maxAspectRatio هیچ تاثیری ندارند.
برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) را هدف قرار میدهند، محدودیتهای جهتگیری برنامه، قابلیت تغییر اندازه و نسبت ابعاد به طور پیشفرض در صفحه نمایشهای بزرگ نادیده گرفته میشوند، اما هر برنامهای که کاملاً آماده نیست میتواند با انصراف (که منجر به رفتار قبلی قرار گرفتن در حالت سازگاری میشود) موقتاً این رفتار را نادیده بگیرد.
استثنائات
محدودیتهای جهتگیری، تغییر اندازه و نسبت تصویر اندروید ۱۶ در شرایط زیر اعمال نمیشوند:
- بازیها (بر اساس پرچم
android:appCategory) - کاربرانی که صریحاً رفتار پیشفرض برنامه را در تنظیمات نسبت ابعاد دستگاه انتخاب میکنند
- صفحه نمایشهایی که کوچکتر از
sw600dpهستند
انصراف موقت
برای غیرفعال کردن یک فعالیت خاص، ویژگی manifest مربوط به PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY را اعلان کنید:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
اگر بخشهای زیادی از برنامه شما برای اندروید ۱۶ آماده نیستند، میتوانید با اعمال همین ویژگی در سطح برنامه، بهطور کامل از آن صرفنظر کنید:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
سلامت و تناسب اندام
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر در رابطه با دادههای سلامت و تناسب اندام است.
مجوزهای سلامت و تناسب اندام
برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهند، مجوزهای BODY_SENSORS از مجوزهای جزئیتری تحت android.permissions.health استفاده میکنند که Health Connect نیز از آن استفاده میکند. از اندروید ۱۶، هر API که قبلاً به BODY_SENSORS یا BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND نیاز داشت، به جای آن به مجوز android.permissions.health مربوطه نیاز دارد. این امر بر انواع داده، APIها و انواع سرویسهای پیشزمینه زیر تأثیر میگذارد:
-
HEART_RATE_BPMاز سرویسهای سلامت در Wear OS -
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEاز مدیریت حسگر اندروید -
heartRateAccuracyوheartRateBpmازProtoLayoutدر Wear OS -
FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHکه در آن به جایBODY_SENSORSمجوزandroid.permission.healthمربوطه مورد نیاز است.
اگر برنامه شما از این APIها استفاده میکند، باید مجوزهای جزئی مربوطه را درخواست کند:
- برای نظارت بر ضربان قلب، SpO2 یا دمای پوست در حین استفاده: مجوز جزئی را در
android.permissions.healthدرخواست کنید، مانندREAD_HEART_RATEبه جایBODY_SENSORS. - برای دسترسی به حسگرهای پسزمینه: به جای
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDREAD_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDدرخواست کنید.
این مجوزها همان مجوزهایی هستند که دسترسی به خواندن دادهها از Health Connect ، پایگاه داده اندروید برای دادههای سلامت، تناسب اندام و تندرستی، را محدود میکنند.
اپلیکیشنهای موبایل
برنامههای موبایلی که به استفاده از READ_HEART_RATE و سایر مجوزهای جزئی مهاجرت میکنند، باید فعالیتی را نیز برای نمایش سیاست حفظ حریم خصوصی برنامه اعلام کنند . این همان الزام Health Connect است.
اتصال
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر در پشته بلوتوث برای بهبود اتصال با دستگاههای جانبی است.
اهداف جدید برای مدیریت از دست دادن اوراق قرضه و تغییرات رمزگذاری
به عنوان بخشی از بهبود مدیریت از دست دادن اوراق قرضه ، اندروید 16 همچنین 2 هدف جدید را معرفی می کند تا برنامه ها را با آگاهی بیشتر از از دست دادن اوراق قرضه و تغییرات رمزگذاری ارائه کند.
برنامه هایی که اندروید 16 را هدف قرار می دهند اکنون می توانند:
- هنگامی که از دست دادن اوراق قرضه از راه دور شناسایی شد، یک هدف
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGدریافت کنید، که به آنها امکان می دهد بازخورد آموزنده تری از کاربر ارائه دهند و اقدامات مناسب را انجام دهند. - هر زمان که وضعیت رمزگذاری پیوند تغییر کرد، یک هدف
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEدریافت کنید. این شامل تغییر وضعیت رمزگذاری، تغییر الگوریتم رمزگذاری و تغییر اندازه کلید رمزگذاری است. اگر بعداً پس از دریافت هدفACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEپیوند با موفقیت رمزگذاری شد، برنامهها باید پیوند را بازیابی شده در نظر بگیرند.
انطباق با پیاده سازی های مختلف OEM
در حالی که اندروید 16 این اهداف جدید را معرفی میکند، پیادهسازی و پخش آنها میتواند در تولیدکنندگان مختلف دستگاه (OEM) متفاوت باشد. برای اطمینان از اینکه برنامه شما یک تجربه ثابت و قابل اعتماد را در همه دستگاهها ارائه میکند، توسعهدهندگان باید مدیریت تلفات اوراق قرضه خود را طوری طراحی کنند که بهخوبی با این تغییرات بالقوه سازگار شوند.
ما رفتارهای برنامه زیر را توصیه می کنیم:
اگر هدف
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGپخش شود:پیوند ACL (اتصال ناهمگام-کمتر) توسط سیستم قطع خواهد شد، اما اطلاعات پیوند دستگاه حفظ خواهد شد (همانطور که در اینجا توضیح داده شده است).
برنامه شما باید از این هدف بهعنوان سیگنال اصلی برای تشخیص از دست دادن اوراق قرضه استفاده کند و کاربر را راهنمایی کند تا قبل از شروع فراموشی یا جفتسازی مجدد دستگاه تأیید کند که دستگاه راه دور در محدوده است.
اگر دستگاهی پس از دریافت
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGقطع شود، برنامه شما باید در مورد اتصال مجدد محتاط باشد، زیرا ممکن است دستگاه دیگر به سیستم متصل نباشد.اگر هدف
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGپخش نشد:پیوند ACL متصل باقی میماند، و اطلاعات پیوند دستگاه توسط سیستم حذف میشود، مانند رفتار در Android 15.
در این سناریو، برنامه شما باید به مکانیسمهای مدیریت از دست دادن اوراق قرضه موجود خود مانند نسخههای قبلی اندروید ادامه دهد تا رویدادهای از دست دادن اوراق قرضه را شناسایی و مدیریت کند.
روش جدید برای حذف اتصال بلوتوث
همه برنامههایی که اندروید 16 را هدف قرار میدهند، اکنون میتوانند با استفاده از یک API عمومی در CompanionDeviceManager ، دستگاههای بلوتوث را لغو جفت کنند. اگر یک دستگاه همراه به عنوان یک انجمن CDM مدیریت میشود، برنامه میتواند با استفاده از API جدید removeBond(int) در دستگاه مرتبط، حذف پیوند بلوتوث را آغاز کند. این برنامه میتواند با گوش دادن به رویداد پخش دستگاه بلوتوث ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED تغییرات وضعیت پیوند را کنترل کند.
امنیت
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات امنیتی زیر است.
قفل شدن نسخه MediaStore
برای برنامههایی که اندروید 16 یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهند، MediaStore#getVersion() اکنون برای هر برنامه منحصر به فرد خواهد بود. این ویژگی های شناسایی را از رشته نسخه حذف می کند تا از سوء استفاده و استفاده از تکنیک های انگشت نگاری جلوگیری شود. برنامه ها نباید هیچ فرضی در مورد قالب این نسخه داشته باشند. برنامهها از قبل باید هنگام استفاده از این API تغییرات نسخه را کنترل کنند و در بیشتر موارد نیازی به تغییر رفتار فعلی خود ندارند، مگر اینکه توسعهدهنده تلاش کرده باشد اطلاعات بیشتری را استنباط کند که فراتر از محدوده مورد نظر این API است.
مقاصد امنتر
ویژگی Safer Intents یک ابتکار امنیتی چند مرحلهای است که برای بهبود امنیت مکانیسم تشخیص هدف اندروید طراحی شده است. هدف، محافظت از برنامهها در برابر اقدامات مخرب با افزودن بررسیها در طول پردازش هدف و فیلتر کردن اهدافی است که معیارهای خاصی را برآورده نمیکنند.
در اندروید ۱۵، این ویژگی که بر برنامهی فرستنده متمرکز بود، اکنون در اندروید ۱۶، کنترل را به برنامهی گیرنده منتقل میکند و به توسعهدهندگان اجازه میدهد تا با استفاده از مانیفست برنامهی خود، وضوح دقیق هدف را انتخاب کنند.
دو تغییر اساسی در حال اجرا هستند:
اهداف صریح باید با فیلتر هدف کامپوننت هدف مطابقت داشته باشند: اگر یک هدف به صراحت یک کامپوننت را هدف قرار دهد، باید با فیلتر هدف آن کامپوننت مطابقت داشته باشد.
اینتنتهای بدون اکشن نمیتوانند با هیچ فیلتر اینتنتی مطابقت داشته باشند: اینتنتهایی که اکشن مشخصی ندارند، نباید با هیچ فیلتر اینتنتی تطبیق داده شوند.
این تغییرات فقط زمانی اعمال میشوند که چندین برنامه درگیر باشند و بر مدیریت قصد (intent handling) در یک برنامه واحد تأثیری ندارند.
تأثیر
ماهیت اختیاری آن به این معنی است که توسعهدهندگان باید آن را به صراحت در مانیفست برنامه خود فعال کنند تا فعال شود. در نتیجه، تأثیر این ویژگی محدود به برنامههایی خواهد بود که توسعهدهندگان آنها:
- از ویژگی Safer Intents و مزایای آن آگاه هستند.
- فعالانه تصمیم میگیرند که شیوههای سختگیرانهتری را برای مدیریت قصد (intent handling) در برنامههای خود بگنجانند.
این رویکرد انتخابی، خطر از کار افتادن برنامههای موجود را که ممکن است به رفتار فعلیِ با امنیت کمتر برای حل اینتنت متکی باشند، به حداقل میرساند.
اگرچه ممکن است تأثیر اولیه در اندروید ۱۶ محدود باشد، اما ابتکار Safer Intents نقشه راهی برای تأثیر گستردهتر در نسخههای آینده اندروید دارد. این طرح در نهایت به این صورت است که تفکیکپذیری دقیق intent به رفتار پیشفرض تبدیل شود.
ویژگی Safer Intents این پتانسیل را دارد که با دشوارتر کردن سوءاستفاده از آسیبپذیریها در مکانیسم تشخیص هدف (intent resolution)، امنیت اکوسیستم اندروید را به میزان قابل توجهی افزایش دهد.
با این حال، گذار به انصراف و اجرای اجباری باید با دقت مدیریت شود تا مشکلات سازگاری بالقوه با برنامههای موجود برطرف شود.
پیادهسازی
توسعهدهندگان باید با استفاده از ویژگی intentMatchingFlags در مانیفست برنامه خود، تطبیق دقیقتر اینتنت را به صراحت فعال کنند. در اینجا مثالی آورده شده است که در آن این ویژگی برای کل برنامه فعال است، اما در یک گیرنده غیرفعال/غیرفعال است:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد پرچمهای پشتیبانیشده:
| نام پرچم | توضیحات |
|---|---|
| فیلتر intent را اعمال کنید | تطبیق دقیقتری را برای اهداف ورودی اعمال میکند |
| هیچ کدام | تمام قوانین تطبیق ویژه را برای ورودیهای ورودی غیرفعال میکند. هنگام تعیین چندین پرچم، مقادیر متناقض با اولویت دادن به پرچم "none" حل میشوند. |
| اجازه دادن به NullAction | قوانین تطبیق را آسان میکند تا به intent های بدون اکشن اجازه تطبیق داده شود. این پرچم همراه با "enforceIntentFilter" برای دستیابی به یک رفتار خاص استفاده میشود. |
تست و اشکالزدایی
وقتی اجرای فعال باشد، اگر فراخوانندهی intent به درستی intent را پر کرده باشد، برنامهها باید به درستی کار کنند. با این حال، intentهای مسدود شده پیامهای هشداری مانند "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" و "Access blocked:" با برچسب "PackageManager." این نشان دهندهی یک مشکل بالقوه است که میتواند بر برنامه تأثیر بگذارد و نیاز به توجه دارد.
فیلتر لاگکت:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
فیلتر کردن فراخوانیهای سیستمی GPU
برای مقاومسازی سطح پردازنده گرافیکی Mali، IOCTLهای پردازنده گرافیکی Mali که منسوخ شدهاند یا صرفاً برای توسعه پردازنده گرافیکی در نظر گرفته شدهاند، در نسخههای تولیدی مسدود شدهاند. علاوه بر این، IOCTLهای مورد استفاده برای پروفایلسازی پردازنده گرافیکی به فرآیند پوسته یا برنامههای اشکالزداییشده محدود شدهاند. برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد سیاست سطح پلتفرم، به بهروزرسانی SAC مراجعه کنید.
این تغییر در دستگاههای پیکسل که از پردازنده گرافیکی Mali (پیکسل ۶-۹) استفاده میکنند، رخ میدهد. آرم دستهبندی رسمی IOCTL های خود را در Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst از نسخه r54p2 خود ارائه کرده است. این لیست در نسخههای درایور آینده همچنان حفظ خواهد شد.
این تغییر بر APIهای گرافیکی پشتیبانیشده (از جمله Vulkan و OpenGL) تأثیری ندارد و انتظار نمیرود که توسعهدهندگان یا برنامههای موجود را نیز تحت تأثیر قرار دهد. ابزارهای پروفایلینگ GPU مانند Streamline Performance Analyzer و Android GPU Inspector تحت تأثیر قرار نخواهند گرفت.
آزمایش
اگر با خطای عدم پذیرش SELinux مشابه تصویر زیر مواجه شدید، احتمالاً برنامه شما تحت تأثیر این تغییر قرار گرفته است:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
اگر برنامه شما نیاز به استفاده از IOCTL های مسدود شده دارد، لطفاً یک اشکال (bug) ثبت کنید و آن را به android-partner-security@google.com ارجاع دهید.
سوالات متداول
آیا این تغییر سیاست برای همه تولیدکنندگان اصلی تجهیزات (OEM) اعمال میشود؟ این تغییر اختیاری خواهد بود، اما برای هر تولیدکننده اصلی تجهیزاتی که مایل به استفاده از این روش مقاومسازی باشند، در دسترس خواهد بود. دستورالعملهای اجرای این تغییر را میتوانید در مستندات پیادهسازی بیابید.
آیا برای پیادهسازی این تغییر، ایجاد تغییرات در کدبیس تولیدکننده اصلی (OEM) اجباری است یا اینکه بهطور پیشفرض با یک نسخه جدید AOSP همراه خواهد بود؟ تغییر در سطح پلتفرم بهطور پیشفرض با یک نسخه جدید AOSP همراه خواهد بود. فروشندگان میتوانند در صورت تمایل به اعمال این تغییر در کدبیس خود، آن را بپذیرند.
آیا SoCها مسئول بهروز نگه داشتن لیست IOCTL هستند؟ به عنوان مثال، اگر دستگاه من از پردازنده گرافیکی ARM Mali استفاده میکند، آیا باید برای هرگونه تغییر با ARM تماس بگیرم؟ SoCهای جداگانه باید لیستهای IOCTL خود را برای هر دستگاه پس از انتشار درایور بهروزرسانی کنند. به عنوان مثال، ARM لیست IOCTL منتشر شده خود را پس از بهروزرسانی درایور بهروزرسانی میکند. با این حال، OEMها باید مطمئن شوند که بهروزرسانیها را در SEPolicy خود لحاظ میکنند و در صورت نیاز، IOCTLهای سفارشی انتخاب شده را به لیستها اضافه میکنند.
آیا این تغییر به طور خودکار برای همه دستگاههای پیکسل موجود در بازار اعمال میشود یا برای اعمال این تغییر، اقدام کاربر لازم است؟ این تغییر برای همه دستگاههای پیکسل موجود در بازار که از پردازنده گرافیکی Mali استفاده میکنند (پیکسل ۶-۹) اعمال میشود. برای اعمال این تغییر نیازی به اقدام کاربر نیست.
آیا استفاده از این سیاست بر عملکرد درایور هسته تأثیر میگذارد؟ این سیاست با استفاده از GFXBench روی پردازنده گرافیکی Mali آزمایش شد و هیچ تغییر قابل اندازهگیری در عملکرد پردازنده گرافیکی مشاهده نشد.
آیا لازم است لیست IOCTL با نسخههای فعلی درایور فضای کاربری و هسته هماهنگ شود؟ بله، لیست IOCTLهای مجاز باید با IOCTLهای پشتیبانی شده توسط درایورهای فضای کاربری و هسته هماهنگ شوند. اگر IOCTLهای موجود در فضای کاربری یا درایور هسته بهروزرسانی شوند، لیست IOCTL در SEPolicy نیز باید بهروزرسانی شود تا با آنها مطابقت داشته باشد.
ARM، IOCTLها را به عنوان «محدود» / «ابزار دقیق» طبقهبندی کرده است، اما ما میخواهیم از برخی از آنها در موارد استفاده در تولید استفاده کنیم و/یا برخی دیگر را رد کنیم. تولیدکنندگان اصلی تجهیزات/SoCها مسئول تصمیمگیری در مورد نحوه طبقهبندی IOCTLهایی هستند که بر اساس پیکربندی کتابخانههای Mali فضای کاربری خود، استفاده میکنند. فهرست ARM میتواند برای تصمیمگیری در مورد این موارد استفاده شود، اما موارد استفاده هر تولیدکننده اصلی تجهیزات/SoC ممکن است متفاوت باشد.
حریم خصوصی
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات حریم خصوصی زیر است.
مجوز شبکه محلی
دستگاههای موجود در شبکه محلی (LAN) میتوانند توسط هر برنامهای که مجوز INTERNET دارد، قابل دسترسی باشند. این امر اتصال برنامهها به دستگاههای محلی را آسان میکند، اما پیامدهایی برای حریم خصوصی مانند تشکیل اثر انگشت کاربر و تبدیل شدن به یک پروکسی برای موقعیت مکانی نیز دارد.
پروژه حفاظت از شبکههای محلی (Local Network Protections) با هدف محافظت از حریم خصوصی کاربر، دسترسی به شبکه محلی را با مجوز زمان اجرا (runtime permission) جدیدی مسدود میکند.
طرح انتشار
این تغییر به ترتیب بین دو نسخه، سهماهه دوم ۲۵ و سهماهه دوم ۲۶، اعمال خواهد شد. ضروری است که توسعهدهندگان این راهنما را برای سهماهه دوم ۲۵ دنبال کنند و بازخورد خود را به اشتراک بگذارند، زیرا این محافظتها در نسخه بعدی اندروید اعمال خواهند شد . علاوه بر این، آنها باید سناریوهایی را که به دسترسی ضمنی به شبکه محلی بستگی دارند، با استفاده از راهنمای زیر بهروزرسانی کنند و برای رد کاربر و لغو مجوز جدید آماده شوند.
تأثیر
در مرحله فعلی، LNP یک ویژگی اختیاری است، به این معنی که فقط برنامههایی که این ویژگی را انتخاب میکنند تحت تأثیر قرار میگیرند. هدف از مرحله اختیاری این است که توسعهدهندگان برنامه بفهمند کدام بخشهای برنامهشان به دسترسی ضمنی به شبکه محلی نیاز دارد تا بتوانند برای انتشار بعدی، از آنها محافظت کنند.
اگر برنامهها با استفاده از روشهای زیر به شبکه محلی کاربر دسترسی پیدا کنند، تحت تأثیر قرار خواهند گرفت:
- استفاده مستقیم یا کتابخانهای از سوکتهای خام روی آدرسهای شبکه محلی (مثلاً mDNS یا پروتکل کشف سرویس SSDP)
- استفاده از کلاسهای سطح چارچوب که به شبکه محلی دسترسی دارند (مثلاً NsdManager)
ترافیک ورودی و خروجی از یک آدرس شبکه محلی نیاز به مجوز دسترسی به شبکه محلی دارد. جدول زیر برخی از موارد رایج را فهرست میکند:
| عملیات شبکه سطح پایین برنامه | مجوز شبکه محلی مورد نیاز است |
|---|---|
| ایجاد یک اتصال TCP خروجی | بله |
| پذیرش اتصالات TCP ورودی | بله |
| ارسال UDP به صورت تک پخشی، چندپخشی، پخش همگانی | بله |
| دریافت یک UDP ورودی به صورت تک پخشی، چندپخشی، پخش همگانی | بله |
این محدودیتها در اعماق پشته شبکه پیادهسازی شدهاند و بنابراین بر همه APIهای شبکه اعمال میشوند. این شامل سوکتهای ایجاد شده با کد بومی یا مدیریتشده، کتابخانههای شبکه مانند Cronet و OkHttp و هر API پیادهسازی شده بر روی آنها میشود. تلاش برای حل مشکلات سرویسها در شبکه محلی (یعنی آنهایی که پسوند .local دارند) به مجوز شبکه محلی نیاز دارد.
استثنائات قوانین فوق:
- اگر سرور DNS یک دستگاه در یک شبکه محلی باشد، ترافیک ورودی یا خروجی از آن (در پورت ۵۳) نیازی به مجوز دسترسی به شبکه محلی ندارد.
- برنامههایی که از Output Switcher به عنوان انتخابگر درونبرنامهای خود استفاده میکنند، به مجوزهای شبکه محلی نیاز نخواهند داشت (راهنمایی بیشتر در سهماهه چهارم 2025 ارائه خواهد شد).
راهنمایی توسعهدهنده (انتخابی)
برای اعمال محدودیتهای شبکه محلی، موارد زیر را انجام دهید:
- دستگاه را به نسخهای با نسخه بتا ۳ از ۲۵Q2 یا بالاتر فلش کنید.
- برای تست، برنامه را نصب کنید.
تغییر وضعیت پرچم Appcompat در adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>دستگاه را ریبوت کنید
اکنون دسترسی برنامه شما به شبکه محلی محدود شده است و هرگونه تلاشی برای دسترسی به شبکه محلی منجر به خطاهای سوکت خواهد شد. اگر از APIهایی استفاده میکنید که عملیات شبکه محلی را خارج از فرآیند برنامه شما انجام میدهند (مثلاً: NsdManager)، در مرحله انتخاب، تحت تأثیر قرار نخواهند گرفت.
برای بازیابی دسترسی، باید به برنامه خود اجازه دسترسی به NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES را بدهید.
- مطمئن شوید که برنامه مجوز
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESرا در مانیفست خود اعلام کرده است. - به تنظیمات > برنامهها > [نام برنامه] > مجوزها > دستگاههای نزدیک > مجاز بروید.
اکنون دسترسی برنامه شما به شبکه محلی باید بازیابی شده باشد و تمام سناریوهای شما باید مانند قبل از فعال کردن برنامه، کار کنند.
زمانی که اجرای قانون حفاظت از شبکه محلی آغاز شود، در اینجا نحوه تأثیر آن بر ترافیک شبکه برنامه آمده است.
| اجازه | درخواست شبکه محلی خروجی | درخواست اینترنت خروجی/ورودی | درخواست شبکه محلی ورودی |
|---|---|---|---|
| اعطا شده | آثار | آثار | آثار |
| اعطا نشده | شکستها | آثار | شکستها |
برای غیرفعال کردن پرچم App-Compat از دستور زیر استفاده کنید.
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
خطاها
خطاهای ناشی از این محدودیتها، هر زمان که سوکت فراخوانی کننده، تابع send یا نوع دیگری از send را به یک آدرس شبکه محلی فراخوانی کند، به آن بازگردانده میشوند.
خطاهای مثال:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
تعریف شبکه محلی
منظور از شبکه محلی در این پروژه، شبکهای مبتنی بر IP است که از یک رابط شبکه با قابلیت پخش همگانی، مانند Wi-Fi یا Ethernet، استفاده میکند، اما اتصالات تلفن همراه (WWAN) یا VPN را شامل نمیشود.
موارد زیر به عنوان شبکههای محلی در نظر گرفته میشوند:
آیپیوی۴:
- ۱۶۹.۲۵۴.۰.۰/۱۶ // لینک محلی
- ۱۰۰.۶۴.۰.۰/۱۰ // سیجیانایتی
- ۱۰.۰.۰.۰/۸ // RFC۱۹۱۸
- ۱۷۲.۱۶.۰.۰/۱۲ // RFC۱۹۱۸
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
آیپیوی۶:
- لینک-محلی
- مسیرهای متصل مستقیم
- شبکههای خرد مانند Thread
- زیرشبکههای چندگانه (تاریخ انتشار نامشخص)
علاوه بر این، هر دو آدرس چندپخشی (224.0.0.0/4، ff00::/8) و آدرس پخش IPv4 (255.255.255.255) به عنوان آدرسهای شبکه محلی طبقهبندی میشوند.
عکسهای متعلق به برنامه
هنگامی که برنامهای که SDK 36 یا بالاتر را در دستگاههای دارای Android 16 یا بالاتر هدف قرار میدهد، مجوزهای عکس و ویدیو را درخواست میکند، کاربرانی که انتخاب میکنند دسترسی به رسانه انتخابشده را محدود کنند، هر عکسی را که متعلق به برنامه از پیش انتخاب شده در انتخابگر عکس است، میبینند. کاربران می توانند هر یک از این موارد از پیش انتخاب شده را لغو انتخاب کنند، که دسترسی برنامه به آن عکس ها و ویدیوها را لغو می کند.

