Android 16, önceki sürümlerde olduğu gibi uygulamanızı etkileyebilecek davranış değişiklikleri içerir. Aşağıdaki davranış değişiklikleri yalnızca Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar için geçerlidir. Uygulamanız Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefliyorsa uygulanabilir durumlarda bu davranışları destekleyecek şekilde uygulamanızı değiştirmeniz gerekir.
Uygulamanızın targetSdkVersion'sinden bağımsız olarak Android 16'da çalışan tüm uygulamaları etkileyen davranış değişiklikleri
listesini de inceleyin.
Kullanıcı deneyimi ve sistem arayüzü
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), daha tutarlı ve sezgisel bir kullanıcı deneyimi oluşturmak için aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Uçtan uca kapsam dışında kalma seçeneği kaldırılıyor
Android 15 enforced edge-to-edge for apps targeting Android 15 (API
level 35), but your app could opt-out by setting
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement to true. For apps
targeting Android 16 (API level 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement is deprecated and disabled, and your
app can't opt-out of going edge-to-edge.
- If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 15 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinues to work. - If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 16 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementis disabled.
For testing in Android 16, ensure your app supports edge-to-edge and
remove any use of R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement so that your app
also supports edge-to-edge on an Android 15 device. To support edge-to-edge,
see the Compose and Views guidance.
Tahmini geri özelliği için taşıma veya devre dışı bırakma işlemi gerekir
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher and running on an
Android 16 or higher device, the predictive back system animations
(back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity) are enabled by default.
Additionally, onBackPressed is not called and
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK is not dispatched anymore.
If your app intercepts the back event and you haven't migrated to predictive
back yet, update your app to use supported back navigation APIs, or
temporarily opt out by setting the
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback attribute to false in the
<application> or <activity> tag of your app's AndroidManifest.xml file.
Elegant Font API'leri kullanımdan kaldırıldı ve devre dışı bırakıldı
Apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) have the
elegantTextHeight
TextView attribute set to true by
default, replacing the compact font with one that is much more readable. You
could override this by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to false.
Android 16 deprecates the
elegantTextHeight attribute,
and the attribute will be ignored once your app targets Android 16. The "UI
fonts" controlled by these APIs are being discontinued, so you should adapt any
layouts to ensure consistent and future proof text rendering in Arabic, Lao,
Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu or Thai.
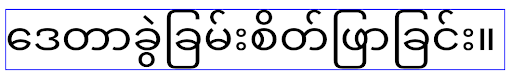
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
14 (API level 34) and lower, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35)
that overrode the default by setting the elegantTextHeight
attribute to false.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
16 (API level 36), or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) that didn't
override the default by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute
to false.Temel işlevler
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), Android sisteminin çeşitli temel özelliklerini değiştiren veya genişleten aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Sabit ücretli iş planlaması optimizasyonu
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
Cihaz form faktörleri
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), büyük ekranlı cihazlarda gösterilen uygulamalar için aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Uyarlanabilir düzenler
With Android apps now running on a variety of devices (such as phones, tablets, foldables, desktops, cars, and TVs) and windowing modes on large screens (such as split screen and desktop windowing), developers should build Android apps that adapt to any screen and window size, regardless of device orientation. Paradigms like restricting orientation and resizability are too restrictive in today's multidevice world.
Ignore orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), Android 16 includes changes to how the system manages orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions. On displays with smallest width >= 600dp, the restrictions no longer apply. Apps also fill the entire display window, regardless of aspect ratio or a user's preferred orientation, and pillarboxing isn't used.
This change introduces a new standard platform behavior. Android is moving toward a model where apps are expected to adapt to various orientations, display sizes, and aspect ratios. Restrictions like fixed orientation or limited resizability hinder app adaptability, so we recommend making your app adaptive to deliver the best possible user experience.
You can also test this behavior by using the
app compatibility framework and
enabling the UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag.
Common breaking changes
Ignoring orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions might impact your app's UI on some devices, especially elements that were designed for small layouts locked in portrait orientation: for example, issues like stretched layouts and off-screen animations and components. Any assumptions about aspect ratio or orientation can cause visual issues with your app. Learn more about how to avoid them and improve your app's adaptive behaviour.
Allowing device rotation results in more activity re-creation, which can result in losing user state if not properly preserved. Learn how to correctly save UI state in Save UI states.
Implementation details
The following manifest attributes and runtime APIs are ignored across large screen devices in full-screen and multi-window modes:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
The following values for screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), and
getRequestedOrientation() are ignored:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Regarding display resizability, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, and android:maxAspectRatio have no effect.
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), app orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio constraints are ignored on large screens by default, but every app that isn't fully ready can temporarily override this behavior by opting out (which results in the previous behavior of being placed in compatibility mode).
Exceptions
The Android 16 orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions don't apply in the following situations:
- Games (based on the
android:appCategoryflag) - Users explicitly opting in to the app's default behavior in aspect ratio settings of the device
- Screens that are smaller than
sw600dp
Opt out temporarily
To opt out a specific activity, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
If too many parts of your app aren't ready for Android 16, you can opt out completely by applying the same property at the application level:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Sağlık ve fitness
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), sağlık ve fitness verileriyle ilgili aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Sağlık ve fitness izinleri
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher,
BODY_SENSORS permissions use more granular permissions
under android.permissions.health, which Health Connect
also uses. As of Android 16, any API previously requiring BODY_SENSORS
or BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requires the corresponding
android.permissions.health permission instead. This affects the following data
types, APIs, and foreground service types:
HEART_RATE_BPMfrom Health Services on Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEfrom Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyandheartRateBpmfromProtoLayouton Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHwhere the respectiveandroid.permission.healthpermission is needed in place ofBODY_SENSORS
If your app uses these APIs, it should request the respective granular permissions:
- For while-in-use monitoring of Heart Rate, SpO2, or Skin Temperature:
request the granular permission under
android.permissions.health, such asREAD_HEART_RATEinstead ofBODY_SENSORS. - For background sensor access: request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDinstead ofBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
These permissions are the same as those that guard access to reading data from Health Connect, the Android datastore for health, fitness, and wellness data.
Mobile apps
Mobile apps migrating to use the READ_HEART_RATE and other granular
permissions must also declare an activity to display
the app's privacy policy. This is the same requirement as Health Connect.
Bağlantı
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), çevre birimi cihazlarla bağlantıyı iyileştirmek için Bluetooth yığınında aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Bağlantı kaybı ve şifreleme değişikliklerini işlemek için yeni amaçlar
As part of the Improved bond loss handling, Android 16 also introduces 2 new intents to provide apps with greater awareness of bond loss and encryption changes.
Apps targeting Android 16 can now:
- Receive an
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent when remote bond loss is detected, allowing them to provide more informative user feedback and take appropriate actions. - Receive an
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent whenever encryption status of the link changes. This includes encryption status change, encryption algorithm change, and encryption key size change. Apps must consider the bond restored if the link is successfully encrypted upon receivingACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent later.
Adapting to varying OEM implementations
While Android 16 introduces these new intents, their implementation and broadcasting can vary across different device manufacturers (OEMs). To ensure your app provides a consistent and reliable experience across all devices, developers should design their bond loss handling to gracefully adapt to these potential variations.
We recommend the following app behaviors:
If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is broadcast:The ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) link will be disconnected by the system, but the bond information for the device will be retained (as described here).
Your app should use this intent as the primary signal for bond loss detection and guiding the user to confirm the remote device is in range before initiating device forgetting or re-pairing.
If a device disconnects after
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGis received, your app should be cautious about reconnecting, as the device may no longer be bonded with the system.If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is NOT broadcast:The ACL link will remain connected, and the bond information for the device will be removed by the system, same to behavior in Android 15.
In this scenario, your app should continue its existing bond loss handling mechanisms as in previous Android releases, to detect and manage bond loss events.
Bluetooth eşlemesini kaldırmanın yeni yolu
All apps targeting Android 16 are now able to unpair bluetooth devices using a
public API in CompanionDeviceManager. If a companion device is
being managed as a CDM association, then the app can trigger
bluetooth bond removal by using the new removeBond(int) API
on the associated device. The app can monitor the bond state changes by
listening to the bluetooth device broadcast event
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
Güvenlik
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) aşağıdaki güvenlik değişikliklerini içerir.
MediaStore sürüm kilitleme
For apps targeting Android 16 or higher, MediaStore#getVersion() will now
be unique to each app. This eliminates identifying properties from the version
string to prevent abuse and usage for fingerprinting techniques. Apps shouldn't
make any assumptions around the format of this version. Apps should already
handle version changes when using this API and in most cases shouldn't need to
change their current behavior, unless the developer has attempted to infer
additional information that is beyond the intended scope of this API.
Daha güvenli intent'ler
The Safer Intents feature is a multi-phase security initiative designed to improve the security of Android's intent resolution mechanism. The goal is to protect apps from malicious actions by adding checks during intent processing and filtering intents that don't meet specific criteria.
In Android 15 the feature focused on the sending app, now with Android 16, shifts control to the receiving app, allowing developers to opt-in to strict intent resolution using their app manifest.
Two key changes are being implemented:
Explicit Intents Must Match the Target Component's Intent Filter: If an intent explicitly targets a component, it should match that component's intent filter.
Intents Without an Action Cannot Match any Intent Filter: Intents that don't have an action specified shouldn't be resolved to any intent filter.
These changes only apply when multiple apps are involved and don't affect intent handling within a single app.
Impact
The opt-in nature means that developers must explicitly enable it in their app manifest for it to take effect. As a result, the feature's impact will be limited to apps whose developers:
- Are aware of the Safer Intents feature and its benefits.
- Actively choose to incorporate stricter intent handling practices into their apps.
This opt-in approach minimizes the risk of breaking existing apps that may rely on the current less-secure intent resolution behavior.
While the initial impact in Android 16 may be limited, the Safer Intents initiative has a roadmap for broader impact in future Android releases. The plan is to eventually make strict intent resolution the default behavior.
The Safer Intents feature has the potential to significantly enhance the security of the Android ecosystem by making it more difficult for malicious apps to exploit vulnerabilities in the intent resolution mechanism.
However, the transition to opt-out and mandatory enforcement must be carefully managed to address potential compatibility issues with existing apps.
Implementation
Developers need to explicitly enable stricter intent matching using the
intentMatchingFlags attribute in their app manifest.
Here is an example where the feature is opt-in for the entire app,
but disabled/opt-out on a receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
More on the supported flags:
| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Enforces stricter matching for incoming intents |
| none | Disables all special matching rules for incoming intents. When specifying multiple flags, conflicting values are resolved by giving precedence to the "none" flag |
| allowNullAction | Relaxes the matching rules to allow intents without an action to match. This flag to be used in conjunction with "enforceIntentFilter" to achieve a specific behavior |
Testing and Debugging
When the enforcement is active, apps should function correctly if the intent
caller has properly populated the intent.
However, blocked intents will trigger warning log messages like
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" and "Access blocked:"
with the tag "PackageManager."
This indicates a potential issue that could impact the app and requires
attention.
Logcat filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU sistem çağrısı filtreleme
To harden the Mali GPU surface, Mali GPU IOCTLs that have been deprecated or are intended solely for GPU development have been blocked in production builds. Additionally, IOCTLs used for GPU profiling have been restricted to the shell process or debuggable applications. Refer to the SAC update for more details on the platform-level policy.
This change takes place on Pixel devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). Arm
has provided official categorization of their IOCTLs in
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst of their r54p2 release. This
list will continue to be maintained in future driver releases.
This change does not impact supported graphics APIs (including Vulkan and OpenGL), and is not expected to impact developers or existing applications. GPU profiling tools such as the Streamline Performance Analyzer and the Android GPU Inspector won't be affected.
Testing
If you see a SELinux denial similar to the following, it is likely your application has been impacted by this change:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
If your application needs to use blocked IOCTLs, please file a bug and assign it to android-partner-security@google.com.
FAQ
Does this policy change apply to all OEMs? This change will be opt-in, but available to any OEMs who would like to use this hardening method. Instructions for implementing the change can be found in the implementation documentation.
Is it mandatory to make changes in the OEM codebase to implement this, or does it come with a new AOSP release by default? The platform-level change will come with a new AOSP release by default. Vendors may opt-in to this change in their codebase if they would like to apply it.
Are SoCs responsible for keeping the IOCTL list up to date? For example, if my device uses an ARM Mali GPU, would I need to reach out to ARM for any of the changes? Individual SoCs must update their IOCTL lists per device upon driver release. For example, ARM will update their published IOCTL list upon driver updates. However, OEMs should make sure that they incorporate the updates in their SEPolicy, and add any selected custom IOCTLs to the lists as needed.
Does this change apply to all Pixel in-market devices automatically, or is a user action required to toggle something to apply this change? This change applies to all Pixel in-market devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). No user action is required to apply this change.
Will use of this policy impact the performance of the kernel driver? This policy was tested on the Mali GPU using GFXBench, and no measurable change to GPU performance was observed.
Is it necessary for the IOCTL list to align with the current userspace and kernel driver versions? Yes, the list of allowed IOCTLs must be synchronized with the IOCTLs supported by both the userspace and kernel drivers. If the IOCTLs in the user space or kernel driver are updated, the SEPolicy IOCTL list must be updated to match.
ARM has categorized IOCTLs as 'restricted' / 'instrumentation', but we want to use some of them in production use-cases, and/or deny others. Individual OEMs/SoCs are responsible for deciding on how to categorize the IOCTLs they use, based on the configuration of their userspace Mali libraries. ARM's list can be used to help decide on these, but each OEM/SoC's use-case may be different.
Gizlilik
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) aşağıdaki gizlilik değişikliklerini içerir.
Yerel Ağ İzni
LAN'daki cihazlara, INTERNET iznine sahip tüm uygulamalar erişebilir.
Bu, uygulamaların yerel cihazlara bağlanmasını kolaylaştırır ancak kullanıcının parmak izini oluşturma ve konum için proxy olma gibi gizlilik etkileri de vardır.
Yerel Ağ Korumaları projesi, yerel ağa erişimi yeni bir çalışma zamanı izniyle sınırlayarak kullanıcının gizliliğini korumayı amaçlar.
Yayın planı
Bu değişiklik, sırasıyla 25Q2 ve TBD olmak üzere iki sürüm arasında uygulanacaktır. Geliştiricilerin 25Q2 için bu yönergelere uyması ve geri bildirim paylaşması zorunludur. Çünkü bu korumalar daha sonraki bir Android sürümünde zorunlu kılınacaktır. Ayrıca, aşağıdaki yönergeleri kullanarak örtülü yerel ağ erişimine bağlı senaryoları güncellemeleri ve kullanıcıların yeni izni reddetmesine ve iptal etmesine hazırlanmaları gerekir.
Etki
LNP, şu anki aşamada etkinleştirilmesi gereken bir özelliktir. Bu nedenle, yalnızca etkinleştirilen uygulamalar etkilenir. Katılma aşamasının amacı, uygulama geliştiricilerin uygulamalarının hangi bölümlerinin örtülü yerel ağ erişimine bağlı olduğunu anlamalarını sağlamaktır. Böylece, bir sonraki sürümde bu bölümler için izin koruması hazırlayabilirler.
Uygulamalar, kullanıcının yerel ağına şu yöntemlerle erişirse etkilenir:
- Yerel ağ adreslerinde (ör. mDNS veya SSDP hizmeti keşif protokolü) ham soketlerin doğrudan veya kitaplık aracılığıyla kullanımı
- Yerel ağa erişen çerçeve düzeyindeki sınıfların (ör. NsdManager) kullanılması
Yerel ağ adresine giden ve gelen trafik için yerel ağ erişimi izni gerekir. Aşağıdaki tabloda sık karşılaşılan bazı durumlar listelenmiştir:
| Uygulama Düşük Düzeyli Ağ İşlemi | Yerel Ağ İzni Gerekli |
|---|---|
| Giden TCP bağlantısı oluşturma | evet |
| Gelen TCP bağlantılarını kabul etme | evet |
| UDP tek noktaya yayın, çok noktaya yayın veya yayın gönderme | evet |
| Gelen bir UDP tek yayını, çoklu yayını veya yayını alma | evet |
Bu kısıtlamalar ağ yığınına derinlemesine uygulanır ve bu nedenle tüm ağ API'leri için geçerlidir. Yerel veya yönetilen kodda oluşturulan soketler, Cronet ve OkHttp gibi ağ kitaplıkları ve bunların üzerinde uygulanan tüm API'ler buna dahildir. Yerel ağdaki hizmetleri (ör. .local soneki olanlar) çözmeye çalışmak için yerel ağ izni gerekir.
Yukarıdaki kurallarla ilgili istisnalar:
- Bir cihazın DNS sunucusu yerel ağdaysa bu sunucuya veya bu sunucudan gelen trafik (53 numaralı bağlantı noktasında) için yerel ağ erişim izni gerekmez.
- Uygulama içi seçici olarak Çıkış Değiştirici'yi kullanan uygulamaların yerel ağ izinlerine ihtiyacı olmayacak (2025'in 4. çeyreğinde daha fazla bilgi paylaşılacak).
Geliştirici Yönergeleri (Etkinleştirme)
Yerel ağ kısıtlamalarını etkinleştirmek için aşağıdakileri yapın:
- Cihazda 25Q2 Beta 3 veya sonraki bir sürümü yükleyin.
- Test edilecek uygulamayı yükleyin.
adb'de Appcompat işaretini açın/kapatın:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Cihazı yeniden başlatın
Artık uygulamanızın yerel ağa erişimi kısıtlanmıştır ve yerel ağa erişme girişimleri soket hatalarına yol açar. Uygulama sürecinizin dışında yerel ağ işlemleri gerçekleştiren API'ler (ör. NsdManager) kullanıyorsanız bu API'ler, kayıt aşamasında etkilenmez.
Erişimi geri yüklemek için uygulamanıza NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES izni vermeniz gerekir.
- Uygulamanın, manifest dosyasında
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESiznini beyan ettiğinden emin olun. - Ayarlar > Uygulamalar > [Uygulama Adı] > İzinler > Yakındaki cihazlar > İzin ver'e gidin.
Uygulamanızın yerel ağa erişimi geri yüklenir ve tüm senaryolarınız, uygulamayı kaydetmeden önceki gibi çalışır.
Yerel ağ koruması zorunlu kılındığında uygulama ağ trafiği şu şekilde etkilenecek:
| İzin | Giden LAN İsteği | Giden/Gelen İnternet İsteği | Gelen LAN İsteği |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verildi | Works | Works | Works |
| İzin Verilmedi | Başarısızlar | Works | Başarısızlar |
Uygulama uyumluluğu işaretini devre dışı bırakmak için aşağıdaki komutu kullanın.
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Hatalar
Bu kısıtlamalardan kaynaklanan hatalar, yerel ağ adresine gönderme veya gönderme varyantı çağrıldığında arayan sokete döndürülür.
Örnek hatalar:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Yerel Ağ Tanımı
Bu projedeki yerel ağ, kablosuz veya Ethernet gibi yayın yapabilen bir ağ arayüzü kullanan bir IP ağıdır ancak hücresel (WWAN) veya VPN bağlantıları hariçtir.
Aşağıdakiler yerel ağ olarak kabul edilir:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Bağlantı Yerel
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Bağlantı yerel
- Doğrudan bağlı rotalar
- Thread gibi saplama ağlar
- Birden fazla alt ağ (henüz belli değil)
Ayrıca, hem çok noktalı yayın adresleri (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) hem de IPv4 yayın adresi (255.255.255.255) yerel ağ adresleri olarak sınıflandırılır.
Uygulamaya ait fotoğraflar
When prompted for photo and video permissions by an app targeting SDK 36 or higher on devices running Android 16 or higher, users who choose to limit access to selected media will see any photos owned by the app pre-selected in the photo picker. Users can deselect any of these pre-selected items, which will revoke the app's access to those photos and videos.

