Android 14 為開發人員推出了強大的功能和 API。以下各節可協助您瞭解應用程式功能,並開始使用相關的 API。
如需新增、修改及移除 API 的詳細清單,請參閱 API 差異比較表。如要進一步瞭解新增的 API,請參閱 Android API 參考資料。針對 Android 14,請尋找 API 級別 34 中新增的 API。如要瞭解平台變更可能對應用程式造成的影響,請務必查看指定 Android 14 的應用程式和所有應用程式的 Android 14 行為變更。
國際化
個別應用程式語言偏好
Android 14 進一步延伸 Android 13 (API 級別 33) 所推出的個別應用程式語言功能,並新增多項功能:
自動產生應用程式的
localeConfig:自 Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 和 AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 起,您可以將應用程式設為自動支援個別應用程式語言偏好設定。Android Gradle 外掛程式會根據您的專案資源產生LocaleConfig檔案,並在最終資訊清單檔案中為該檔案新增參照,為您省去手動建立或更新檔案的需求。AGP 會使用應用程式模組res資料夾中的資源和任何程式庫模組依附元件,以決定要納入LocaleConfig檔案的語言代碼。應用程式
localeConfig的動態更新:請使用 法LocaleManager中的setOverrideLocaleConfig()和getOverrideLocaleConfig()方法,以動態方式更新應用程式在裝置的系統設定中的支援語言清單。如果應用程式使用伺服器端推送進行本地化,則可利用此彈性自訂各區域的支援語言清單、執行 A/B 實驗,或提供更新的語言代碼清單。輸入法編輯器 (IME) 的應用程式語言瀏覽權限:輸入法編輯器可透過
getApplicationLocales()方法檢查當前應用程式的語言,並和輸入法編輯器的語言進行比對。
文法轉變 API
30 億人使用性別化語言:即名詞、動詞、形容詞和介系詞會隨著交談或談論對象或目標的性別,而有不同變化形式的文法類別語言。一般來說,許多性別化語言都會使用陽性文法性別做為預設或通用性別。
若以錯誤的文法性別稱呼使用者,例如:以陽性文法性別稱呼女性,可能會對其表現及態度產生負面影響。相較之下,如果使用者介面的用語正確反映了使用者的文法性別,便可提高使用者參與度,同時提供更個人化且更自然親切的使用者體驗。
為了協助你針對使用文法性別的語言,建構以使用者為中心的使用者介面,Android 14 採用了文法轉變 API,可讓你新增對文法性別的支援,而不必重構應用程式。
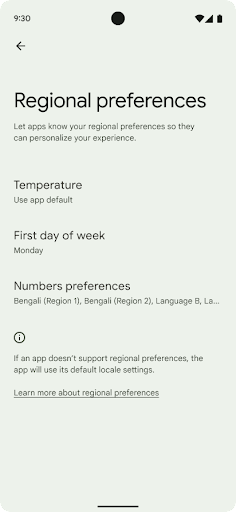
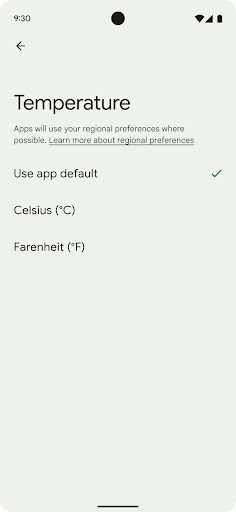
地區偏好設定
地區偏好設定可讓使用者自訂溫度單位,這是第一項 包括星期幾和編號系統住在美國的歐洲人 最好將溫度單位設定為攝氏,而非華氏, 應用程式,將星期一視為一週的起始日,而非美國的預設設定。 週日。
全新 Android 設定選單是針對這些偏好設定設計,可讓使用者透過集中的管理位置自行探索,並視需要變更應用程式的偏好設定。即使裝置經過備份與還原,這些偏好設定也不會改變。有幾個 API 和
意圖 (例如
getTemperatureUnit敬上
和
getFirstDayOfWeek:
授予應用程式讀取使用者偏好設定的權限,以便應用程式調整其運作方式
顯示資訊。您也可以註冊
BroadcastReceiver已開啟
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
處理地區偏好設定變更時的地區設定變更。
如要找到這些設定,請開啟「設定」應用程式,並依序前往 [系統] > [ 語言與輸入 >地區偏好設定:
無障礙設定
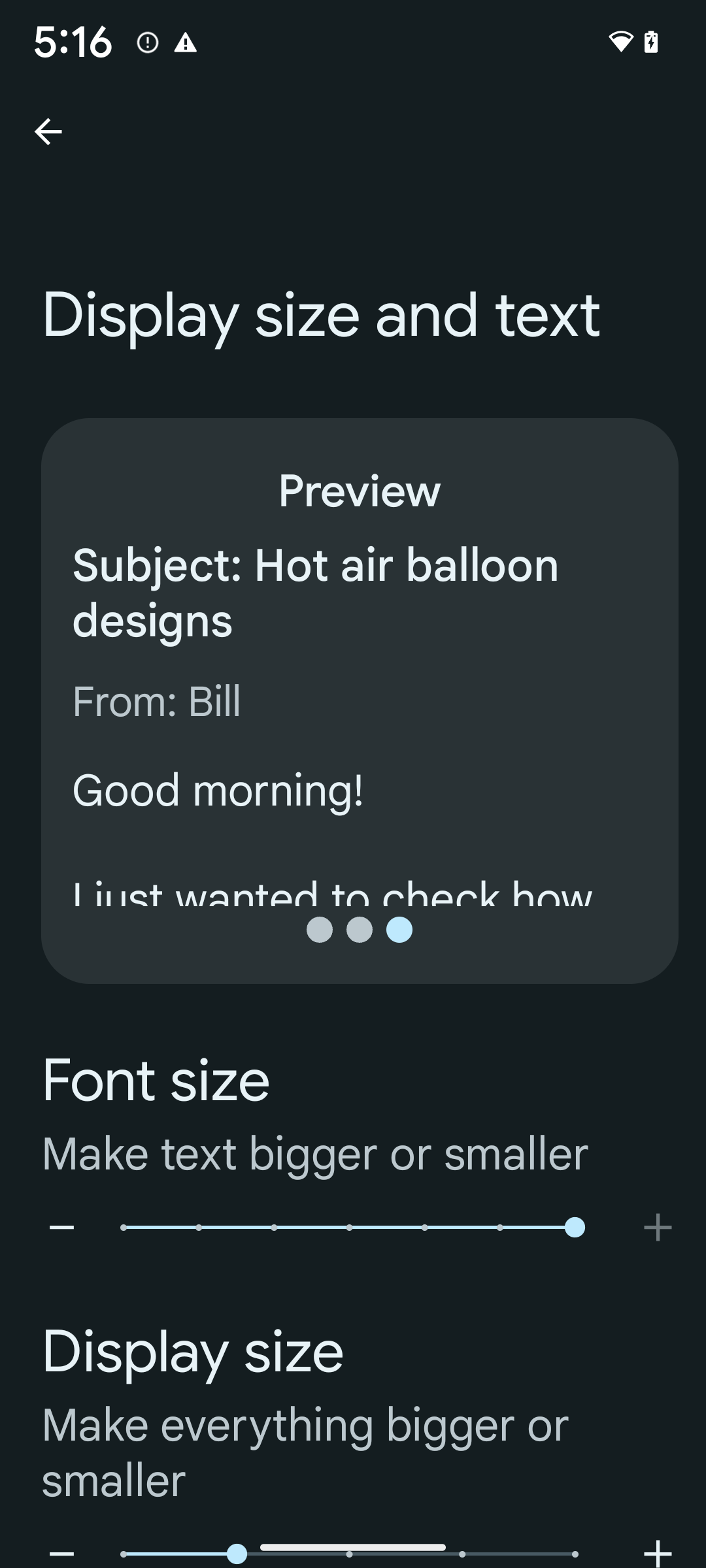
非線性字型縮放至 200%
自 Android 14 起,系統將支援高達 200% 的字型縮放倍數,為使用者提供額外的無障礙選項。
為避免畫面上的大型文字元素縮放過大,系統會套用非線性縮放曲線。套用此縮放策略後,大型文字的縮放比例會和小型文字的縮放比例有所區別。非線性字型縮放有助於在不同大小元素之間維持比例階層,同時減少高度縮放時的線性文字問題 (如:文字遭到截斷,或因為顯示大小過大而導致文字難以辨識)。
使用非線性字型縮放測試應用程式
如果您已使用可縮放像素 (sp) 單位定義文字大小,這些額外選項和縮放功能改善項目就會自動套用至應用程式中的文字。不過,您仍應啟用最大字型大小 (200%) 執行 UI 測試,確保應用程式正確套用字型大小,並在不影響可用性的情況下,因應更大的字型。
如要啟用 200% 的字型大小,請按照下列步驟進行:
- 開啟「設定」應用程式,然後依序前往「無障礙中心」>「顯示大小與文字」。
- 在「字型大小」選項中,輕觸加號 (+) 圖示,直到達字型大小上限為止,如本節隨附的圖片所示。
使用經過調整像素 (sp) 的單位處理文字大小
請記得一律以 sp 單位為單位指定文字大小。如果您的應用程式使用 sp 單位,Android 可套用使用者偏好的文字大小,並適當縮放。
請勿使用 sp 單位做為邊框間距,也不要假設有隱含邊框間距而定義檢視畫面高度:使用非線性字型縮放 sp 維度可能會導致比例失衡,因此 4sp + 20sp 不一定會等於 24sp。
轉換經過調整像素 (sp) 的單位
使用 TypedValue.applyDimension() 將 sp 單位轉換為像素,並使用 TypedValue.deriveDimension() 將像素轉換為 sp。這些方法會自動套用至適當的非線性縮放曲線。
避免使用硬式編碼方程式,使用
Configuration.fontScale 或
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity。由於字型縮放功能不是線性方式,因此 scaledDensity 欄位不再具備準確性。fontScale 欄位僅供參考,因為字型不再使用單一純量值縮放。
使用 sp 單位設定 lineHeight
請一律使用 sp 單位定義 android:lineHeight,而非 dp,這樣行高就會隨著文字縮放。否則,如果文字是 sp,但 lineHeight 是 dp 或 px,文字就不會縮放,看起來會很擁擠。TextView 會自動修正 lineHeight,保留您預期的比例,但前提是 textSize 和 lineHeight 都以 sp 單位定義。
相機和媒體
Ultra HDR 圖片

Android 14 新增了對高動態範圍 (HDR) 圖片的支援,可在拍攝相片時保留更多感應器資訊,進而呈現鮮豔的色彩和更強烈的對比。Android 使用 Ultra HDR 格式,可與 JPEG 圖片完全相容,讓應用程式與 HDR 圖片無縫互動,並視需要以標準動態範圍 (SDR) 顯示。
當應用程式選擇為活動視窗使用 HDR UI (透過資訊清單項目或在執行階段呼叫 Window.setColorMode()),架構會自動在 UI 中以 HDR 格式轉譯這些圖片。您也可以在支援的裝置上拍攝壓縮的超高動態範圍靜態圖片。感應器可復原更多顏色,因此後製編輯的彈性更高。與 Ultra HDR 影像相關聯的 Gainmap 可用於使用 OpenGL 或 Vulkan 轉譯這些影像。
相機擴充功能中的縮放、對焦、後視等功能
Android 14 會升級及改善相機擴充功能,讓應用程式能夠處理更長的處理時間,在支援裝置上使用低光源攝影等需要大量運算的演算法,改善圖片品質。這些功能可讓使用者在使用相機擴充功能時,享有更完善的體驗。這些改善措施包括:
- 動態靜態攝影處理延遲時間預估功能會根據目前的場景和環境條件,提供更準確的靜態攝影延遲時間預估值。呼叫
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()取得具有兩種延遲時間估計方法的StillCaptureLatency物件。getCaptureLatency()方法會傳回onCaptureStarted和onCaptureProcessStarted()之間的預估延遲時間,而getProcessingLatency()方法會傳回onCaptureProcessStarted()和可用的最終處理影格之間的預估延遲時間。 - 支援擷取進度回呼,讓應用程式可顯示長時間執行的靜態影像處理作業目前的進度。您可以檢查
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable是否支援這項功能,如果可以,請實作onCaptureProcessProgressed()回呼,其中進度 (從 0 到 100) 會做為參數傳入。 擴充功能專屬中繼資料,例如用於調整擴充功能效果數量的
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTH,例如使用EXTENSION_BOKEH調整背景模糊效果的數量。相機擴充功能中的靜態影像拍攝功能,可提供比最終圖片更少經過處理的圖片。如果擴充功能導致處理延遲時間增加,您可以提供後端圖片做為預留位置,以改善使用者體驗,並在稍後切換為最終圖片。您可以查看
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable是否支援這項功能。接著,您可以將OutputConfiguration傳遞至ExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration。支援
SurfaceView,可提供更經過最佳化且省電的預覽算繪路徑。支援在擴充功能使用期間輕觸聚焦和縮放功能。
感應器內變焦
當 CameraCharacteristics 中的 REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE 包含 SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW 時,應用程式可以使用進階感應器功能,透過 CaptureRequest 和 RAW 目標 (其串流用途已設為 CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW),為經裁剪的 RAW 串流提供與全景視野相同的像素。透過實作要求覆寫控制項,更新後的相機可在其他相機控制項準備就緒前,提供縮放控制選項。
無損 USB 音訊
Android 14 支援無損音訊格式,可透過 USB 有線耳機提供頂級音響體驗。您可以查詢 USB 裝置的偏好混合器屬性、註冊偏好混合器屬性變更的事件監聽器,以及使用 AudioMixerAttributes 類別設定混合器屬性。這個類別代表音訊調音器的格式,例如通道遮罩、取樣率和行為。這個類別可讓您直接傳送音訊,不必進行混合、音量調整或處理效果。
開發人員工作效率和工具
Credential Manager
Android 14 會新增 Credential Manager 做為平台 API,並透過使用 Google Play 服務的 Jetpack 程式庫,進一步支援 Android 4.4 (API 級別 19) 裝置。Credential Manager 的目標是透過 API 協助使用者輕鬆登入,這些 API 會透過使用者設定的憑證提供者擷取及儲存憑證。Credential Manager 可在單一 API 中支援多種登入方式,包括使用者名稱和密碼、密碼金鑰,以及聯合登入解決方案 (例如使用 Google 帳戶登入)。
密碼金鑰具有許多優點,舉例來說,密碼金鑰採用業界標準,可在不同作業系統和瀏覽器環境中運作,也能與網站和應用程式搭配使用。
如需更多資訊,請參閱 Credential Manager 和密碼金鑰說明文件,以及Credential Manager 和密碼金鑰相關網誌文章。
Health Connect
Health Connect 是裝置端的使用者健康與健身資料存放區。這項功能可讓使用者在喜愛的應用程式之間分享資料,並透過單一介面控管要與這些應用程式分享的資料。
在 Android 14 以下版本的裝置上,Health Connect 可透過 Google Play 商店下載為應用程式。自 Android 14 起,Health Connect 將成為平台的一部分,並透過 Google Play 系統更新接收更新,無須另外下載。如此一來,Health Connect 就能經常更新,您的應用程式也可以在搭載 Android 14 以上版本的裝置上使用 Health Connect。使用者可以透過裝置的「設定」存取 Health Connect,系統設定中已整合隱私權控制選項。
Health Connect 在 Android 14 中提供多項新功能,例如運動路線,可讓使用者分享健身路線,並在地圖上顯示。路線的定義是指在一段時間內儲存的地點清單,應用程式可將路線插入運動時段,將路線連結在一起。為確保使用者能完全控管這類私密資料,使用者必須允許與其他應用程式共用個別路線。
詳情請參閱 Health Connect 說明文件和「Android 健康資料新功能」一文。
OpenJDK 17 更新
Android 14 持續更新 Android 核心程式庫,以便與最新版 OpenJDK LTS 中的功能保持一致,其中包括程式庫更新以及應用程式與平台開發人員的 Java 17 語言支援。
新功能和改善項目如下:
- 已將約 300 個
java.base類別更新至可支援 Java 17。 - 文字模塊已針對 Java 程式設計語言推出多行字串常值。
- instanceof 的模式比對可讓您在
instanceof中,不需要使用其他變數,即可將物件視為具有特定類型處理。 - 密封類別可讓您限制可進行擴充或實作的類別與介面。
進行 Google Play 系統更新 (Mainline 計畫) 之後,超過 6 億部裝置將可收到包含這些變更的最新 Android 執行階段 (ART) 更新。這是我們承諾的一部分,讓應用程式在各種裝置上都能夠擁有更一致、安全的環境,同時為各平台版本的使用者提供新的功能與能力。
Java 和 OpenJDK 是 Oracle 和/或其關係企業的商標或註冊商標。
應用程式商店改善項目
Android 14 引進幾個 PackageInstaller API,可讓應用程式商店改善使用者體驗。
在下載之前要求安裝核准
安裝或更新應用程式可能需要使用者核准。例如:當使用 REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES 權限的安裝程式試著要安裝新的應用程式時。在先前的 Android 版本中,應用程式商店只能夠在 APK 寫入安裝工作階段,且該工作階段已履行之後,才可要求使用者核准。
自 Android 14 起,requestUserPreapproval() 方法可讓安裝程式在履行安裝工作階段之前要求使用者核准。這項改善項目讓應用程式商店將下載任何 APK 的時間延後,直到使用者核准安裝為止。此外,在使用者核准安裝後,應用程式商店可以在背景下載並安裝應用程式,避免對使用者造成困擾。
聲明日後更新的責任
setRequestUpdateOwnership() 方法可讓安裝程式向系統表示,日後為應用程式安裝的更新皆由其負責處理。這項功能可啟用更新擁有權強制執行機制,也就是只有更新擁有者才能安裝應用程式的自動更新。強制更新擁有權有助於確保使用者一律從預期的應用程式商店收到更新。
任何其他安裝程式 (包括使用 INSTALL_PACKAGES 權限的安裝程式) 都必須明確獲得使用者核准,才能安裝更新。如果使用者決定繼續執行其他來源的更新,則將失去更新擁有權。
在較不受干擾的情況下更新應用程式
一般來說,應用程式商店會希望避免更新正在使用中的應用程式,以免導致應用程式正在執行的程序終止,進而中斷使用者正在執行的操作。
自 Android 14 起,InstallConstraints API 可讓安裝程式確保應用程式更新作業能在適當時機執行。舉例來說,應用程式商店可呼叫 commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() 方法,以確保只有在使用者不再與應用程式互動時才會執行更新。
順利安裝選用分割項目
使用分割 APK 時,應用程式的功能可透過個別 APK 檔案提供,而不是以單體 APK 為單位提供。分割 APK 可讓應用程式商店以最佳方式提供不同的應用程式元件。例如,應用程式商店可能會根據目標裝置的屬性進行最佳化。自 API 級別 22 推出以來,PackageInstaller API 已支援分割。
在 Android 14 中,setDontKillApp() 方法可讓安裝程式指出在安裝新的分割項目時,不應導致應用程式執行中的處理程序終止。應用程式商店可在使用者使用應用程式時,透過此功能順利安裝應用程式的新功能。
應用程式中繼資料套件
從 Android 14 開始,Android 套件安裝程式可讓您指定應用程式中繼資料 (例如資料安全性做法),以加入 Google Play 等應用程式商店頁面。
在使用者擷取裝置螢幕畫面時偵測
為建立更標準化的螢幕截圖偵測體驗,Android 14 推出了具隱私保護功能的螢幕截圖偵測 API。此 API 可讓應用程式依個別活動登錄回呼。當使用者在具備瀏覽權限的活動中拍攝螢幕截圖時,系統會叫用這些回呼,並傳送通知給使用者。
使用者體驗
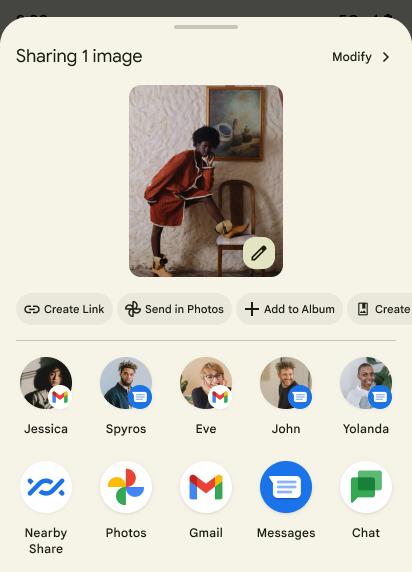
Sharesheet 自訂動作與改善排名
Android 14 會更新系統 Sharesheet,以支援自訂應用程式動作,使用者也能取得更豐富的預覽結果。
新增自訂動作
在 Android 14 中,應用程式可將自訂動作新增至其叫用的系統 Sharesheet。
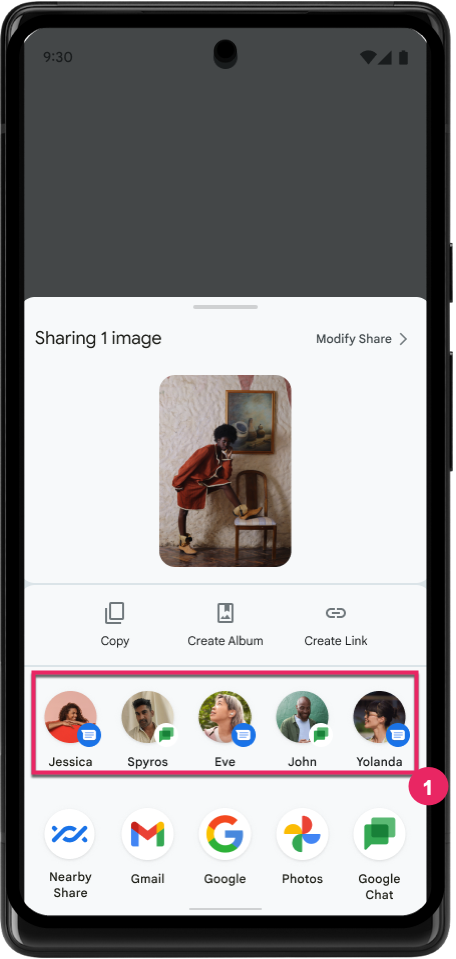
改善直接分享目標的排名
Android 14 會使用更多應用程式信號來判斷直接分享目標的排名,以便為使用者提供更實用的結果。如要提供最實用的信號來提升排名,請按照提升直接分享目標排名的相關指南操作。通訊應用程式也可以回報捷徑使用情形,包括傳送和接收的訊息。
支援預測返回功能的內建和自訂動畫
Android 13 推出了在開發人員選項背後顯示「預測返回主畫面」動畫的功能。只要使用支援的應用程式,並啟用開發人員選項,當您執行滑動返回的操作時,系統就會顯示動畫,指出返回手勢可讓應用程式結束並返回主畫面。
Android 14 內含多項改善項目,並提供有關預測返回手勢的全新指南:
- 您可以設定
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=true,選擇針對個別活動啟用預測返回系統動畫,而非針對整個應用程式。 - 我們新增了系統動畫,以配合 Android 13 的「返回主畫面」動畫。新的系統動畫具有跨活動和跨工作的特色,您只要改用預測返回功能,即可自動取得。
- 我們為底部功能表、側邊功能表和搜尋頁面新增了 Material 元件動畫。
- 我們製作了設計指南,讓您瞭解如何建立自訂的應用程式內動畫和轉場效果。
- 我們新增了 API,支援自訂的應用程式內轉換動畫:
在這個 Android 14 預先發布版本中,所有預測返回相關功能都保留在開發人員選項後方。請參閱開發人員指南,瞭解如何讓應用程式改用預測返回功能,以及如何建立自訂的應用程式內轉場效果。
大螢幕裝置製造商個別應用程式覆寫值
個別應用程式覆寫值可讓裝置製造商變更大螢幕裝置上的應用程式行為。舉例來說,即使應用程式資訊清單中已設定 resizeableActivity="false",FORCE_RESIZE_APP 覆寫值仍會指示系統根據螢幕尺寸調整應用程式大小 (避免大小相容性模式)。
覆寫設定的用意是改善大螢幕的使用者體驗。
新的資訊清單屬性可讓您為應用程式停用部分裝置製造商覆寫值。
大螢幕使用者個別應用程式覆寫值
個別應用程式覆寫值可變更應用程式在大螢幕裝置上的行為。舉例來說,無論應用程式設定為何,OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE 裝置製造商覆寫值都會將應用程式顯示比例設為 16:9。
在 Android 14 QPR1 中,使用者可透過新的設定選單,在大螢幕裝置上套用個別應用程式覆寫值。
應用程式分享螢幕畫面
分享應用程式畫面功能可讓使用者在錄製螢幕內容時,分享應用程式視窗,而非整個裝置畫面。
透過應用程式螢幕分享功能,系統會從共用畫面中排除狀態列、導覽列、通知和其他系統 UI 元素。只會分享所選應用程式的內容。
應用程式螢幕分享功能可讓使用者執行多個應用程式,但只分享單一應用程式的內容,進而提升工作效率和隱私權。
Pixel 8 Pro 上的 Gboard 智慧回覆功能 (由 LLM 驅動)
在搭載 12 月功能更新的 Pixel 8 Pro 裝置上,開發人員可以試用 Gboard 中採用 Google Tensor 晶片的大型語言模型 (LLM) 所提供的更高品質智慧回覆功能。
這項功能目前僅在 WhatsApp、Line 和 KakaoTalk 提供美式英文的限量預覽版。你必須使用 Pixel 8 Pro 裝置,並將 Gboard 做為鍵盤。
如要試用這項功能,請先依序前往「設定」>「開發人員選項」>「AI Core 設定」>「啟用 Aicore 持續性」。
接著,在支援的應用程式中開啟對話,即可在 Gboard 的建議列中看到 LLM 支援的智慧回覆功能,以回覆傳入的訊息。
圖形
路徑可供查詢及內插
Android 的 Path API 是一種強大且靈活的機制,可用於建立和算繪向量圖形,並具有描邊或填入路徑、從線段或二次方或三次方曲線建構路徑、執行布林運算以取得更複雜的形狀,或同時執行所有這些操作的功能。但有一個限制,就是無法找出路徑物件中的實際內容;物件的內部部分在建立後,無法明確顯示於呼叫端。
如要建立 Path,您必須呼叫 moveTo()、lineTo() 和 cubicTo() 等方法,以便新增路徑區隔。不過,您無法透過對該路徑提出詢問以瞭解確切的區隔,因此必須在建立時保留該資訊。
自 Android 14 起,您便可查詢路徑,找出其中的內容。首先,您需要使用 Path.getPathIterator API 取得 PathIterator 物件:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
接下來,您可以呼叫 PathIterator 逐一疊代區隔,並擷取每個區隔的所有必要資料。本範例使用封裝資料的 PathIterator.Segment 物件:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator 也提供 next() 的非分配式版本,可供您傳入緩衝區,以便保留單點資料。
內插類型是查詢 Path 資料的重要用途之一。例如,您可能想要在兩個不同路徑之間建立動畫 (或 變形)。為進一步簡化該使用情境,Android 14 也在 Path 中加入 interpolate() 方法。假設兩個路徑具有相同的內部結構,interpolate() 方法會使用該內插結果建立新的 Path。此範例會傳回形狀介於 path 和 otherPath 之間半行 (0 .5 的線性內插) 的路徑:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Jetpack graphics-path 程式庫也會為舊版 Android 啟用類似的 API。
使用頂點和片段著色器的自訂網格
Android 一直支援使用自訂著色繪製三角形網格,但輸入網格格式僅限於少數預先定義的屬性組合。Android 14 新增了自訂網格支援功能,可將其定義為 三角形 或 三角形條,並視需要編入索引。這些網格會使用自訂屬性、頂點步幅、變化,以及以 AGSL 編寫的頂點和片段著色器指定。
頂點著色器會定義變化,例如位置和顏色,而片段著色器則可選擇定義像素的顏色,通常是使用頂點著色器建立的變化。如果片段著色器提供顏色,系統會使用繪製網格時選取的混合模式,將該顏色與目前的 Paint 顏色混合。統一變數可傳遞至片段和頂點著色器,以提供更多彈性。
Canvas 的硬體緩衝區算繪器
為協助使用 Android 的 Canvas API 以硬體加速繪製至 HardwareBuffer,Android 14 推出了 HardwareBufferRenderer。如果您的用途涉及透過 SurfaceControl 與系統合成器通訊,以便繪製低延遲畫面,這個 API 就特別實用。
