Android 14 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた機能と API が導入されました。以下では、アプリの機能を確認し、関連する API を試すことができます。
追加、変更、削除された API の詳細な一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。追加された API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。Android 14 の場合は、API レベル 34 で追加された API を探してください。プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する可能性がある領域については、Android 14 の動作変更(Android 14 をターゲットとするアプリの場合とすべてのアプリの場合)をご確認ください。
多言語対応
アプリ別の言語設定
Android 14 では、Android 13(API レベル 33)で導入されたアプリ別の言語機能が拡張され、以下の機能が追加されています。
アプリの
localeConfigの自動生成: Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 および AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 以降では、アプリで自動的にアプリ別の言語設定をサポートするよう設定できます。Android Gradle プラグインは、プロジェクト リソースに基づいてLocaleConfigファイルを生成し、そのファイルへの参照を最終マニフェスト ファイルに追加します。そのため、手動でファイルを作成または更新する必要はありません。AGP は、アプリ モジュールのresフォルダ内のリソースと、ライブラリ モジュールの依存関係を使用して、LocaleConfigファイルに含めるロケールを決定します。アプリの
localeConfigの動的アップデート:LocaleManagerのsetOverrideLocaleConfig()メソッドとgetOverrideLocaleConfig()メソッドを使用して、デバイスのシステム設定にある、アプリでサポートされる言語のリストを動的にアップデートします。この柔軟性を利用して、サポートされる言語のリストを地域ごとにカスタマイズしたり、A/B テストを実施したりできます。また、アプリがローカライズのためにサーバー側の push を使用する場合は、更新されたロケールのリストを提供できます。インプット メソッド エディタ(IME)によるアプリの言語の確認: IME は
getApplicationLocales()メソッドを使用して現在のアプリの言語を確認し、IME 言語をその言語と一致させます。
Grammatical Inflection API
30 億人もの人々が、性別で文法が変わる言語を話します。こうした言語では、話す相手、または言及する人や物の性別に応じて、各文法範疇(名詞、動詞、形容詞、前置詞など)の語形が変化します。伝統的に、性別で文法が変わる多くの言語では、男性形をデフォルトまたは汎用の性別として使用しています。
女性を男性形で呼ぶなど、ユーザーに対して不適切な文法的性を使用すると、そのユーザーのパフォーマンスと態度に悪影響を及ぼす可能性があります。一方、ユーザーの文法的性を適切に反映した言語を使用して UI を作成すると、ユーザー エンゲージメントが向上し、より自然でパーソナライズされたユーザー エクスペリエンスを提供できます。
Android 14 では、性別で文法が変わる言語に合わせてユーザー中心の UI を構築するため、アプリをリファクタリングせずに文法上の性別への対応を追加できる Grammatical Inflection API が導入されています。
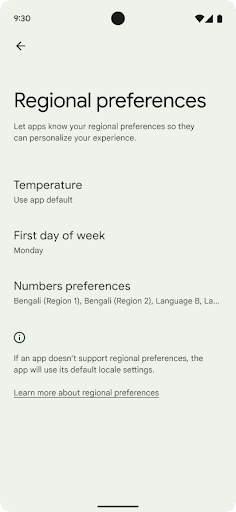
地域の設定
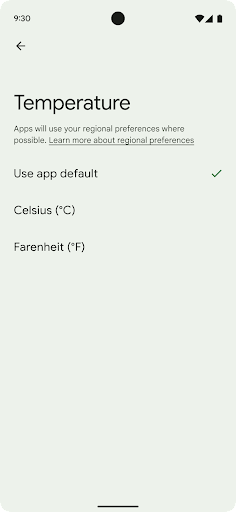
地域の設定を使用すると、ユーザーは温度単位、週の最初の曜日、番号体系をカスタマイズできます。米国に住んでいる欧州のユーザーの場合、温度の単位は華氏ではなく摂氏で表示し、アプリで週の始まりを米国のデフォルトの日曜日ではなく月曜日に指定することを好む可能性があります。
Android の新しい設定メニューは見つけやすく、ユーザーはここでアプリのそうした設定を一元的に変更できます。これらの設定は、バックアップや復元を行った場合も保持されます。複数の API とインテント(getTemperatureUnit や getFirstDayOfWeek など)により、アプリにそうしたユーザー設定への読み取りアクセス権を付与することで、アプリでの情報の表示方法を調整できます。また、ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED に BroadcastReceiver を登録して、地域の設定が変更されたときに言語 / 地域の構成の変更を処理することも可能です。
これらの設定を確認するには、設定アプリを開いて [システム] > [言語と入力] > [地域の設定] に移動します。
ユーザー補助
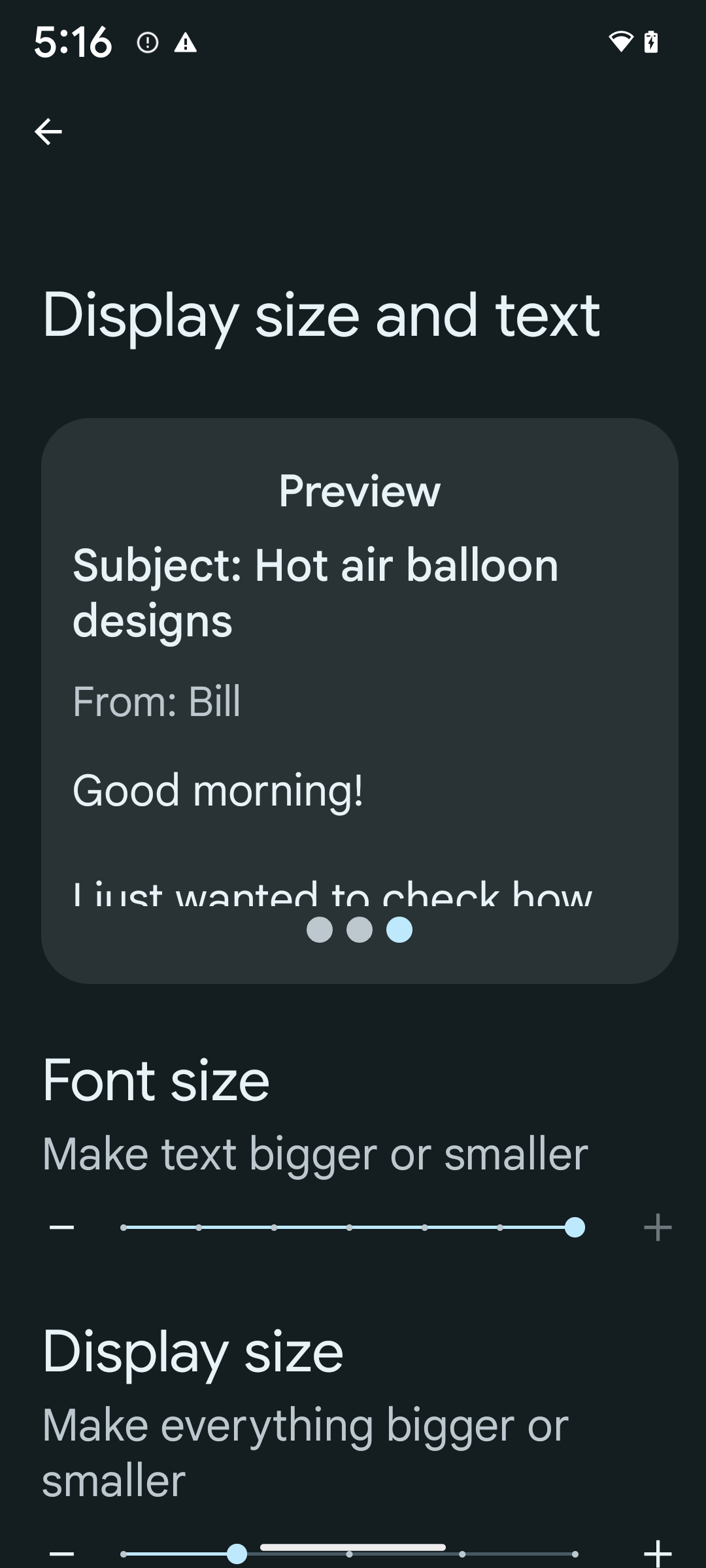
非線形フォント スケーリングを 200% にする
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing users with additional accessibility options.
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
カメラとメディア
画像のウルトラ HDR

Android 14 では、ハイ ダイナミック レンジ(HDR)画像のサポートが追加されました。HDR 画像では、写真の撮影時にセンサーからの情報の多くを保持できるため、鮮やかな色と高いコントラストを実現できます。Android では ウルトラ HDR 形式が使用されます。これは JPEG 画像と完全に下位互換性があるため、アプリは HDR 画像とシームレスに相互運用し、必要に応じて標準ダイナミック レンジ(SDR)で表示できます。
これらの画像を HDR で UI にレンダリングすることは、アプリがアクティビティ ウィンドウで HDR UI の使用をオプトインした場合、マニフェスト エントリを介して、または実行時に Window.setColorMode() を呼び出すことで、フレームワークによって自動的に実行されます。サポートされているデバイスでは、圧縮されたウルトラ HDR 静止画をキャプチャすることもできます。センサーから回復できる色が増えると、ポスト処理での編集がより柔軟になります。ウルトラ HDR 画像に関連付けられた Gainmap を使用して、OpenGL または Vulkan でレンダリングできます。
カメラ拡張機能のズーム、フォーカス、ポストビューなど
Android 14 では、カメラ拡張機能がアップグレードされ、改善されています。これにより、アプリはより長い処理時間を処理できるため、サポートされているデバイスで暗い場所での撮影などのコンピューティング負荷の高いアルゴリズムを使用して画像を改善できます。これらの機能により、カメラの拡張機能を使用する際のユーザー エクスペリエンスがさらに堅牢になります。主な改善点は次のとおりです。
- 動的な静止画撮影処理レイテンシの推定では、現在のシーンと環境条件に基づいて、はるかに正確な静止画撮影レイテンシの推定値が得られます。
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()を呼び出して、2 つのレイテンシ推定メソッドを持つStillCaptureLatencyオブジェクトを取得します。getCaptureLatency()メソッドは、onCaptureStartedとonCaptureProcessStarted()間の推定レイテンシを返します。getProcessingLatency()メソッドは、onCaptureProcessStarted()と利用可能な最終的な処理済みフレーム間の推定レイテンシを返します。 - キャプチャの進行状況コールバックをサポートし、アプリが長時間実行の静止画キャプチャ処理オペレーションの現在の進行状況を表示できるようにします。この機能が
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailableで使用可能かどうかを確認します。使用可能であれば、onCaptureProcessProgressed()コールバックを実装します。このコールバックには、進行状況(0 ~ 100)がパラメータとして渡されます。 拡張機能固有のメタデータ(
EXTENSION_BOKEHによる背景のぼかしの量など、拡張機能の効果の量を調整するためのCaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHなど)。カメラ拡張機能の静止画撮影用ポストビュー機能。最終的な画像よりも処理が少ない画像をより迅速に提供します。拡張機能で処理レイテンシが増加している場合は、UX を改善するためにポストビュー画像をプレースホルダとして提供し、後で最終的な画像に切り替えることができます。この機能が使用可能かどうかは、
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailableで確認できます。次に、OutputConfigurationをExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfigurationに渡すことができます。SurfaceViewのサポートにより、より最適化され、電力効率の高いプレビュー レンダリング パスが可能になりました。拡張機能の使用中にタップしてフォーカスとズームをサポート。
センサー内ズーム
CameraCharacteristics の REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE に SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW が含まれている場合、アプリは高度なセンサー機能を使用して、ストリームのユースケースが CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW に設定されている RAW ターゲットで CaptureRequest を使用して、切り抜き RAW ストリームに全画角と同じピクセルを設定できます。リクエスト オーバーライド コントロールを実装することで、更新されたカメラでは、他のカメラ コントロールの準備が整う前にユーザーがズームを操作できるようになります。
ロスレス USB オーディオ
Android 14 では、USB 有線ヘッドセットを介してオーディオファイル レベルのエクスペリエンスを実現するロスレス音声フォーマットがサポートされています。USB デバイスの優先ミキサー属性をクエリしたり、優先ミキサー属性の変更をリッスンするリスナーを登録したり、AudioMixerAttributes クラスを使用してミキサー属性を設定したりできます。このクラスは、チャンネル マスク、サンプルレート、オーディオ ミキサーの動作などの形式を表します。このクラスを使用すると、ミキシング、音量調整、エフェクト処理を行わずに音声を直接送信できます。
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
認証情報マネージャー
Android 14 では、プラットフォーム API として 認証情報マネージャーが追加され、Google Play 開発者サービスを使用する Jetpack ライブラリを介して Android 4.4(API レベル 19)デバイスまでサポートが拡張されています。認証情報マネージャーは、ユーザーが構成した認証情報プロバイダを使用して認証情報を取得して保存する API を使用して、ユーザーのログインを容易にすることを目的としています。認証情報マネージャーは、ユーザー名とパスワード、パスキー、フェデレーション ログイン ソリューション(Google でログインなど)といった複数のログイン方法を単一の API でサポートしています。
パスキーには多くのメリットがあります。たとえば、パスキーは業界標準に基づいて構築されており、さまざまなオペレーティング システムやブラウザのエコシステムで動作し、ウェブサイトとアプリの両方で使用できます。
詳細については、認証情報マネージャーとパスキーのドキュメントと、認証情報マネージャーとパスキーに関するブログ投稿をご覧ください。
ヘルスコネクト
Health Connect is an on-device repository for user health and fitness data. It allows users to share data between their favorite apps, with a single place to control what data they want to share with these apps.
On devices running Android versions prior to Android 14, Health Connect is available to download as an app on the Google Play store. Starting with Android 14, Health Connect is part of the platform and receives updates through Google Play system updates without requiring a separate download. With this, Health Connect can be updated frequently, and your apps can rely on Health Connect being available on devices running Android 14 or higher. Users can access Health Connect from the Settings in their device, with privacy controls integrated into the system settings.
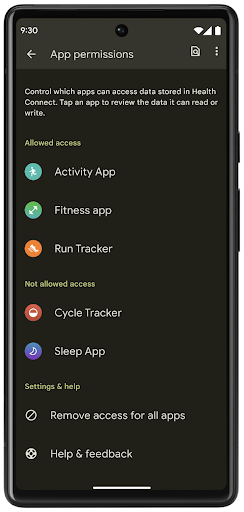
Health Connect includes several new features in Android 14, such as exercise routes, allowing users to share a route of their workout which can be visualized on a map. A route is defined as a list of locations saved within a window of time, and your app can insert routes into exercise sessions, tying them together. To ensure that users have complete control over this sensitive data, users must allow sharing individual routes with other apps.
For more information, see the Health Connection documentation and the blogpost on What's new in Android Health.
OpenJDK 17 の更新
Android 14 では、最新の OpenJDK LTS リリースの機能に合わせて Android のコアライブラリを更新する取り組みが引き続き行われています。これには、アプリ デベロッパーとプラットフォーム デベロッパー向けのライブラリの更新と Java 17 言語のサポートが含まれます。
主な機能と改善点は次のとおりです。
- 約 300 の
java.baseクラスを、Java 17 をサポートするように更新しました。 - テキスト ブロック: Java プログラミング言語で複数行の文字列リテラルを記述できます。
- instanceof: パターン マッチング: 追加の変数なしで、オブジェクトを
instanceof内で特定の型を持つものとして扱うことができます。 - シールクラス: 拡張または実装できるクラスとインターフェースを制限できます。
Google Play システム アップデート(プロジェクト Mainline)により、6 億台を超えるデバイスが、こうした変更を含む最新の Android ランタイム(ART)アップデートを受け取ることができます。これは、さまざまなデバイスでアプリにとって一貫した安全性の高い環境を実現し、プラットフォーム リリースに依存することなく新機能をユーザーに提供するための Google の取り組みの一環です。
Java および OpenJDK は、Oracle およびその関連会社の商標または登録商標です。
アプリストアの改善
Android 14 では、アプリストアでのユーザー エクスペリエンスを改善するための PackageInstaller API がいくつか導入されています。
ダウンロードする前にインストールの承認をリクエストする
アプリをインストールまたは更新する際に、ユーザーの承認が必要になる場合があります。たとえば、REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES 権限を使用するインストーラが新しいアプリをインストールしようとした場合などです。以前のバージョンの Android では、APK がインストール セッションに書き込まれ、セッションが commit された後にのみ、アプリストアはユーザーの承認をリクエストできました。
Android 14 以降では、requestUserPreapproval() メソッドを使用して、インストール セッションを commit する前に、ユーザーの承認をリクエストできます。この改善により、ユーザーがインストールを承認するまで、アプリストアで APK のダウンロードが延期されます。さらに、ユーザーがインストールを承認すると、アプリストアはユーザーの作業を妨げることなく、バックグラウンドでアプリをダウンロードしてインストールできます。
今後の更新に責任を持つことを示す
setRequestUpdateOwnership() メソッドを使用すると、インストーラはインストールしているアプリの今後の更新に責任を持つことをシステムに示すことができます。この機能により、更新の所有権の適用が有効になります。つまり、更新の所有者のみがアプリに自動更新をインストールできます。更新の所有権を適用することで、ユーザーは想定されるアプリストアからのみ更新を受け取ることができます。
その他のインストーラ(INSTALL_PACKAGES 権限を利用するものを含む)は、更新をインストールするために、ユーザーの明示的な承認を得る必要があります。ユーザーが別のソースから更新を進めた場合、更新の所有権は失われます。
影響が少ないタイミングでアプリを更新する
アプリストアは通常、アクティブに使用されているアプリを更新することはありません。これは、アプリの実行中のプロセスが強制終了され、ユーザーの操作が中断される可能性があるためです。
Android 14 以降では、InstallConstraints API を使用することで、インストーラはアプリの更新を適切なタイミングで行えます。たとえば、アプリストアで commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() メソッドを呼び出して、ユーザーがそのアプリを操作しなくなったときにのみ更新が commit されるようにできます。
オプションの分割をシームレスにインストールする
分割 APK を使用すると、アプリの機能をモノリシック APK としてではなく、別々の APK ファイルで配信できます。これにより、アプリストアでさまざまなアプリ コンポーネントの配信を最適化できます。たとえば、アプリストアは、ターゲット デバイスのプロパティに基づいて最適化できます。PackageInstaller API は、API レベル 22 で導入されて以来、分割をサポートしています。
Android 14 では、setDontKillApp() メソッドを使用して、新しい分割がインストールされたときに、アプリの実行中のプロセスを強制終了すべきでないことを示せます。アプリストアでは、この機能を使用して、ユーザーがアプリを使用しているときに、アプリの新しい機能をシームレスにインストールできます。
アプリのメタデータ バンドル
Android 14 以降では、Android パッケージ インストーラを使用して、Google Play などのアプリストア ページにデータ セーフティ方針などのアプリのメタデータを指定できます。
ユーザーがデバイスのスクリーンショットを撮影したときに検出する
Android 14 では、スクリーンショットの検出の標準化されたエクスペリエンスを実現するため、プライバシーを保護するスクリーンショット検出 API が導入されました。この API を使用すると、アプリはアクティビティごとにコールバックを登録できます。アクティビティが表示されている間にユーザーがスクリーンショットを撮ると、これらのコールバックが呼び出され、ユーザーに通知されます。
ユーザー エクスペリエンス
共有シートのカスタム アクションとランキングの改善
Android 14 では、システム共有シートが更新され、カスタムのアプリ アクションと有益なプレビュー結果をユーザーに提供できるようになりました。
カスタム アクションを追加する
Android 14 では、アプリで呼び出すシステム共有シートにカスタム アクションを追加できます。
直接共有ターゲットのランキングを改善する
Android 14 では、アプリからの多数のシグナルを使用して、直接共有ターゲットのランキングを決定し、より有用な結果をユーザーに提供しています。ランキングに最も有用なシグナルを提供するには、直接共有ターゲットのランキングを改善するためのガイダンスに沿って対応してください。通信アプリは、送受信メッセージのショートカットの使用状況を報告することもできます。
予測型「戻る」の組み込みアニメーションとカスタム アニメーションのサポート
Android 13 では、開発者向けオプションの背後に予測型「戻る」アニメーションが導入されました。開発者向けオプションが有効になっているサポート対象アプリで使用すると、後方にスワイプすると、戻るジェスチャーでアプリが終了してホーム画面に戻ることを示すアニメーションが表示されます。
Android 14 では、予測型「戻る」機能の改善が複数行われ、新しいガイダンスが追加されています。
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueを設定すると、アプリ全体ではなくアクティビティごとに、予測型「戻る」システム アニメーションを有効にできます。- Android 13 の「ホームに戻る」アニメーションに伴い、新しいシステム アニメーションが追加されました。新しいシステム アニメーションはアクティビティ間およびタスク間で動作し、予測型「戻る」に移行すると自動的に適用されます。
- ボトムシート、サイドシート、検索に新しいマテリアル コンポーネント アニメーションを追加しました。
- カスタムのアプリ内アニメーションと遷移を作成する際の設計ガイダンスを作成しました。
- カスタムのアプリ内遷移アニメーションをサポートする新しい API が追加されました。
handleOnBackStarted、handleOnBackProgressed、handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted、onBackProgressed、onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- ユーザーが後方にスワイプしたときに遷移を再生するには、
overridePendingTransitionではなくoverrideActivityTransitionを使用します。
この Android 14 プレビュー リリースでは、予測型「戻る」のすべての機能は開発者向けオプションに引き続き隠されています。アプリを予測型「戻る」に移行するデベロッパー ガイドと、カスタム アプリ内遷移を作成するデベロッパー ガイドをご覧ください。
大画面デバイスのメーカーによるアプリごとのオーバーライド
Per-app overrides enable device manufacturers to change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the FORCE_RESIZE_APP override instructs the system to resize the app to fit display dimensions (avoiding size compatibility mode) even if resizeableActivity="false" is set in the app manifest.
Overrides are intended to improve the user experience on large screens.
New manifest properties enable you to disable some device manufacturer overrides for your app.
大画面ユーザーのアプリごとのオーバーライド
アプリごとのオーバーライドを使用すると、大画面デバイスでのアプリの動作を変更できます。たとえば、デバイス メーカーのオーバーライド OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE は、アプリの構成に関係なく、アプリのアスペクト比を 16:9 に設定します。
Android 14 QPR1 では、大画面デバイスの新しい設定メニューを使用して、アプリごとのオーバーライドを適用できるようになりました。
アプリの画面共有
アプリ画面共有を使用すると、画面コンテンツの録画中にデバイスの画面全体ではなく、アプリ ウィンドウを共有できます。
アプリの画面共有では、ステータスバー、ナビゲーション バー、通知などのシステム UI 要素は共有ディスプレイから除外されます。選択したアプリのコンテンツのみが共有されます。
アプリの画面共有では、ユーザーが複数のアプリを実行しながら、コンテンツの共有を 1 つのアプリに制限できるため、生産性とプライバシーが向上します。
Google Pixel 8 Pro の Gboard で LLM を活用したスマート リプライを使用する
12 月の機能ドロップが適用された Google Pixel 8 Pro デバイスでは、Google Tensor で実行されるオンデバイスの大規模言語モデル(LLM)を活用した、Gboard の品質の高いスマート リプライをデベロッパーが試すことができます。
この機能は、WhatsApp、Line、KakaoTalk で米国英語の限定プレビューとしてご利用いただけます。Google Pixel 8 Pro デバイスを Gboard をキーボードとして使用する必要があります。
試すには、まず [設定] > [開発者向けオプション] > [AICore の設定] > [Aicore Persistent を有効にする] でこの機能を有効にします。
次に、対応するアプリで会話を開くと、受信したメッセージに応じて Gboard の候補ストリップに LLM を活用したスマート リプライが表示されます。
グラフィック
パスのクエリと補間に対応
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
頂点シェーダーとフラグメント シェーダーを使用したカスタム メッシュ
Android では長い間、カスタム シェーディングによる三角形メッシュの描画をサポートしてきましたが、入力メッシュ形式は、事前定義された属性の組み合わせに限定されていました。Android 14 では、カスタムメッシュのサポートが追加されました。これは、三角形または三角形ストリップとして定義でき、必要に応じてインデックスを付けることができます。これらのメッシュは、カスタム属性、頂点ストライド、変化、AGSL で記述された頂点シェーダーとフラグメント シェーダーで指定されます。
頂点シェーダーは位置や色などの変化を定義しますが、フラグメント シェーダーは、通常は頂点シェーダーによって作成された変化を使用して、ピクセルの色を定義することもできます。フラグメント シェーダーによって色が指定されている場合は、メッシュの描画時に選択されたブレンドモードを使用して、現在の Paint 色とブレンドされます。ユニフォームをフラグメント シェーダーと頂点シェーダーに渡して柔軟性を高めることができます。
Canvas のハードウェア バッファ レンダラ
Android の Canvas API を使った描画をサポートする
HardwareBuffer へのハードウェア アクセラレーション(Android 14)
HardwareBufferRenderer が導入されました。この API は、低レイテンシの描画のために SurfaceControl を介してシステム コンポーザとの通信が必要なユースケースに特に便利です。
