Android 14에는 개발자를 위한 훌륭한 기능과 API가 도입되었습니다. 다음은 앱의 기능을 알아보고 관련 API를 시작하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
추가된 API, 수정된 API, 삭제된 API에 관한 자세한 목록은 API 차이점 보고서를 참고하세요. 추가된 API에 관한 자세한 내용은 Android API 참조를 참고하세요. Android 14의 경우 API 수준 34에 추가된 API를 찾아보세요. 플랫폼 변경이 앱에 영향을 줄 수 있는 분야에 관해 알아보려면 Android 14를 타겟팅하는 앱 및 모든 앱의 Android 14 동작 변경사항을 확인해야 합니다.
다국어 지원
앱별 언어 설정
Android 14에서는 Android 13(API 수준 33)에서 도입된 앱별 언어 기능을 다음과 같은 추가 기능으로 확장합니다.
앱의
localeConfig자동으로 생성: Android 스튜디오 Giraffe Canary 7 및 AGP 8.1.0-alpha07부터 앱이 앱별 언어 설정을 자동으로 지원하도록 구성할 수 있습니다. Android Gradle 플러그인은 프로젝트 리소스를 기반으로LocaleConfig파일을 생성하고 최종 매니페스트 파일에 이에 대한 참조를 추가하므로 더 이상 수동으로 파일을 만들거나 업데이트할 필요가 없습니다. AGP는 앱 모듈의res폴더에 있는 리소스 및 모든 라이브러리 모듈 종속 항목을 사용하여LocaleConfig파일에 포함할 언어를 결정합니다.앱의
localeConfig동적 업데이트:LocaleManager에서setOverrideLocaleConfig()및getOverrideLocaleConfig()메서드를 사용하여 기기의 시스템 설정에서 앱의 지원되는 언어 목록을 동적으로 업데이트합니다. 앱에서 현지화에 서버 측 푸시를 활용하는 경우 이러한 유연성을 사용하여 지역별 지원되는 언어 목록을 맞춤설정하거나 A/B 실험을 실행하거나 업데이트된 언어 목록을 제공합니다.입력 방식 편집기(IME)의 앱 언어 공개 상태: IME는
getApplicationLocales()메서드를 활용하여 현재 앱의 언어를 확인하고 IME 언어를 해당 언어와 일치시킬 수 있습니다.
Grammatical Inflection API
30억 명의 사용자가 성별이 지정된 언어를 사용합니다. 이 언어는 이야기하는 사람과 사물의 성별에 따라 문법적 카테고리(예: 명사, 동사, 형용사, 전치사)가 영향을 받는 언어입니다. 일반적으로 성별이 지정된 많은 언어에서 남성형 문법적 성별을 기본 성별이나 일반 성별로 사용합니다.
여성을 남성형 문법적 성별로 언급하는 등 잘못된 문법적 성별로 사용자를 언급하면 사용자의 실적과 태도에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 반면 사용자의 문법적 성별을 올바르게 반영하는 언어로 된 UI는 사용자 참여를 개선하고 보다 맞춤설정되고 자연스러운 사용자 환경을 제공할 수 있습니다.
성별이 지정된 언어의 사용자 중심 UI를 빌드할 수 있도록 Android 14에서는 앱 리팩터링 없이 문법적 성별에 관한 지원을 추가할 수 있는 Grammatical Inflection API를 도입합니다.
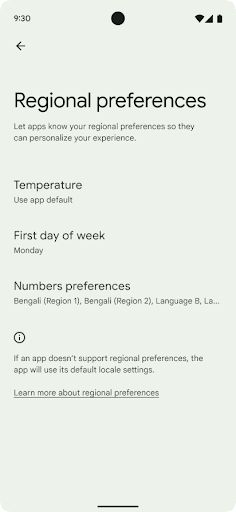
지역 설정
지역 설정을 통해 사용자는 온도 단위, 한 주의 첫째 날, 번호 매기기 시스템을 맞춤설정할 수 있습니다. 미국에 거주하는 유럽인은 온도 단위로 화씨보다 섭씨를 선호하고, 앱이 미국의 기본값인 일요일이 아닌 월요일을 한 주의 시작으로 간주하는 것을 선호할 수 있습니다.
이러한 환경설정에 관한 새로운 Android 설정 메뉴는 사용자에게 앱 환경설정을 변경할 수 있는 쉽게 검색 가능한 중앙 집중식 위치를 제공합니다. 이러한 환경설정은 백업 및 복원에도 유지됩니다. 여러 API 및 인텐트(예: getTemperatureUnit 및 getFirstDayOfWeek)는 앱에 사용자 환경설정에 대한 읽기 액세스 권한을 부여하므로 앱에서 정보를 표시하는 방식을 조정할 수 있습니다. ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED에 BroadcastReceiver를 등록하여 지역 설정이 변경될 때 언어 구성 변경을 처리할 수도 있습니다.
이러한 설정을 찾으려면 설정 앱을 열고 시스템 > 언어 및 입력 > 지역 설정으로 이동하세요.
접근성
비선형 글꼴 크기 200%로 조정
Android 14부터 시스템은 글꼴 크기를 최대 200%까지 지원하므로 사용자에게 추가 접근성 옵션을 제공할 수 있습니다.
화면의 큰 텍스트 요소가 너무 커지지 않도록 시스템에서는 비선형 크기 조정 곡선을 적용합니다. 이 크기 조정 전략은 큰 텍스트가 작은 텍스트와 동일한 비율로 조정되지 않음을 의미합니다. 비선형 글꼴 크기 조정은 다양한 크기의 요소 간에 비례 계층 구조를 유지하는 동시에 높은 수준으로 크기가 조정되는 선형 텍스트 문제 (예: 텍스트가 잘리거나 너무 큰 디스플레이 크기로 인해 텍스트를 읽기 어려워지는 경우)를 완화하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
비선형 글꼴 크기 조정으로 앱 테스트
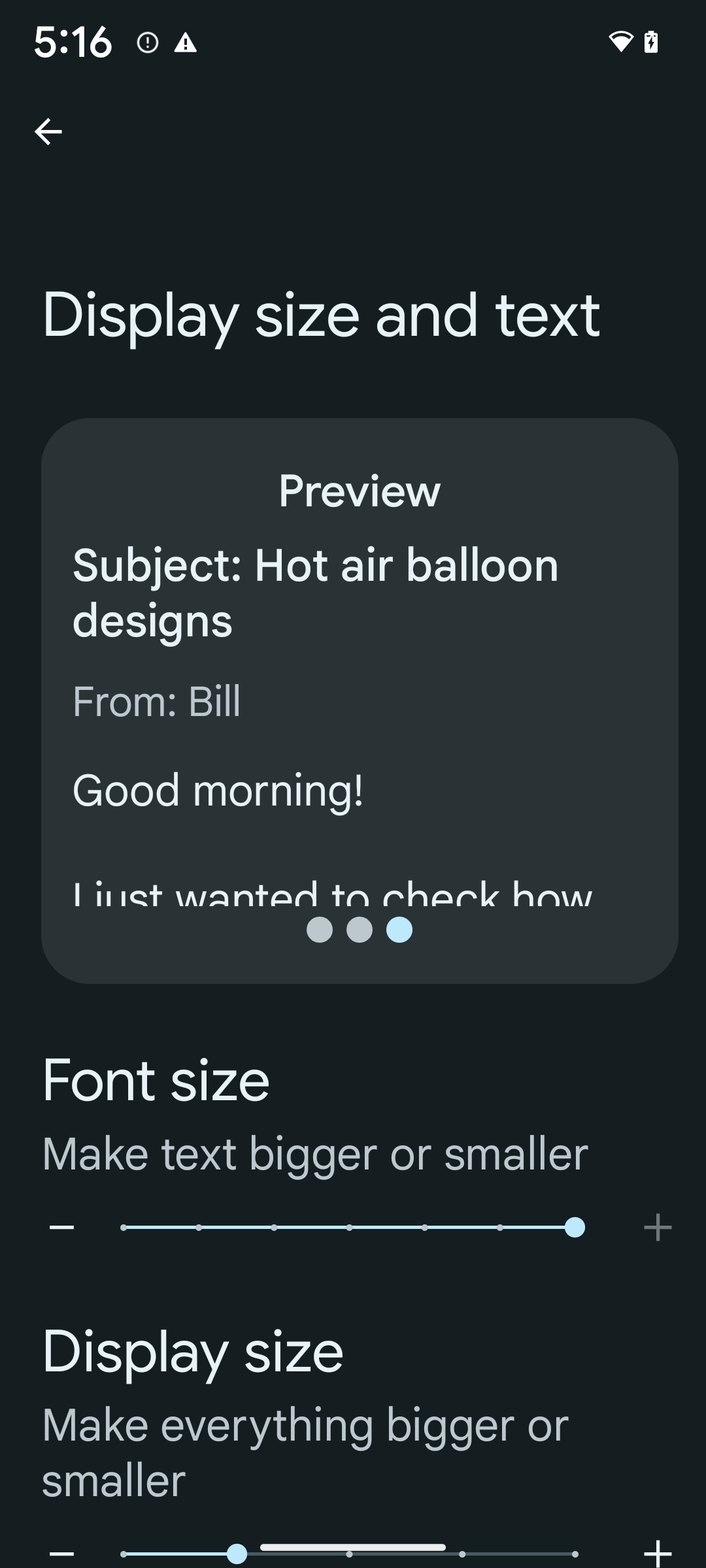
이미 확장 가능 픽셀 (sp) 단위를 사용하여 텍스트 크기를 정의하는 경우 이러한 추가 옵션과 크기 조정 개선사항이 앱의 텍스트에 자동으로 적용됩니다. 하지만 앱이 글꼴 크기를 올바르게 적용하고 사용성에 영향을 미치지 않으면서 더 큰 글꼴 크기를 수용할 수 있는지 확인하려면 최대 글꼴 크기 (200%)를 사용 설정하여 UI 테스트를 실행해야 합니다.
200% 글꼴 크기를 사용 설정하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 설정 앱을 열고 접근성 > 디스플레이 크기 및 텍스트로 이동합니다.
- 글꼴 크기 옵션의 경우 이 섹션에 제공되는 이미지와 같이 최대 글꼴 크기 설정이 사용 설정될 때까지 더하기(+) 아이콘을 탭합니다.
텍스트 크기에 조정된 픽셀(sp) 단위 사용
항상 sp 단위로 텍스트 크기를 지정해야 합니다. 앱에서 sp 단위를 사용하면 Android에서는 사용자의 기본 텍스트 크기를 적용하고 적절하게 크기를 조정할 수 있습니다.
패딩에 sp 단위를 사용하거나 암시적 패딩을 가정하여 뷰 높이를 정의하지 마세요. 비선형 글꼴 크기 조정 sp 치수는 비례하지 않을 수 있으므로 4sp + 20sp가 24sp와 같지 않을 수 있습니다.
조정된 픽셀(sp) 단위 변환
TypedValue.applyDimension()을 사용하여 sp 단위에서 픽셀로 변환하고 TypedValue.deriveDimension()을 사용하여 픽셀을 sp로 변환합니다. 이러한 메서드는 적절한 비선형 크기 조정 곡선을 자동으로 적용합니다.
Configuration.fontScale 또는 DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity를 사용하여 수식을 하드코딩하지 마세요. 글꼴 크기 조정이 비선형이므로 scaledDensity 필드가 더 이상 정확하지 않습니다. 글꼴은 더 이상 단일 스칼라 값으로 확장되지 않으므로 fontScale 필드는 정보 제공 목적으로만 사용해야 합니다.
lineHeight에 sp 단위 사용
항상 dp 대신 sp 단위를 사용하여 android:lineHeight를 정의하여 행 간격이 텍스트와 함께 조정되도록 합니다. 그렇지 않고 텍스트가 sp인데 lineHeight가 dp 또는 px인 경우 크기가 조정되지 않고 답답해 보입니다.
TextView는 의도한 비율이 유지되도록 lineHeight를 자동으로 수정하지만, textSize와 lineHeight가 모두 sp 단위로 정의된 경우에만 가능합니다.
카메라 및 미디어
이미지용 울트라 HDR

Android 14에서는 사진을 찍을 때 센서의 정보를 더 많이 유지하여 생생한 색상과 더 높은 대비를 제공하는 HDR (High Dynamic Range) 이미지를 지원합니다. Android는 JPEG 이미지와 완전히 하위 호환되는 울트라 HDR 형식을 사용하므로 앱이 HDR 이미지와 원활하게 상호 운용하여 필요에 따라 표준 동적 범위 (SDR)로 표시할 수 있습니다.
앱이 매니페스트 항목을 통해 또는 런타임에 Window.setColorMode() 호출을 통해 활동 창에 HDR UI를 사용하도록 선택하면 UI에서 이러한 이미지를 HDR로 렌더링하는 작업은 프레임워크에서 자동으로 실행됩니다. 지원되는 기기에서 압축된 울트라 HDR 스틸 이미지를 캡처할 수도 있습니다. 센서에서 더 많은 색상을 복구하면 후반 작업에서 더 유연하게 수정할 수 있습니다. 울트라 HDR 이미지와 연결된 Gainmap를 사용하여 OpenGL 또는 Vulkan을 사용하여 렌더링할 수 있습니다.
카메라 확장 프로그램의 확대/축소, 초점, Postview 등
Android 14에서는 카메라 확장 프로그램을 업그레이드하고 개선하여 앱이 더 긴 처리 시간을 처리할 수 있도록 지원합니다. 이를 통해 지원되는 기기에서 저조도 사진과 같은 컴퓨팅 집약적인 알고리즘을 사용하여 이미지를 개선할 수 있습니다. 이러한 기능을 통해 사용자는 카메라 확장 기능을 사용할 때 더욱 강력한 환경을 경험할 수 있습니다. 이러한 개선사항의 예는 다음과 같습니다.
- 동적 스틸 캡처 처리 지연 시간 추정치는 현재 장면과 환경 조건을 기반으로 훨씬 더 정확한 스틸 캡처 지연 시간 추정치를 제공합니다.
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()를 호출하여 지연 시간 추정 메서드가 두 개인StillCaptureLatency객체를 가져옵니다.getCaptureLatency()메서드는onCaptureStarted와onCaptureProcessStarted()간의 예상 지연 시간을 반환하고getProcessingLatency()메서드는onCaptureProcessStarted()와 사용 가능한 최종 처리된 프레임 간의 예상 지연 시간을 반환합니다. - 앱이 장기 실행 스틸 캡처 처리 작업의 현재 진행 상황을 표시할 수 있도록 캡처 진행 상황 콜백을 지원합니다.
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable에서 이 기능을 사용할 수 있는지 확인할 수 있으며, 사용할 수 있는 경우 진행률 (0~100)이 매개변수로 전달되는onCaptureProcessProgressed()콜백을 구현합니다. 확장 프로그램별 메타데이터(예:
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTH:EXTENSION_BOKEH를 사용하여 배경 흐리게 처리의 양과 같은 확장 프로그램 효과의 양을 조정하는 데 사용)카메라 확장 프로그램의 스틸 캡처를 위한 포스트뷰 기능으로, 최종 이미지보다 처리가 덜된 이미지를 더 빠르게 제공합니다. 확장 프로그램의 처리 지연 시간이 늘어난 경우 UX를 개선하기 위해 포스트뷰 이미지를 자리표시자로 제공하고 나중에 최종 이미지로 전환할 수 있습니다.
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable를 사용하여 이 기능을 사용할 수 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다. 그런 다음OutputConfiguration를ExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration에 전달할 수 있습니다.더 최적화되고 전력 효율적인 미리보기 렌더링 경로를 허용하는
SurfaceView지원확장 프로그램 사용 중에 탭하여 초점 맞추기 및 확대/축소를 지원합니다.
인센서 줌
CameraCharacteristics의 REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE에 SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW가 포함된 경우 앱은 고급 센서 기능을 사용하여 스트림 사용 사례가 CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW로 설정된 RAW 타겟과 함께 CaptureRequest를 사용하여 잘린 RAW 스트림에 전체 시야와 동일한 픽셀을 제공할 수 있습니다.
요청 재정의 컨트롤을 구현하면 업데이트된 카메라에서 다른 카메라 컨트롤이 준비되기 전에도 사용자에게 확대/축소 컨트롤을 제공할 수 있습니다.
무손실 USB 오디오
Android 14에서는 USB 유선 헤드셋을 통한 오디오필 수준의 환경을 위한 무손실 오디오 형식을 지원합니다. USB 기기에서 기본 믹서 속성을 쿼리하고, 기본 믹서 속성 변경에 관한 리스너를 등록하고, AudioMixerAttributes 클래스를 사용하여 믹서 속성을 구성할 수 있습니다. 이 클래스는 채널 마스크, 샘플링 레이트, 오디오 믹서의 동작과 같은 형식을 나타냅니다. 이 클래스를 사용하면 믹싱, 볼륨 조정 또는 효과 처리 없이 오디오를 직접 전송할 수 있습니다.
개발자 생산성 및 도구
인증 관리자
Android 14에서는 인증 관리자를 플랫폼 API로 추가하고 Google Play 서비스를 사용하는 Jetpack 라이브러리를 통해 Android 4.4 (API 수준 19) 기기까지 추가로 지원합니다. 인증 관리자의 목표는 사용자가 구성한 사용자 인증 정보 제공업체로 사용자 인증 정보를 검색하고 저장하는 API를 사용하여 사용자가 더 쉽게 로그인할 수 있도록 하는 것입니다. 인증 관리자는 단일 API에서 사용자 이름과 비밀번호, 패스키, 제휴 로그인 솔루션 (예: Google 계정으로 로그인)과 같은 멀티 로그인 방식을 지원합니다.
패스키는 여러 이점을 제공합니다. 예를 들어 패스키는 업계 표준을 기반으로 구축되며, 다양한 운영체제와 브라우저 생태계에서 작동할 수 있으며, 웹사이트와 앱 모두에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
자세한 내용은 인증 관리자 및 패스키 문서 및 인증 관리자 및 패스키에 관한 블로그 게시물을 참고하세요.
헬스 커넥트
헬스 커넥트는 사용자 건강/피트니스 데이터를 위한 기기 내 저장소입니다. 이를 통해 사용자는 자주 사용하는 앱 간에 데이터를 공유할 수 있으며, 한곳에서 이러한 앱과 공유할 데이터를 제어할 수 있습니다.
Android 14 이전 버전의 Android를 실행하는 기기에서는 Google Play 스토어에서 헬스 커넥트를 앱으로 다운로드할 수 있습니다. Android 14부터 헬스 커넥트는 플랫폼의 일부가 되며 별도의 다운로드 없이 Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 통해 업데이트를 수신합니다. 이를 통해 헬스 커넥트를 자주 업데이트할 수 있으며 앱은 Android 14 이상을 실행하는 기기에서 헬스 커넥트를 사용할 수 있다는 점을 활용할 수 있습니다. 사용자는 시스템 설정에 통합된 개인 정보 보호 설정을 통해 기기의 설정에서 헬스 커넥트에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
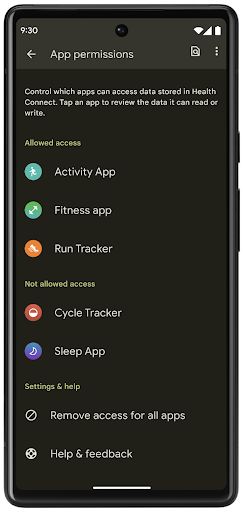
헬스 커넥트에는 운동 경로와 같은 Android 14의 몇 가지 새로운 기능이 포함되어 있어 사용자가 지도에 시각화할 수 있는 운동 경로를 공유할 수 있습니다. 경로는 일정 기간 내에 저장된 위치 목록으로 정의되며 앱은 운동 세션에 경로를 삽입하여 서로 연결할 수 있습니다. 사용자가 이 민감한 정보를 완전히 제어할 수 있도록 하려면 사용자가 개별 경로를 다른 앱과 공유하도록 허용해야 합니다.
자세한 내용은 헬스 커넥트 문서 및 Android 헬스의 새로운 기능 블로그 게시물을 참고하세요.
OpenJDK 17 업데이트
Android 14에서는 앱 및 플랫폼 개발자를 위한 라이브러리 업데이트와 Java 17 언어 지원을 비롯하여 최신 OpenJDK LTS 출시의 기능과 일치하도록 Android의 핵심 라이브러리를 새로고침하는 작업을 계속하고 있습니다.
다음과 같은 기능과 개선사항이 포함됩니다.
- Java 17을 지원하도록 약 300개의
java.base클래스를 업데이트했습니다. - 텍스트 블록: Java 프로그래밍 언어에 여러 줄의 문자열 리터럴을 도입합니다.
- instanceof의 패턴 일치: 추가 변수 없이 객체를
instanceof에 특정 유형이 있는 것으로 취급할 수 있습니다. - 봉인 클래스: 이를 확장하거나 구현할 수 있는 클래스와 인터페이스를 제한할 수 있습니다.
Google Play 시스템 업데이트(Project Mainline) 덕분에 6억 개가 넘는 기기에서 이러한 변경사항이 포함된 최신 Android 런타임(ART) 업데이트를 받을 수 있습니다. 이는 여러 기기에서 앱에 보다 일관되고 안전한 환경을 제공하고 플랫폼 출시와 관계없이 사용자에게 새로운 기능을 제공하기 위한 노력의 일환입니다.
Java 및 OpenJDK는 Oracle 및/또는 그 계열사의 상표 또는 등록 상표입니다.
앱 스토어 개선사항
Android 14에서는 앱 스토어에서 사용자 환경을 개선할 수 있는 여러 PackageInstaller API를 도입했습니다.
다운로드하기 전에 설치 승인 요청
앱을 설치하거나 업데이트하려면 사용자 승인이 필요할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES 권한을 사용하는 설치 프로그램이 새 앱을 설치하려고 할 때를 예로 들 수 있습니다. 이전 Android 버전에서는 APK가 설치 세션에 기록되고 세션이 커밋된 후에만 앱 스토어에서 사용자 승인을 요청할 수 있습니다.
Android 14부터 requestUserPreapproval() 메서드를 사용하면 설치 프로그램이 설치 세션을 커밋하기 전에 사용자 승인을 요청할 수 있습니다. 이러한 개선을 통해 사용자가 설치를 승인할 때까지 앱 스토어에서 APK 다운로드를 연기할 수 있습니다. 또한 사용자가 설치를 승인하면 앱 스토어는 사용자를 방해하지 않고 백그라운드에서 앱을 다운로드하여 설치할 수 있습니다.
향후 업데이트에 관한 책임 주장
setRequestUpdateOwnership() 메서드를 사용하면 설치 프로그램이 설치되는 앱의 향후 업데이트를 책임진다고 시스템에 알릴 수 있습니다. 이 기능은 업데이트 소유권 적용을 사용 설정합니다. 즉, 업데이트 소유자만 앱에 자동 업데이트를 설치할 수 있습니다. 업데이트 소유권 적용은 사용자가 예상되는 앱 스토어에서만 업데이트를 수신하도록 합니다.
업데이트를 설치하려면 INSTALL_PACKAGES 권한을 사용하는 설치 프로그램을 비롯한 다른 모든 설치 프로그램이 명시적인 사용자 승인을 받아야 합니다. 사용자가 다른 소스의 업데이트를 진행하기로 하면 업데이트 소유권이 손실됩니다.
방해가 되지 않는 시간에 앱 업데이트
앱 스토어는 일반적으로 활발히 사용되고 있는 앱은 업데이트하지 않으려고 합니다. 이 경우 앱의 실행 중인 프로세스가 종료되어 사용자가 하던 작업이 중단될 수 있기 때문입니다.
Android 14부터 InstallConstraints API를 사용하면 설치 프로그램이 적절한 시점에 앱 업데이트를 실행할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 앱 스토어는 commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() 메서드를 호출하여 사용자가 더 이상 앱과 상호작용하지 않을 때만 업데이트가 커밋되도록 할 수 있습니다.
선택적 분할을 원활하게 설치
분할 APK를 사용하면 앱의 기능을 모놀리식 APK가 아닌 별도의 APK 파일로 제공할 수 있습니다. 분할 APK를 사용하면 앱 스토어에서 다양한 앱 구성요소의 전송을 최적화할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 앱 스토어는 대상 기기의 속성을 기반으로 최적화할 수 있습니다. PackageInstaller API는 API 수준 22에 도입된 이후 분할을 지원했습니다.
Android 14에서 setDontKillApp() 메서드를 사용하면 설치 프로그램이 새 분할이 설치될 때 앱의 실행 중인 프로세스를 종료해서는 안 된다고 나타낼 수 있습니다. 앱 스토어는 이 기능을 사용하여 사용자가 앱을 사용하는 동안 앱의 새로운 기능을 원활하게 설치할 수 있습니다.
앱 메타데이터 번들
Android 14부터 Android 패키지 설치 프로그램을 사용하면 데이터 보안 관행과 같은 앱 메타데이터를 지정하여 Google Play와 같은 앱 스토어 페이지에 포함할 수 있습니다.
사용자가 기기 스크린샷을 찍을 때 감지
스크린샷 감지를 위한 보다 표준화된 환경을 만들기 위해 Android 14에서는 개인 정보 보호 스크린샷 감지 API를 도입했습니다. 이 API를 사용하면 앱에서 활동별로 콜백을 등록할 수 있습니다. 활동이 표시되는 동안 사용자가 스크린샷을 찍으면 이러한 콜백이 호출되고 사용자에게 알림이 전송됩니다.
사용자 환경
Sharesheet 맞춤 작업 및 개선된 순위 지정
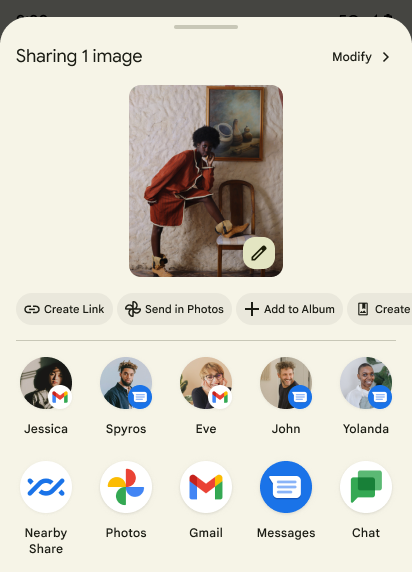
Android 14에서는 맞춤 앱 작업과 사용자에게 더 많은 정보를 제공하는 미리보기 결과를 지원하도록 시스템 Sharesheet를 업데이트합니다.
맞춤 작업 추가
Android 14에서는 앱에서 호출하는 시스템 Sharesheet에 맞춤 작업을 추가할 수 있습니다.
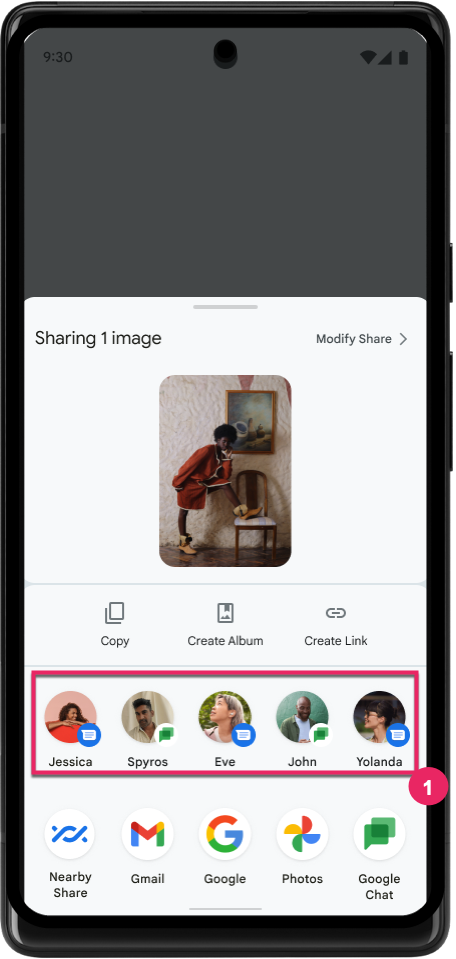
직접 공유 타겟의 순위 향상
Android 14는 앱에서 더 많은 신호를 사용하여 직접 공유 타겟의 순위를 결정하고 사용자에게 더 유용한 결과를 제공합니다. 순위에 가장 유용한 신호를 제공하려면 직접 공유 타겟의 순위 향상에 관한 안내를 따르세요. 커뮤니케이션 앱은 발신 및 수신 메시지의 단축키 사용을 보고할 수도 있습니다.
뒤로 탐색 예측을 위한 내장 및 맞춤 애니메이션 지원
Android 13에서는 개발자 옵션 뒤에 홈으로 이어지는 뒤로 탐색 예측 애니메이션이 도입되었습니다. 개발자 옵션이 사용 설정된 지원 앱에서 사용하면 뒤로 스와이프할 때 뒤로 동작이 앱에서 나와 다시 홈 화면으로 돌아갔음을 나타내는 애니메이션이 표시됩니다.
Android 14에는 뒤로 탐색 예측을 위한 여러 개선사항과 새로운 안내가 포함되어 있습니다.
- 앱 전체가 아닌 활동별로 뒤로 탐색 예측 시스템 애니메이션을 선택하도록
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=true를 설정할 수 있습니다. - Android 13의 홈으로 돌아가기 애니메이션과 함께 새로운 시스템 애니메이션이 추가되었습니다. 새로운 시스템 애니메이션은 뒤로 탐색 예측으로 이전한 후에 자동으로 가져오는 교차 활동 및 교차 작업입니다.
- 하단 시트, 사이드 시트, 검색을 위한 새 Material 구성요소 애니메이션을 추가했습니다.
- 맞춤 인앱 애니메이션 및 전환을 만들기 위한 디자인 가이드를 만들었습니다.
- 맞춤 인앱 전환 애니메이션을 지원하는 새 API를 추가했습니다.
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- 사용자가 뒤로 스와이프할 때 응답하는 전환의 경우
overridePendingTransition대신overrideActivityTransition을 사용합니다.
이 Android 14 미리보기 출시에서는 뒤로 탐색 예측의 모든 기능이 개발자 옵션 뒤에 남아 있습니다. 뒤로 탐색 예측으로 앱을 이전하기 위한 개발자 가이드와 맞춤 인앱 전환 생성을 위한 개발자 가이드를 참고하세요.
대형 화면 기기 제조업체 앱별 재정의
앱별 재정의를 사용하면 기기 제조업체가 대형 화면 기기에서 앱의 동작을 변경할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 FORCE_RESIZE_APP 재정의는 앱 매니페스트에 resizeableActivity="false"가 설정되어 있더라도 디스플레이 크기에 맞게 앱의 크기를 조절하도록 시스템에 지시합니다 (크기 호환성 모드 피하기).
재정의는 대형 화면에서 사용자 환경을 개선하기 위한 것입니다.
새 매니페스트 속성을 사용하면 앱에 대한 일부 기기 제조업체 재정의를 사용 중지할 수 있습니다.
대형 화면 사용자 앱별 재정의
앱별 재정의는 대형 화면 기기에서 앱의 동작을 변경합니다. 예를 들어 OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE 기기 제조업체 재정의는 앱 구성과 관계없이 앱 가로세로 비율을 16:9로 설정합니다.
Android 14 QPR1을 사용하면 사용자가 대형 화면 기기에서 새 설정 메뉴를 통해 앱별 재정의를 적용할 수 있습니다.
앱 화면 공유
앱 화면 공유를 사용하면 사용자가 화면 콘텐츠를 녹화하는 동안 전체 기기 화면 대신 앱 창을 공유할 수 있습니다.
앱 화면 공유를 사용하면 상태 표시줄, 탐색 메뉴, 알림, 기타 시스템 UI 요소가 공유 디스플레이에서 제외됩니다. 선택한 앱의 콘텐츠만 공유됩니다.
앱 화면 공유를 사용하면 사용자가 여러 앱을 실행하면서 콘텐츠 공유를 단일 앱으로 제한하여 생산성과 개인 정보 보호를 개선할 수 있습니다.
Pixel 8 Pro의 Gboard에서 LLM 기반 스마트 답장
12월 기능 업데이트가 적용된 Pixel 8 Pro 기기에서 개발자는 Google Tensor에서 실행되는 온디바이스 대규모 언어 모델 (LLM)을 기반으로 하는 Gboard의 고품질 스마트 답장을 사용해 볼 수 있습니다.
이 기능은 WhatsApp, Line, KakaoTalk에서 미국 영어로 제한된 미리보기로 제공됩니다. Gboard를 키보드로 사용하는 Pixel 8 Pro 기기를 사용해야 합니다.
이 기능을 사용해 보려면 먼저 설정 > 개발자 옵션 > AiCore 설정 > Aicore Persistent 사용 설정에서 기능을 사용 설정하세요.
그런 다음 지원되는 앱에서 대화를 열어 수신 메시지에 대한 응답으로 Gboard의 추천 표시줄에 LLM 기반 스마트 답장이 표시되는지 확인합니다.
그래픽
경로를 쿼리하고 보간할 수 있음
Android의 Path API는 벡터 그래픽을 만들고 렌더링하기 위한 강력하고 유연한 메커니즘으로, 경로를 획 처리하거나 채우고, 선분이나 이차 또는 삼차 곡선으로 경로를 구성하고, 불리언 연산을 실행하여 훨씬 더 복잡한 도형을 가져오거나 이 모든 작업을 동시에 실행할 수 있습니다. 한 가지 제한사항은 경로 객체에 실제로 무엇이 있는지 찾을 수 있다는 것입니다. 객체의 내부는 생성 후 호출자에게 불투명합니다.
Path를 만들려면 moveTo(), lineTo(), cubicTo()와 같은 메서드를 호출하여 경로 세그먼트를 추가하세요. 그러나 이 경로에 세그먼트가 무엇인지 물어볼 방법이 없으므로 생성 시 해당 정보를 유지해야 합니다.
Android 14부터 경로를 쿼리하여 그 안에 포함된 항목을 확인할 수 있습니다.
먼저 Path.getPathIterator API를 사용하여 PathIterator 객체를 가져와야 합니다.
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
자바
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
그런 다음 PathIterator를 호출하여 세그먼트를 하나씩 반복하면서 각 세그먼트에 필요한 모든 데이터를 검색할 수 있습니다. 이 예에서는 데이터를 패키징하는 PathIterator.Segment 객체를 사용합니다.
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
자바
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator에는 포인트 데이터를 보유할 버퍼를 전달할 수 있는 비할당 버전의 next()도 있습니다.
Path 데이터 쿼리에 관한 중요한 사용 사례 중 하나는 보간 유형입니다. 예를 들어 서로 다른 두 경로 간에 애니메이션을 적용하거나 모핑할 수 있습니다. 이러한 사용 사례를 더욱 단순화하기 위해 Android 14에는 Path에 interpolate() 메서드도 포함되어 있습니다. 두 경로의 내부 구조가 같다고 가정하면 interpolate() 메서드는 보간된 결과를 사용하여 새 Path를 만듭니다. 이 예에서는 path 및 otherPath 사이의 도형이 중간(선형 보간 유형 0.5)인 경로를 반환합니다.
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
자바
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Jetpack graphics-path 라이브러리를 사용하면 이전 버전의 Android에서도 유사한 API를 사용할 수 있습니다.
버텍스 및 프래그먼트 셰이더가 있는 맞춤 메시
Android는 오랫동안 맞춤 음영 처리로 삼각형 메시 그리기를 지원해 왔지만 입력 메시 형식은 사전 정의된 몇 가지 속성 조합으로 제한되었습니다. Android 14에서는 삼각형 또는 삼각형 스트립으로 정의할 수 있고 원하는 경우 색인을 생성할 수 있는 커스텀 메시 지원을 추가했습니다. 이러한 메시는 커스텀 속성, 정점 행렬, 변경, AGSL로 작성된 정점 및 프래그먼트 셰이더로 지정됩니다.
정점 셰이더는 위치 및 색상과 같은 가변을 정의하는 반면, 프래그먼트 셰이더는 원하는 경우 일반적으로 정점 셰이더에서 만든 가변을 사용하여 픽셀의 색상을 정의할 수 있습니다. 색상이 프래그먼트 셰이더에서 제공되면 메시를 그릴 때 선택한 혼합 모드를 사용하여 현재 Paint 색상과 혼합됩니다. 유니폼을 프래그먼트 및 정점 셰이더에 전달하여 유연성을 높일 수 있습니다.
캔버스의 하드웨어 버퍼 렌더러
Android의 Canvas API를 사용하여 하드웨어 가속으로 HardwareBuffer에 그리는 것을 지원하기 위해 Android 14에서는 HardwareBufferRenderer를 도입합니다. 이 API는
시스템과의 통신이 포함된 사용 사례에 특히 유용합니다
짧은 지연 시간을 위해 SurfaceControl를 통한 컴포지터
있습니다.

