Android 14 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた機能と API が導入されました。以下では、アプリの機能を確認し、関連する API を試すことができます。
追加、変更、削除された API の詳細な一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。追加された API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。Android 14 の場合は、API レベル 34 で追加された API をご確認ください。プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する可能性がある領域については、Android 14 の動作変更(Android 14 をターゲットとするアプリの場合とすべてのアプリの場合)をご確認ください。
多言語対応
アプリ別の言語設定
Android 14 expands on the per-app language features that were introduced in Android 13 (API level 33) with these additional capabilities:
Automatically generate an app's
localeConfig: Starting with Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 and AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, you can configure your app to support per-app language preferences automatically. Based on your project resources, the Android Gradle plugin generates theLocaleConfigfile and adds a reference to it in the final manifest file, so you no longer have to create or update the file manually. AGP uses the resources in theresfolders of your app modules and any library module dependencies to determine the locales to include in theLocaleConfigfile.Dynamic updates for an app's
localeConfig: Use thesetOverrideLocaleConfig()andgetOverrideLocaleConfig()methods inLocaleManagerto dynamically update your app's list of supported languages in the device's system settings. Use this flexibility to customize the list of supported languages per region, run A/B experiments, or provide an updated list of locales if your app utilizes server-side pushes for localization.App language visibility for input method editors (IMEs): IMEs can utilize the
getApplicationLocales()method to check the language of the current app and match the IME language to that language.
Grammatical Inflection API
30 億人もの人々が、性別で文法が変わる言語を話します。こうした言語では、話す相手、または言及する人や物の性別に応じて、各文法範疇(名詞、動詞、形容詞、前置詞など)の語形が変化します。伝統的に、性別で文法が変わる多くの言語では、男性形をデフォルトまたは汎用の性別として使用しています。
女性を男性形で呼ぶなど、ユーザーに対して不適切な文法的性を使用すると、そのユーザーのパフォーマンスと態度に悪影響を及ぼす可能性があります。一方、ユーザーの文法的性を適切に反映した言語を使用して UI を作成すると、ユーザー エンゲージメントが向上し、より自然でパーソナライズされたユーザー エクスペリエンスを提供できます。
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
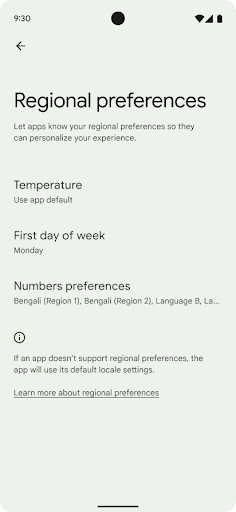
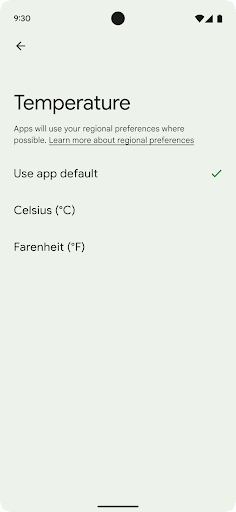
地域の設定
Regional preferences enable users to personalize temperature units, the first day of the week, and numbering systems. A European living in the United States might prefer temperature units to be in Celsius rather than Fahrenheit and for apps to treat Monday as the beginning of the week instead of the US default of Sunday.
New Android Settings menus for these preferences provide users with a
discoverable and centralized location to change app preferences. These
preferences also persist through backup and restore. Several APIs and
intents—such as
getTemperatureUnit
and
getFirstDayOfWeek—
grant your app read access to user preferences, so your app can adjust how it
displays information. You can also register a
BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
to handle locale configuration changes when regional preferences change.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
ユーザー補助
非線形フォント スケーリングを 200% にする
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing low-vision users with additional accessibility options that align with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
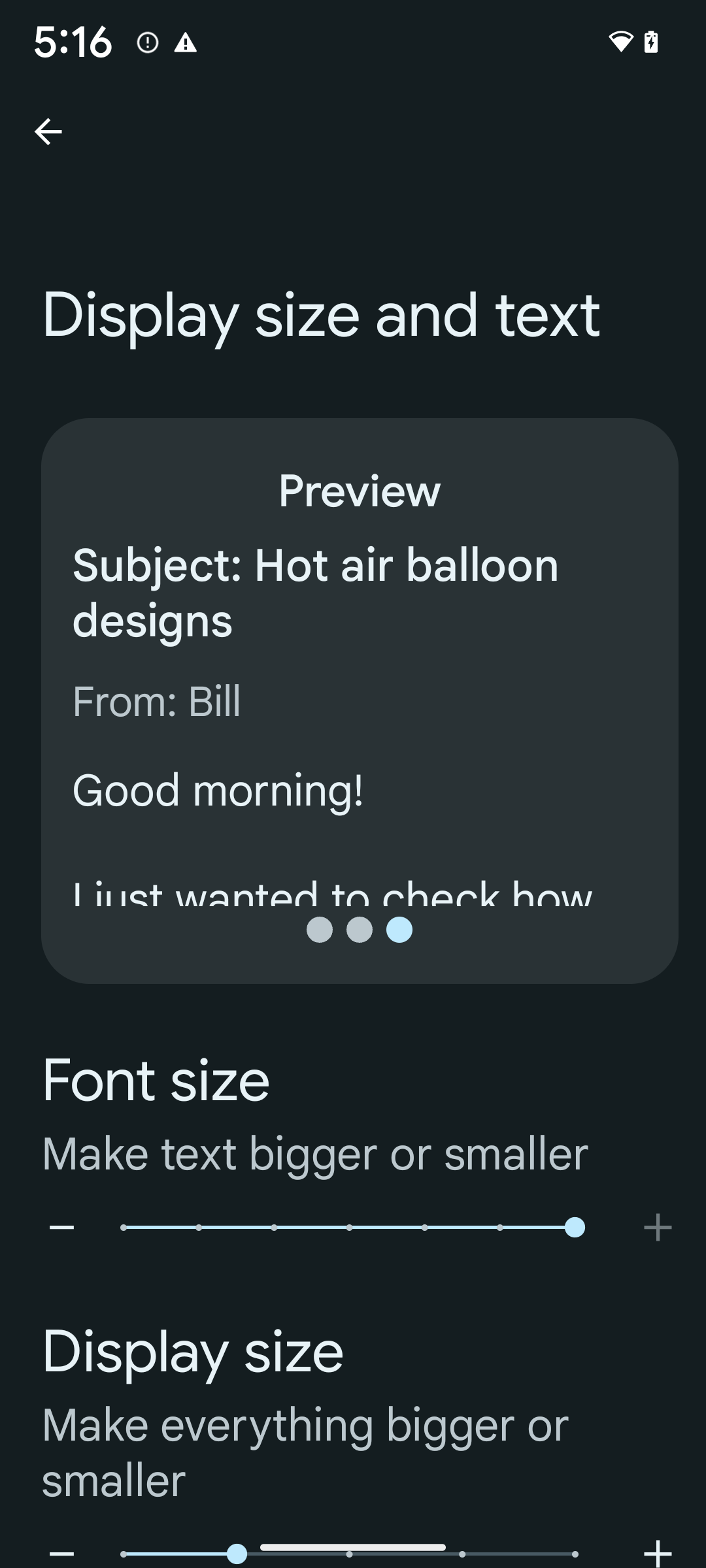
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
カメラとメディア
画像のウルトラ HDR

Android 14 adds support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) images that retain more of the information from the sensor when taking a photo, which enables vibrant colors and greater contrast. Android uses the Ultra HDR format, which is fully backward compatible with JPEG images, allowing apps to seamlessly interoperate with HDR images, displaying them in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) as needed.
Rendering these images in the UI in HDR is done automatically by the framework
when your app opts in to using HDR UI for its Activity Window, either through a
manifest entry or at runtime by calling
Window.setColorMode(). You can also capture compressed Ultra
HDR still images on supported devices. With more colors recovered
from the sensor, editing in post can be more flexible. The
Gainmap associated with Ultra HDR images can be used to render
them using OpenGL or Vulkan.
カメラ拡張機能のズーム、フォーカス、ポストビューなど
Android 14 では、カメラ拡張機能がアップグレードされ、改善されています。これにより、アプリはより長い処理時間を処理できるため、サポートされているデバイスで暗い場所での撮影などのコンピューティング負荷の高いアルゴリズムを使用して画像を改善できます。これらの機能により、カメラの拡張機能を使用する際のユーザー エクスペリエンスがさらに堅牢になります。主な改善点は次のとおりです。
- 動的な静止画撮影処理レイテンシの推定では、現在のシーンと環境条件に基づいて、はるかに正確な静止画撮影レイテンシの推定値が得られます。
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()を呼び出して、2 つのレイテンシ推定メソッドを持つStillCaptureLatencyオブジェクトを取得します。getCaptureLatency()メソッドは、onCaptureStartedとonCaptureProcessStarted()間の推定レイテンシを返します。getProcessingLatency()メソッドは、onCaptureProcessStarted()と利用可能な最終的な処理済みフレーム間の推定レイテンシを返します。 - キャプチャの進行状況コールバックをサポートし、アプリが長時間実行の静止画キャプチャ処理オペレーションの現在の進行状況を表示できるようにします。この機能が
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailableで使用可能かどうかを確認します。使用可能であれば、onCaptureProcessProgressed()コールバックを実装します。このコールバックには、進行状況(0 ~ 100)がパラメータとして渡されます。 拡張機能固有のメタデータ(
EXTENSION_BOKEHによる背景のぼかしの量など、拡張機能の効果の量を調整するためのCaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHなど)。カメラ拡張機能の静止画撮影用ポストビュー機能。最終的な画像よりも処理が少ない画像をより迅速に提供します。拡張機能で処理レイテンシが増加している場合は、UX を改善するためにポストビュー画像をプレースホルダとして提供し、後で最終的な画像に切り替えることができます。この機能が使用可能かどうかは、
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailableで確認できます。次に、OutputConfigurationをExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfigurationに渡すことができます。SurfaceViewのサポートにより、より最適化され、電力効率の高いプレビュー レンダリング パスが可能になりました。拡張機能の使用中にタップしてフォーカスとズームをサポート。
センサー内ズーム
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
ロスレス USB オーディオ
Android 14 gains support for lossless audio formats for audiophile-level
experiences over USB wired headsets. You can query a USB device for its
preferred mixer attributes, register a listener for changes in preferred mixer
attributes, and configure mixer attributes using the
AudioMixerAttributes class. This class represents the
format, such as channel mask, sample rate, and behavior of the audio mixer. The
class allows for audio to be sent directly, without mixing,
volume adjustment, or processing effects.
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
認証情報マネージャー
Android 14 adds Credential Manager as a platform API, with additional support back to Android 4.4 (API level 19) devices through a Jetpack Library using Google Play services. Credential Manager aims to make sign-in easier for users with APIs that retrieve and store credentials with user-configured credential providers. Credential Manager supports multiple sign-in methods, including username and password, passkeys, and federated sign-in solutions (such as Sign-in with Google) in a single API.
Passkeys provide many advantages. For example, passkeys are built on industry standards, can work across different operating systems and browser ecosystems, and can be used with both websites and apps.
For more information, see the Credential Manager and passkeys documentation and the blogpost about Credential Manager and passkeys.
ヘルスコネクト
Health Connect is an on-device repository for user health and fitness data. It allows users to share data between their favorite apps, with a single place to control what data they want to share with these apps.
On devices running Android versions prior to Android 14, Health Connect is available to download as an app on the Google Play store. Starting with Android 14, Health Connect is part of the platform and receives updates through Google Play system updates without requiring a separate download. With this, Health Connect can be updated frequently, and your apps can rely on Health Connect being available on devices running Android 14 or higher. Users can access Health Connect from the Settings in their device, with privacy controls integrated into the system settings.
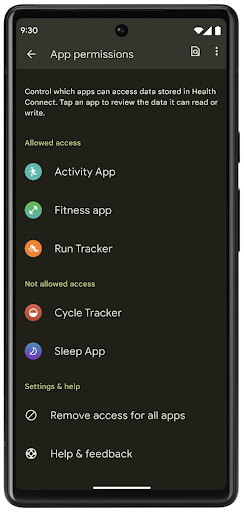
Health Connect includes several new features in Android 14, such as exercise routes, allowing users to share a route of their workout which can be visualized on a map. A route is defined as a list of locations saved within a window of time, and your app can insert routes into exercise sessions, tying them together. To ensure that users have complete control over this sensitive data, users must allow sharing individual routes with other apps.
For more information, see the Health Connection documentation and the blogpost on What's new in Android Health.
OpenJDK 17 の更新
Android 14 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases, including both library updates and Java 17 language support for app and platform developers.
The following features and improvements are included:
- Updated approximately 300
java.baseclasses to Java 17 support. - Text Blocks, which introduce multi-line string literals to the Java programming language.
- Pattern Matching for instanceof, which allows an object to
be treated as having a specific type in an
instanceofwithout any additional variables. - Sealed classes, which allow you restrict which classes and interfaces can extend or implement them.
Thanks to Google Play system updates (Project Mainline), over 600 million devices are enabled to receive the latest Android Runtime (ART) updates that include these changes. This is part of our commitment to give apps a more consistent, secure environment across devices, and to deliver new features and capabilities to users independent of platform releases.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
アプリストアの改善
Android 14 introduces several PackageInstaller APIs that
allow app stores to improve their user experience.
Request install approval before downloading
Installing or updating an app might require user approval.
For example, when an installer making use of the
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission attempts to install a
new app. In prior Android versions, app stores can only request user approval
after APKs are written to the install session and the
session is committed.
Starting with Android 14, the requestUserPreapproval()
method lets installers request user approval before committing the install
session. This improvement lets an app store defer downloading any APKs until
after the installation has been approved by the user. Furthermore, once a user
has approved installation, the app store can download and install the app in the
background without interrupting the user.
Claim responsibility for future updates
The setRequestUpdateOwnership() method allows an installer
to indicate to the system that it intends to be responsible for future updates
to an app it is installing. This capability enables update ownership
enforcement, meaning that only the update owner is permitted
to install automatic updates to the app. Update ownership enforcement helps to
ensure that users receive updates only from the expected app store.
Any other installer, including those making use of the
INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, must receive explicit user
approval in order to install an update. If a user decides to proceed with an
update from another source, update ownership is lost.
Update apps at less-disruptive times
App stores typically want to avoid updating an app that is actively in use because this leads to the app's running processes being killed, which potentially interrupts what the user was doing.
Starting with Android 14, the InstallConstraints API
gives installers a way to ensure that their app updates happen at an opportune
moment. For example, an app store can call the
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() method to
make sure that an update is only committed when the user is no longer
interacting with the app in question.
Seamlessly install optional splits
With split APKs, features of an app can be delivered in separate APK files,
rather than as a monolithic APK. Split APKs allow app stores to optimize the
delivery of different app components. For example, app stores might optimize
based on the properties of the target device. The
PackageInstaller API has supported splits since its
introduction in API level 22.
In Android 14, the setDontKillApp() method allows an
installer to indicate that the app's running processes shouldn't be killed when
new splits are installed. App stores can use this feature to seamlessly install
new features of an app while the user is using the app.
アプリのメタデータ バンドル
Starting in Android 14, the Android package installer lets you specify app metadata, such as data safety practices, to include on app store pages such as Google Play.
ユーザーがデバイスのスクリーンショットを撮影したときに検出する
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
ユーザー エクスペリエンス
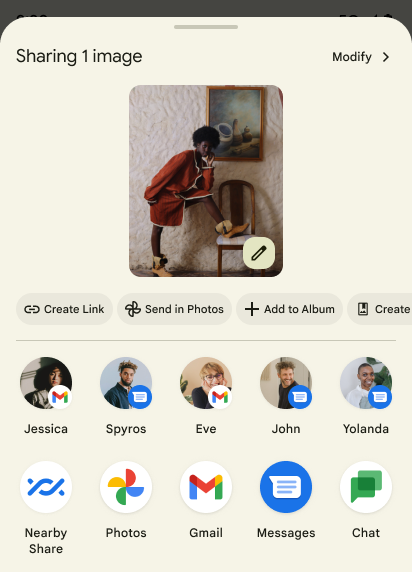
共有シートのカスタム アクションとランキングの改善
Android 14 updates the system sharesheet to support custom app actions and more informative preview results for users.
Add custom actions
With Android 14, your app can add custom actions to the system sharesheet it invokes.
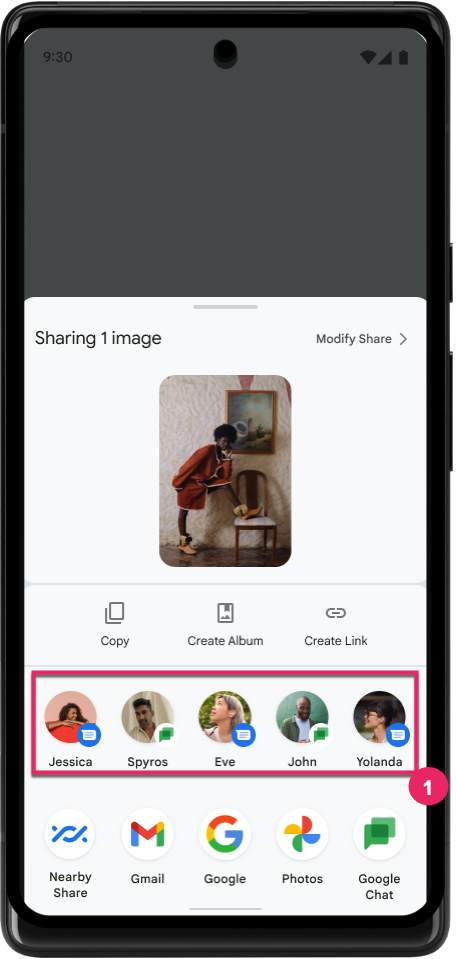
Improve ranking of Direct Share targets
Android 14 uses more signals from apps to determine the ranking of the direct share targets to provide more helpful results for the user. To provide the most useful signal for ranking, follow the guidance for improving rankings of your Direct Share targets. Communication apps can also report shortcut usage for outgoing and incoming messages.
予測型「戻る」の組み込みアニメーションとカスタム アニメーションのサポート
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
大画面デバイスのメーカーによるアプリごとのオーバーライド
Per-app overrides enable device manufacturers to change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the FORCE_RESIZE_APP override instructs the system to resize the app to fit display dimensions (avoiding size compatibility mode) even if resizeableActivity="false" is set in the app manifest.
Overrides are intended to improve the user experience on large screens.
New manifest properties enable you to disable some device manufacturer overrides for your app.
大画面ユーザーのアプリごとのオーバーライド
Per-app overrides change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE device manufacturer override sets the app aspect ratio to 16:9 regardless of the app's configuration.
Android 14 QPR1 enables users to apply per‑app overrides by means of a new settings menu on large screen devices.
アプリの画面共有
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
Google Pixel 8 Pro の Gboard で LLM を活用したスマート リプライを使用する
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
グラフィック
パスのクエリと補間に対応
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
頂点シェーダーとフラグメント シェーダーを使用したカスタム メッシュ
Android では長い間、カスタム シェーディングによる三角形メッシュの描画をサポートしてきましたが、入力メッシュ形式は、事前定義された属性の組み合わせに限定されていました。Android 14 では、カスタムメッシュのサポートが追加されました。これは、三角形または三角形ストリップとして定義でき、必要に応じてインデックスを付けることができます。これらのメッシュは、カスタム属性、頂点ストライド、変化、AGSL で記述された頂点シェーダーとフラグメント シェーダーで指定されます。
頂点シェーダーは位置や色などの変化を定義しますが、フラグメント シェーダーは、通常は頂点シェーダーによって作成された変化を使用して、ピクセルの色を定義することもできます。フラグメント シェーダーによって色が指定されている場合は、メッシュの描画時に選択されたブレンドモードを使用して、現在の Paint 色とブレンドされます。ユニフォームをフラグメント シェーダーと頂点シェーダーに渡して柔軟性を高めることができます。
Canvas のハードウェア バッファ レンダラ
To assist in using Android's Canvas API to draw with
hardware acceleration into a HardwareBuffer, Android 14
introduces HardwareBufferRenderer. This API is
particularly useful when your use case involves communication with the system
compositor through SurfaceControl for low-latency
drawing.

